INTRODUCTION
CASE REPORT
 | Fig. 1Pure-tone audiometry. (A) Before cochlear implant, severe sensorineural hearing loss of both ears observed. (B) Two months after cochlear implant, aided audiogram showed a 30 dB threshold through all frequencies. |
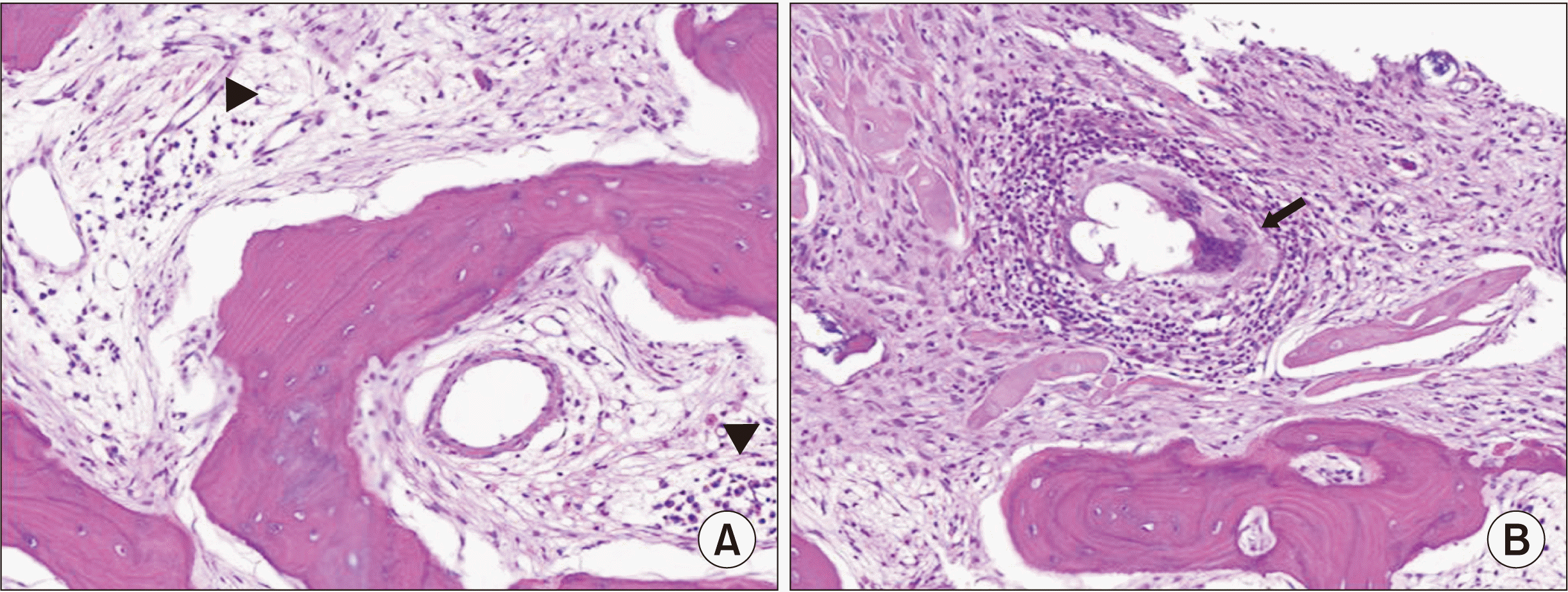
 | Fig. 2Pathology slides demon-strating chronic osteitis in the left incus (H&E, ×400). (A) Lymphoplasmacytic infiltration (triangles). (B) Granulomatous inflammation (arrow). |
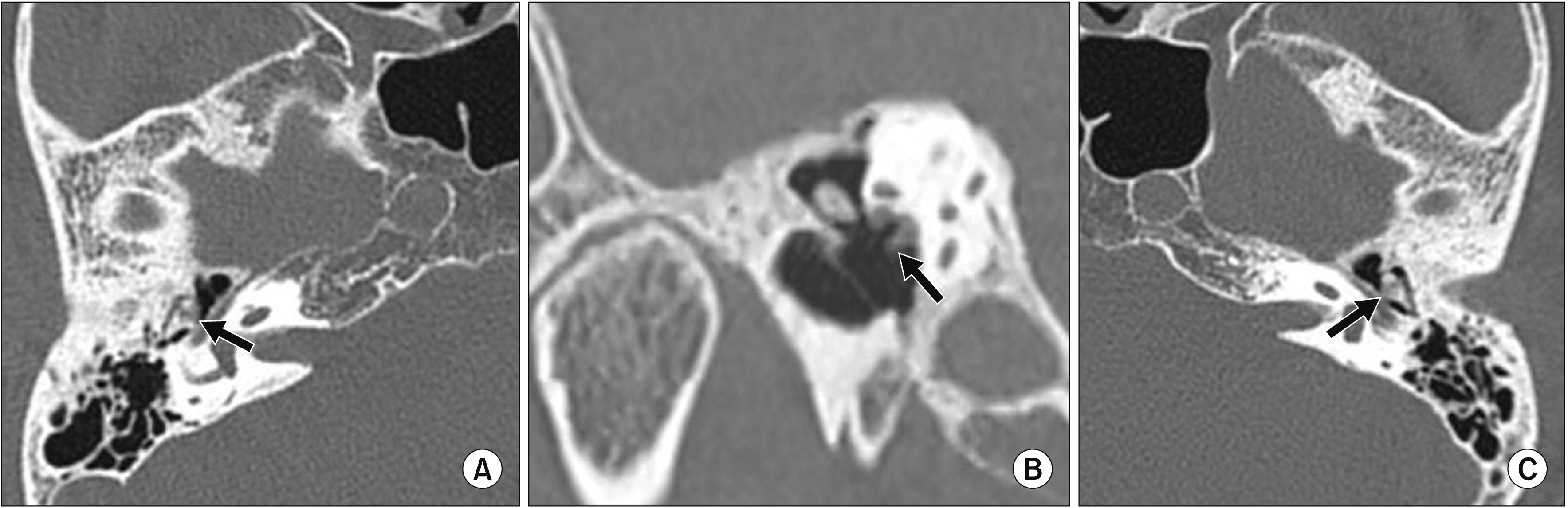
 | Fig. 3CT findings of the temporal bone. CT scan of the right middle ear cavity of a 70-year-old female with hearing loss. The arrows indicate the erosive change and deformity of the incudomalleolar joints with soft tissue infiltration (A, C) in the axial plane and soft tissue infiltration at the stapes in the stenvers plane (B). CT: computed tomography. |
DISCUSSION
Table 1
| Author | Disease | Number of patients | Mean age (yr) | Hearing impairment, number (%) | Abnormal tympanogram, number (%) | Pathology findings of the middle ear | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goodwill et al. [22] | RA | 76 | 52.8 |
7 (9.2) : SNHL 5, CHL 2 |
None | Bone absorption, fibrous tissue | HL was not related with RA duration or activity |
| Rosenberg et al. [23] | RA | 68 | N/A | None | 16 (42) | (-) | The conducting system was abnormal in RA but HL is rare |
| Poorey and Khatri [24] | RA | 25 | N/A |
16 (64) : SNHL 13, CHL 3 |
8 (32) | (-) | CHL was common in early and active RA |
| Ozcan et al. [11] | RA | 37 | 47.7 |
19 (51.4) : SNHL 10, MHL 4, CHL 5 |
14 (37.8) | (-) | HL could be caused by multifocal involvement of the audiologic system in RA |
| Takatsu et al. [17] | RA | 36 | 54.6 |
13 (36.1) : SNHL 13 |
18 (25) | (-) | SNHL is related to ESR and plasma IL-6, and MMP-3. Latent-type CHL can be caused by stiffness of the middle ear |
| Halligan et al. [25] | RA | 29 | 63 (median) |
17 (59) : SNHL 13, MHL 1, CHL 3 |
5 (17) | (-) | No difference in audiometric measurement between patients with RA and controls |
| Milisavljevic et al. [18] | RA | 9 | 66.9 | N/A | N/A | (-) | SEM showed increased lysis and surface degeneration of the auditory ossicles in patients with RA |
| Tavernier and Ranfaing [26] | RA | 1 | 59.0 | MHL | N/A | Mass consisting of fibrous tissue riddled with inflammatory elements, primarily mononucleates | Inflammatory fibrous tissue in the middle ear could result in HL in patients with RA |
| Pascual-Ramos et al. [27] | RA | 113 | 43.3 |
27 (24) : SNHL 25, MHL 2 |
20 (18) | (-) | SNHL the most common type of HL in patients with RA, and older age was a risk factor for HL |
| Lobo et al. [14] | RA | 43 | 48.9 |
20 (46.5) : SNHL 16, MHL 2, CHL 2 |
6 (11.9) | (-) | SNHL was the main HL in patients with RA and was associated with anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies |
| Ahmadzadeh et al. [28] | RA | 42 | 53.0 |
9 (21.3) : SNHL 5, MHL 1, CHL 3 |
13/84 ears (15.4) | (-) | SNHL was more prevalent in patients with refractory RA |
| Magarò et al. [8] | AS | 1 | 56 | CHL | + | (-) | CHL can be induced by ear arthritis in patients with AS |
| Casellini et al. [5] | RA/AS |
RA 19 AS 22 |
RA 56 AS 45.5 (median) |
RA 13 (68.4) : SNHL 11, MHL 1, CHL 1 AS 15 (68.2) : SNHL 13, CHL 2 |
RA 4 (14.3) AS 3 (15.8) |
(-) | HL can occur in patients with AS patients as well as those with RA. Small numbers of patients with otosclerosis among those with AS |
| Dagli et al. [4] | AS | 28 | 34.3 |
10 (35) : SNHL 10 |
None | (-) | Damage of the outer hair cells in patients with AS |
| Adam et al. [3] | AS | 45 | 39.6 |
32 (71.1) : SNHL 32 |
N/A | (-) | High-frequency SNHL was common in AS; risk factors include disease duration and extraspinal involvement |
| Amor-Dorado et al. [9] | AS | 50 | 52.5 |
29 (58) : SNHL 29 |
4 (8) | (-) | High-frequency SNHL and abnormal vestibular tests more common in patients with AS than controls. |
| Amor-Dorado et al. [2] | PsA | 60 | 52.9 |
36 (60) : SNHL 36 |
N/A | (-) | High-frequency SNHL was the predominant pattern of HL in patients with PsA |
| Siamopoulou-Mavridou et al. [7] | JIA | 18 | 10.6 | N/A | 17/36 ears (47.2) | (-) | JIA changes middle ear function by stiffness of the tympanic membrane and ossicular chain |
| Takatsu et al. [17] | JIA | 19 | 12.2 | None | 12/38 ears (31.6) | (-) | A dual effect of JIA on both the middle and inner ears |
RA: rheumatoid arthritis, SNHL: sensorineural hearing loss, CHL: conductive hearing loss, HL: hearing loss, N/A: not available, MHL: mixed hearing loss, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, IL-6: interleukin-6, MMP-3: matrix metalloproteinase-3, SEM: scanning electron microscope, AS: ankylosing spondylitis, PsA: psoriatic arthritis, JIA: juvenile idiopathic arthritis.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download