Abstract
An epileptic seizure is defined as the transient occurrence of signs and/or symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. The type of seizure is defined by the mode of onset and termination, clinical manifestation, and by the abnormal enhanced synchrony. If seizures recur, that state is defined as epilepsy. Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are the mainstay of treatment. Knowledge about initiating and maintaining adequate AEDs is beneficial for the clinician who treats children with epilepsy. This article will delineate the general principles for selecting, introducing, and discontinuing AEDs and outline guidelines for monitoring adverse effects. In general, AED therapy following a first unprovoked seizure in children is not recommended. However, treatment should be considered after a second seizure. In children and adolescents, if they are seizure-free for at least 2 years, attempts to withdraw medication/s should be made, taking into account the risks vs. benefits for the individual patient. The decision on when and what AED to use should be tailored according to the patient. For optimal treatment, the selection of adequate AEDs can be achieved by considering the precise definition of the patient’s seizure and epilepsy syndrome. Continuous monitoring of both therapeutic and adverse effects is critical for successful treatment with AEDs.
Go to : 
An epileptic seizure is defined as the transient occurrence of signs and/or symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. The type of seizure is defined by the mode of onset and termination, clinical manifestation, and abnormal enhanced synchrony [16]. If a seizure recurs, the state is defined as epilepsy. The operational definition provided by the International League Against Epilepsy defines epilepsy as “a condition characterized by recurrent (two or more) epileptic seizures, unprovoked by any immediate identified cause” [11]. In 2014, the definition of epilepsy was revised to : 1) at least two unprovoked (or reflex) seizures occurring >24 hours apart; 2) one unprovoked (or reflex) seizure and a probability of further seizures similar to the general recurrence risk (at least 60%) after two unprovoked seizures, occurring over the next 10 years; and 3) diagnosis of an epilepsy syndrome [15]. The primary objective in treating epilepsy is to prevent further seizures and to reduce the acute and chronic side effects of treatment. Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) is the mainstay of treatment of epilepsy. Knowledge about introducing and maintaining adequate AEDs is beneficial to the children with epilepsy. This article will delineate the general principles of selecting, initiating, and discontinuing AEDs, and outline the guidelines for monitoring any adverse effects.
Go to : 
The recurrence rate after the first seizure is estimated to be approximately 30–40%. After the second seizure, it is about 70%. Recurrence risk is higher among patients with remote symptomatic etiology and for those who experienced a second seizure within 6 months of the first seizure [33,36]. AED is effective in reducing the risk of a recurrent seizure. However, treatment does not alter the underlying disorder and does not change the long-term prognosis [31]. Generally, introducing AED after the first unprovoked seizure is not recommended for children. Treatment is usually considered in children with high risks of recurrence. In contrast, in adults, treatment is usually indicated after the first seizure. However, it is debated whether children diagnosed with genetic or unknown self-limited epilepsy syndromes, such as selflimited (previously benign) epilepsy with centro-temporal spike discharges, require immediate introduction of AED [2,17]. The recurrence rate is low among those with epileptic syndromes. Evidence suggests that approximately 25% of patients with recurrence, experience 10 or more seizures over a 10-year period [33]. Therefore, for children with genetic or unknown epilepsy who had a second seizure, the decision to treat with AED should be individualized. The clinician should consider whether the patient has a self-limited epilepsy syndrome, the frequency, and the relative risks vs. benefits of the treatment. A seizure itself is a very frightening symptom, however, the long-term psychosocial impact of a single seizure in children is minimal. In adolescents and adults, the psychosocial impact could be serious, and the social stigma a big problem. Psychosocial impact and related factors should also be reviewed when considering AEDs after the first seizure [22].
There are reports supporting that most patients with epilepsy remain seizure-free with AEDs within the first few years of diagnosis [3,6,35]. Long-term use of AEDs could bring about morbidities [1]. Whether the patient can withdraw AEDs after a certain period of being seizure-free is a critical issue to consider. Many studies have investigated the issue of remission and relapse after withdrawal of AEDs. Most of the studies have reported that 60% to 75% of children and adolescents with epilepsy who have been seizure-free for more than 2 to 4 years on medication, will be seizure-free after discontinuation of AEDs [3,4,6,8,13,37]. A meta-analysis reported a pooled risk of relapse of 25% at 1 year and 29% at 2 years after withdrawal [5]. In addition, it was also found that adolescent onset epilepsy has a higher recurrence risk following AED withdrawal than either childhood- (relative risk, 1.79) or adult-onset (relative risk, 1.34) epilepsy. The recurrences tend to occur during the gradual reduction of AED or soon after discontinuation. About half of the recurrences present within 6 months of medication withdrawal and more than 85% occur within 5 years [3,5,37].
Clinically, it is important to find out the high-risk group for recurrence after withdrawal of AEDs. Patients with epilepsy, who have congenital malformation of the brain, previous neurologic insult, brain tumor, inborn error of metabolism, trauma, or stroke, belong to the poor prognostic group [35]. In one study of 264 pediatric patients, the cumulative recurrence risk in 2 years after discontinuation of AEDs was 42% in patients with the above causes [32]. Another study including patients with cerebral palsy and epilepsy showed that most of the patients did not have full seizure control. However, 58% of the patients who did achieve a seizure-free state for over 2 years remained seizure-free even after discontinuation of AEDs [12]. The type of cerebral palsy influenced the differential risk of recurrence. An estimation from a metaanalysis revealed that the relative risk of recurrence in patients with remote structural causes compared with epilepsy of genetic or unknown causes was 1.55 [5].
Although abnormal interictal electroencephalography (EEG) is often considered as a major predictor of recurrence after withdrawal, there are conflicting evidences. Many studies have reported that a normal EEG prior to discontinuation was an important prognostic factor [3,5,32]. The presence of both slow waves and spike discharges was associated with high risks of relapse [34]. Some studies did not support EEG abnormalities as being prognostic [21]. However, changes in the EEG between initial study and the time of discontinuation could have some prognostic value [34]. Other factors such as duration of epilepsy, number of seizures, and type of seizures are not consistent prognostic factors of recurrence [21,32,35].
Go to : 
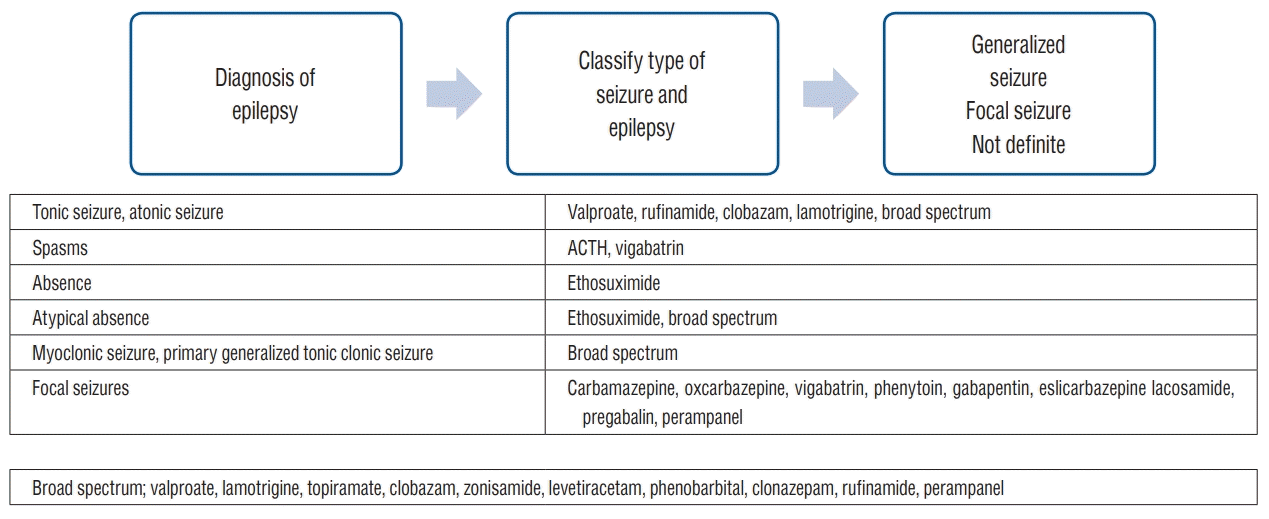
After the diagnosis of epilepsy is established and the decision to introduce AED is made, the next step is choosing and ensuring adequate AEDs for treatment. The first step in AED selection is defining the type of seizure and the classification of epilepsy or epilepsy syndrome. There are AEDs which have specified indications for focal seizures, such as carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine. Vigabatrin is indicated for epileptic spasms, as well as for focal seizures. If those medications are used in generalized onset seizures such as absence (non-motor) or myoclonic seizures, the seizures will get worsened [9,10]. There are medications with specified indications : ethosuximide for absence (non-motor) seizures and clobazam or clonazepam for myoclonic seizures [28]. For generalized epilepsy, valproate is one of the most frequently prescribed medication. Levetiracetam, lamotrigine, zonisamide, topiramate, clonazepam, clobazam, and rufinamide are classified as broad spectrum and are indicated for most seizure types. For the initial dose, usually a minimal dose is prescribed. The dose is then titrated at regular intervals, considering the half-life of the medication, therapeutic effect, and side effects. Knowledge about each medication such as its metabolism, specific adverse effects, and drug interactions is valuable for adjusting the dose for optimal therapeutic effects. Once seizure control is achieved, the dose is maintained, and side effects are monitored. Fig. 1 illustrates the recommended steps for choosing and ensuring adequate AEDs.
Go to : 
Plasma drug levels are usually monitored for traditional AEDs such as carbamazepine, valproate, phenobarbital, and phenytoin. The drug level measurement is indicated for keeping within the therapeutic range, checking before dose-escalation, monitoring suspicion of poor compliance or drug interaction, lack or loss of therapeutic effect, or toxic symptoms. Plasma drug level can be measured for most of the newer AEDs. However, it is not required because the plasma level is usually well correlated with the dose [9,10,29].
AEDs are associated with various adverse effects, which should be considered during treatment. In about 15% of patients, AEDs are discontinued due to acute or idiosyncratic adverse effect/s. There are two kinds of adverse effects : one is dose-dependent; the other is idiosyncratic. The most important dose-dependent adverse effects are drowsiness, dizziness, diplopia, decrease in concentration, and mental slowing. For dose-dependent adverse effects, it is very important to educate the patients and family to report these early, if observed. With early suspicion, those adverse effects could be controlled with dose adjustment. Allergic reactions such as skin rash, is an important idiosyncratic adverse effect, and patients and family should be informed of the risk, at the time of treatment initiation.
Go to : 
There are various cognitive and behavioral adverse effects that are more prominent in children [20,38]. Although these are common in children, they are somewhat difficult to recognize, especially for preschool-aged children. Regular evaluation for changes in cognitive functions and behaviors and education for the parents are recommended. These adverse effects are generally resolved via neurocognitive therapy and adjustment or alteration of the medication.
Go to : 
Cutaneous adverse drug reactions to AEDs are a common major problem in the treatment of epilepsy [25-27]. When an adverse reaction occurs, the drug in question needs to be withdrawn immediately in order to minimize its effects. Reintroducing the sensitized drug should be avoided because moresevere hypersensitivity reactions or even life-threatening conditions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis can occur [14]. In addition, the development of cross-reactivity to other AEDs reportedly occurs in 40–58% of the cases [19,24]. Cutaneous adverse drug reactions may, therefore, have a decisive impact on the course of treatment. Applying a desensitization protocol to the causative drug may be an option, especially if the patient has previously shown a favorable response to AED and has subsequently shown resistance or cross-reactivity to other AEDs [26].
Go to : 
Depression and anxiety are common adverse effects in patients with epilepsy, which are often underestimated in the pediatric population [7]. For example, behavioral adverse effects can occur with levetiracetam, topiramate, zonisamide, and phenobarbital. Irritability and hostility are the main concerns with levetiracetam, often seen soon after initiation [18].
Patients or family members are often unaware of cognitive and mood changes associated with AED therapy. Mood disorders are common comorbidities in patients with epilepsy that may or may not be associated with AED therapy [23]. For prevention, it is recommended that patients be evaluated for mood disturbances before and during treatment. The result can then be taken into account when choosing adequate AEDs. The association between AEDs and the risk for suicidal ideation and completed suicide was the subject of a recent US Food and Drug Administration (FDA; www.fda.gov). It is still unclear if AED therapy is causes suicidal ideation and if so, the possible mechanism behind it. Rather than an association with AEDs, mood disorders (and suicidality) may be the result of fronto-temporal connections; wherein hippocampal damage from seizures may affect serotonin and other neuromodulators related to depression and anxiety [30]. On the contrary, several AEDs, such as carbamazepine, lamotrigine, and valproate, have positive psychotropic effects. For example, FDA approval has been issued for lamotrigine for the treatment of bipolar depression [10].
Go to : 
Guidelines should be developed to advise when to initiate AED therapy because there are diverse situations for each seizure. If the results of EEG, magnetic resonance imaging, or the physical exam are significantly abnormal, there is nearly a 50% risk of recurrence after a new onset seizure [9,10]. In general, it is not recommended to initiate AED therapy following the first unprovoked seizure in children. After a second seizure, treatment needs to be considered. In children and adolescents, if they are seizure-free for at least 2 years, an attempt to withdraw the medication should be made considering risks vs. benefits for the individual patient. The decision on when and what AED to use should be tailored according to the case. In adolescents, issues with driving need to be considered with AED initiation and discontinuation. For optimal treatment, the selection of adequate AEDs can be achieved by the precise definition of a patient’s seizure and epilepsy syndrome. Continuous monitoring of the therapeutic and adverse effects is critical for the successful treatment with AEDs.
Go to : 
References
1. Aldenkamp AP, Alpherts WC, Sandstedt T, Blennow G, Elmqvist G, Heijbel J, et al. Antiepileptic drug-related cognitive complaints in seizurefree children with epilepsy before and after drug discontinuation. Epilepsia. 39:1070–1074. 1998.

2. Ambrosetto G, Tassinari CA. Antiepileptic drug treatment of benign childhood epilepsy with rolandic spikes: is it necessary? Epilepsia. 31:802–805. 1990.

3. Andersson T, Braathen G, Persson A, Theorell K. A comparison between one and three years of treatment in uncomplicated childhood epilepsy: a prospective study. II. The EEG as predictor of outcome after withdrawal of treatment. Epilepsia. 38:225–232. 1997.

4. Beghi E, Giussani G, Grosso S, Iudice A, La Neve A, Pisani F, et al. Withdrawal of antiepileptic drugs: guidelines of the Italian League Against Epilepsy. Epilepsia 54 Suppl. 7:2–12. 2013.

5. Berg AT, Shinnar S. Relapse following discontinuation of antiepileptic drugs: a meta-analysis. Neurology. 44:601–608. 1994.

6. Berg AT, Shinnar S, Levy SR, Testa FM, Smith-Rapaport S, Beckerman B, et al. Two-year remission and subsequent relapse in children with newly diagnosed epilepsy. Epilepsia. 42:1553–1562. 2001.

7. Blumer D, Montouris G, Hermann B. Psychiatric morbidity in seizure patients on a neurodiagnostic monitoring unit. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 7:445–456. 1995.

8. Braathen G, Andersson T, Gylje H, Melander H, Naglo AS, Norén L, et al. Comparison between one and three years of treatment in uncomplicated childhood epilepsy: a prospective study. I. Outcome in different seizure types. Epilepsia. 37:822–832. 1996.

10. Chong DJ, Lerman AM. Practice update: review of anticonvulsant therapy. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 16:39. 2016.

11. Commission on Epidemiology and Prognosis; International League Against Epilepsy. Guidelines for epidemiologic studies on epilepsy. Commission on Epidemiology and Prognosis, International League Against Epilepsy. Epilepsia. 34:592–596. 1993.
12. Delgado MR, Riela AR, Mills J, Pitt A, Browne R. Discontinuation of antiepileptic drug treatment after two seizure-free years in children with cerebral palsy. Pediatrics. 97:192–197. 1996.

13. Dooley J, Gordon K, Camfield P, Camfield C, Smith E. Discontinuation of anticonvulsant therapy in children free of seizures for 1 year: a prospective study. Neurology. 46:969–974. 1996.

14. Fégueux S, De Truchis P, Balloul H, Maslo C, Matheron S, Coulaud JP. Sulphadiazine desensitization in AIDS patients. AIDS. 5:1275–1276. 1991.

15. Fisher RS, Acevedo C, Arzimanoglou A, Bogacz A, Cross JH, Elger CE, et al. ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 55:475–482. 2014.

16. Fisher RS, van Emde Boas W, Blume W, Elger C, Genton P, Lee P, et al. Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia. 46:470–472. 2005.

17. Freeman JM, Tibbles J, Camfield C, Camfield P. Benign epilepsy of childhood: a speculation and its ramifications. Pediatrics. 79:864–868. 1987.

18. Halma E, de Louw AJ, Klinkenberg S, Aldenkamp AP, DM IJ, Majoie M. Behavioral side-effects of levetiracetam in children with epilepsy: a systematic review. Seizure. 23:685–691. 2014.

19. Hirsch LJ, Arif H, Nahm EA, Buchsbaum R, Resor SR Jr, Bazil CW. Crosssensitivity of skin rashes with antiepileptic drug use. Neurology. 71:1527–1534. 2008.

20. Hirtz D, Berg A, Bettis D, Camfield C, Camfield P, Crumrine P, et al. Practice parameter: treatment of the child with a first unprovoked seizure: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology. 60:166–175. 2003.

21. Holowach J, Thurston DL, O’Leary J. Prognosis in childhood epilepsy. Follow-up study of 148 cases in which therapy had been suspended after prolonged anticonvulsant control. N Engl J Med. 286:169–174. 1972.
22. Jacoby A, Johnson A, Chadwick D. Psychosocial outcomes of antiepileptic drug discontinuation. The Medical Research Council AED Withdrawal Study Group. Epilepsia. 33:1123–1131. 1992.

23. Kanner AM, Balabanov A. Depression and epilepsy: how closely related are they? Neurology. 58(8 Suppl 5):S27–S39. 2002.

24. Klassen BD, Sadler RM. Induction of hypersensitivity to a previously tolerated antiepileptic drug by a second antiepileptic drug. Epilepsia. 42:433–435. 2001.

25. Kuyucu S, Caubet JC. Hypersensitivity reactions to antiepileptic drugs in children: epidemiologic, pathogenetic, clinical, and diagnostic aspects. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 6:1879–1891. e1. 2018.

26. Lee J, Park EG, Lee M, Lee J. Desensitization to oxcarbazepine: longterm efficacy and tolerability. J Clin Neurol. 13:47–54. 2017.

27. Mehta M, Shah J, Khakhkhar T, Shah R, Hemavathi KG. Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome associated with carbamazepine administration: case series. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 5:59–62. 2014.

28. Panayiotopoulos CP, Obeid T, Tahan AR. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: a 5-year prospective study. Epilepsia. 35:285–296. 1994.

29. Patsalos PN, Berry DJ, Bourgeois BF, Cloyd JC, Glauser TA, Johannessen SI, et al. Antiepileptic drugs--best practice guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring: a position paper by the subcommission on therapeutic drug monitoring, ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia. 49:1239–1276. 2008.

30. Schmitz EB, Moriarty J, Costa DC, Ring HA, Ell PJ, Trimble MR. Psychiatric profiles and patterns of cerebral blood flow in focal epilepsy: interactions between depression, obsessionality, and perfusion related to the laterality of the epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 6. 2:458–463. 1997.

31. Shinnar S, Berg AT. Does antiepileptic drug therapy prevent the development of “chronic” epilepsy? Epilepsia. 37:701–708. 1996.

32. Shinnar S, Berg AT, Moshé SL, Kang H, O’Dell C, Alemany M, et al. Discontinuing antiepileptic drugs in children with epilepsy: a prospective study. Ann Neurol. 35:534–545. 1994.

33. Shinnar S, Berg AT, O’Dell C, Newstein D, Moshe SL, Hauser WA. Predictors of multiple seizures in a cohort of children prospectively followed from the time of their first unprovoked seizure. Ann Neurol. 48:140–147. 2000.

34. Shinnar S, Vining EP, Mellits ED, D’Souza BJ, Holden K, Baumgardner RA, et al. Discontinuing antiepileptic medication in children with epilepsy after two years without seizures. A prospective study. N Engl J Med. 313:976–980. 1985.

35. Sillanpää M, Jalava M, Kaleva O, Shinnar S. Long-term prognosis of seizures with onset in childhood. N Engl J Med. 338:1715–1722. 1998.

36. Stroink H, Brouwer OF, Arts WF, Geerts AT, Peters AC, van Donselaar CA. The first unprovoked, untreated seizure in childhood: a hospital based study of the accuracy of the diagnosis, rate of recurrence, and long term outcome after recurrence. Dutch study of epilepsy in childhood. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 64:595–600. 1998.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download