INTRODUCTION
Interventional cardiologists are facing an increasing burden of calcified coronary arteries in keeping with an ageing population and rising prevalence of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease.
1)2) Heavily calcified plaques impede balloon dilatation and successful stent delivery, resulting stent under-expansion, malapposition, and damage to the drug-eluting polymer coats.
2) This translates to poorer procedural outcomes and increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
3)4)
Several treatment options already exist.
5) Rotational atherectomy (RA), widely regarded as standard of care for lesions not responding to balloon-based therapies, uses a rapidly rotating burr to ablate and modify calcified plaques. RA has been showed to achieve superior acute luminal gain and successful stent delivery compared to balloon angioplasty alone.
2) However, these positive outcomes are counterbalanced by higher rates of periprocedural and in-hospital complications after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
6)
In comparison, intravascular lithotripsy (IVL; Shockwave Medical, Santa Clara, CA, USA) is a balloon-based device containing lithotripsy emitters. IVL delivers uniformly distributed sonic waves which causes intraplaque calcium fractures that can then be visualized on optical coherence tomography. The development of these fractures is an important determinant of optimal stent expansion and predicts subsequent risk of stent thrombosis or restenosis.
7) The other benefits of IVL include reduced vascular intimal injury while preserving vessel wall fibroelastic integrity, and a low complication rate.
8)9) The balloon based IVL design also makes it an attractive option to operators due to its ease of use and shallow learning curve.
10)
Several single-armed studies have demonstrated favourable outcomes using IVL, including the prospective multi-centre DISRUPT CAD phase I, II & III trials. Observational studies in the real-world setting have also reported encouraging results.
8)10) However, there currently are no trials comparing IVL to other calcium modification strategies.
In our novel paper, we postulate that IVL therapy is a safe alternative to RA in real-world patients. We present the first comparison of clinical outcomes between IVL therapy with RA.
METHODS
Ethical statement
Additional consent for IVL use was required for elective cases. For urgent cases, IVL use without consent was permitted as “bail-out” therapy after initial lesion modification techniques had failed. IVL outcomes data was collected under local regulatory directives for healthcare audit; as such all IVL cases from our institution were included in the registry, and informed consent for data collection was waived with permission from the Singhealth Centralized Institutional Review Board (reference number 2020/2029).
Study design
We conducted a retrospective study looking at clinical outcomes of all patients who received IVL from January 2017 to July 2020 for difficult-to-treat severely calcified coronary lesions refractory to conventional therapy at our tertiary centre in Singapore. This data was compared against a separate cohort of patients who received RA at our centre from January 2017 to December 2018 prior to the availability of IVL. Twelve operators from our centre participated in this study. Baseline demographics and clinical outcomes data were collected from the Singapore Cardiac Data Bank which was established in 2000 as a national data bank of cardiovascular diseases and procedures, and contains epidemiological, clinical, and procedural data frequently used for national audit, quality improvement and research purposes.
11)
Participants
As per local regulations, participants were only eligible for IVL therapy if they had either 1) severe calcification on intravascular imaging as defined as ≥270-degree arc of calcium, or 2) angiographic evidence of severe calcification where devices cannot cross, or a non-compliant balloon cannot adequately expand.
Participants received RA as per standard indications for heavily calcified lesions as deemed suitable by the primary operator. Cases with missing values in age, gender or complications were excluded.
Study device and procedures
The IVL catheter (Shockwave C
2; Shockwave Medical) contains an integrated balloon enclosing multiple lithotripsy emitters that generate sonic pressure waves. As per standard technique, the balloon catheter was sized 1:1 to the reference artery and deployed by mono-railing over a 0.014″ coronary guidewire to the target lesion. The balloon was then inflated to low pressures (4 atmospheres [atm]) to allow contact with the vessel wall while minimizing barotrauma. If the operator was unable to pass the IVL catheter across the lesion, adjunctive tools such as buddy wire, small balloon, or guide catheter extension, were allowed. Up to 10 impulses were delivered (at 1 pulse/sec over 10 seconds). Subsequently, the balloon was further dilated to the nominal pressure (6 atm), then deflated to allow blood flow. In event of multiple lesions, each lesion was treated with a minimum of 20 pulses. A single IVL catheter may deliver a total of 80 impulses. If lesion preparation was incomplete, further IVL catheters with the same or different balloon sizes were allowed. If the target lesion had significant vessel tapering, different IVL balloon sizes were allowed. A video showcasing the mechanism of IVL is enclosed in the
Supplementary Video 1.
RA was performed using the Rotablator (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) as per standard of care.
Pre- and post-dilatation was allowed if needed at the individual operator’s discretion. All patients received dual antiplatelet therapy prior to PCI, namely aspirin with either clopidogrel or ticagrelor, and intraprocedural heparin in accordance to established clinical guidelines.
12)13)
Endpoints
The primary endpoints were in-hospital and 30-day MACE, defined as all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), target vessel revascularization (TVR) or stroke as prespecified by local healthcare authorities. The secondary endpoints were angiographic success, intraprocedural perforation or persistent slow or no-reflow, and stent thrombosis.
MI was defined as per the Fourth Universal Definition for MI.
14) Angiographic success was defined as success in facilitating stent delivery with <30% residual stenosis and without serious angiographic complications.
15)
Statistical analysis
Continuous data were given as median (interquartile range). Categorical data are presented as counts and proportions (%). Pearson’s χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test were performed in comparison between groups in categorical variables, and Mann-Whitney U test were performed for continuous variables. A p value of ≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Logistic regression and Firth’s logistic regression were performed to predict risk factors of in-hospital and 30-day outcomes for MACE. All variables with p<0.2 on univariable logistic regression and Firth’s logistic regression and other clinically relevant variables, namely age, gender, and treatment group were included in multivariable logistic and Firth’s logistic regression. Propensity score adjustment model was used to analyse the correlation between MACE and IVL after adjustment for differences in observed covariates (age, females, diabetes mellitus, acute coronary syndrome [ACS], current dialysis, and left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF]) against treatment. These variables were chosen based on prior literature which had identified associations with increased MACE in the setting of calcified coronary lesions.
2)16)17) Propensity scores were computed based on a logistic regression with variables age, females, diabetes mellitus, ACS, current dialysis and LVEF on Treatment Group as an outcome. The propensity scores were then entered together with treatment group in both logistic regression and Firth’s logistic regression to predict the odds of in-hospital and 30-day MACE.
Statistical analysis was done using IBM SPSS Statistics Version 26 (IBM, Armonk, New York, NY, USA) and R software version 3.6.3(R Foundation, Vienna, Austria). The R package logistf were used for Firth logistic regression respectively.
RESULTS
Patients and procedures
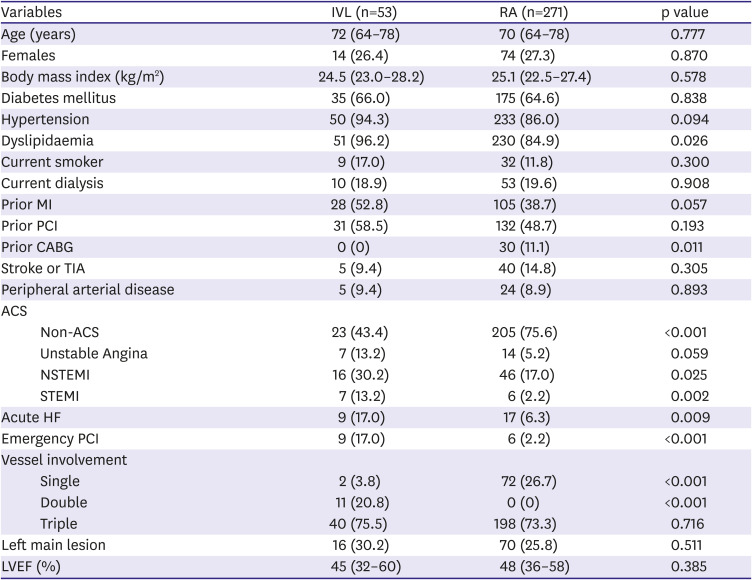
During the study periods, 53 IVL patients (73.6% male, median 72 years) and 271 RA patients (72.7% male, median 70 years) were included. Baseline characteristics are shown in
Table 1. Angiographic and procedural characteristics of the IVL cohort were described in a prior publication
18) and presented in
Supplementary Tables 1,
2, and
3.
Table 1
Baseline and clinical demographics
|
Variables |
IVL (n=53) |
RA (n=271) |
p value |
|
Age (years) |
72 (64–78) |
70 (64–78) |
0.777 |
|
Females |
14 (26.4) |
74 (27.3) |
0.870 |
|
Body mass index (kg/m2) |
24.5 (23.0–28.2) |
25.1 (22.5–27.4) |
0.578 |
|
Diabetes mellitus |
35 (66.0) |
175 (64.6) |
0.838 |
|
Hypertension |
50 (94.3) |
233 (86.0) |
0.094 |
|
Dyslipidaemia |
51 (96.2) |
230 (84.9) |
0.026 |
|
Current smoker |
9 (17.0) |
32 (11.8) |
0.300 |
|
Current dialysis |
10 (18.9) |
53 (19.6) |
0.908 |
|
Prior MI |
28 (52.8) |
105 (38.7) |
0.057 |
|
Prior PCI |
31 (58.5) |
132 (48.7) |
0.193 |
|
Prior CABG |
0 (0) |
30 (11.1) |
0.011 |
|
Stroke or TIA |
5 (9.4) |
40 (14.8) |
0.305 |
|
Peripheral arterial disease |
5 (9.4) |
24 (8.9) |
0.893 |
|
ACS |
|
|
|
|
Non-ACS |
23 (43.4) |
205 (75.6) |
<0.001 |
|
Unstable Angina |
7 (13.2) |
14 (5.2) |
0.059 |
|
NSTEMI |
16 (30.2) |
46 (17.0) |
0.025 |
|
STEMI |
7 (13.2) |
6 (2.2) |
0.002 |
|
Acute HF |
9 (17.0) |
17 (6.3) |
0.009 |
|
Emergency PCI |
9 (17.0) |
6 (2.2) |
<0.001 |
|
Vessel involvement |
|
|
|
|
Single |
2 (3.8) |
72 (26.7) |
<0.001 |
|
Double |
11 (20.8) |
0 (0) |
<0.001 |
|
Triple |
40 (75.5) |
198 (73.3) |
0.716 |
|
Left main lesion |
16 (30.2) |
70 (25.8) |
0.511 |
|
LVEF (%) |
45 (32–60) |
48 (36–58) |
0.385 |
Within the IVL group, 7 patients required adjuvant RA. In 6 out of these 7 patients, IVL was performed after RA alone had failed to achieve adequate lesion preparation. In one case, IVL was used as “bail-out” in a patient who deteriorated after no-reflow with RA. Within the RA group, there were no crossovers to IVL.
There was a high prevalence of comorbidities in both groups, including Diabetes Mellitus (66.0% vs 64.6%) and long-term dialysis (18.9% vs 19.6%). Comparing the groups, IVL patients were more likely to present acutely with heart failure (17.0% vs 6.3%, p=0.09), ACS (non-ST elevation myocardial infarction 30.2% vs 17.0%, p=0.025; ST elevation myocardial infarction 13.2% vs 2.2%, p=0.002) or require emergency PCI (17.0% vs 2.2%, p <0.001). IVL patients also had a higher incidence of multivessel disease (96.2% vs 73.3%, p <0.001), prior MI (52.8% vs 38.7%, p=0.057) but none had prior coronary artery bypass grafting (0% vs 11.1%, p=0.011).
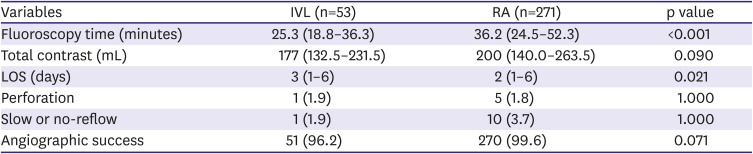
Procedural details are provided in
Table 2. IVL was associated with lower fluoroscopy time (25.3 minutes vs 36.3 minutes, p <0.001) and smaller contrast volumes (177 mL vs 200 mL, p=0.09). High rates of angiographic success was achieved with both IVL and RA (96.2% vs 99.6%, p=0.071), and the incidence of perforation was low (1.9% vs 1.8%, p=1.000). There was a lower incidence of slow or no-reflow with IVL (1.9% vs 3.7%, p=1.000) although this did not reach statistical significance.
Table 2
Procedural details
|
Variables |
IVL (n=53) |
RA (n=271) |
p value |
|
Fluoroscopy time (minutes) |
25.3 (18.8–36.3) |
36.2 (24.5–52.3) |
<0.001 |
|
Total contrast (mL) |
177 (132.5–231.5) |
200 (140.0–263.5) |
0.090 |
|
LOS (days) |
3 (1–6) |
2 (1–6) |
0.021 |
|
Perforation |
1 (1.9) |
5 (1.8) |
1.000 |
|
Slow or no-reflow |
1 (1.9) |
10 (3.7) |
1.000 |
|
Angiographic success |
51 (96.2) |
270 (99.6) |
0.071 |
Still images of IVL deployment for an acutely under-expanded stent from our IVL cohort are included in
Figure 1.
Figure 1
Example of IVL.
(A) An acutely under-expanded stent due to concentric calcification despite high pressure OPN balloon dilatation. (B) Markedly improved stent expansion after 30 pulses of a 3.5 mm Shockwave balloon (refer to
Supplementary Video 2 for fluoroscopy run).
IVL = intravascular lithotripsy.

Endpoints
In-hospital outcomes are presented in
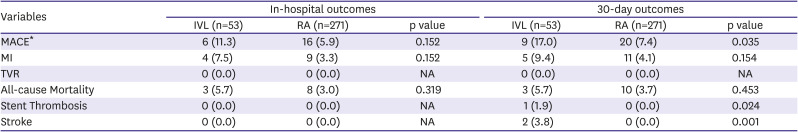
Table 3. There was a trend towards higher MACE, MI, and all-cause mortality in the IVL group as compared to RA which was not statistically significant because of the small study population. None of the patients had in-hospital stroke or stent thrombosis. In the IVL group, 3 patients had asymptomatic post-PCI isolated cardiac troponin rise that contributed to the higher incidence of MACE and MI.
Table 3
In-hospital and 30-day outcomes
|
Variables |
In-hospital outcomes |
30-day outcomes |
|
IVL (n=53) |
RA (n=271) |
p value |
IVL (n=53) |
RA (n=271) |
p value |
|
MACE*
|
6 (11.3) |
16 (5.9) |
0.152 |
9 (17.0) |
20 (7.4) |
0.035 |
|
MI |
4 (7.5) |
9 (3.3) |
0.152 |
5 (9.4) |
11 (4.1) |
0.154 |
|
TVR |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
NA |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
NA |
|
All-cause Mortality |
3 (5.7) |
8 (3.0) |
0.319 |
3 (5.7) |
10 (3.7) |
0.453 |
|
Stent Thrombosis |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
NA |
1 (1.9) |
0 (0.0) |
0.024 |
|
Stroke |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
NA |
2 (3.8) |
0 (0.0) |
0.001 |
30-day outcomes are also presented in
Table 3. There was a higher incidence of MACE in the IVL group as compared to RA (17.0% vs 7.4%, p=0.035). One IVL patient had stent-thrombosis (1.9% vs 0%, p=0.024) and 2 patients had stroke (3.8% vs 0%, p=0.001) compared to none with RA.
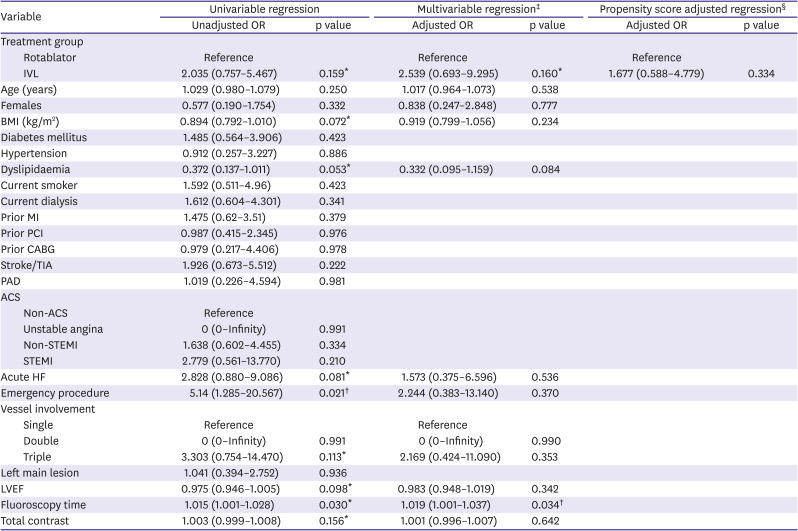
Logistic regression was performed using a combination of multivariable analysis and propensity score adjustment done to evaluate the association between MACE and IVL (
Tables 4 and
5). Propensity score adjusted regression using IVL was performed on in-hospital MACE (odds ratio [OR], 1.677; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.588–4.779) and 30-day MACE (OR, 1.910; 95% CI, 0.774–4.718). Results of the Firth logistic regression are included in
Tables 6 and
7. Our results were due to a wide range of effects, including substantial decreases or increases in clinical events. The overall clinical utility of IVL remains uncertain.
Table 4
Logistic regression (in-hospital MACE)
|
Variable |
Univariable regression |
Multivariable regression‡
|
Propensity score adjusted regression§
|
|
Unadjusted OR |
p value |
Adjusted OR |
p value |
Adjusted OR |
p value |
|
Treatment group |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rotablator |
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
|
IVL |
2.035 (0.757–5.467) |
0.159*
|
2.539 (0.693–9.295) |
0.160*
|
1.677 (0.588–4.779) |
0.334 |
|
Age (years) |
1.029 (0.980–1.079) |
0.250 |
1.017 (0.964–1.073) |
0.538 |
|
|
|
Females |
0.577 (0.190–1.754) |
0.332 |
0.838 (0.247–2.848) |
0.777 |
|
|
|
BMI (kg/m2) |
0.894 (0.792–1.010) |
0.072*
|
0.919 (0.799–1.056) |
0.234 |
|
|
|
Diabetes mellitus |
1.485 (0.564–3.906) |
0.423 |
|
|
|
|
|
Hypertension |
0.912 (0.257–3.227) |
0.886 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dyslipidaemia |
0.372 (0.137–1.011) |
0.053*
|
0.332 (0.095–1.159) |
0.084 |
|
|
|
Current smoker |
1.592 (0.511–4.96) |
0.423 |
|
|
|
|
|
Current dialysis |
1.612 (0.604–4.301) |
0.341 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior MI |
1.475 (0.62–3.51) |
0.379 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior PCI |
0.987 (0.415–2.345) |
0.976 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior CABG |
0.979 (0.217–4.406) |
0.978 |
|
|
|
|
|
Stroke/TIA |
1.926 (0.673–5.512) |
0.222 |
|
|
|
|
|
PAD |
1.019 (0.226–4.594) |
0.981 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-ACS |
Reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unstable angina |
0 (0–Infinity) |
0.991 |
|
|
|
|
|
Non-STEMI |
1.638 (0.602–4.455) |
0.334 |
|
|
|
|
|
STEMI |
2.779 (0.561–13.770) |
0.210 |
|
|
|
|
|
Acute HF |
2.828 (0.880–9.086) |
0.081*
|
1.573 (0.375–6.596) |
0.536 |
|
|
|
Emergency procedure |
5.14 (1.285–20.567) |
0.021†
|
2.244 (0.383–13.140) |
0.370 |
|
|
|
Vessel involvement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Single |
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
|
|
|
Double |
0 (0–Infinity) |
0.991 |
0 (0–Infinity) |
0.990 |
|
|
|
Triple |
3.303 (0.754–14.470) |
0.113*
|
2.169 (0.424–11.090) |
0.353 |
|
|
|
Left main lesion |
1.041 (0.394–2.752) |
0.936 |
|
|
|
|
|
LVEF |
0.975 (0.946–1.005) |
0.098*
|
0.983 (0.948–1.019) |
0.342 |
|
|
|
Fluoroscopy time |
1.015 (1.001–1.028) |
0.030*
|
1.019 (1.001–1.037) |
0.034†
|
|
|
|
Total contrast |
1.003 (0.999–1.008) |
0.156*
|
1.001 (0.996–1.007) |
0.642 |
|
|
Table 5
Logistic regression (30-day MACE)
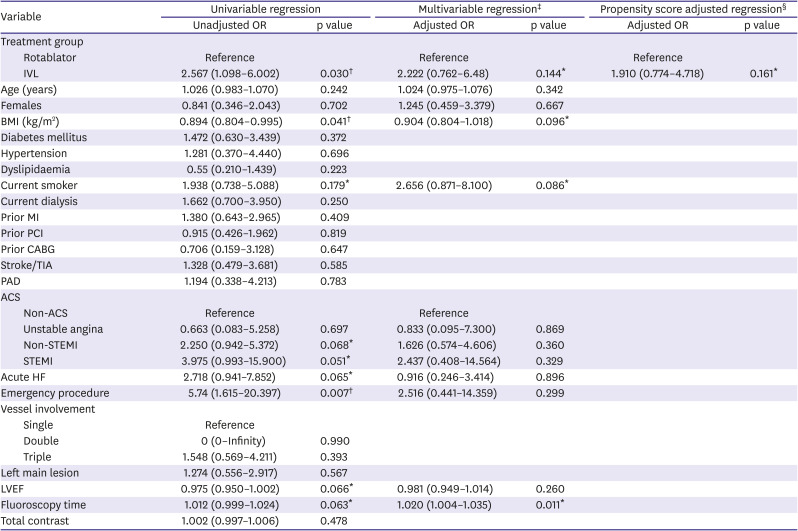
|
Variable |
Univariable regression |
Multivariable regression‡
|
Propensity score adjusted regression§
|
|
Unadjusted OR |
p value |
Adjusted OR |
p value |
Adjusted OR |
p value |
|
Treatment group |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rotablator |
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
|
IVL |
2.567 (1.098–6.002) |
0.030†
|
2.222 (0.762–6.48) |
0.144*
|
1.910 (0.774–4.718) |
0.161*
|
|
Age (years) |
1.026 (0.983–1.070) |
0.242 |
1.024 (0.975–1.076) |
0.342 |
|
|
|
Females |
0.841 (0.346–2.043) |
0.702 |
1.245 (0.459–3.379) |
0.667 |
|
|
|
BMI (kg/m2) |
0.894 (0.804–0.995) |
0.041†
|
0.904 (0.804–1.018) |
0.096*
|
|
|
|
Diabetes mellitus |
1.472 (0.630–3.439) |
0.372 |
|
|
|
|
|
Hypertension |
1.281 (0.370–4.440) |
0.696 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dyslipidaemia |
0.55 (0.210–1.439) |
0.223 |
|
|
|
|
|
Current smoker |
1.938 (0.738–5.088) |
0.179*
|
2.656 (0.871–8.100) |
0.086*
|
|
|
|
Current dialysis |
1.662 (0.700–3.950) |
0.250 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior MI |
1.380 (0.643–2.965) |
0.409 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior PCI |
0.915 (0.426–1.962) |
0.819 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior CABG |
0.706 (0.159–3.128) |
0.647 |
|
|
|
|
|
Stroke/TIA |
1.328 (0.479–3.681) |
0.585 |
|
|
|
|
|
PAD |
1.194 (0.338–4.213) |
0.783 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-ACS |
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
|
|
|
Unstable angina |
0.663 (0.083–5.258) |
0.697 |
0.833 (0.095–7.300) |
0.869 |
|
|
|
Non-STEMI |
2.250 (0.942–5.372) |
0.068*
|
1.626 (0.574–4.606) |
0.360 |
|
|
|
STEMI |
3.975 (0.993–15.900) |
0.051*
|
2.437 (0.408–14.564) |
0.329 |
|
|
|
Acute HF |
2.718 (0.941–7.852) |
0.065*
|
0.916 (0.246–3.414) |
0.896 |
|
|
|
Emergency procedure |
5.74 (1.615–20.397) |
0.007†
|
2.516 (0.441–14.359) |
0.299 |
|
|
|
Vessel involvement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Single |
Reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Double |
0 (0–Infinity) |
0.990 |
|
|
|
|
|
Triple |
1.548 (0.569–4.211) |
0.393 |
|
|
|
|
|
Left main lesion |
1.274 (0.556–2.917) |
0.567 |
|
|
|
|
|
LVEF |
0.975 (0.950–1.002) |
0.066*
|
0.981 (0.949–1.014) |
0.260 |
|
|
|
Fluoroscopy time |
1.012 (0.999–1.024) |
0.063*
|
1.020 (1.004–1.035) |
0.011*
|
|
|
|
Total contrast |
1.002 (0.997–1.006) |
0.478 |
|
|
|
|
Table 6
Firth logistic regression (in-hospital MACE)
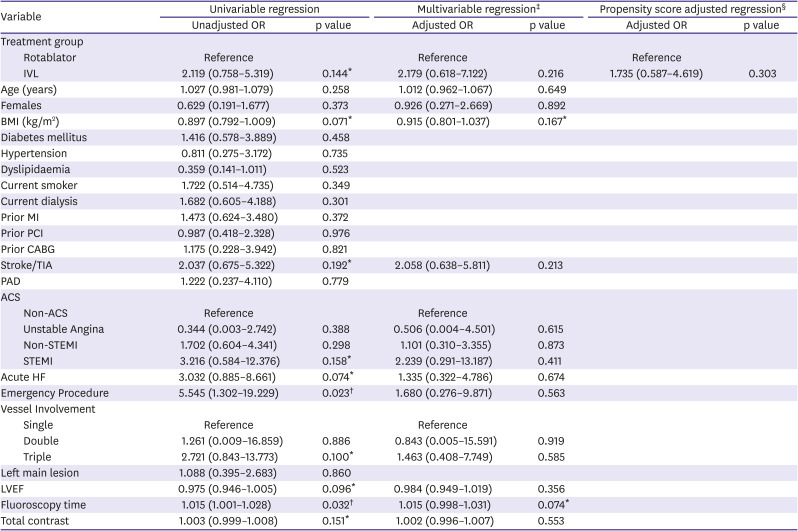
|
Variable |
Univariable regression |
Multivariable regression‡
|
Propensity score adjusted regression§
|
|
Unadjusted OR |
p value |
Adjusted OR |
p value |
Adjusted OR |
p value |
|
Treatment group |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rotablator |
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
|
IVL |
2.119 (0.758–5.319) |
0.144*
|
2.179 (0.618–7.122) |
0.216 |
1.735 (0.587–4.619) |
0.303 |
|
Age (years) |
1.027 (0.981–1.079) |
0.258 |
1.012 (0.962–1.067) |
0.649 |
|
|
|
Females |
0.629 (0.191–1.677) |
0.373 |
0.926 (0.271–2.669) |
0.892 |
|
|
|
BMI (kg/m2) |
0.897 (0.792–1.009) |
0.071*
|
0.915 (0.801–1.037) |
0.167*
|
|
|
|
Diabetes mellitus |
1.416 (0.578–3.889) |
0.458 |
|
|
|
|
|
Hypertension |
0.811 (0.275–3.172) |
0.735 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dyslipidaemia |
0.359 (0.141–1.011) |
0.523 |
|
|
|
|
|
Current smoker |
1.722 (0.514–4.735) |
0.349 |
|
|
|
|
|
Current dialysis |
1.682 (0.605–4.188) |
0.301 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior MI |
1.473 (0.624–3.480) |
0.372 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior PCI |
0.987 (0.418–2.328) |
0.976 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior CABG |
1.175 (0.228–3.942) |
0.821 |
|
|
|
|
|
Stroke/TIA |
2.037 (0.675–5.322) |
0.192*
|
2.058 (0.638–5.811) |
0.213 |
|
|
|
PAD |
1.222 (0.237–4.110) |
0.779 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-ACS |
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
|
|
|
Unstable Angina |
0.344 (0.003–2.742) |
0.388 |
0.506 (0.004–4.501) |
0.615 |
|
|
|
Non-STEMI |
1.702 (0.604–4.341) |
0.298 |
1.101 (0.310–3.355) |
0.873 |
|
|
|
STEMI |
3.216 (0.584–12.376) |
0.158*
|
2.239 (0.291–13.187) |
0.411 |
|
|
|
Acute HF |
3.032 (0.885–8.661) |
0.074*
|
1.335 (0.322–4.786) |
0.674 |
|
|
|
Emergency Procedure |
5.545 (1.302–19.229) |
0.023†
|
1.680 (0.276–9.871) |
0.563 |
|
|
|
Vessel Involvement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Single |
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
|
|
|
Double |
1.261 (0.009–16.859) |
0.886 |
0.843 (0.005–15.591) |
0.919 |
|
|
|
Triple |
2.721 (0.843–13.773) |
0.100*
|
1.463 (0.408–7.749) |
0.585 |
|
|
|
Left main lesion |
1.088 (0.395–2.683) |
0.860 |
|
|
|
|
|
LVEF |
0.975 (0.946–1.005) |
0.096*
|
0.984 (0.949–1.019) |
0.356 |
|
|
|
Fluoroscopy time |
1.015 (1.001–1.028) |
0.032†
|
1.015 (0.998–1.031) |
0.074*
|
|
|
|
Total contrast |
1.003 (0.999–1.008) |
0.151*
|
1.002 (0.996–1.007) |
0.553 |
|
|
Table 7
Firth logistic regression (30-day MACE)
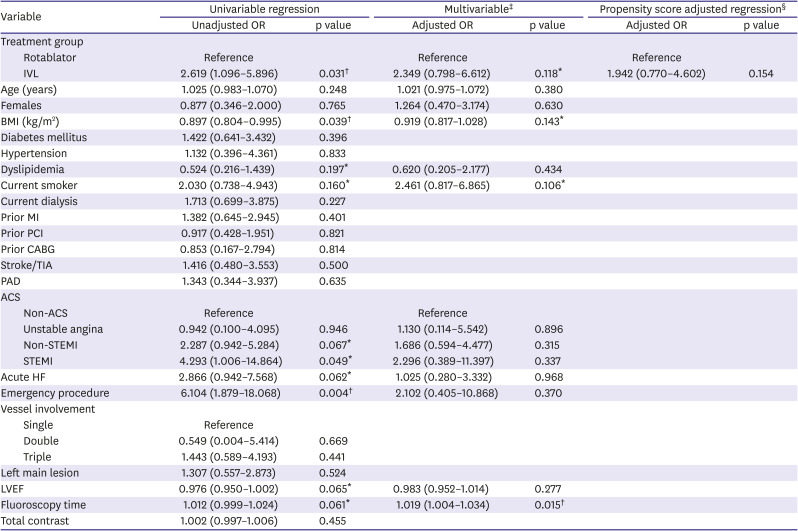
|
Variable |
Univariable regression |
Multivariable‡
|
Propensity score adjusted regression§
|
|
Unadjusted OR |
p value |
Adjusted OR |
p value |
Adjusted OR |
p value |
|
Treatment group |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rotablator |
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
|
IVL |
2.619 (1.096–5.896) |
0.031†
|
2.349 (0.798–6.612) |
0.118*
|
1.942 (0.770–4.602) |
0.154 |
|
Age (years) |
1.025 (0.983–1.070) |
0.248 |
1.021 (0.975–1.072) |
0.380 |
|
|
|
Females |
0.877 (0.346–2.000) |
0.765 |
1.264 (0.470–3.174) |
0.630 |
|
|
|
BMI (kg/m2) |
0.897 (0.804–0.995) |
0.039†
|
0.919 (0.817–1.028) |
0.143*
|
|
|
|
Diabetes mellitus |
1.422 (0.641–3.432) |
0.396 |
|
|
|
|
|
Hypertension |
1.132 (0.396–4.361) |
0.833 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dyslipidemia |
0.524 (0.216–1.439) |
0.197*
|
0.620 (0.205–2.177) |
0.434 |
|
|
|
Current smoker |
2.030 (0.738–4.943) |
0.160*
|
2.461 (0.817–6.865) |
0.106*
|
|
|
|
Current dialysis |
1.713 (0.699–3.875) |
0.227 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior MI |
1.382 (0.645–2.945) |
0.401 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior PCI |
0.917 (0.428–1.951) |
0.821 |
|
|
|
|
|
Prior CABG |
0.853 (0.167–2.794) |
0.814 |
|
|
|
|
|
Stroke/TIA |
1.416 (0.480–3.553) |
0.500 |
|
|
|
|
|
PAD |
1.343 (0.344–3.937) |
0.635 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-ACS |
Reference |
|
Reference |
|
|
|
|
Unstable angina |
0.942 (0.100–4.095) |
0.946 |
1.130 (0.114–5.542) |
0.896 |
|
|
|
Non-STEMI |
2.287 (0.942–5.284) |
0.067*
|
1.686 (0.594–4.477) |
0.315 |
|
|
|
STEMI |
4.293 (1.006–14.864) |
0.049*
|
2.296 (0.389–11.397) |
0.337 |
|
|
|
Acute HF |
2.866 (0.942–7.568) |
0.062*
|
1.025 (0.280–3.332) |
0.968 |
|
|
|
Emergency procedure |
6.104 (1.879–18.068) |
0.004†
|
2.102 (0.405–10.868) |
0.370 |
|
|
|
Vessel involvement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Single |
Reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Double |
0.549 (0.004–5.414) |
0.669 |
|
|
|
|
|
Triple |
1.443 (0.589–4.193) |
0.441 |
|
|
|
|
|
Left main lesion |
1.307 (0.557–2.873) |
0.524 |
|
|
|
|
|
LVEF |
0.976 (0.950–1.002) |
0.065*
|
0.983 (0.952–1.014) |
0.277 |
|
|
|
Fluoroscopy time |
1.012 (0.999–1.024) |
0.061*
|
1.019 (1.004–1.034) |
0.015†
|
|
|
|
Total contrast |
1.002 (0.997–1.006) |
0.455 |
|
|
|
|
Of the 3 IVL mortalities at 30 days, 2 patients (one with pre-existing malignancy and another with end stage renal failure) demised due to nosocomial infections after prolonged admissions for high-risk ACS. Both patients had initially undergone successful high-risk PCI with IVL support. The third IVL mortality was the aforementioned patient who had no-reflow after RA where IVL was used as rescue therapy (Results, Patients and Procedures, Paragraph 2).
DISCUSSION
With recent publications, there is mounting evidence to support the efficacy of IVL in heavily calcified coronary lesions.
9)10) However, questions remain about how IVL compares to other more established calcium modification therapies and how it changes our approach to calcified lesions.
The numerically higher incidence of MACE in our IVL group may be attributable to a number of factors. Firstly, the IVL cohort had a higher risk profile in terms of multivessel disease, ACS, and usage as an emergency procedure. Secondly, due to a combination of regulatory as well as financial constraints (as described under Methods), our operators used IVL as adjunctive therapy after initial lesion modification techniques had already failed. This element of selection bias resulted in the patients in the IVL arm being inherently more complex. Thirdly, the small IVL cohort size likely limited the interpretation of the results. Fourth, current IVL technology is still somewhat limited by its deliverability across heavily calcified lesions, sometimes requiring adjunctive RA (also known as ‘Rota-Tripsy’). Hence, we feel that all these factors should be considered when interpreting the higher 30-day MACE rates in our IVL arm.
Although 2 IVL patients experienced strokes at 30-days, the cause is not clear and could be attributed to the high prevalence of established atherosclerotic disease as. In terms of intraprocedural outcomes, IVL therapy required shorter fluoroscopy time and smaller contrast volumes. We also observed low rates of complications in both IVL and RA groups, as well as high rates of angiographic success.
The safety of IVL has also been reported in other trials. The prospective single-armed international multicentre DISRUPT CAD III trial (n=384) demonstrated high procedural success of 92.2% with low residual stenosis ≤30% and similarly low rates of intra-procedural perforation (0.3%), slow or no-reflow (0%), in-hospital TVR (0.5%) and stent thrombosis (0.8%). MACE occurred less often (7.0%). The differences in clinical outcomes compared to our study can be explained by a different baseline patient profile. Our study also included patients with ACS (56.6%), acute heart failure (17%), long-term dialysis (18.9%) and unprotected left main lesions which were all excluded from the DISRUPT CAD III cohort.
9)10) The higher risk profile of our IVL patients is an important determinant for the differences in clinical outcomes between our study and DISRUPT CAD III.
Studies done in the real-word setting have also demonstrated good outcomes with IVL therapy. A retrospective analysis at 1 UK and 3 Italian centres (n=93) reported 2 cases of perforation (2%) resulting in 1 in-hospital mortality of (1%). At median 150 days of follow-up, there was no cardiac death, target vessel MI or target lesion revascularization.
19) Another prospective multicentre all-comers cohort of 2 German and 1 Spanish centres (n=78) at 30 days reported 1.3% MACE, zero perforations, and zero slow or no-reflow.
8)
Beyond randomized data, the real-world experience of IVL will be important in determining how this novel technology is used. As an example, the IVL device (Shockwave C
2) alone currently costs approximately USD $4,700 in the United States, and is more than double the cost of RA devices which starts at USD $2,000.
20) With such high costs, physicians may balk at using the device and only use it in “bail-out” situations. Furthermore, insurers and payors may also require evidence that conventional techniques have been unsuccessful. Some may also require intravascular imaging proof of circumferential or near-circumferential intracoronary calcium. This mandated use of intravascular imaging will also contribute to costs. On the other hand, unbridled use of technology may also drive-up overall healthcare costs. It remains to be seen if the higher upfront costs of using IVL may be balanced by superior long-term outcomes or eventual cost-savings.
We believe that our early experience with IVL reflects the nature of our restricted use of the device and the very sick patients in whom we used the therapy as a “bail-out” option. With experience and a less restricted group of patients, we anticipate that the therapy will provide benefit to more patients with overall better cardiovascular outcomes. We also propose that IVL should be considered first-line therapy for focal concentric calcified coronary lesions which are not responsive to dilatation using conventional or scoring balloons, and that IVL can also be an important adjunct to rotational or orbital atherectomy in addressing deep coronary calcium resistant to ablation.
There are several study limitations to be considered. Firstly, our study was a small, retrospective non-randomized study conducted at a single centre. Secondly, this is a report of our initial local experience with IVL, where our operators were both still gaining exposure to the device and contending with a number of regulatory and financial constraints. Thirdly, by virtue of the fact that IVL was used as adjunctive therapy after failure of conventional measures, this led to a higher incidence of multi-vessel disease, ACS, and emergency PCI in the IVL group. Due to the small sample size, we were able to adjust for a maximum of 6 variables (age, sex, diabetes, dialysis, ACS at presentation, and LVEF). All these factors may have contributed to the higher-than-expected MACE rates in the IVL arm.
In conclusion, these findings represent our initial IVL experience in a high-risk, real-world cohort. Although the event rate in the IVL arm was numerically higher, the small numbers and retrospective nature of this study preclude definitive conclusions. These clinical outcomes are likely to improve with greater experience and better case selection, allowing IVL to effectively treat complex calcified coronary lesions.












 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download