Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study is to identify the risk factors associated with the development of germinal matrix-intraventricular hemorrhage (GM-IVH) and the relationship of the severity of disease and prematurity.
Methods
A total of 168 premature neonates whose birth weight ≤1500 g or gestational age ≤34 weeks were examined by cranial ultrasound (CUS) for detection of GM-IVH among the babies admitted between January 2011 and December 2012 in our medical center neonatal intensive care unit. The babies were divided into two groups : GM-IVH and non-IVH. Clinical presentations, precipitating factors of the patients and maternal factors were analyzed.
Results
In univariate analysis, gestational age, birth weight, delivery method, presence of premature rupture of membrane (PROM) and level of sodium and glucose were statistically meaningful factors (p<0.05). But only two factors, gestational age and presence of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) were statistically meaningful in multivariate logistic regression (p<0.05). Delivery method [normal vaginal delivery (NVD) to Caeserean section] was borderline significant (p<0.10).
Go to : 
Germinal matrix-intraventricular hemorrhage (GM-IVH) is one of the most common complications in the premature infant. The incidence of this disease has been decreased in recent years. But it is still important because of two reasons. First, the outbreak is directly related with the degree of prematurity. Second, survival rate for smaller premature infants increases consistently. Therefore, there are many previous reports in order to identify risk factors associated with development of GM-IVH and to establish effective strategies. Perinatal risk factors such as a low birth weight and low gestational age, vaginal delivery, intrauterine infection, low Apgar score, sepsis have been proposed as associated with the pathogenesis of GM-IVH16). Therefore, the purpose of this study is to identify the risk factors associated with the development of GM-IVH and the relationship of the severity of disease and prematurity.
Go to : 
A total of 168 premature neonates whose birth weight ≤1500 g or gestational age ≤34 weeks were examined by cranial ultrasound (CUS) for detection of GM-IVH among the babies admitted between January 2011 and December 2012 in our medical center neonatal intensive care unit. Antenatal steroids were injected to all premature neonates. Patient's data were collected retrospectively such as sex, gestational age, birth weight, delivery method, disease diagnosis and its grade, initial blood glucose, sodium levels and presence of comorbidities such as respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) and anemia. And maternal data were collected retrospectively such as maternal age, gravidity, presence of preeclampsia and premature rupture of membrane (PROM).
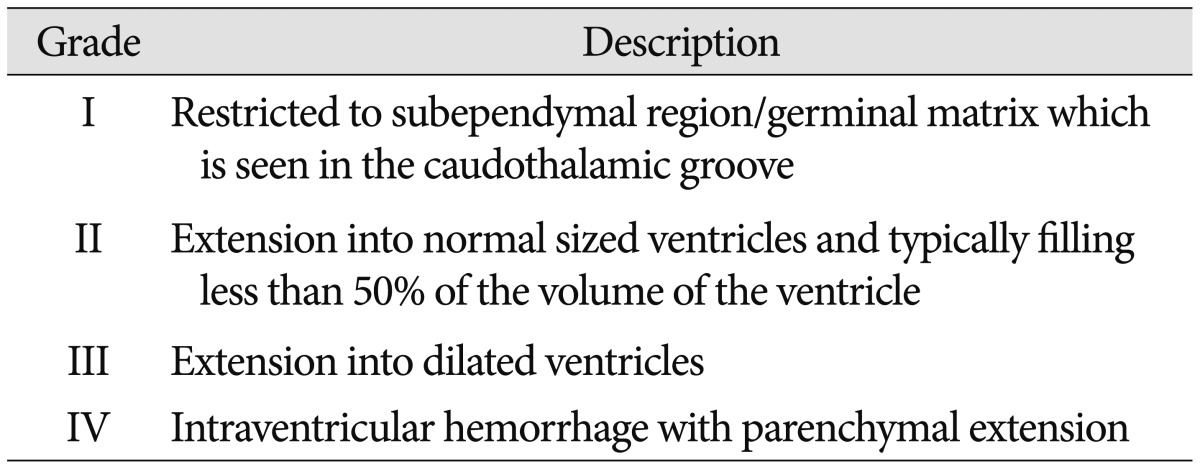
CUS was performed for all neonates in this study in the first week of life for detection of IVH and its grading were done. If a neonate had GM-IVH, then serial CUS would be done weekly. If not, follow up CUS was taken after 2 weeks. All subjects were divided into two groups-GM-IVH group and Non-IVH groups according to presence of GM-IVH. GM-IVH group was subdivided by grading system proposed by Papile et al.19) (Table 1). Grade I and II group were considered as mild GM-IVH group, Grade III and IV group were as severe GM-IVH group.
Statistical analysis was performed by using SPSS version 21.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). To compare the continuous variables, the Student's t-test was used. Pearson's chi-square test was used for categorical variables. Logistic regression analysis was used to find the independent association between development of GM-IVH and explanatory variables. Variables that were p≤0.20 as determined by univariate analysis were entered into multivariate logistic regression. The odds ratios (ORs) with a 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. p value<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Go to : 
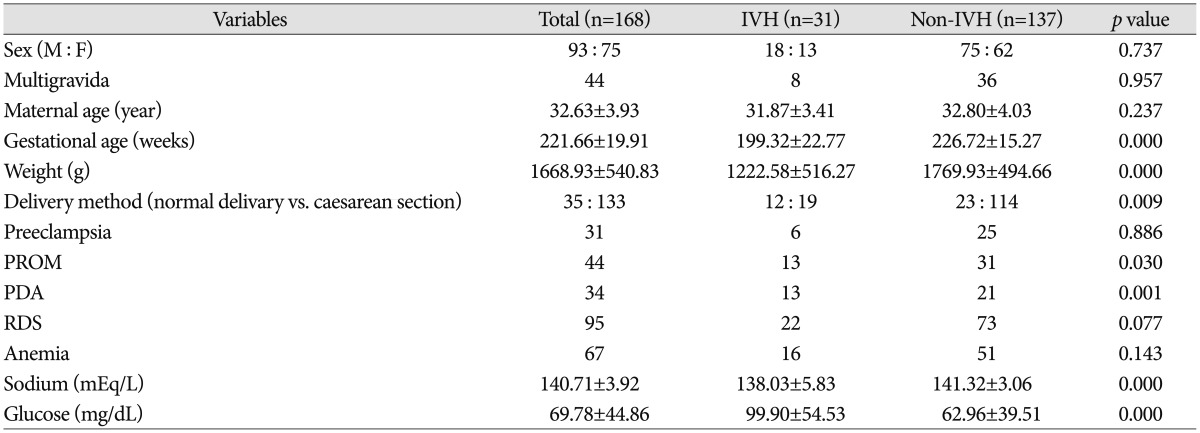
Total 168 patients were included. 93 patients (55.36%) were male. Infants born from mother with multigravida were 44 (26.19%). Mean maternal age was 32 years. Mean gestational age and birth weight are 221 days and 1668 g, respectively. 35 babies (20.83%) were born by normal vaginal delivery (NVD). The mothers who had past history were 31 cases (18.45%) for preeclampsia and 44 cases (26.19%) for PROM. 34 babies (20.24%) had PDA, 95 babies (56.55%) with RDS, 67 babies (39.88%) with anemia. Among 168 subjects, GM-IVH was diagnosed in 31 cases (18.45%); 15 cases (48.39%) with grade 1, 9 cases (29.03%) with grade 2, 2 cases (6.45%) with grade 3, 5 cases (16.13%) with grade 4.
In univariate analysis, gestational age, birth weight, delivery method, presence of PROM and level of sodium and glucose were statistically meaningful factors (p<0.05). To operate multivariate analysis, gestational age, birth weight, delivery method, presence of PROM, PDA, RDS, anemia and level of sodium and glucose were selected. All these results were demonstrated on Table 2.
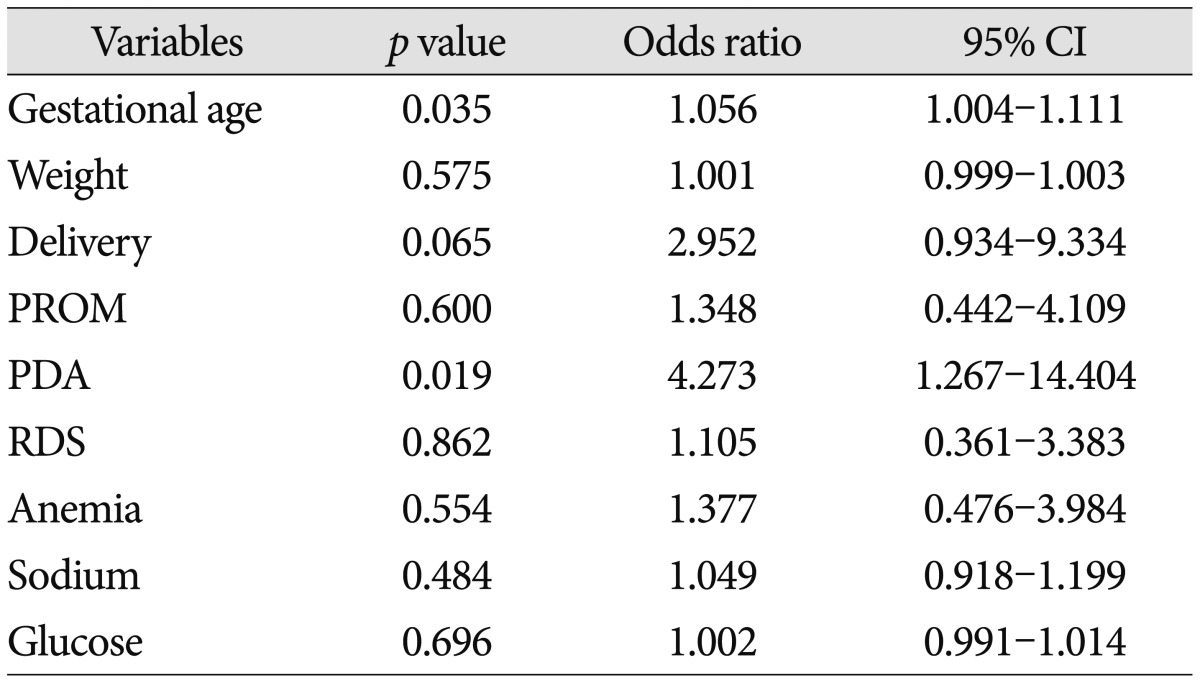
Only two factors-gestational age and presence of PDA were statistically meaningful in multivariate logistic regression (p<0.05). Delivery method (NVD to Caeserean section) was borderline significant (p<0.10). All these results were demonstrated in Table 3.
Unpaired t-test was done between two groups by variables. Mild group was 24 cases, severe groups was 7 cases. Meaningful difference in gestational age between two groups was revealed (p<0.05). No other variable was statistically meaningful factor.
Go to : 
GM-IVH is rare in full-term babies11), but more common in preterm babies and it leaves significant sequelae such as cerebral palsy and mental retardation. Therefore, it is very important to find the risk factors associated with development of GM-IVH and prepare for them. Many risk factors for the development of GM-IVH have been reported. These contain gender, lack of antenatal steroids, low Apgar score, PROM, intrauterine infection, vaginal delivery, in vitro fertilization, mechanical ventilation, a large PDA, RDS and transfusion of blood products7,12,14,16,18,25,26).
However, in our study, there was no significant difference in gender, birth weight, delivery method, preeclampsia, PROM, anemia. The only two factors, gestational age and presence of PDA, were statistically meaningful risk factors for development of GM-IVH. This result could be understood easily because gestational age reflects fetal maturity more accurately than birth weight. As several reports 15,21,23) and our results has shown, it is certain that younger gestational age is related with higher risk for severe GM-IVH. It can be described in terms of the anatomy and pathophysiology of it. It occurs in germinal matrix, an intensively vascularized glioblast tissue13). If children were born before the 32 weeks of gestation, the subependymal region is equipped with a tight net of capillaries that are mainly supplied by the Heubner's artery. After the 32 weeks into pregnancy, the germinal matrix involutes and the vessels will be differentiated10). Preterm infants are quite helpless against cerebrovascular injury due to a unique constellation of pathophysiological factors. Preterm newborns have difficulty maintaining an adequate cerebral perfusion pressure. Maintain cerebral perfusion pressure is more difficult due to normally reduced hypotension and low cardiac output for the new borns to adjst extrauterine life, especially in the first day of life. In addition, intrinsic cerebral vasoreactivity and autoregulatory mechanisms are poorly developed in the immature brain. As decreasing gestational age, the autoregulation pressure range is narrower and lower5).
Normal vaginal delivery was borderline significant risk factor (p<0.1). Although there is a objection20,21,24), some retrospective studies reported that Caesarean delivery does not improve neonatal survival of very low birth weight infants but decreases GM-IVH occurrence2,4,17,27). In addition, following hypoperfusion-reperfusion hypothesis seemed to support this5). The germinal matrix is a transient neural cell proliferative zone with poor developed vasculature and located on the head of caudate nucleus. This involutes gradually in third trimester. Fragile vessels and the lack of cerebrovascular resistance make GM-IVH1,22). The resistance to ischemic injury is weaker and autoregulation range of blood pressure is lower as decreasing gestational age. Certain situation like presence of PDA or normal vaginal delivery could result in hypoperfusion-reperfusion state. Several possible factors are suggested cardiorespiratory system (hypotension, PDA, hypoperfusion-reperfusion pattern, hypercarpnia, hypoglycemia, hypernatremia), hematologic (anemia, thrombocytopenia), immunologic response, impared cerebral reactivity, immature anatomy, eventhough they are not proven yet1,5,7,10,12,13,14,16,18,22,25,26). Another reason why the hemorrhage occurs in this region, beside the massive vascularization, is the fact that the area around the caudate nucleus represents a border zone between ventriculopetal and fugal blood supply3). Furthermore, the endothelium of the vessels located in the brain of premature newborns is more sensitive to hypoxemia. Hydrostatic and osmotic changes lead more often to the ruptures of the vessels9).
An important pathophysiological parameter is the missing or disruptured autoregulation mechanism of premature newborns. This means that the cerebral blood flow is directly influenced by changes of the systemic blood pressure. Hence hypertension, as well as hypotension, will lead directly to changes in the cerebral blood flow4,6,8). Other triggers that can cause an ICH are rupture of the alveolars, RDS, pneumothorax and artificial ventilation of the new born. Endotracheal intubation with positive pressure ventilation increases central venous pressure, which can lead to episodic poor cerebral perfusion. But, in the present study, high risk pregnancy situations such as preeclampsia, PROM and RDS were not related to the development of GM-IVH.
There are several limitations in our study. First, the population of our study was small in number. So we couldn't sort all the cases by gestational age and estimate odds ratio by decreasing gestational age. Second is a retrospective study from a single institution, although this also might be an advantage due to consistency of practice and expertise. Last, this study did not evaluate the neurodevelopmental outcome of patients.
Go to : 
Despite of several limitations, our study revealed that presence of PDA and gestational age were the important risk factors associated with development of GM-IVH. How the severity of disese relates to gestational age will be necessary to study with larger population in multicenter.
Go to : 
References
1. Ballabh P. Intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants : mechanism of disease. Pediatr Res. 2010; 67:1–8. PMID: 19816235.

2. Dani C, Poggi C, Bertini G, Pratesi S, Di Tommaso M, Scarselli G, et al. Method of delivery and intraventricular haemorrhage in extremely preterm infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010; 23:1419–1423. PMID: 20236026.

3. De Reuck JL. Cerebral angioarchitecture and perinatal brain lesions in premature and full-term infants. Acta Neurol Scand. 1984; 70:391–395. PMID: 6516787.

4. Deulofeut R, Sola A, Lee B, Buchter S, Rahman M, Rogido M. The impact of vaginal delivery in premature infants weighing less than 1,251 grams. Obstet Gynecol. 2005; 105:525–531. PMID: 15738019.

5. du Plessis AJ. Cerebrovascular injury in premature infants : current understanding and challenges for future prevention. Clin Perinatol. 2008; 35:609–641. PMID: 19026331.

6. Dykes FD, Lazzara A, Ahmann P, Blumenstein B, Schwartz J, Brann AW. Intraventricular hemorrhage : a prospective evaluation of etiopathogenesis. Pediatrics. 1980; 66:42–49. PMID: 7402791.

7. Ertan AK, Tanriverdi HA, Meier M, Schmidt W. Perinatal risk factors for neonatal intracerebral hemorrhage in preterm infants. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2006; 127:29–34. PMID: 16815469.

8. Goldberg RN, Chung D, Goldman SL, Bancalari E. The association of rapid volume expansion and intraventricular hemorrhage in the preterm infant. J Pediatr. 1980; 96:1060–1063. PMID: 7373468.

9. Goldstein GW. Pathogenesis of brain edema and hemorrhage : role of the brain capillary. Pediatrics. 1979; 64:357–360. PMID: 481981.
10. Hambleton G, Wigglesworth JS. Origin of intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm infant. Arch Dis Child. 1976; 51:651–659. PMID: 999324.

11. Hayden CK Jr, Shattuck KE, Richardson CJ, Ahrendt DK, House R, Swischuk LE. Subependymal germinal matrix hemorrhage in full-term neonates. Pediatrics. 1985; 75:714–718. PMID: 3885154.

12. Heuchan AM, Evans N, Henderson Smart DJ, Simpson JM. Perinatal risk factors for major intraventricular haemorrhage in the Australian and New Zealand Neonatal Network, 1995-97. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2002; 86:F86–F90. PMID: 11882549.

13. Jensen A. Das hirnblutungsrisiko des neugeborenen. Gynakologe. 1992; 25:176–186. PMID: 1505799.
14. Lee JY, Kim HS, Jung E, Kim ES, Shim GH, Lee HJ, et al. Risk factors for periventricular-intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:418–424. PMID: 20191041.

15. Levene MI, Fawer CL, Lamont RF. Risk factors in the development of intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate. Arch Dis Child. 1982; 57:410–417. PMID: 7092304.

16. Linder N, Haskin O, Levit O, Klinger G, Prince T, Naor N, et al. Risk factors for intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight premature infants : a retrospective case-control study. Pediatrics. 2003; 111(5 Pt 1):e590–e595. PMID: 12728115.
17. Ment LR, Oh W, Ehrenkranz RA, Philip AG, Duncan CC, Makuch RW. Antenatal steroids, delivery mode, and intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995; 172:795–800. PMID: 7892866.

18. Osborn DA, Evans N, Kluckow M. Hemodynamic and antecedent risk factors of early and late periventricular/intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants. Pediatrics. 2003; 112(1 Pt 1):33–39. PMID: 12837865.

19. Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage a study of infants with birth weights less than 1500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978; 92:529–534. PMID: 305471.

20. Paul DA, Sciscione A, Leef KH, Stefano JL. Caesarean delivery and outcome in very low birthweight infants. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2002; 42:41–45. PMID: 11926639.

21. Riskin A, Riskin-Mashiah S, Bader D, Kugelman A, Lerner-Geva L, Boyko V, et al. Delivery mode and severe intraventricular hemorrhage in single, very low birth weight, vertex infants. Obstet Gynecol. 2008; 112:21–28. PMID: 18591303.

22. Robinson S. Neonatal posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus from prematurity : pathophysiology and current treatment concepts. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2012; 9:242–258. PMID: 22380952.

23. Spinillo A, Ometto A, Bottino R, Piazzi G, Iasci A, Rondini G. Antenatal risk factors for germinal matrix hemorrhage and intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1995; 60:13–19. PMID: 7635224.

24. Vergani P, Locatelli A, Doria V, Assi F, Paterlini G, Pezzullo JC, et al. Intraventricular hemorrhage and periventricular leukomalacia in preterm infants. Obstet Gynecol. 2004; 104:225–231. PMID: 15291991.

25. Vergani P, Patané L, Doria P, Borroni C, Cappellini A, Pezzullo JC, et al. Risk factors for neonatal intraventricular haemorrhage in spontaneous prematurity at 32 weeks gestation or less. Placenta. 2000; 21:402–407. PMID: 10833376.

26. Vermeulen GM, Bruinse HW, de Vries LS. Perinatal risk factors for adverse neurodevelopmental outcome after spontaneous preterm birth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2001; 99:207–212. PMID: 11788173.

27. Wylie BJ, Davidson LL, Batra M, Reed SD. Method of delivery and neonatal outcome in very low-birthweight vertex-presenting fetuses. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008; 198:640.e1–640.e7. discussion e1-e4. PMID: 18313634.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download