1. Aarabi B, Chesler D, Maulucci C, Blacklock T, Alexander M. Dynamics of subdural hygroma following decompressive craniectomy : a comparative study. Neurosurg Focus. 2009; 26:E8. PMID:
19485721.
2. Aarabi B, Hesdorffer DC, Ahn ES, Aresco C, Scalea TM, Eisenberg HM. Outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant swelling due to severe head injury. J Neurosurg. 2006; 104:469–479. PMID:
16619648.

3. Cardoso ER, Galbraith S. Posttraumatic hydrocephalus--a retrospective review. Surg Neurol. 1985; 23:261–264. PMID:
3975808.

4. Cho BR, Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Yi JS, Yang JH, Lee IW. Risk factors for the post-traumatic hydrocephalus following decompressive craniectomy in severe traumatic injury patients. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2012; 8:110–114.

5. Choi I, Park HK, Chang JC, Cho SJ, Choi SK, Byun BJ. Clinical factors for the development of posttraumatic hydrocephalus after decompressive craniectomy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 43:227–231. PMID:
19096601.

6. Da Costa DG, Adson AW. Subdural hygroma. Arch Surg. 1941; 43:559–567.
7. De Bonis P, Pompucci A, Mangiola A, Rigante L, Anile C. Post-traumatic hydrocephalus after decompressive craniectomy : an underestimated risk factor. J Neurotrauma. 2010; 27:1965–1970. PMID:
20812777.

8. Dünisch P, Walter J, Sakr Y, Kalff R, Waschke A, Ewald C. Risk factors of aseptic bone resorption : a study after autologous bone flap reinsertion due to decompressive craniotomy. J Neurosurg. 2013; 118:1141–1147. PMID:
23451904.

9. Foltz EL, Ward AA Jr. Communicating hydrocephalus from subarachnoid bleeding. J Neurosurg. 1956; 13:546–566. PMID:
13377208.

10. Gebel JM, Sila CA, Sloan MA, Granger CB, Weisenberger JP, Green CL, et al. Comparison of the ABC/2 estimation technique to computer-assisted volumetric analysis of intraparenchymal and subdural hematomas complicating the GUSTO-1 trial. Stroke. 1998; 29:1799–1801. PMID:
9731597.

11. Greene KA, Marciano FF, Johnson BA, Jacobowitz R, Spetzler RF, Harrington TR. Impact of traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage on outcome in nonpenetrating head injury. Part I : a proposed computerized tomography grading scale. J Neurosurg. 1995; 83:445–452. PMID:
7666221.

12. Honeybul S. Complications of decompressive craniectomy for head injury. J Clin Neurosci. 2010; 17:430–435. PMID:
20181482.

13. Honeybul S, Ho KM. Decompressive craniectomy for severe traumatic brain injury : the relationship between surgical complications and the prediction of an unfavourable outcome. Injury. 2014; 45:1332–1339. PMID:
24704150.

14. Honeybul S, Ho KM. Incidence and risk factors for post-traumatic hydrocephalus following decompressive craniectomy for intractable intracranial hypertension and evacuation of mass lesions. J Neurotrauma. 2012; 29:1872–1878. PMID:
22583391.

15. Honeybul S, Ho KM. Long-term complications of decompressive craniectomy for head injury. J Neurotrauma. 2011; 28:929–935. PMID:
21091342.

16. Huh PW, Yoo DS, Cho KS, Park CK, Kang SG, Park YS, et al. Diagnostic method for differentiating external hydrocephalus from simple subdural hygroma. J Neurosurg. 2006; 105:65–70. PMID:
16874890.

17. Jeon SW, Choi JH, Jang TW, Moon SM, Hwang HS, Jeong JH. Risk factors associated with subdural hygroma after decompressive craniectomy in patients with traumatic brain injury : a comparative study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 49:355–358. PMID:
21887394.

18. Kaen A, Jimenez-Roldan L, Alday R, Gomez PA, Lagares A, Alén JF, et al. Interhemispheric hygroma after decompressive craniectomy : does it predict posttraumatic hydrocephalus? J Neurosurg. 2010; 113:1287–1293. PMID:
20486895.

19. Kilincer C, Simsek O, Hamamcioglu MK, Hicdonmez T, Cobanoglu S. Contralateral subdural effusion after aneurysm surgery and decompressive craniectomy : case report and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2005; 107:412–416. PMID:
16023537.

20. Lee KS. The pathogenesis and clinical significance of traumatic subdural hygroma. Brain Inj. 1998; 12:595–603. PMID:
9653522.

21. Marmarou A, Foda MA, Bandoh K, Yoshihara M, Yamamoto T, Tsuji O, et al. Posttraumatic ventriculomegaly : hydrocephalus or atrophy? A new approach for diagnosis using CSF dynamics. J Neurosurg. 1996; 85:1026–1035. PMID:
8929491.

22. Murata K. Chronic subdural hematoma may be preceded by persistent traumatic subdural effusion. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1993; 33:691–696. PMID:
7505896.

23. Ohno K, Suzuki R, Masaoka H, Matsushima Y, Inaba Y, Monma S. Chronic subdural haematoma preceded by persistent traumatic subdural fluid collection. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987; 50:1694–1697. PMID:
3437306.

24. Rahme R, Weil AG, Sabbagh M, Moumdjian R, Bouthillier A, Bojanowski MW. Decompressive craniectomy is not an independent risk factor for communicating hydrocephalus in patients with increased intracranial pressure. Neurosurgery. 2010; 67:675–678. discussion 678PMID:
20651634.

25. Stiver SI. Complications of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg Focus. 2009; 26:E7. PMID:
19485720.

26. Su TM, Lee TH, Huang YH, Su FW, Chen WF. Contralateral subdural effusion after decompressive craniectomy in patients with severe traumatic brain injury : clinical features and outcome. J Trauma. 2011; 71:833–837. PMID:
21610528.

27. Vanneste J, Augustijn P, Davies GA, Dirven C, Tan WF. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Is cisternography still useful in selecting patients for a shunt? Arch Neurol. 1992; 49:366–370. PMID:
1558516.
28. Waziri A, Fusco D, Mayer SA, McKhann GM 2nd, Connolly ES Jr. Postoperative hydrocephalus in patients undergoing decompressive hemicraniectomy for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. Neurosurgery. 2007; 61:489–493. discussion 493-494PMID:
17881960.

29. Yang XF, Wen L, Shen F, Li G, Lou R, Liu WG, et al. Surgical complications secondary to decompressive craniectomy in patients with a head injury : a series of 108 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008; 150:1241–1247. discussion 1248PMID:
19005615.

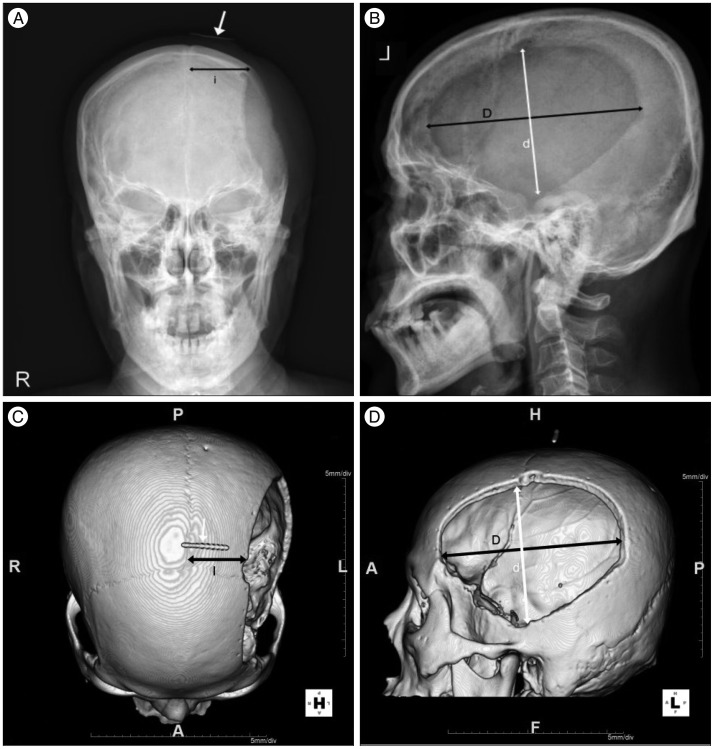
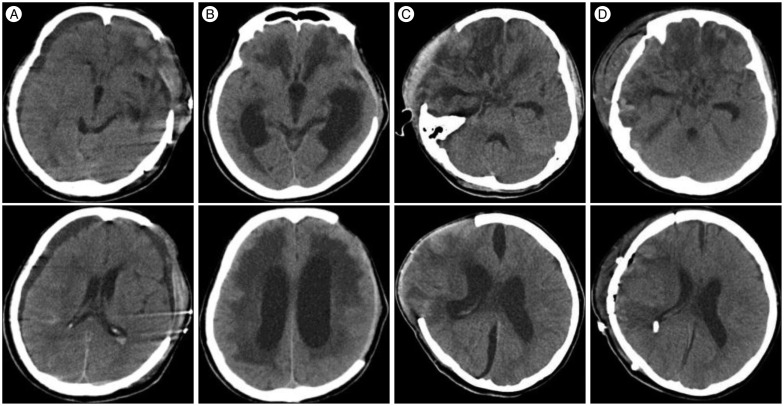
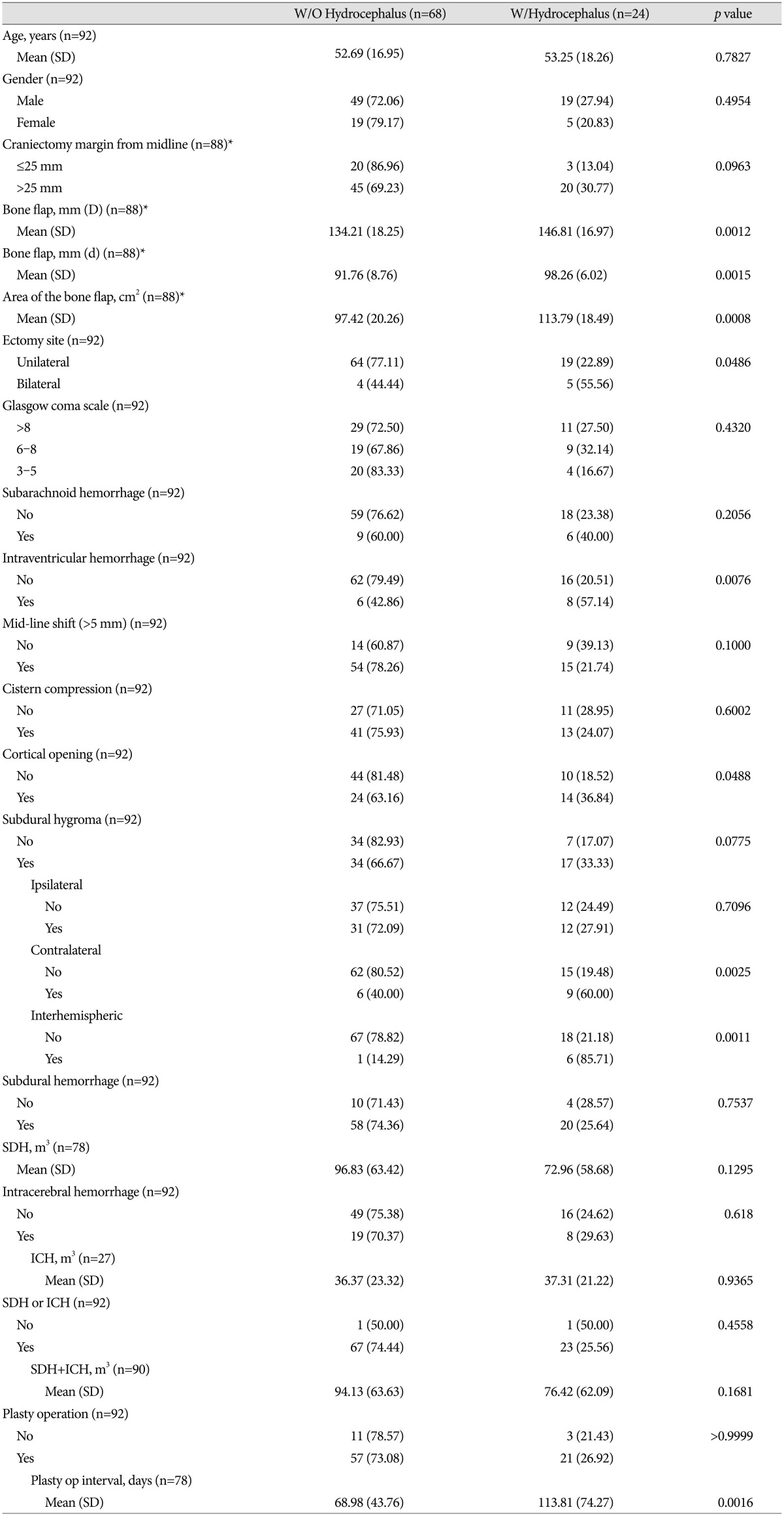
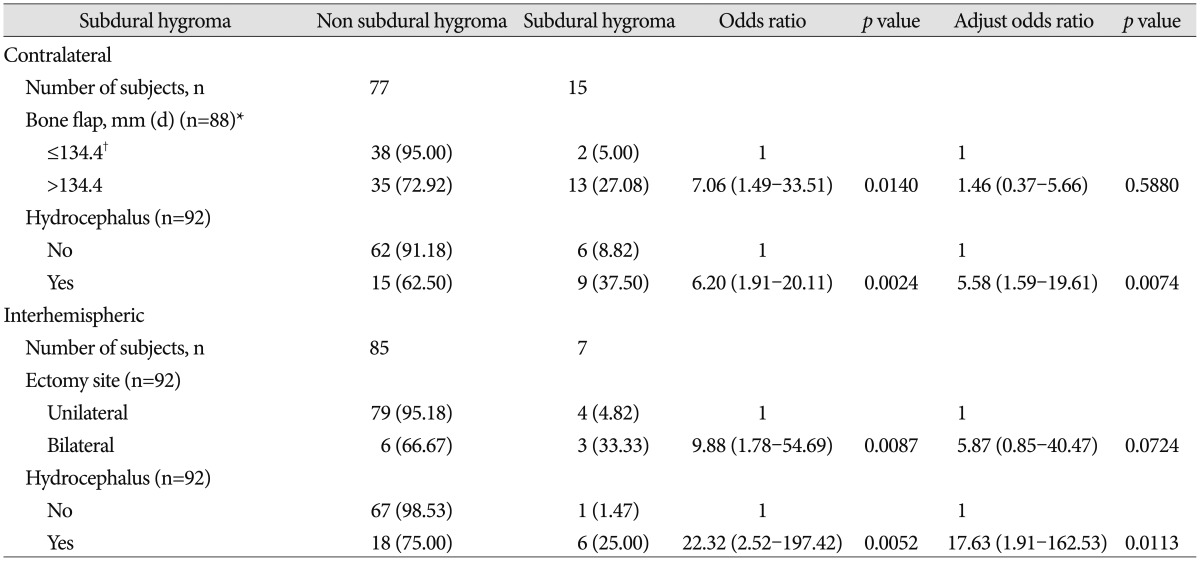




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download