Abstract
Spinal cord herniation is a rare condition that has become increasingly recognised in the last few years. The authors report a case of idiopathic spinal cord herniation in a 33 year old woman performed with progressive Brown-Sequard syndrome. The diagnosis was made on MR imaging. After repairing the herniation, the patient made a gradual improvement. Potential causes are discussed, including a possible role of dural defect. In conclusion, idiopathic spinal cord herniation is a potentially treatable condition that should be more readily diagnosed that increasing awareness and improved imaging techniques.
Idiopathic spinal cord herniation (ISCH) is a very rare condition causing spinal cord myelopathy and approximately 180 cases have been reported since Wortzman et al.35) reported the first case25). Although various hypotheses were formed, pathophysiology and treatment still remain uncertain. ISCH usually occurs from T3 to T7 by spontaneous herniation of the spinal cord through anterior or antero-lateral dural defect826). The most common clinical presentation is Brown-Sequard syndrome, which has shown improvement through surgical treatment in many cases682431). We found that three cases of ISCH have been reported and surgical treatment was applied in only one case in South Korea111416). We present a case diagnosed as ISCH accompanied by Brown-Sequard syndrome and treated with surgical repair.
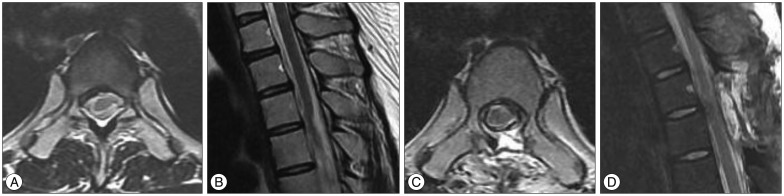
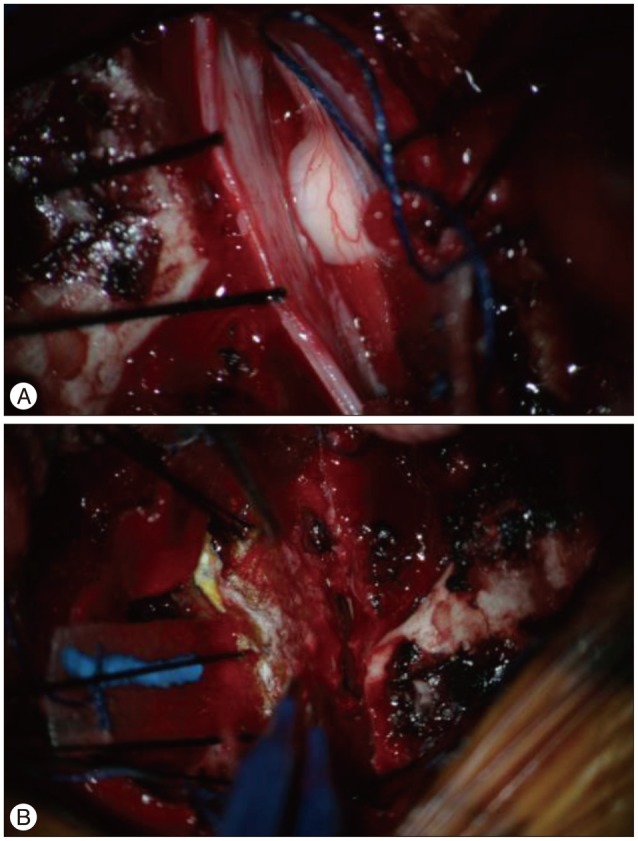
A 33-year-old woman visited our hospital for slowly developing left leg weakness for 3 month without history of trauma. She also had progressive right side paresthesia which had developed six years ago. At that time, she had orthostatic headache and examinations to find cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage were performed to rule out spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) at another university hospital. However, there were no specific findings and orthostatic headache improved spontaneously. She has been suffering from nocturia and residual urine sense for five months with no sign of defecation disorder. Neurological examination revealed some indications of Brown-Sequard syndrome, such as decreased pain and temperature sensation (70/100) in the region below right T4 dermatome and muscular weakness (Grade IV) and a poor tactile and vibration sense (70/100) in the region below left T4 dermatome. Deep tendon reflex (DTR) was increased in both lower limbs. The blood test showed no specific finding. Initial MRI showed left antero-lateral displacement of the thoracic spinal cord in T3-4 with expanded subarachnoid space, but there was no abnormal signal change within the spinal cord (Fig. 1). With the diagnosis of ISCH, we performed T3 total laminectomy and found that spinal cord was herniated through the dural defect on the left antero-medial side of T3 level (Fig. 2). After reduction of herniated spinal cord into intra-dural space, we patched dural defect with Tacho-comb® both intradurally and extradurally (Fig. 2). Postoperatively, the patient's symptoms gradually alleviated. Decreased pain and temperature sensation improved by 90% and left side weakness was restored to full muscular strength after 10 days. Dysuria due to the neurogenic bladder was slowly cured and was fully recovered approximately 6 months later.
ISCH that occurs without surgery or injury as in this case is very rare18). While several surgical cases of the condition have been reported, a definite mechanism of ISCH has not yet been found. The mean age of the patients was reportedly 49 years, ranging from 22 to 78, and there were about two times more females than males826). The most frequently reported clinical symptom was Brown-Sequard syndrome (75%), which developed slowly in most cases. It took patients 4.25 years on average (from 6 months to 20 years) to get surgery after appearance of symptoms682431). ISCH occurs mainly between T4 and T7, ventrally or ventrolaterally to the dural membrane and some findings related to ISCH could be observed mostly by sagittal MRI826).
The cause of ISCH has not been firmly established; however, a variety of mechanisms have been postulated, including minor or unrecognized trauma93335), congenital meningeal malformation4721), CSF flow pulsation7132932), and dural erosion due to a calcified disc or osteophyte352027). Among patients, dural defect is most frequently found in the thoracic spine, probably because the thoracic spine is located more ventrally than cervical or the lumbar vertebrae due to normal curvature of the entire spine and its' remarkable forward and backward movements of the spinal cord along with cardiovascular exercises713222932). The thoracic spine has less movement than the other spinal regions and it appears that great pressure is exerted on its ventral dural membrane due to the pulsatile CSF flow, which is very likely to cause a wider ventral dural defect and, ultimately, ISCH4182632). In some cases, ISCH was accompanied by a calcified disc or osteophyte, which appears to cause dural defect ventrally and then ISCH in the same mechanism352027). In our case, although we failed to obtain the prior medical record or image from the other hospital, the history of paresthesia accompanied by orthostatic headache implies that dural defect existed along with orthostatic headache, which was relieved from a the decrease in CSF leakage as ISCH led to the plug of the injured region.
Isu et al.12) suggested that the ventral dural membrane gradually became get thinner due to the pressure of the spinal cord, which was caused by a dorsal arachnoid cyst. Since then, several cases in which patient's symptoms improved better after removal of the arachnoid cyst with a surgery of the dorsal ventral dural membrane have been reported132). However, it is difficult to explain ISCH with arachnoid cyst alone because it has been found only in about 17% of cases. Sioutos et al.30) and Wada et al.34) reported that removal of arachnoid cyst alone led to no change and that ventral dislocation of the spinal cord persisted even after pressure from the cyst was relieved. Ewald et al.7) reported that spine MRI showed no specific finding in the early stage of patients with Brown-Sequard syndrome and follow-up MRI and CT myelogram, both of which were used after the condition had worsened, finally discovered ISCH. Therefore, it is reasonable to say that the condition is acquired, instead of occurring congenitally.
While the symptom and idiopathic ISCH occurred with the history of traumas in some cases, traumatic or iatrogenic defect is mainly located dorsally to the cervical vertebrae. Also, there was no notable spinal lesion or neurological symptom although trauma was serious enough to cause injury in the dural membrane9193335). It is therefore difficult to regard trauma as a cause of the condition.
In addition, some Japanese authors noted that while congenitally duplicated dural membranes were located ventrally to the spinal cord, damage to the inner membrane caused ISCH into the space between the two membranes219).
ISCH can be confirmed by MRI on the basis of clinical findings : ventral obstruction and dorsal expansion of the subarachnoid space as well as 'C' deformity due to the forward movement of the thoracic spinal cord have been observed. Spinal cord shrinkage was found in some cases, though not in this case. It can be diagnosed in its early stage by CT myelography as well as by phase-contrast cine MRI8102628).
There are surgical and conservative treatments; in the surgical treatment, posterior approach laminectomy is used to relax the spinal cord properly and to return it to the normal location while either primary suturing or duroplasty is applied to the region of dural defect. Wortzman et al.35), who reported the first case of ISCH, used primary suturing. But ISCH occurs ventrally or ventrolaterally to the dural membrane, so it is difficult to secure a clear view in making a posterior approach and to avoid damage of the spinal cord by operating it excessively. Primary suturing was actually used in many cases in which the condition worsened postoperatively. To avoid this, duroplasty using either muscle fascia or a patch was performed in several cases but there was ongoing debate243031). In this case, T3 total laminectomy was done for relaxing the spinal cord, then a Tacho-comb® was used in performing duroplasty in the intra- and extra-dural spaces and then covered by Tisseel® (Fig. 2). Tacho-comb® is a sterile ready-to-use absorbable fibrinogen/thrombin-coated collagen patch. When applied to wet tissue surfaces, the coagulation factors dissolve and form a stable fibrin clot which tightly glues the collagen fleece to the tissue surface. In many literatures, Tacho-comb® was used to sealing air leakage site of lung, bleeding vessels, even cardiac rupture and it was efficient and safety compared with surgical suturing or stapling151723).
Massicotte et al.18) reported on follow up of eight patients, who did not undergo surgery due to a mild condition. They also found that another four patients showed no change in their condition and that other patients received surgery from aggravated condition, but no notable improvement. Summers et al.31) reported that no neurological change was found even 33 months later on average among 15 patients with mild symptoms. These results may imply that it is possible to use conservative treatment for mild ISCH.
Outcome is favorable in most patients with Brown-Sequard syndrome : 90% of the patients showed improvement, with muscular strength showing the most remarkable recovery, but paresthesia or numbness signified incomplete improvement682027). Patients complaining of spastic paraplegia were less likely to see their condition get better and a few patients worsened postoperatively, probably due to spinal cord injury caused by the excessive operation of the spinal cord32430). In this case, the patient's muscular strength, sensation, and dysuria improved postoperatively. Ventral and dorsal subarachnoid spaces were normalized, and forward dislocation of the spinal cord improved, as confirmed by MRI two weeks postoperatively (Fig. 1).
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by research fund of Chungnam National University in 2011.
References
1. Abe M, Komori H, Yamaura I, Kayano T. Spinal cord herniation into an extensive extradural meningeal cyst : postoperative analysis of intracystic flow by phase-contrast cine MRI. J Orthop Sci. 1999; 4:450–456. PMID: 10664429.

2. Aizawa T, Sato T, Tanaka Y, Kotajima S, Sekiya M, Kokubun S. Idiopathic herniation of the thoracic spinal cord : report of three cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:E488–E491. PMID: 11598531.
3. Barbagallo GM, Marshman LA, Hardwidge C, Gullan RW. Thoracic idiopathic spinal cord herniation at the vertebral body level : a subgroup with a poor prognosis? Case reports and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97(3 Suppl):369–374. PMID: 12408396.

4. Borges LF, Zervas NT, Lehrich JR. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : a treatable cause of the Brown-Sequard syndrome--case report. Neurosurgery. 1995; 36:1028–1032. discussion 1032-1033PMID: 7791969.
5. Brugières P, Malapert D, Adle-Biassette H, Fuerxer F, Djindjian M, Gaston A. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation: value of MR phase-contrast imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:935–939. PMID: 10369369.
6. Ellger T, Schul C, Heindel W, Evers S, Ringelstein EB. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation causing progressive Brown-Séquard syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2006; 108:388–391. PMID: 16483712.

7. Ewald C, Kühne D, Hassler WE. Progressive spontaneous herniation of the thoracic spinal cord : case report. Neurosurgery. 2000; 46:493–495. discussion 495-496PMID: 10690741.
8. Gandhi D, Goyal M, Bourque PR. Case 138 : Idiopathic spinal cord herniation. Radiology. 2008; 249:384–388. PMID: 18796690.
9. Ghostine S, Baron EM, Perri B, Jacobson P, Morsette D, Hsu FP. Thoracic cord herniation through a dural defect : description of a case and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 2009; 71:362–366. discussion 366-367PMID: 18207514.

10. Haber MD, Nguyen DD, Li S. Differentiation of idiopathic spinal cord herniation from CSF-isointense intraspinal extramedullary lesions displacing the cord. Radiographics. 2014; 34:313–329. PMID: 24617681.

11. Heo SH, Kim JH, Ahn TB, Kim EJ, Park KC, Yoon SS, et al. A case suggesting spontaneous spinal cord herniation presented as brown-sequard syndrome. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2007; 25:133–135.
12. Isu T, Iizuka T, Iwasaki Y, Nagashima M, Akino M, Abe H. Spinal cord herniation associated with an intradural spinal arachnoid cyst diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery. 1991; 29:137–139. PMID: 1870677.

13. Iyer RV, Coutinho C, Lye RH. Spontaneous spinal cord herniation. Br J Neurosurg. 2002; 16:507–510. PMID: 12498498.

14. Jin SC, Lee SR, Park DW, Joo KB. Spontaneous herniation of the thoracic spinal cord : a case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2001; 45:353–355.

15. Joseph T, Adeosun A, Paes T, Bahal V. Randomised controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of TachoComb H patches in controlling PTFE suture-hole bleeding. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004; 27:549–552. PMID: 15079782.

16. Kim JM, Oh SH, Kim KJ, Park SH, Park KS. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation as a treatable cause of progressive brown-sequard syndrome. J Clin Neurol. 2007; 3:204–207. PMID: 19513134.

17. Lang G, Csekeö A, Stamatis G, Lampl L, Hagman L, Marta GM, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical application of human fibrinogen/thrombin-coated collagen patch (TachoComb) for treatment of air leakage after standard lobectomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004; 25:160–166. PMID: 14747106.

18. Massicotte EM, Montanera W, Ross Fleming JF, Tucker WS, Willinsky R, TerBrugge K, et al. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : report of eight cases and review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:E233–E241. PMID: 11979181.
19. Matsumura T, Takahashi MP, Nozaki S, Kang J. [A case of idiopathic spinal cord herniation]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1996; 36:566–570. PMID: 8810851.
20. Miyaguchi M, Nakamura H, Shakudo M, Inoue Y, Yamano Y. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation associated with intervertebral disc extrusion : a case report and review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1090–1094. PMID: 11337631.

21. Miyake S, Tamaki N, Nagashima T, Kurata H, Eguchi T, Kimura H. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation. Report of two cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1998; 88:331–335. PMID: 9452246.
22. Mokri B. Spontaneous low cerebrospinal pressure/volume headaches. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2004; 4:117–124. PMID: 14984683.

23. Muto A, Nishibe T, Kondo Y, Sato M, Yamashita M, Ando M. Sutureless repair with TachoComb sheets for oozing type postinfarction cardiac rupture. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005; 79:2143–2145. PMID: 15919331.

24. Najjar MW, Baeesa SS, Lingawi SS. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : a new theory of pathogenesis. Surg Neurol. 2004; 62:161–170. discussion 170-171PMID: 15261515.
25. Novak K, Widhalm G, de Camargo AB, Perin N, Jallo G, Knosp E, et al. The value of intraoperative motor evoked potential monitoring during surgical intervention for thoracic idiopathic spinal cord herniation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012; 16:114–126. PMID: 22117142.

26. Parmar H, Park P, Brahma B, Gandhi D. Imaging of idiopathic spinal cord herniation. Radiographics. 2008; 28:511–518. PMID: 18349454.

27. Sagiuchi T, Iida H, Tachibana S, Utsuki S, Tanaka R, Fujii K. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation associated with calcified thoracic disc extrusion--case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2003; 43:364–368. PMID: 12924599.

28. Salvador Álvarez E, Jiménez De La Peña M, Herraiz Hidalgo L, Pardo Moreno J. [Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : a rare condition]. Radiologia. 2010; 52:353–356. PMID: 20382404.
29. Sasani M, Ozer AF, Vural M, Sarioglu AC. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : case report and review of the literature. J Spinal Cord Med. 2009; 32:86–94. PMID: 19264054.

30. Sioutos P, Arbit E, Tsairis P, Gargan R. Spontaneous thoracic spinal cord herniation. A case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:1710–1713. PMID: 8839477.
31. Summers JC, Balasubramani YV, Chan PC, Rosenfeld JV. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : clinical review and report of three cases. Asian J Neurosurg. 2013; 8:97–105. PMID: 24049553.

32. Tekkök IH. Spontaneous spinal cord herniation : case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2000; 46:485–491. discussion 491-492PMID: 10690740.
33. Urbach H, Kaden B, Pechstein U, Solymosi L. Herniation of the spinal cord 38 years after childhood trauma. Neuroradiology. 1996; 38:157–158. PMID: 8692429.

34. Wada E, Yonenobu K, Kang J. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : report of three cases and review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:1984–1988. PMID: 10908944.
35. Wortzman G, Tasker RR, Rewcastle NB, Richardson JC, Pearson FG. Spontaneous incarcerated herniation of the spinal cord into a vertebral body : a unique cause of paraplegia. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1974; 41:631–635. PMID: 4424434.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download