Golf is a global sport. It requires a coordinated sequence of whole body muscle activity to efficiently transfer the power generated by the swing
19). During the each phase of a golf swing, there is a potential for injury. There have been a number of reports of golf related injuries (
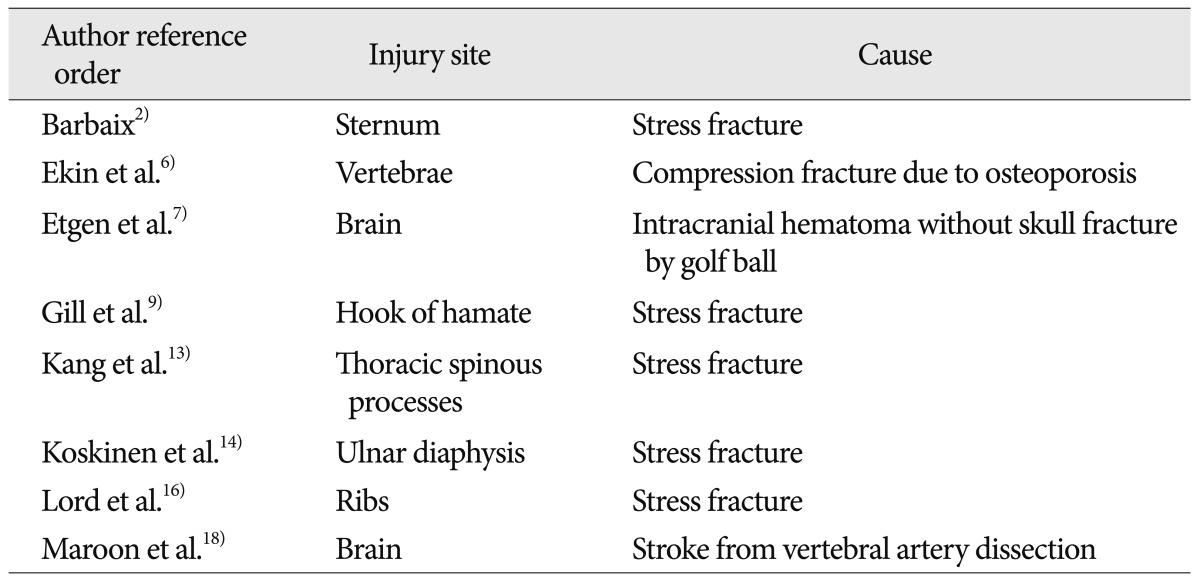
Table 1)
2,
6,
7,
9,
14,
15,
17,
18). But, only one report has described multiple spinous process fractures of the upper thoracic spine caused by golf swing itself
14). The case included acute and delayed stress fractures. Initial MRI revealed a spinous process fracture of first thoracic vertebra. But, the follow-up MRI revealed the additional fracture in the spinous process of the second thoracic vertebra. The pathomechanism of this type injury remained ill-defined and was presumed to be similar to Clay-shoveler's fracture
10). Avulsion of spinous process or Clay-shoveler's fracture was first described in Australia
10). It is most prevalent among those engaged in hard physical labor
10). More recently, it has also been described during Nintendo Wii activity
4), volleyball
13), car accident
1), power lifting
12), and golf
14). It occurs when the head and upper cervical segments are forced into flexion against the opposing action of the interspinous and supraspinous ligaments
11). The injury takes its' name from the fact that, during the throwing phase of shoveling, clay may stick to the shovel and jerk the trapezius and other muscles attached to lower cervical or upper thoracic spinous processes
10). It can also occur with a whiplash injury, injuries that jerk the arms upwards, neck hyperflexion, or a direct blow to the spinous processes
10). In our case, the trapezius muscle also contributed to the injury. The trapezius muscle originates from the medial one-third of the superior nuchal line and the external occipital protuberance of the occipital bone, from the spines of the seventh cervical and all thoracic verbetrae, and from the intervening supraspinal ligament
20). It assists in suspending the shoulder girdle with other muscles. It is relatively flat and thin, but its thickness increases in the lower cervical and upper thoracic region
20). Where its increased thickness is matched by a distinct diamond-shaped accumulation of tendinous fibers of origin
20)(
Fig. 3A). The spinous process is relatively longer in the lower cervical than the upper cervical area. Its fibers converge toward the bones of the shoulder
20). During the back swing, the right upper and middle trapezius muscle contracts
19)(
Fig. 3B, C). During the forward swing, the left middle trapezius muscle contracts
19)(
Fig. 3D). So we can postulate that muscular contraction moves from right side to left side, like a bow. Because of the pectoralis muscle, the force may be amplified during the acceleration phase (
Fig. 3E). When a right-handed golfer swings so the club contacts the ground prior to the ball, the energy accumulated during the back swing cannot be transmitted to the ball (
Fig. 3F). There is a sudden change of muscle contraction from the right upper and middle trapezius to its attachment point (the spinous process). If enough force is transmitted through the trapezius tendon, spinous process fracture is possible. When the force is not strong enough to make fracture, if applied repeatedly, overuse or stress-type fracture may occur. This fracture is stable, and by itself is of little significance. But, it is painful. The present patient was initially misdiagnosed as having an acute cervical sprain. Atypically, this fracture may extend to the lamina, thereby involving the spinal canal with the potential of spinal cord injury
11).
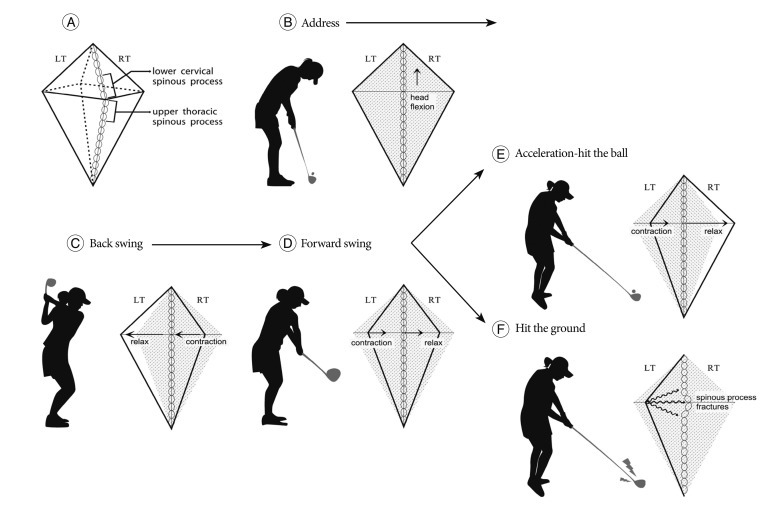 | Fig. 3Schematic draws of trapezius muscle during each swing phase. Trapezius muscle thickness is increased in the lower cervical and upper thoracic region (A). During back swing, right upper and middle trapezius muscle contract from address-neutral state (B and C). During forward swing, the left middle trapezius muscle contracts (D). The force may amplify during the acceleration phase (E). When a right-handed golfer swings such that the club contacts the ground before the ball back swing arc energy cannot be transmitted to the ball (F). 
|
Table 1
Golf related injuries according to literatures

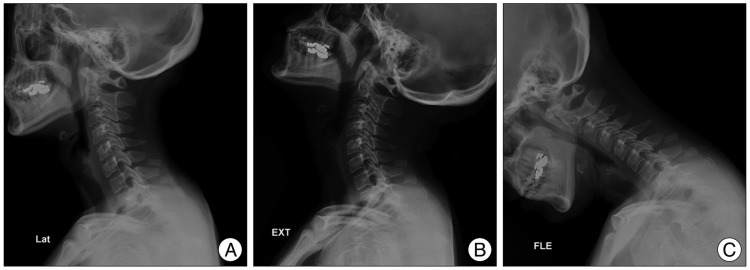
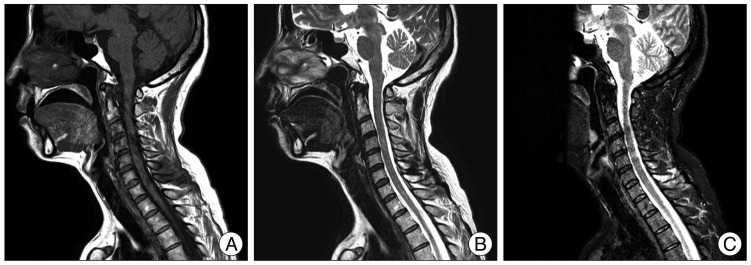
If a patient complains of long lasting neck pain, the attending clinician should have further study (cervical spine radiographs, computed tomography scan or cervical MRI) to rule out other occult fractures or injuries
16). Midline tenderness may be the clue for the presence of fracture. If the lower cervical spine and/or cervico-thoracic junction are not well visualized on cervical spine lateral radiographs, a swimmer's view
5) or CT scan
15) should be obtained. An understanding of correct swing technique will help the golf beginner
3). Golf related injuries increase without warm-up exercise
8). So, warming up and stretching exercise before golf will reduce the risk of golf related injury
8).





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download