Abstract
Cerebral aspergillosis is rare and usually misdiagnosed because its presentation is similar to that of a tumor. The correct diagnosis is usually made intra-operatively. Cerebral abscess with fungal infection is extremely rare and few cases have been reported, but it carries a poor prognosis.
A 73 year-old man presented with decreased visual acuity and paresis of the right cranial nerve III. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a mass in the right cavernous sinus, extened to the anterior crainial fossa and the superior orbital fissure. During surgery, a well encapsulated pus pocket was found, and histopathological examination of the mass resulted in the diagnosis of aspergillosis. Despite appropriate anti-fungal treatment, the patient eventually died from fatal cerebral ischemic change and severe brain swelling.
The correct diagnosis of cerebral aspergillosis can only be achieved by histopathological examination because clinical and radiological findings including MRI are not specific. Surgical intervention and antifungal therapy should be considered the optimal treatment. Early diagnosis and aggressive antifungal treatment provide good results.
Central nervous system (CNS) aspergillus abscess is very rare in immunocompetent patients and a potentially life threatening disease that is usually misdiagnosed because its presentation is similar to that of a tumor. Despite advances in diagnosis and treatment in recent years, CNS aspergillus abscesses still leads to significant morbidity and mortality2,15). Early diagnosis is important for successful treatment.
A case of parasellar aspergillus extending from the cavernous sinus, which was clinically indistinguishable from the intracranial neoplasms, is presented in this report.
A 73-year-old male was admitted to our hospital with the complaints of headache persisting for approximately three months, and presented with progressive visual deterioration and ptosis in the right eye. He had no known disease and no apparent immune deficiencies. On physical examination, he was afebrile, but he had experienced unintentional weight loss and fatigue. His general condition was poor as a result of malnutrition. The neurological examination revealed a ptosis, ophthalmoplegia, and impairment of visual acuity on the right eye. His laboratory results were as follows : white cell count, 9.100/µL; sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, peripheral smear and biochemical tests were all in normal range. Viral markers were negative.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a mass in the right cavernous sinus, extended to the anterior crainial fossa and the superior orbital fissure with an iso-signal intensity in T1-weighted iamge. The lesion showed a slightly low signal intensity in T2-weighted sequences and strong enhancement (Fig. 1). Based on these MRI findings, the impression was inflammatory abscess, but meningioma or metastatic tumor were also suspected. The patient underwent a pterional approach craniotomy for pathologic diagnosis and decompression of neural structures. During surgery, a well-encapsulated pus pocket was found at the clinoid process, and severe adhesion with the surrounding tissue was encountered. An intra-operative frozen biopsy revealed a fungal infection. The biopsy material showed inflammatory granulation tissue and micro abscesses containing a large number of hyphae with 45 degree angulations and spores (Fig. 2). The pathology result was consistent with aspergillus infection.
Postoperatively, the patient was treated by systemic administration of antifungal drug (Amphotericin-B and Voriconazole), to which he showed only a minimal response. Despite appropriate medical and surgical treatment, the disease progressed and the patient eventually died from fatal cerebral ischemic change and severe brain swelling on the 23rd postoperative day (Fig. 3).
CNS aspergillosis is rare. However, the number of reported cases increased significantly in the last decade (Table 1)7,10-14,16,19). Aspergillus can reach the CNS by three different routes. The first is by hematogenous spread from a remote extracranial focus. The second is by extension from a contiguous extracranial location, and the third is direct introduction of aspergillus by a neurosurgical procedure iatrogenically3).
CNS aspergillosis is very serious, with a mortality of more than 90%2,15). CNS aspergillos presents as meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscesses, subdural abscesses, mycotic arteritis or sellar abscess5).
Preoperative diagnosis of parasellar aspergillus abscess is difficult because clinical presentation and imaging findings in these patients are very similar to the symptoms and imaging results in patients with neoplasms9,17). Headaches and unilateral ophthalmologic signs, including orbital pain, visual deterioration and progressive ophthalmoplegia dominate the clinical presentation of parasellar aspergillus abscess. Ptosis is reported in up to 46% of published reports4). MRI is the best technique for the radiological evaluation of a sellar abscess, but the definitive diagnosis is made with histological tests1,8). On an MRI, the sellar abscess usually appears as a hypo-isointense sellar mass on T1-weighted sequences, as a hyperintense mass on T2-weighted sequences, and as a cystic lesion with peripheral ring enhancement after the administration of a contrast medium. In our patients, imaging findings suggested parasellar tumor, but the contrast enhanced rims of the masses and the clinical findings led us to reconsider the preoperative diagnoses.
Patients with aspergillosis have historically been treated with amphotericine B or combined therapy with amphotericine B and flucytosine or itraconazole. The superiority of voriconazole and caspofungin over amphotericin B as initial therapy for aspergillosis infection in terms of response rate, survival rate, and safety has now been demonstrated in a large randomised study6,18). The aim of treatment should be the complete removal of the masses as early as possible. Even with the invasive type, providing intra dural extension had not yet occurred, total excision was curative without systemic use of antifungal agents. However, in patients in whom total removal cannot be achieved or intra dural invasion has already been confirmed, intensive systemic therapy with antifungal agents must be administered postoperatively to prevent subsequent lethal vasculitis or meningoencephalitis developing. In our case, treatment by voriconazole and amphotericine B was effective in patient, but patient died of cerebral ischemic change, possibly due to resistance for antifungal agents, or developing vessel invasion.
Aspergillus infection is strongly invasive into vessels. It is important to consider the possible occurrence of cerebrovascular disease when treating invasion of aspergillosis into the CNS. CNS aspergillosis is very serious, with a high mortality. A combination of surgical resection and antifungal therapy resulted in good outcomes. The prognosis of the patients depends on early diagnosis and prompt aggressive treatment.
References
1. Alapatt JP, Kutty RK, Gopi PP, Challissery J. Middle and posterior fossa aspergilloma. Surg Neurol. 2006; 66:75–78. discussion 78-79. PMID: 16793449.

2. Bodey G, Bueltmann B, Duguid W, Gibbs D, Hanak H, Hotchi M, et al. Fungal infections in cancer patients : an international autopsy survey. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992; 11:99–109. PMID: 1396746.
3. Endo T, Numagami Y, Jokura H, Ikeda H, Shirane R, Yoshimoto T. Aspergillus parasellar abscess mimicking radiation-induced neuropathy. Case report. Surg Neurol. 2001; 56:195–200. PMID: 11597652.
4. Gupta AK, Mann SB, Khosla VK, Sastry KV, Hundal JS. Non-randomized comparison of surgical modalities for paranasal sinus mycoses with intracranial extension. Mycoses. 1999; 42:225–230. PMID: 10424088.
5. Haran RP, Chandy MJ. Intracranial aspergillus granuloma. Br J Neurosurg. 1993; 7:383–388. PMID: 8216908.

6. Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Bennett JE, Greene RE, Oestmann JW, et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:408–415. PMID: 12167683.

7. Hiraga A, Uzawa A, Shibuya M, Numata T, Sunami S, Kamitsukasa I. Neuroaspergillosis in an immunocompetent patient successfully treated with voriconazole and a corticosteroid. Intern Med. 2009; 48:1225–1229. PMID: 19602790.

8. Iplikcioglu AC, Bek S, Bikmaz K, Ceylan D, Gökduman CA. Aspergillus pituitary abscess. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2004; 146:521–524. PMID: 15118891.

9. Jain KC, Varma A, Mahapatra AK. Pituitary abscess : a series of six cases. Br J Neurosurg. 1997; 11:139–143. PMID: 9156001.
10. Koshy R, Malhotra P. Treatment of primary aspergilloma of the central nervous system in a diabetic immunocompetent patient with surgical resection and voriconazole : a case report and review of the literature. Turk Neurosurg. 2011; 21:641–644. PMID: 22194129.
11. Okugawa S, Ota Y, Tatsuno K, Tsukada K, Kishino S, Koike K. A case of invasive central nervous system aspergillosis treated with micafungin with monitoring of micafungin concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Infect Dis. 2007; 39:344–346. PMID: 17454899.

12. Palanisamy A, Chao SD, Fouts M, Kerr D. Central nervous system aspergillosis in an immunocompetent patient : cure in a hospice setting with very high-dose itraconazole. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2005; 22:139–144. PMID: 15853093.

13. Petrick M, Honegger J, Daschner F, Feuerhake F, Zentner J. Fungal granuloma of the sphenoid sinus and clivus in a patient presenting with cranial nerve III paresis : case report rand review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2003; 52:955–958. discussion 958-959. PMID: 12657193.
14. Pinzer T, Reiss M, Bourquain H, Krishnan KG, Schackert G. Primary aspergillosis of the sphenoid sinus with pituitary invasion - a rare differential diagnosis of sellar lesions. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006; 148:1085–1090. discussion 1090. PMID: 16855812.

15. Stevens DA, Kan VL, Judson MA, Morrison VA, Dummer S, Denning DW, et al. Practice guidelines for diseases caused by Aspergillus. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2000; 30:696–709. PMID: 10770732.
16. Ueno A, Hamano T, Fujii A, Matsunaga A, Naganuma S, Yoneda M, et al. [Effects of voriconazole and vascular lesions in invasion of aspergillosis into the central nerve system]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2009; 49:468–473. PMID: 19827595.

17. Vates GE, Berger MS, Wilson CB. Diagnosis and management of pituitary abscess : a review of twenty-four cases. J Neurosurg. 2001; 95:233–241. PMID: 11780892.

18. Walsh TJ, Pappas P, Winston DJ, Lazarus HM, Petersen F, Raffalli J, et al. Voriconazole compared with liposomal amphotericin B for empirical antifungal therapy in patients with neutropenia and persistent fever. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:225–234. PMID: 11807146.

19. Xiao A, Jiang S, Liu Y, Deng K, You C. Invasive intracranial aspergillosis spread by the pterygopalatine fossa in an immunocompetent patient. Braz J Infect Dis. 2012; 16:192–195. PMID: 22552465.

Fig. 1
MRI revealing a mass in the right cavernous sinus, extended to the anterior crainial fossa and the superior orbital fissure with strong enhancement (arrows).
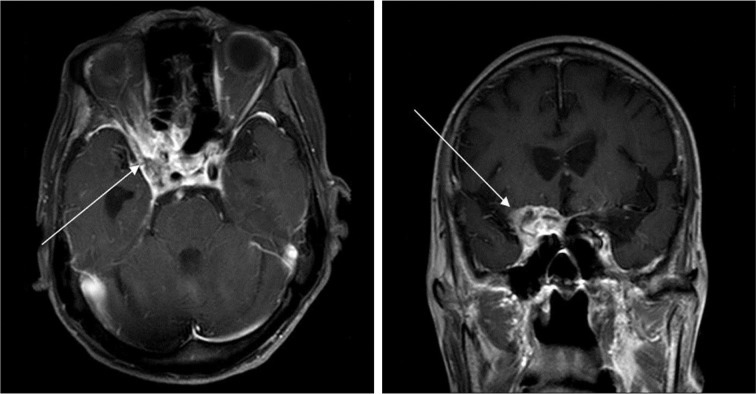
Fig. 2
A : Photomicrograph of the surgical specimen showing pathologic findings of hyaline, branched and septate fungal hyphae typical of aspergillosis in haematoxylin and eosinstain. B : The Grocott's methenamine silver stain shows septate hyphae.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download