INTRODUCTION
METHODS
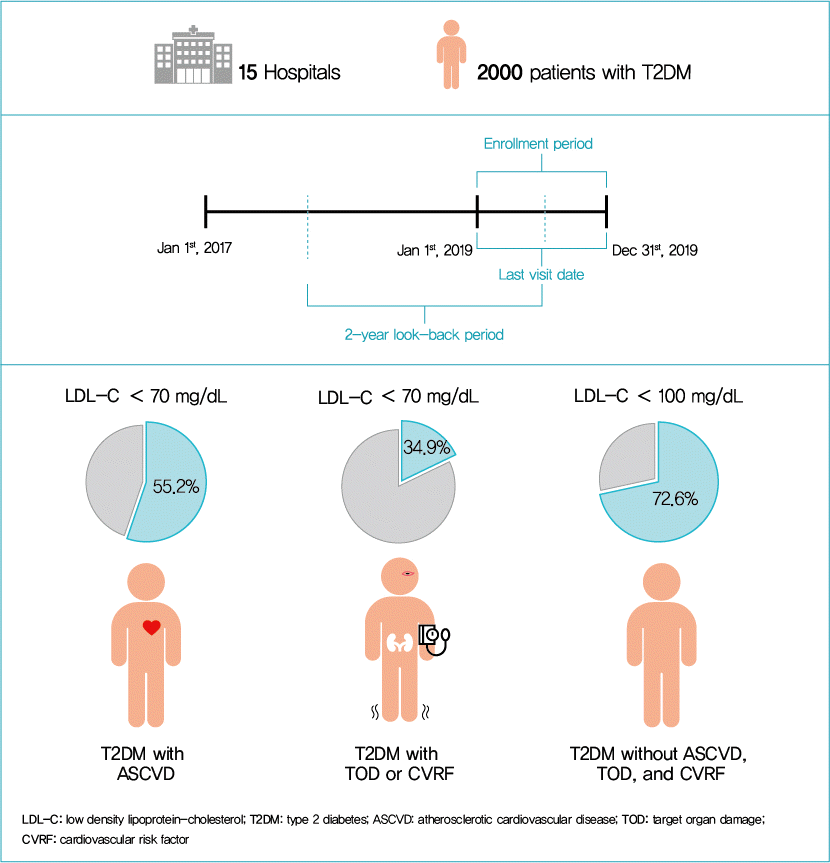
Study design
LDL-C treatment criteria according to dyslipidemia guidelines for patients with diabetes
Table 1.
| Guideline | CVD risk classification in T2DM | Target goal or management |
|---|---|---|
| Korea Diabetes Association 2019a | Very High-I: established ASCVD | LDL-C <70 mg/dL |
| Very High-II: target organ damage (albuminuria, eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or retinopathy), or any CV risk factor (hypertension, smoking, family history of premature CAD, or HDL | ||
| <40 mg/dL) High: others | LDL-C <100 mg/dL | |
| European Society of Cardiology/European Atherosclerosis Society 2019b | Very High-I: established ASCVD | LDL-C <55 mg/dL |
| Very High-II: target organ damage (albuminuria, eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2, retinopathy, or left ventricular hypertrophy) or ≥3 CV risk factors (age ≥50 years, hypertension, smoking, BMI ≥25 kg/m2, dyslipidemia) | ||
| High: diabetes duration ≥10 years without target organ damage plus any CV risk factor | LDL-C <70 mg/dL | |
| Moderate: diabetes duration <10 years without other CV risk factor | LDL-C <100 mg/dL | |
| American Diabetes Association 2019c | Very High-I: established ASCVD | High intensity statind or statin combined with ezetimibe |
| Very High-II: age ≥40 years plus target organ damage (albuminuria, eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or retinopathy) or any CV risk factor (hypertension, smoking, family history of premature CAD, or HDL <40 mg/dL) |
CVD, cardiovascular disease; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; ASCVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; CV, cardiovascular; CAD, coronary artery disease; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
b 2019 ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular disease developed in collaboration with the European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes (EASD),
d Statin dose was determined by 2018 American Heart Association (AHA)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation (AACVPR)/American Association Academy of Physician Assistants (AAPA)/Association of Black Cardiologists (ABC)/American College of Preventive Medicine (ACPM)/American Diabetes Association (ADA)/American Geriatrics Society (AGS)/American Pharmacists Association (APhA)/American Society for Preventive Cardiology (ASPC)/National Lipid Association (NLA)/and Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association (PCNA).
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Baseline characteristics of study subjects
Table 2.
| Variable | Total (n=2,000) |
|---|---|
| Age, yr | 62.6±12.0 |
| Male sex | 1,117 (55.90) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 25.4±3.8 |
| Dyslipidemiaa | |
| Yes | 1,640 (82.00) |
| No | 360 (18.00) |
| Family history of premature CAD | |
| Yes | 49 (2.45) |
| No | 850 (42.50) |
| Unknown | 1,101 (55.05) |
| Smoking history | |
| Current smoker | 285 (14.25) |
| Ex-smoker | 277 (13.85) |
| Non-smoker | 880 (44.00) |
| Unknown | 558 (27.90) |
| HbA1c, % | 7.2±1.3 |
| Diabetes duration, yr | 9.80±8.09b |
| Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease | 493 (24.70) |
| Target organ damage | |
| Yes | 510 (25.50) |
| Proteinuria | 341 (17.10) |
| Left ventricular hypertrophy | 25 (1.30) |
| Retinopathy | 257 (12.90) |
| Renal function | |
| eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 1,710 (85.50) |
| eGFR 30–59 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 246 (12.30) |
| eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 44 (2.20) |
| Blood pressure, mm Hg | |
| Systolic | 128.2±14.7 |
| Diastolic | 74.0±10.9 |
| Lipid profile | |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 149.7±34.4 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 80.3±28.2 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 49.5±13.3 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 141.9±97.4 |
Table 3.
| Variable | Total (n=2,000) |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle modification | 472 (23.5) |
| Statin treatment | 1,455 (72.8) |
| Statin monotherapy | 1,075 (73.9) |
| Statin combined with other drugs | 380 (26.1) |
| Statin-ezetimibea | 231 |
| Statin-fibratea | 101 |
| Statin-omega-3 fatty acidsa | 70 |
| Othersa | 7 |
| Lipid-lowering treatment other than statin | 73 (3.7) |
| Ezetimibea | 21 |
| Fibratea | 35 |
| Omega-3 fatty acidsa | 36 |
LDL-C target achievement rates according to recent guidelines
Fig. 2.
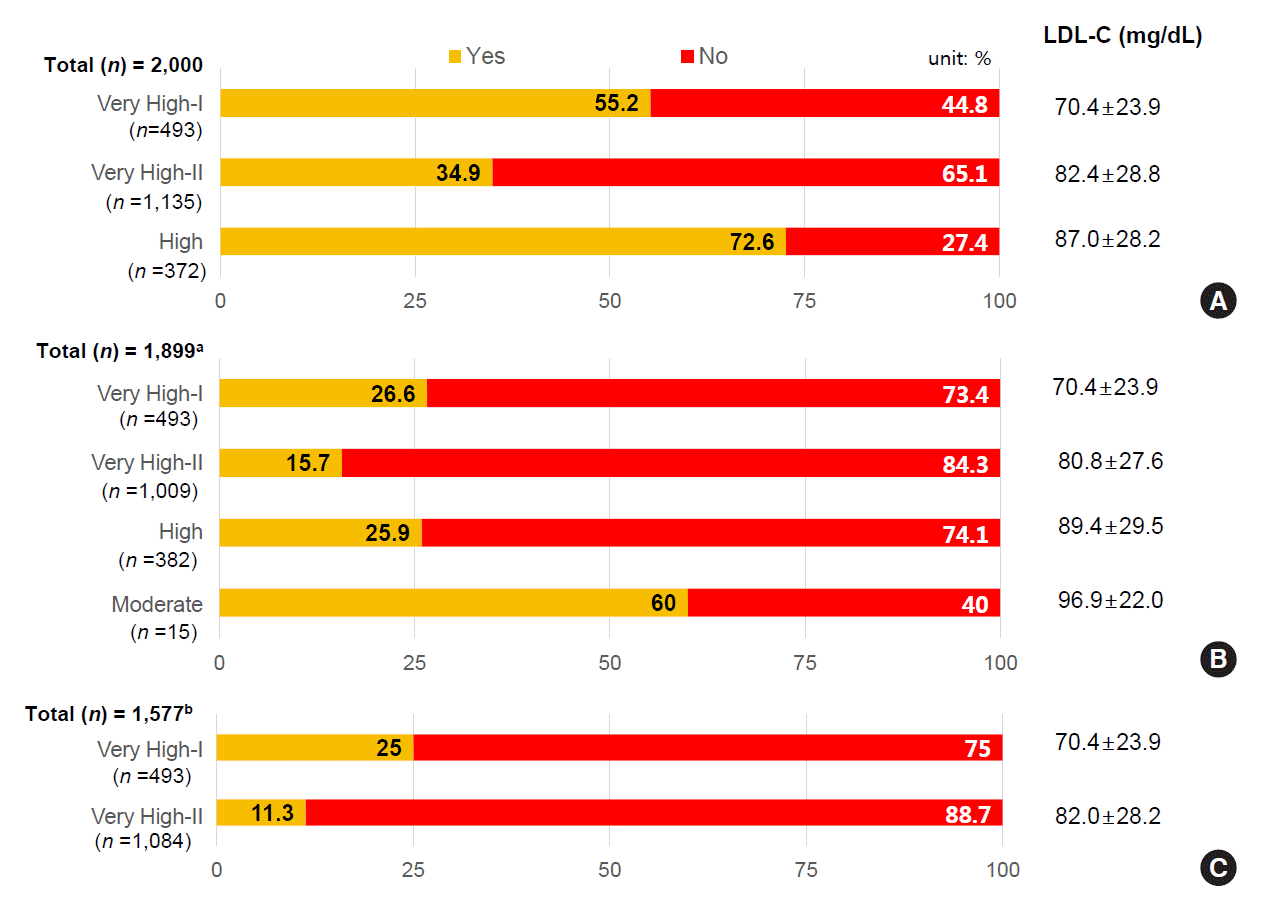
Prescribing pattern of lipid-lowering agents according to KDA guideline risk category and LDL-C target achievement
Fig. 3.
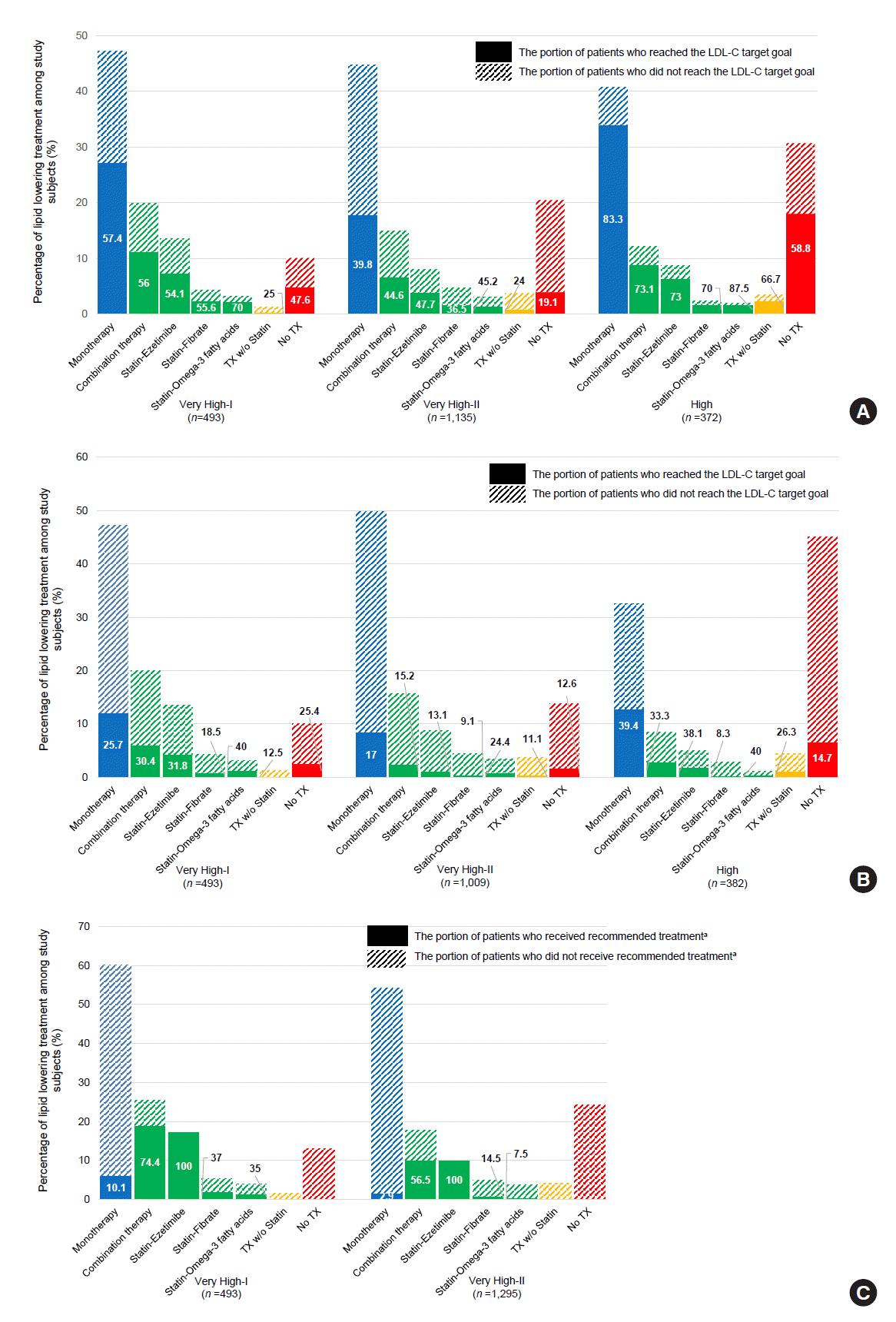




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download