INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals
Spinal cord injury
Cell preparation
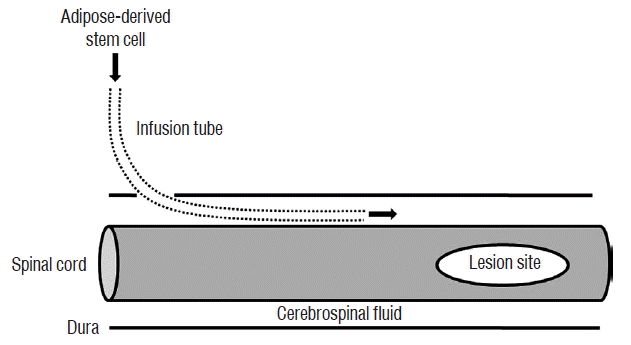
GCSF injection and cell transplantation
Behavioral testing
Immunofluorescent study
Western blotting
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Data processing and statistical analyses
RESULTS
Characterization of ADSCs
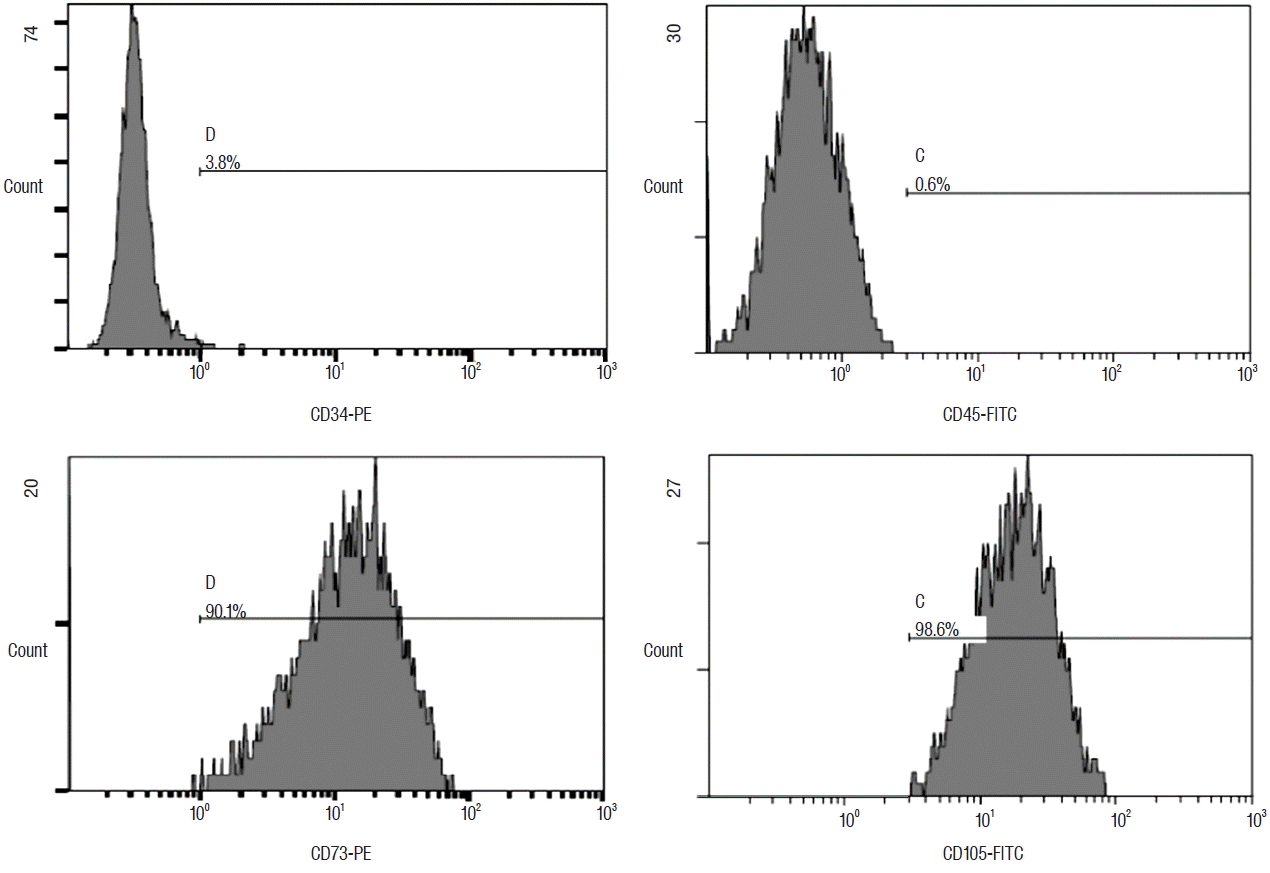 | Fig. 2Flow cytometric histograms of rat ADSCs by FACScan flow cytometer (Beckton Dickson, San Jose, CA, USA). Adipogenic positive marker, CD73, and CD105 were expressed in 90.1% and 98.6%, respectively. Adipogenic negative marker, CD34, and CD45 were indicated as 3.8% and 0.6%, respectively. ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell. |
Behavior tests
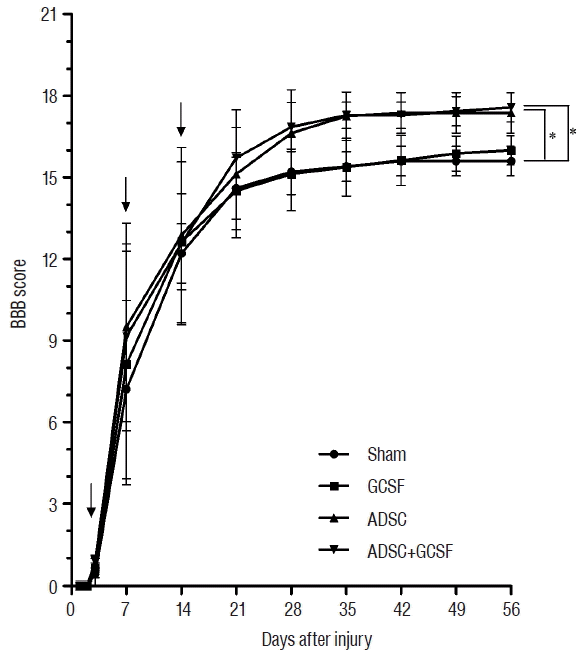 | Fig. 3BBB locomotor scale test. The recovery of BBB locomotor function after SCI in rats treated by infusion with PBS (Sham group), injection with GCSF (GCSF group), infusion with ADSCs (ADSC group), or infusion with ADSCs and GCSF (ADSC+GCSF group). Black arrow is injection time point. *p<0.01. BBB: Basso-Beattie-Bresnahan, SCI: spinal cord injury, PBS: phosphate-buffered saline, GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell. |
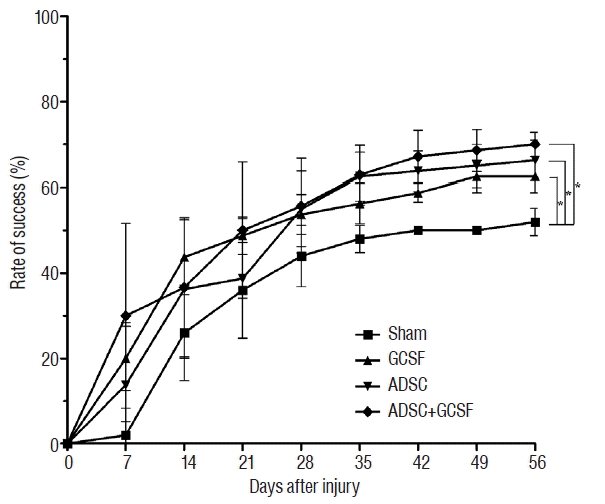 | Fig. 4Ladder rung test. The recovery of hindlimb function after SCI in rats treated by infusion with PBS (Sham group), injection with GCSF (GCSF group), infusion with ADSCs (ADSC group), or infusion with ADSCs and GCSF (ADSC+GCSF group). *p<0.01. SCI: spinal cord injury, PBS: phosphate-buffered saline, GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell. |
Immunofluorescent study
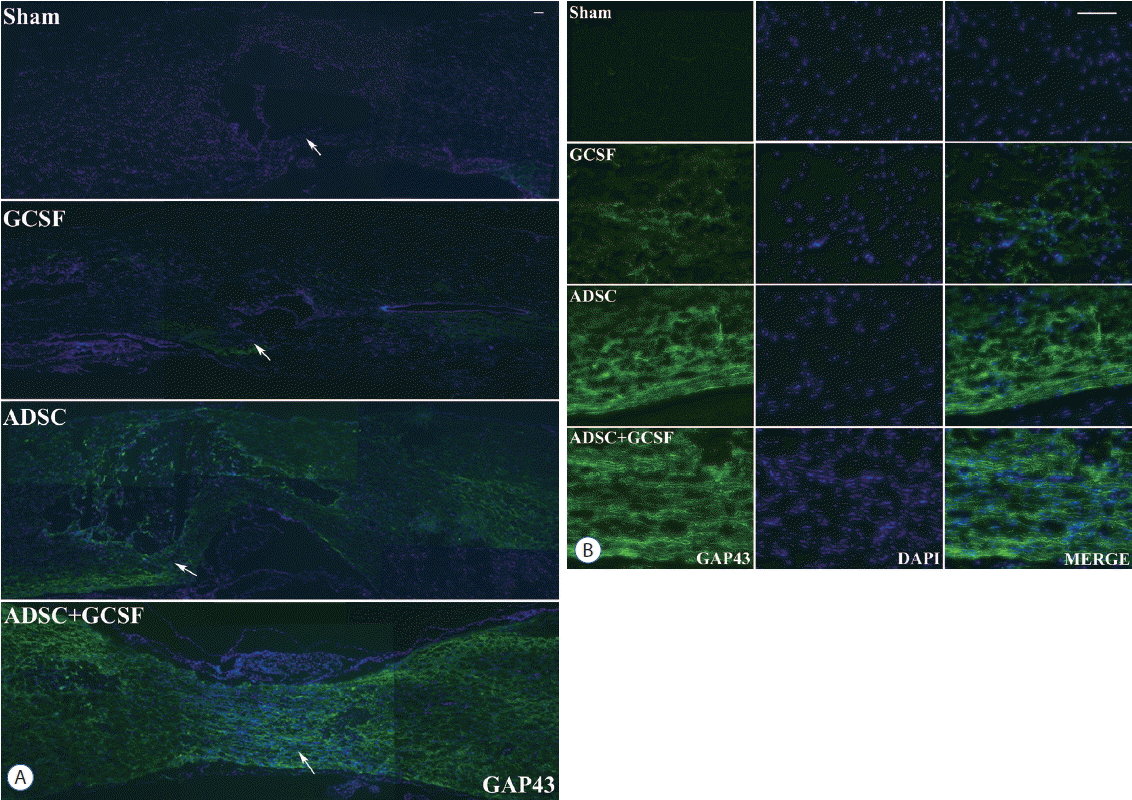 | Fig. 5Histological assessment of axonal regeneration using a GAP43. A: Confocal microscopic pictures revealed that anti-GAP43 antibody staining in the spinal cord was greater in the ADSC and ADSC+GCSF groups than in the Sham or GCSF groups 8 weeks after SCI. B: Magnification of white arrow area from (A). Scale bar: 50 μm. ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell, GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. |
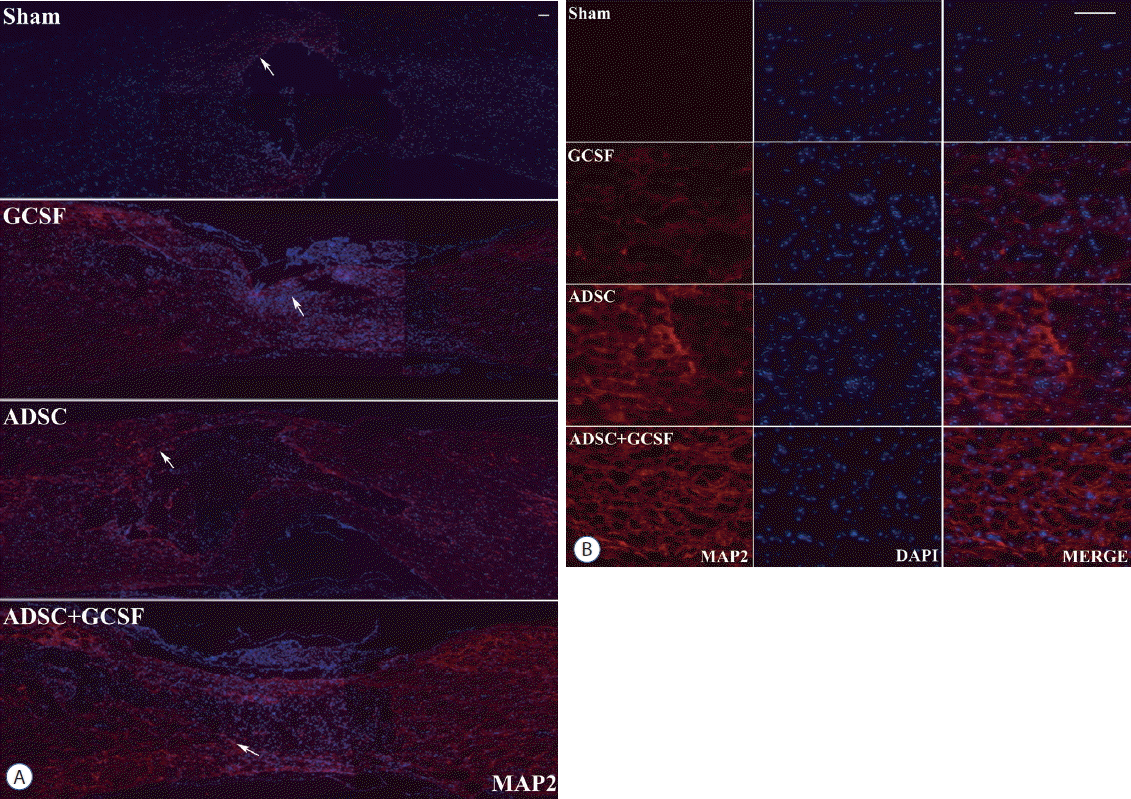 | Fig. 6Histological assessment of axonal regeneration using an MAP2. A: Confocal microscopic pictures revealed that anti-MAP2 antibody staining in the spinal cord was greater in the ADSC and ADSC+GCSF groups than in the Sham or GCSF groups 8 weeks after SCI. B: Magnification of white arrow area from (A). Scale bar: 50 μm. ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell, GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, SCI: spinal cord injury, DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2′-phenylindole. |
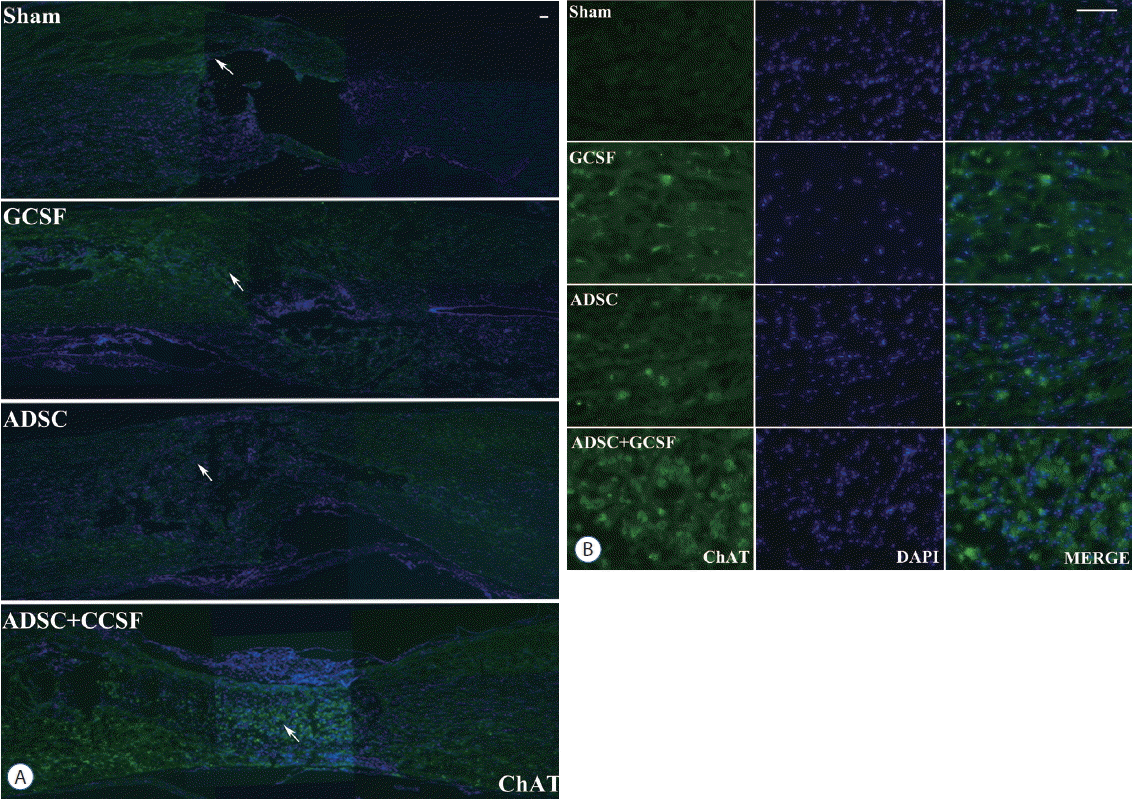 | Fig. 7Histological assessment of motor neuron marker using a ChAT. A: Confocal microscopic pictures revealed that anti-ChAT antibody staining in the spinal cord was greater in the ADSC+GCSF group than in other groups 8 weeks after SCI. B: Magnification of white arrow area from (A). Scale bar: 50 μm. GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell, SCI: spinal cord injury, DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2′-phenylindole. |
Western blotting
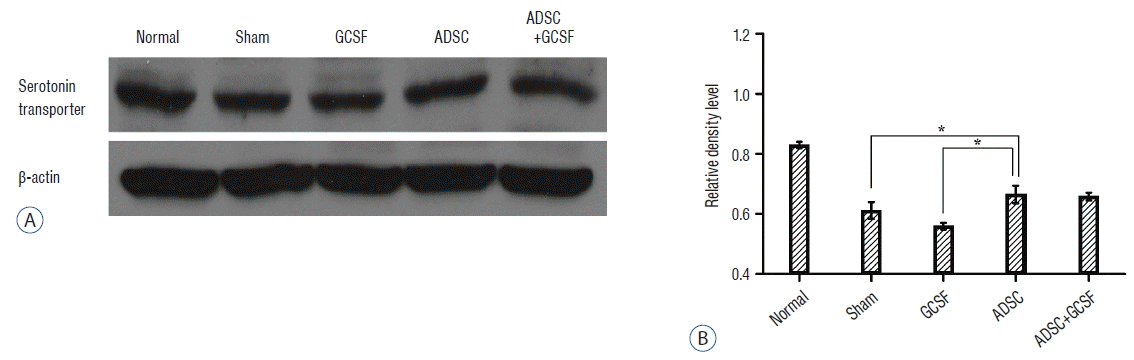 | Fig. 8Western blots analysis of serotonin transporter. A: Injured epicenters of 0.5 cm spinal cord were extracted protein and analyzed by Western blots. B: When the band densities were converted into RDL value, the ADSC group showed significantly high density than Sham and GCSF groups. There was no statistical difference of RDL value between the ADSC and ADSC+GCSF groups. *p<0.05. RDL: relative density level, ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell, GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. |
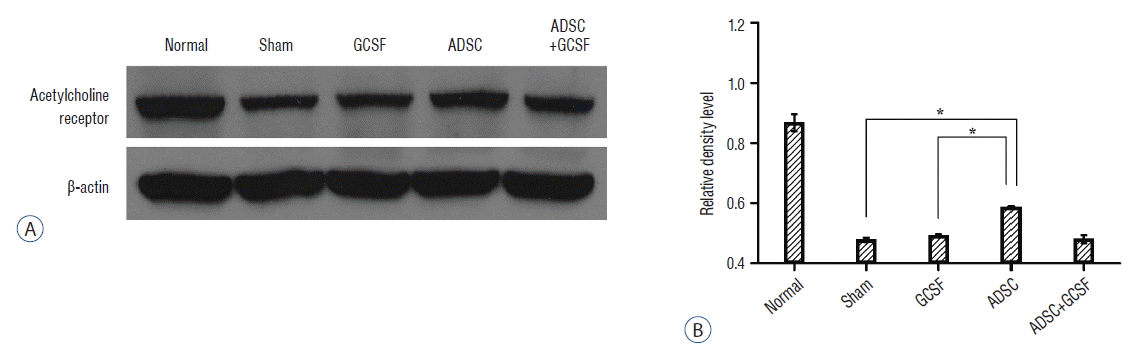 | Fig. 9Western blots analysis of acetylcholine receptor. A: Injured epicenters of 0.5 cm spinal cord were extracted protein and analyzed by Western blots. B: When the band densities were converted into RDL value, the ADSC group showed significantly high density than other groups. *p<0.01. RDL: relative density level, ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell, GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. |
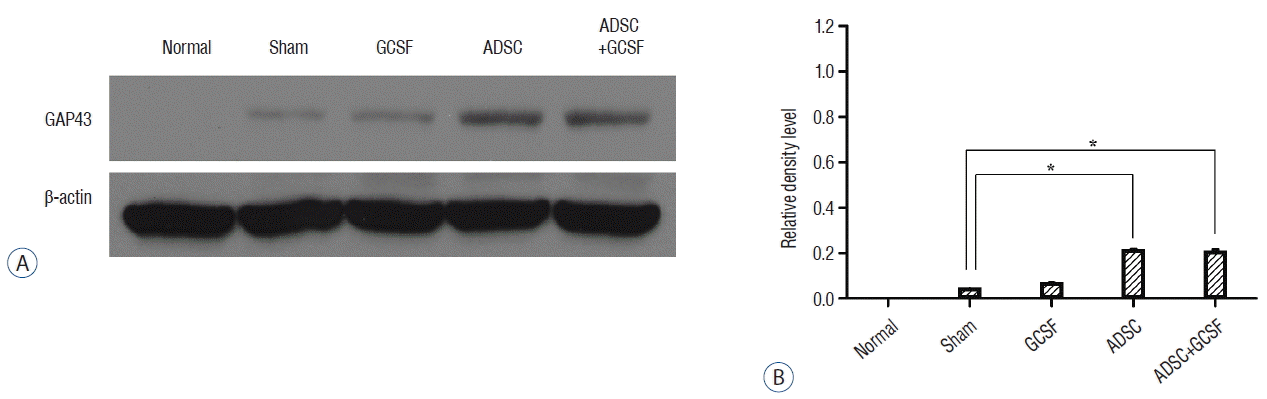 | Fig. 10Western blots analysis of GAP43. A: Injured epicenters of 0.5 cm spinal cord were extracted protein and analyzed by Western blots. B: When the band densities were converted into RDL value, the ADSC and ADSC+GCSF groups showed significantly high density than the Sham and GCSF groups. There was no statistical difference of RDL value between the ADSC and ADSC+GCSF groups. *p<0.01. RDL: relative density level, ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell, GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. |
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
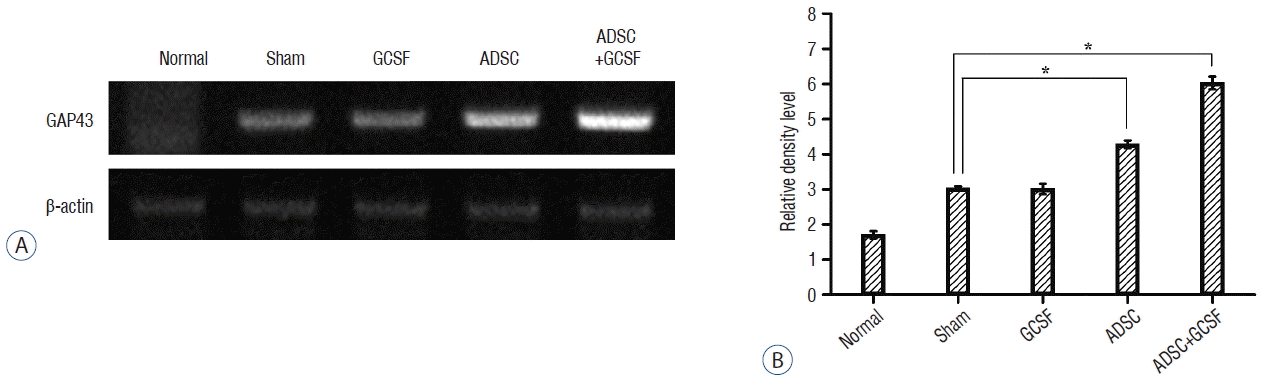 | Fig. 11RT-PCR analysis of GAP43. A: Injured epicenters of 0.5 cm spinal cord were extracted mRNA and analyzed by RT-PCR. B: When the band densities were converted to RDL value, the ADSC and ADSC+GCSF groups showed significantly high density than the Sham and GCSF groups. The ADSC+GCSF group showed significantly higher density than ADSC group. *p<0.01. RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, RDL: relative density level, ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell, GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. |
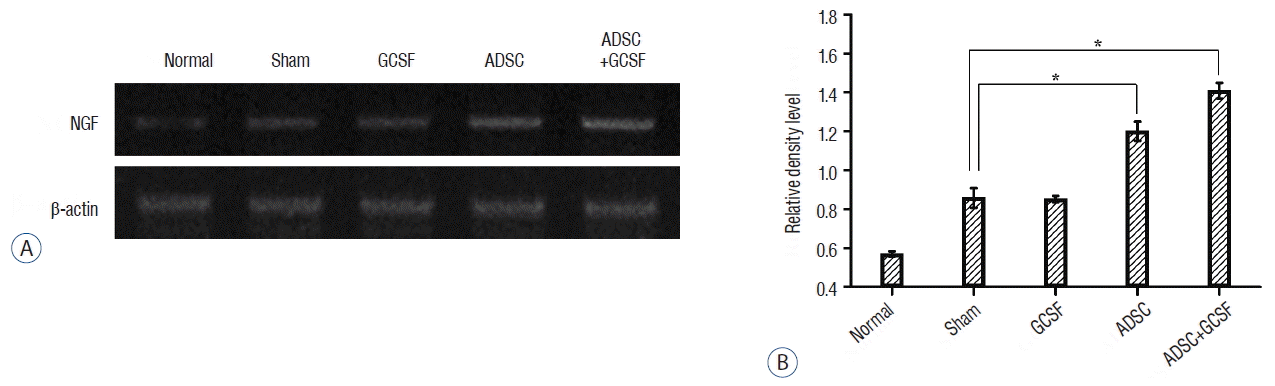 | Fig. 12RT-PCR analysis of NGF. A: Injured epicenters of 0.5 cm spinal cord were extracted mRNA and analyzed by RT-PCR. B: When the band densities were converted into RDL value, the ADSC and ADSC+GCSF groups showed significantly high density than the Sham and GCSF groups. The ADSC+GCSF group showed significantly higher density than ADSC group. *p<0.01. RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, RDL: relative density level, ADSC: adipose-derived stem cell, GCSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download