INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study design and data collection
Definition of diabetes mellitus and comorbidities
Risk factors and self-management behaviors
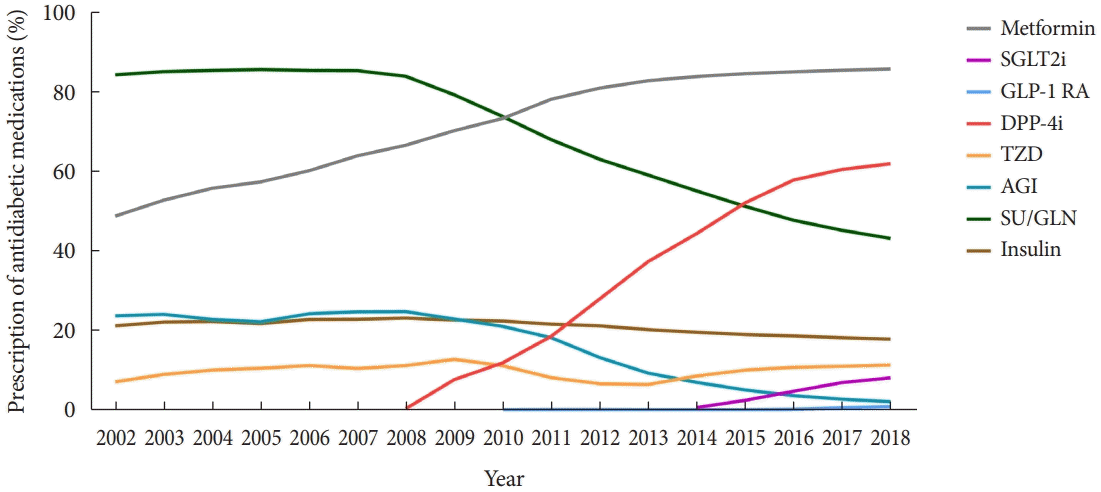
Use of antidiabetic medications
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
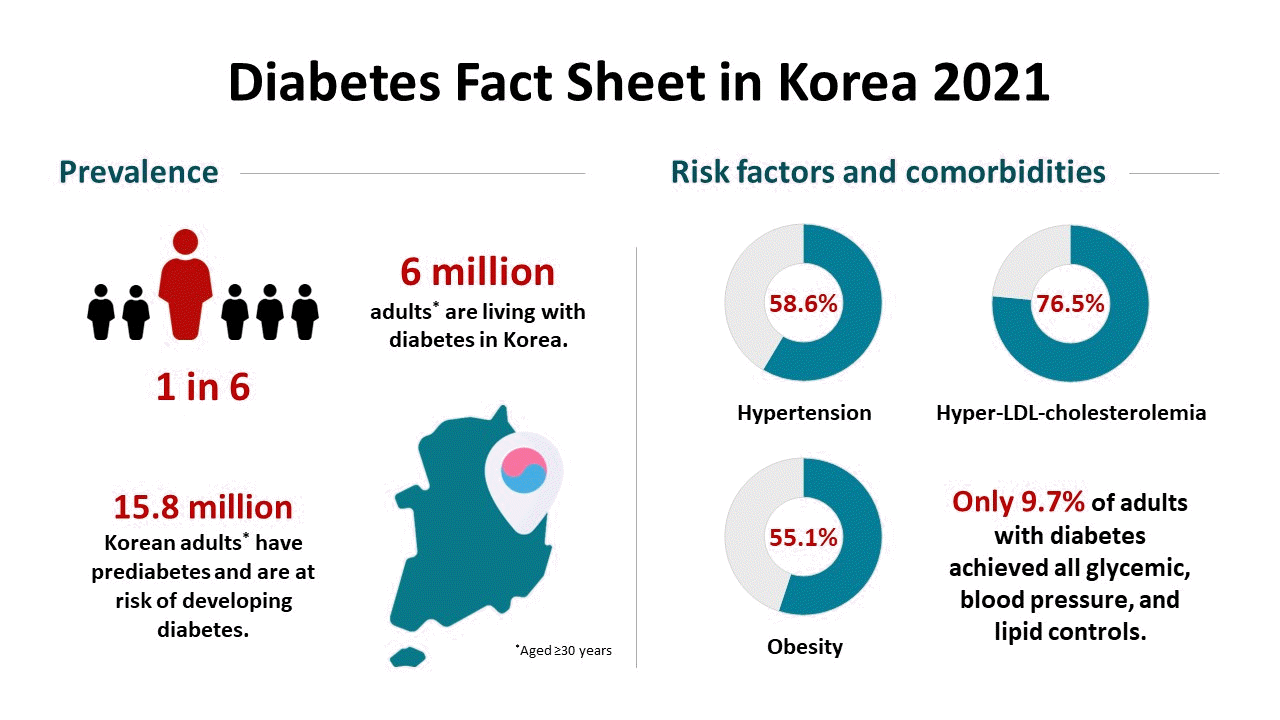
Prevalence of diabetes mellitus
Table 1.
| Variable | Number | Percentage±SE | Estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age group, yr | |||
| ≥19 | |||
| FPG or HbA1ca | 5,612 | 13.9±0.6 | 6,101,158 |
| FPG | 5,613 | 12.2±0.5 | 5,327,384 |
| ≥30 | |||
| FPG or HbA1ca | 4,848 | 16.7±0.7 | 6,047,618 |
| FPG | 4,849 | 14.5±0.6 | 5,273,844 |
| ≥65 | |||
| FPG or HbA1ca | 1,545 | 30.1±1.3 | 2,450,207 |
| FPG | 1,546 | 27.0±1.2 | 2,202,928 |
| 19–29a | 764 | 0.7±0.3 | 53,540 |
| 30–39a | 734 | 4.4±0.8 | 314,033 |
| 40–49a | 936 | 9.0±1.1 | 740,264 |
| 50–59a | 1,025 | 19.1±1.4 | 1,636,363 |
| 60–69a | 1,068 | 25.1±1.6 | 1,626,599 |
| ≥70a | 1,085 | 31.5±1.6 | 1,730,360 |
| Sexa | |||
| Men | |||
| Age ≥19 yr | 2,516 | 15.8±0.9 | 3,417,978 |
| Age ≥30 yr | 2,135 | 19.2±1.0 | 3,393,466 |
| Age ≥65 yr | 671 | 29.8±2.1 | 1,109,812 |
| Women | |||
| Age ≥19 yr | 3,096 | 12.1±0.7 | 3,212,364 |
| Age ≥30 yr | 2,713 | 14.3±0.8 | 3,187,148 |
| Age ≥65 yr | 874 | 30.2±1.5 | 1,459,697 |
| Equivalized household incomea,b | |||
| Quintile 1 (lowest) | 752 | 30.8±2.0 | - |
| Quintile 2 | 911 | 22.1±1.7 | - |
| Quintile 3 | 981 | 14.3±1.3 | - |
| Quintile 4 | 1,084 | 12.9±1.1 | - |
| Quintile 5 (highest) | 1,104 | 12.3±1.1 | - |
Diabetes management
Fig. 1.
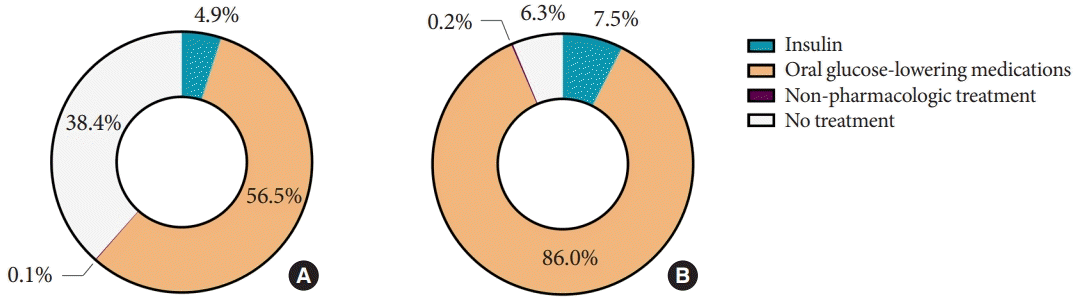
Table 2.
| Variable |
Total diabetes mellitus |
Diagnosed diabetes mellitus |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage±SE | Number | Percentage±SE | |
| Awareness or detectiona | ||||
| Age, yr | ||||
| ≥30 | 1,770 | 65.8±1.4 | - | - |
| ≥65 | 914 | 76.4±1.5 | - | - |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 1,225 | 62.6±1.9 | - | - |
| Women | 1,168 | 69.7±1.8 | - | - |
| Treatment rateb | ||||
| Age, yr | ||||
| ≥30 | 1,770 | 61.4±1.5 | 1,202 | 93.4±1.0 |
| ≥65 | 914 | 73.3±1.6 | 694 | 95.9±0.8 |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 899 | 57.1±2.1 | 589 | 91.2±1.7 |
| Women | 871 | 66.8±1.8 | 613 | 95.8±0.8 |
| Control ratec | ||||
| Age, yr | ||||
| ≥30 | 1,770 | 24.5±1.2 | 1,202 | 26.8±1.4 |
| ≥65 | 914 | 28.3±1.7 | 694 | 31.3±2.0 |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 899 | 24.4±1.6 | 589 | 25.3±2.0 |
| Women | 871 | 24.5±1.7 | 613 | 28.5±2.0 |
a Awareness of diabetes mellitus was defined as the percentage of people previously diagnosed with diabetes mellitus among people with diabetes mellitus,
Fig. 2.
Risk-factor control and comorbidities
Table 3.
| Variable | Total | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c | |||
| <6.5% | 24.5 | 24.4 | 24.5 |
| <7.0% | 55.6 | 55.0 | 56.3 |
| <8.0% | 80.5 | 79.5 | 81.7 |
| <9.0% | 89.9 | 89.3 | 90.5 |
| Hypertensiona | 58.6 | 57.9 | 59.5 |
| BP <140/85 mm Hg | 55.5 | 51.7 | 60.2 |
| Hyper-LDL-cholesterolemiab | 76.5 | 73.3 | 80.5 |
| LDL-C <100 mg/dL | 38.3 | 36.1 | 40.9 |
| Hypertensiona and hyper-LDL- cholesterolemiab | 43.9 | 41.9 | 46.4 |
| HbA1c <6.5% +BP <140/85 mm Hg + LDL-C <100 mg/dL | 9.7 | 11.0 | 8.1 |
| Weight status (BMI, kg/m2) | |||
| Underweight (<18.5) | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.3 |
| Normal weight (18.5–22.9) | 20.7 | 18.2 | 23.8 |
| Overweight (23.0–24.9) | 23.1 | 23.7 | 22.4 |
| Class I obesity (25.0–29.9) | 41.3 | 43.5 | 38.5 |
| Class II obesity (30.0–34.9) | 11.2 | 11.0 | 11.4 |
| Class III obesity (≥35.0) | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| Abdominal obesity (WC, cm) | |||
| No (<90 in men, <85 in women) | 36.7 | 37.8 | 35.4 |
| Yes (≥90 in men, ≥85 in women) | 63.3 | 62.2 | 64.6 |
| Current smokingc | 22.3 | 36.0 | 5.0 |
| High-risk alcohol consumptiond | 22.8 | 31.1 | 4.2 |
| Regular walkinge | 38.1 | 37.2 | 39.4 |
Values are presented as percentages.
KNHANES, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; BP, blood pressure; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference.
a Hypertension was defined as systolic BP ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic BP ≥90 mm Hg or taking antihypertensive medications,
c Current smoking was defined as having smoked five packs (or 100 cigarettes) in his or her lifetime and currently smoking cigarettes,
Self-management behaviors
Table 4.
| Variable | Total diabetes mellitus | Diagnosed diabetes mellitus | Non- diabetes mellitus | P valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy intake, kcal | 1,825 | 1,785 | 1,911 | 0.009 |
| Men | 2,127 | 2,111 | 2,251 | 0.013 |
| Women | 1,439 | 1,402 | 1,596 | <0.001 |
| Excess energy intake, %b | 16.7 | 15.8 | 16.9 | 0.914 |
| Men | 19.5 | 18.9 | 20.5 | 0.637 |
| Women | 13.2 | 12.2 | 13.5 | 0.827 |
| Percentages of energy intake from macronutrients | ||||
| Carbohydrates, % | 66.3 | 66.8 | 62.4 | <0.001 |
| Men | 64.5 | 64.7 | 61.5 | <0.001 |
| Women | 68.6 | 69.2 | 63.3 | <0.001 |
| Protein, % | 15.0 | 14.8 | 15.6 | <0.001 |
| Men | 15.5 | 15.5 | 16.0 | 0.008 |
| Women | 14.3 | 14.0 | 15.1 | <0.001 |
| Fat, % | 18.7 | 18.4 | 22.0 | <0.001 |
| Men | 20.0 | 19.8 | 22.4 | <0.001 |
| Women | 17.1 | 16.9 | 21.6 | <0.001 |
b Excess energy intake was defined as 125% or more of the estimated energy requirement recommended by the Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015 [22].




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download