INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Study design and patient population
Table 1
2. Protocol of genotypic drug resistance testing
3. Interpretation of DRMs
4. Clinical responses
5. Patient subgroup classification according to the degree of DRM
6. Statistical analysis
RESULTS
1. The landscape of DRMs
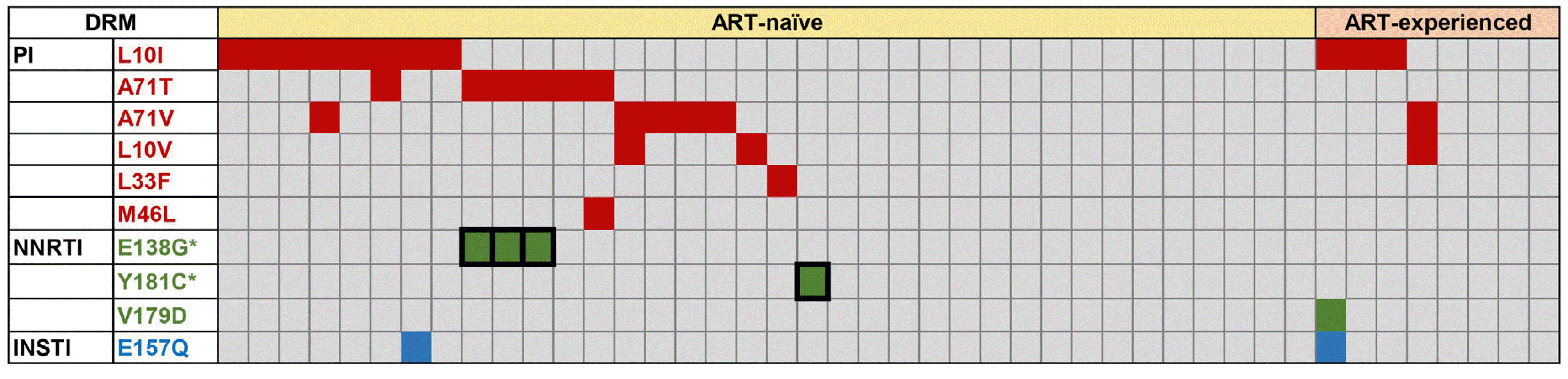 | Fig. 1Landscape of DRM in ART-naïve and ART-experienced patients in South Korea.
*represents major DRMs, and the absence of *represents minor DRMs.
Abbreviations: ART, antiretroviral therapy; DRM, drug resistance mutation; PI, protease inhibitor; NNRTI, nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; INSTI, integrase strand transfer inhibitor.
|
2. DRMs and ART regimens
Table 2
| Patient No. | Drug resistance mutation | Following ART regimen | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| NRTI | NNRTI | PI | INSTI | ||
| 1 | None | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 3 | None | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | EVG/c |
| 5 | NNRTI(E138G)*, PI(A71T) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 8 | NNRTI(E138G)*, PI(A71T) | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | EVG/c |
| 10 | None | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | EVG/c |
| 11 | None | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 12 | None | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 15 | PI(L10I) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 17 | None | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 18 | PI(L10I) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 19 | None | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 21 | PI(L10I) | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | EVG/c |
| 22 | None | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 23 | PI(L10I, A71V) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 24 | PI(L10V, A71V) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 25 | PI(L10I) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 26 | None | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 27 | None | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | EVG/c |
| 30 | PI(A71V) | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | EVG/c |
| 32 | NNRTI(Y181C)* | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 33 | NNRTI(E138G)*, PI(A71T) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 34 | PI(L10I, A71T) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 37 | PI(A71T) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 39 | PI(L10V) | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 43 | PI(L10I), INI(E157Q) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 44 | None | 3TC, ABC, FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | DTG, EVG/c |
| 46 | None | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 47 | PI(A71V) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 48 | PI(M46L, A71T) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 49 | None | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 50 | PI(L33F) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 53 | None | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 55 | PI(A71V) | FTC, TAF | (-) | (-) | EVG/c |
| 56 | None | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 57 | None | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
| 61 | PI(L10I) | 3TC, ABC | (-) | (-) | DTG |
Abbreviations: ART, antiretroviral therapy; DRM, drug resistance mutation; NRTI, nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; NNRTI, nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; PI, protease inhibitor; INSTI, integrase strand transfer inhibitor; 3TC, lamivudine; ABC, abacavir; FTC, emtricitabine; TAF, tenofovir alafenamide; DTG, dolutegravir; EVG/c, elvitegravir/cobicistat.
Table 3
Abbreviations: ART, antiretroviral therapy; SGRT, standard genotypic resistance testing; NRTI, nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; NNRTI, nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; PI, protease inhibitor; INSTI, integrase strand transfer inhibitor; ZDV, zidovudine; 3TC, lamivudine; ABC, abacavir; FTC, emtricitabine; TAF, tenofovir alafenamide; TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate; EFV, efavirenz; LRV/r, lersivirine/ritonavir; ATV/c, atazanavir/cobicistat; DRV/c, darunavir/cobicistat; RAL, raltegravir; DTG, dolutegravir; EVG/c, elvitegravir/cobicistat.
3. Correlation between the degree of drug resistance and the clinical response
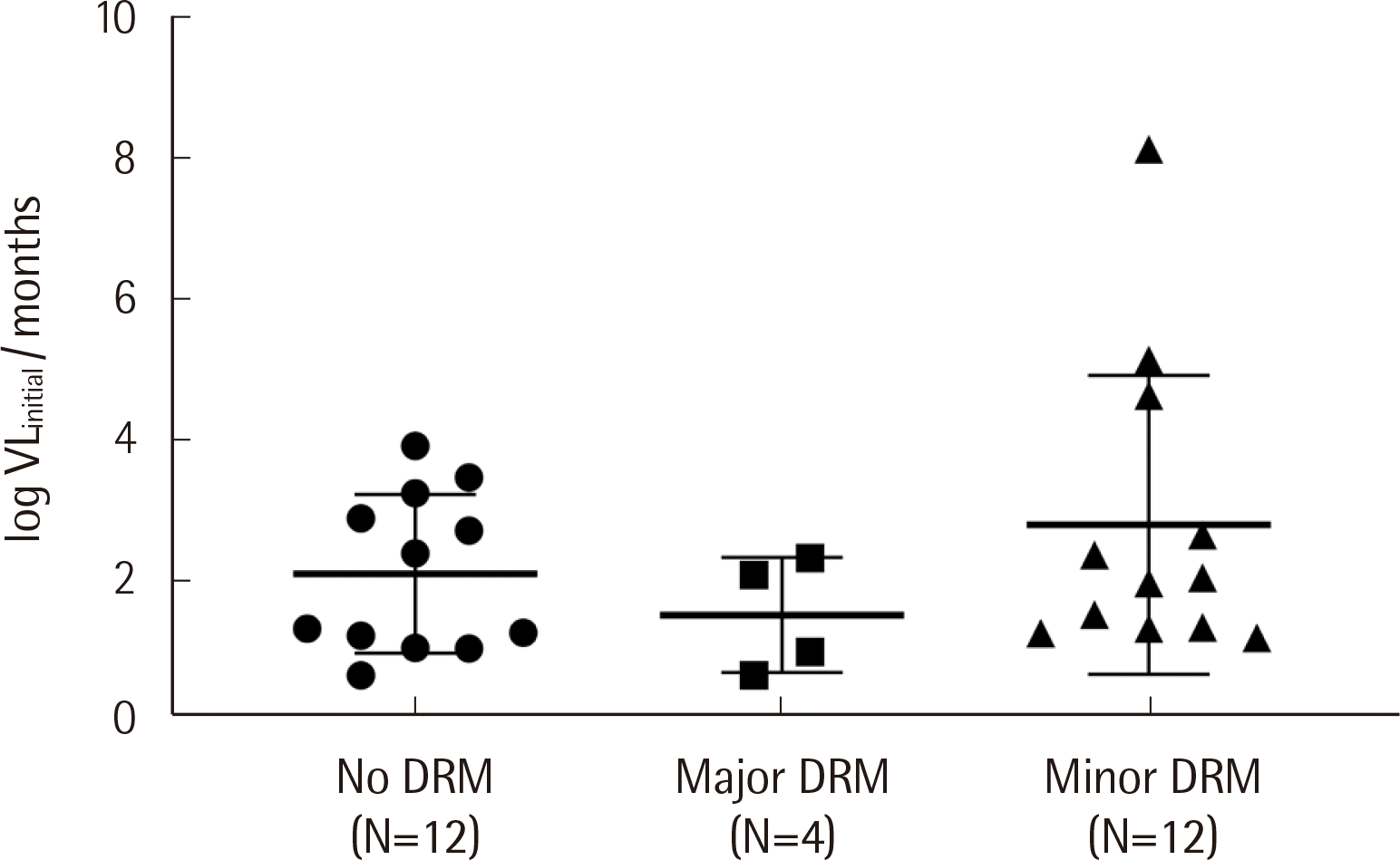 | Fig. 2Log initial viral load per months required to reach virologic suppression according to DRM subtypes in 28 ART-naïve patients. Viro-ogic suppression means the achievement of a viral load of less than the limit of detection (40 copies/mL). Horizontal lines and vertical lines indicate mean values and standard deviations, respectively. There were no differences among the three subgroups (P=0.3429) or between any two groups.
Abbreviations: DRM, drug resistance mutation; VL, viral load.
|
Table 4
| DRM type | Initial CD4 count/μL before ART* | Final CD4 ≥350/μL after ART† | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| <200 | 200–349 | 350–499 | ≥500 | ||
| None (N = 14) | 2 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 12 (85.7%) |
| Minor (N = 14) | 3 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 12 (80.0%) |
| Major (N = 4) | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 (75.0%) |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download