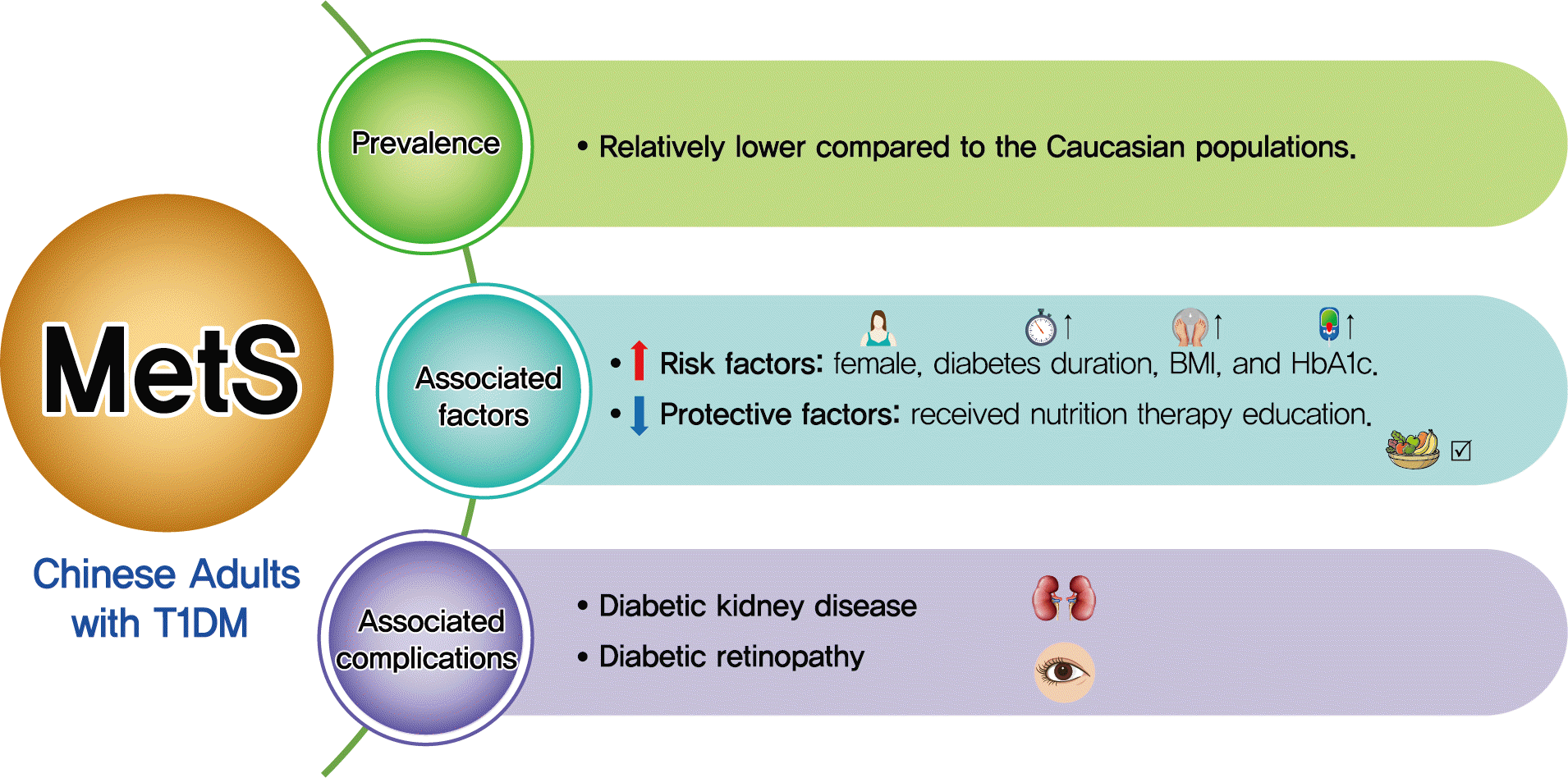
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
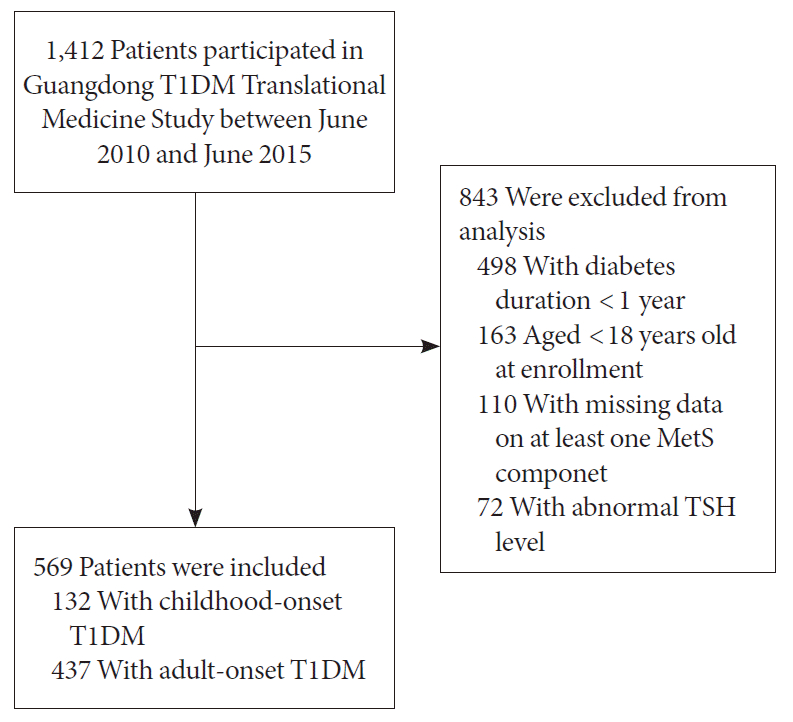
Study design and participants
Definitions
Measurements
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Study population and metabolic syndrome
Table 1.
| Parameter | Alla (n=569) | MetS present (n=86) | MetS absent (n=483) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female sex | 315 (55.4) | 67 (77.9) | 248 (51.3) | <0.001 |
| Age at enrollment, yr | 34.8±12.4 | 35.7±15.1 | 34.6±11.9 | 0.440 |
| Diabetes duration, yr | 5.9 (3.1–10.3) | 6.7 (3.9–11.9) | 5.8 (3.1–9.5) | 0.028 |
| Age at diagnosis, yr | 25.6 (18.3–33.8) | 24.7 (16.0–34.2) | 25.8 (18.6–33.8) | 0.307 |
| Childhood-onset cases | 132 (23.2) | 28 (32.6) | 104 (21.5) | 0.026 |
| Family history of diabetes | 149 (26.5) | 29 (34.1) | 120 (25.1) | 0.083 |
| Family history of T1DM | 25 (4.4) | 3 (3.5) | 22 (4.6) | 1.000 |
| Education level: less than university | 177 (31.4) | 20 (23.5) | 157 (2.8) | 0.088 |
| Having insurance | 490 (86.1) | 70 (81.4) | 420 (87.0) | 0.169 |
| Marital status (married) | 344 (61.3) | 47 (56.0) | 297 (62.3) | 0.273 |
| Living status (alone) | 45 (8.3) | 7 (9.0) | 38 (8.2) | 0.812 |
| Diabetic education | 432 (77.6) | 58 (67.4) | 374 (77.4) | 0.109 |
| Received nutrition therapy education | 239 (42.0) | 23 (26.7) | 216 (44.7) | 0.002 |
| Adhering to diabetic diet | 398 (71.2) | 53 (63.9) | 345 (72.5) | 0.109 |
| Exercise ≥150 min/week | 228 (49.0) | 33 (47.8) | 195 (49.2) | 0.828 |
| Smoker | 92 (16.2) | 9 (10.6) | 83 (17.2) | 0.128 |
| Alcohol drinker | 50 (8.8) | 2 (2.4) | 48 (9.9) | 0.023 |
| Clinical visit times per year <12 | 289 (53.7) | 37 (46.8) | 252 (54.9) | 0.184 |
Values are presented as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range). P value: MetS present vs. MetS absent.
T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; MetS, metabolic syndrome.
a Missing data: family history of diabetes, 7 (1.2%); family history of T1DM, 7 (1.2%); family history of T1DM, 7 (1.2%); living status, 26 (4.6%); marital status, 8 (1.4%); diabetic education, 12 (2.1%); adhering to diabetic diet, 10 (1.8%); exercise status, 104 (18.4%); alcohol drinker, 1 (0.2%); smoker, 1 (0.2%); clinical visit times per year, 31 (5.4%).
Table 2.
| Parameter | Alla (n=569) | MetS present (n=86) | MetS absent (n=483) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI, kg/m2 | 20.7±2.6 | 21.8±2.9 | 20.5±2.4 | <0.001 |
| Underweight | 110 (19.4) | 13 (15.1) | 97 (20.2) | 0.005 |
| Normal weight | 424 (74.9) | 61 (70.9) | 363 (75.6) | |
| Overweight/Obesity | 32 (5.7) | 12 (14) | 20 (4.2) | |
| Waist circumference, cm | 74.5±7.6 | 79.2±8.1 | 73.7±7.2 | <0.001 |
| In female | 73.8±7.5 | 79.5±7.8 | 72.3±6.7 | <0.001 |
| In male | 75.4±7.7 | 78.3±9.2 | 75.0±7.5 | 0.081 |
| WHR | 0.8±0.1 | 0.9±0.1 | 0.8±0.1 | <0.001 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 114.3±14.3 | 122.9±16.9 | 112.8±13.2 | <0.001 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 72.9±9.2 | 78.0±10.9 | 71.9±8.6 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c, % | 8.4 (7.1–10.1) | 9.2 (7.5–10.5) | 8.4 (7.1–10.1) | 0.057 |
| HbA1c ≥9% | 223 (40.9) | 42 (50.6) | 181 (39.2) | 0.051 |
| TC, mmol/L | 4.8±1.2 | 5.3±2.0 | 4.7±1.0 | <0.001 |
| Triglyceride, mmol/L | 0.9 (0.7–1.4) | 1.9 (1.1–2.4) | 0.9 (0.7–1.3) | <0.001 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.5±0.4 | 1.2±0.4 | 1.5±0.4 | <0.001 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 2.5 (2.0–3.2) | 2.7 (2.0–3.6) | 2.5 (2.0–3.1) | 0.030 |
| lnGDR | 1.8±0.4 | 1.7±0.4 | 1.9±0.4 | <0.001 |
| UACR, mg/g | 11.5 (5.9–25.6) | 22.3 (7.2–83.7) | 10.7 (5.8–21.7) | <0.001 |
| UACR ≥30 mg/g | 117 (22.7) | 30 (40.5) | 87 (19.7) | <0.001 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 119.9 (94.3–149.0) | 119.0 (92.3–139.1) | 120.4 (94.4–150.2) | 0.335 |
| eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 32 (6.0) | 6 (7.9) | 26 (5.7) | 0.437 |
| Diabetic complications | ||||
| Hypoglycemic events, /mo | 1 (0–4) | 1 (0–4) | 1 (0–4) | 0.680 |
| Diabetic kidney disease | 122 (21.5) | 31 (36.5) | 91 (18.9) | <0.001 |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 59 (10.4) | 17 (19.8) | 42 (8.7) | 0.002 |
| Insulin regimen | 0.749 | |||
| Insulin pump | 65 (11.5) | 8 (9.5) | 57 (11.9) | |
| Basal-bolus insulin therapy | 195 (34.6) | 28 (33.3) | 167 (34.8) | |
| Others | 304 (53.9) | 48 (57.2) | 256 (53.3) | |
| MetS components | ||||
| Abdominal obesity | 81 (14.2) | 44 (51.2) | 37 (7.6) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 111 (19.5) | 47 (54.7) | 64 (13.3) | <0.001 |
| Abnormal TG | 96 (16.9) | 49 (57.0) | 47 (9.7) | <0.001 |
| Abnormal HDL | 98 (17.2) | 53 (61.6) | 45 (9.3) | <0.001 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation, number (%), or median (interquartile range). P value: MetS present vs. MetS absent.
MetS, metabolic syndrome; BMI, body mass index; WHR, waist-to-hip ratio; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c; TC, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; lnGDR, napierian logarithm of glucose disposal rate; UACR, urinary albumin-creatinine ratio; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; TG, triglyceride.
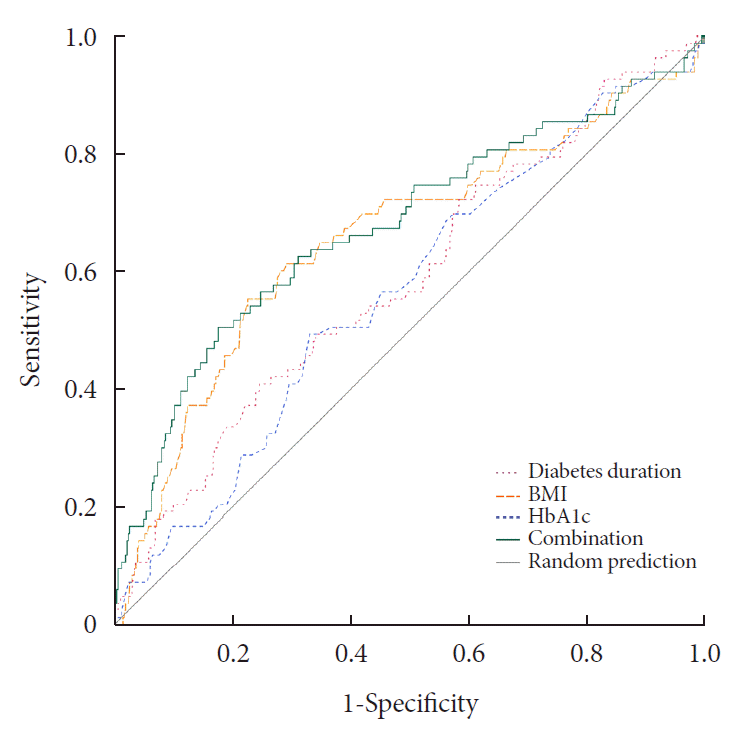
Risk factors associated with MetS
Table 3.
Fig. 2.
Relationship between MetS and microvascular complications
Table 4.
Model 1: unadjusted; Model 2: adjusted for age, gender, and diabetes duration; Model 3: model 2 plus glycosylated hemoglobin A1c; Model 4: model 3 plus university education level, insurance, marital status, diabetic education, received nutrition therapy education, adhering to diabetic diet, exercise status, clinical visit times per year, smoking and alcohol drinking status.
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence intervals.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download