INTRODUCTION
 | Fig. 1.In conventional carotid endarterectomy, the ICA, CCA, and ECA are clamped in that order. From incision on the carotid artery to closure of the arteriotomy, the entire process of endarterectomy is performed in the condition that the ICA, CCA, and ECA are clamped. After finishing the complete closure of the arteriotomy site, the ICA, ECA, and CCA are unclamped. ICA : internal carotid artery, CCA : common carotid artery, ECA : external carotid artery. |
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Surgical technique 1 with a case
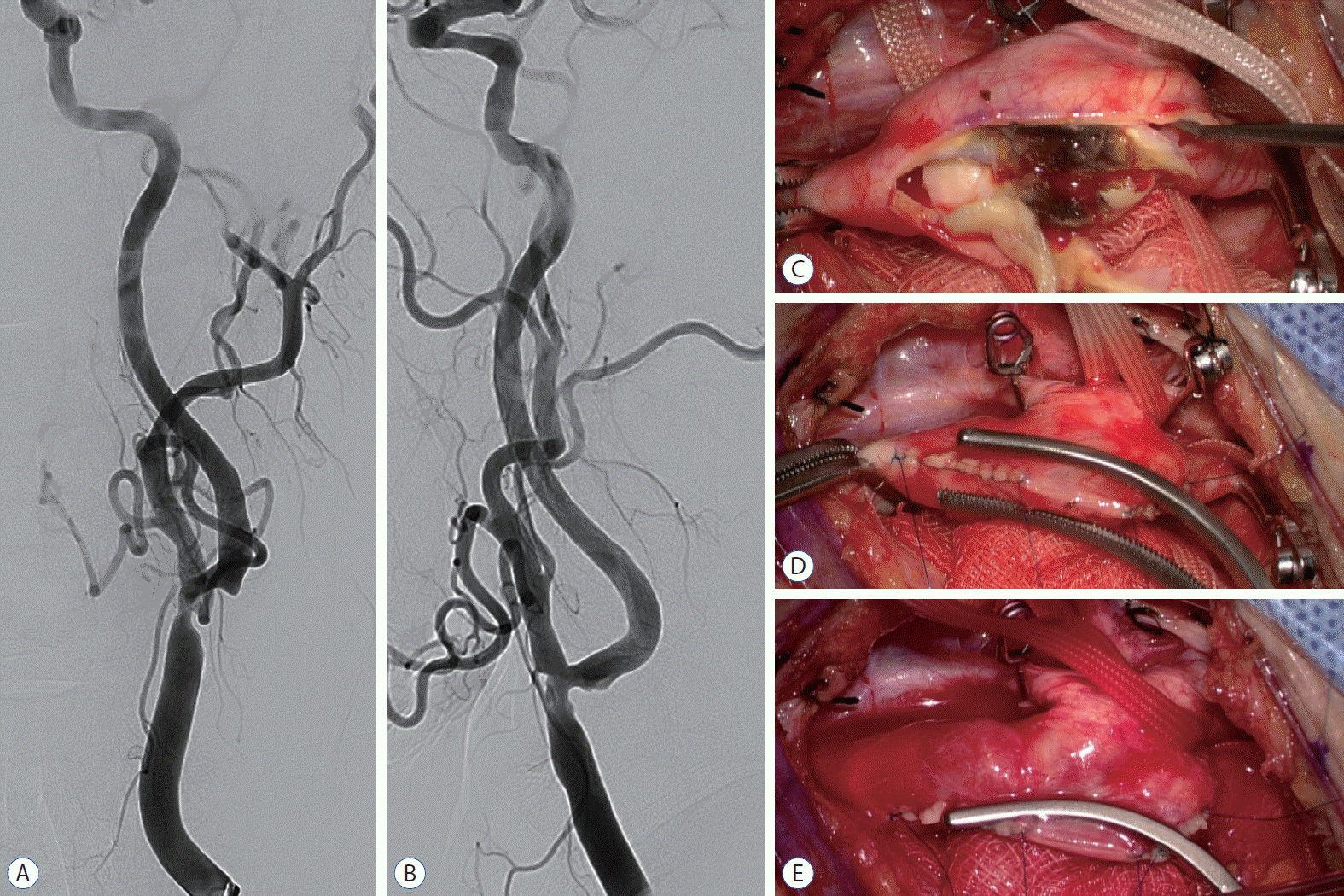 | Fig. 2.A and B : Cerebral angiography revealed NASCET 55% stenosis in the left distal CCA including the ICA origin site. The lesion was accompanied by luminal irregularity (A : anteroposterior view, B : lateral view). C : The atheroma was an unstable plaque with ulceration. D : Applying a Satinsky clamp to isolated unsutured site from the carotid artery lumen. E : After applying a Satinsky clamp, the ECA, ICA, and CCA were opened before finishing the closure of the arteriotomy site. NASCET : The North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial, CCA : common carotid artery, ICA : internal carotid artery, ECA : external carotid artery. |
Surgical technique 2 with a case
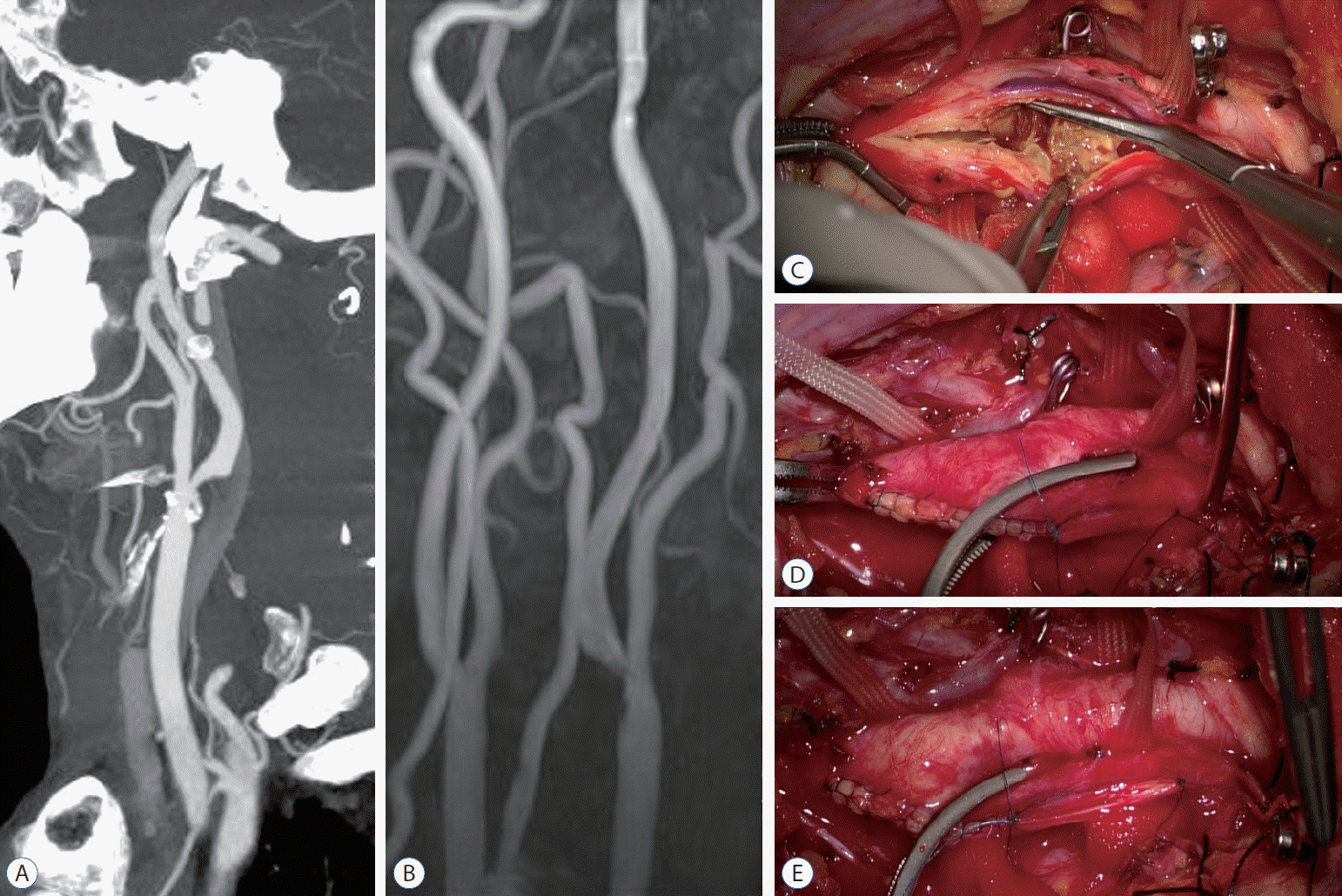 | Fig. 3.A : Computed tomography angiography revealed severe stenosis of the left proximal cervical ICA (NASCET 80%) with calcification. B : Magnetic resonance angiography also demonstrated severe proximal ICA stenosis with ulceration. C : Intraoperative finding of unstable atheroma with ulceration. D : Applying a Satinsky clamp to isolate the unsutured site at the ICA from the CCA lumen. E : After applying a Satinsky clamp, the ECA and CCA were opened before finishing the complete suture of the arteriotomy site. ICA : internal carotid artery, NASCET : The North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial, CCA : common carotid artery, ECA : external carotid artery. |
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
 | Fig. 4.Suture technique 1. The key point of this method is opening the clamps early at the CCA, ICA, and ECA before finishing the complete closure of the arteriotomy, by placing a curved Satinsky clamp at the unsutured site. Black arrows indicate direct blood flow from CCA to ICA. To enable a smooth blood flow, the Satinsky clamp should be placed at the CCA. This method is more applicable in cases that the arteriotomy extends to the CCA. CCA : common carotid artery, ICA : internal carotid artery, ECA : external carotid artery. |
 | Fig. 5.Suture technique 2. This method is using collateral blood flow via multiple anastomoses between the ICA and ECA. First, the arteriotomy at the CCA is sutured. After that, the unsutured site at the ICA is isolated using a curved Satinsky clamp. Afterward, the CCA and ECA are opened to enable blood flow from the CCA to the ECA. Black arrow indicates blood flow from CCA to ECA and dotted black arrow means collateral flow via ECA-ICA anastomoses. This method is easy to apply in cases where the plaque is located at the ICA side and the arteriotomy is not extended to the CCA. ICA : internal carotid artery, ECA : external carotid artery, CCA : common carotid artery. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download