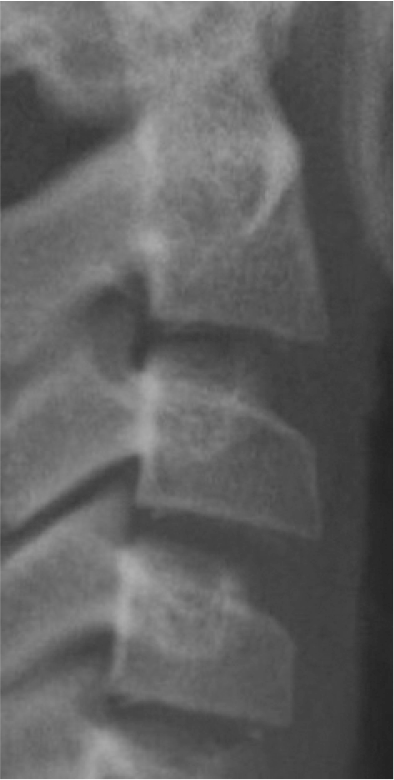
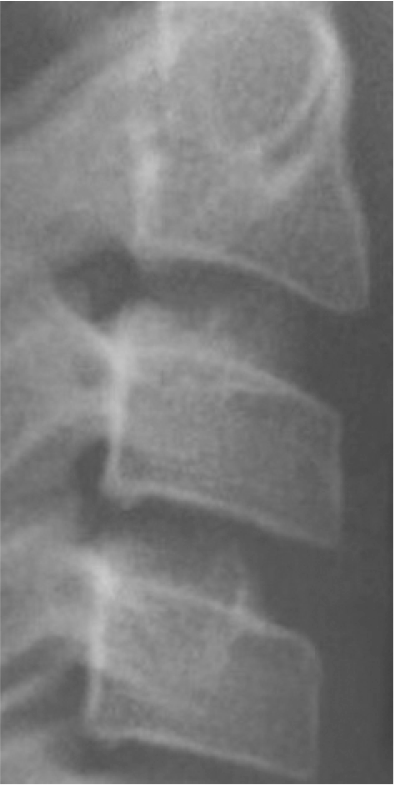
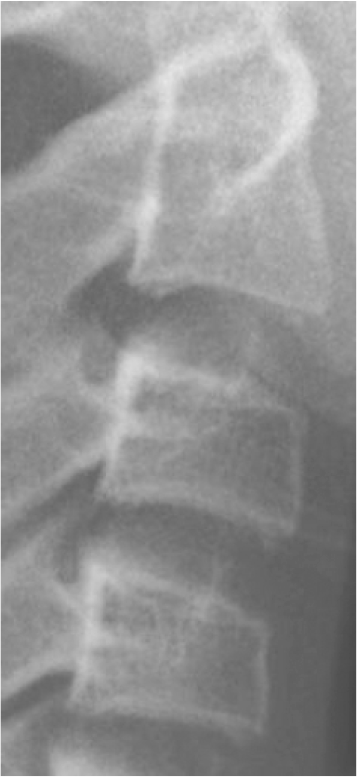
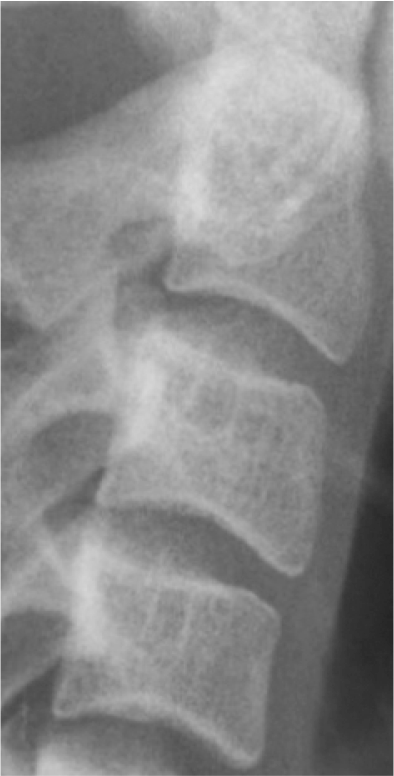
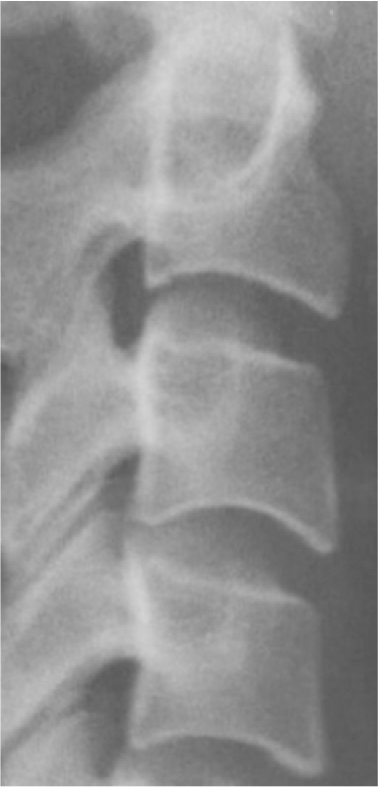
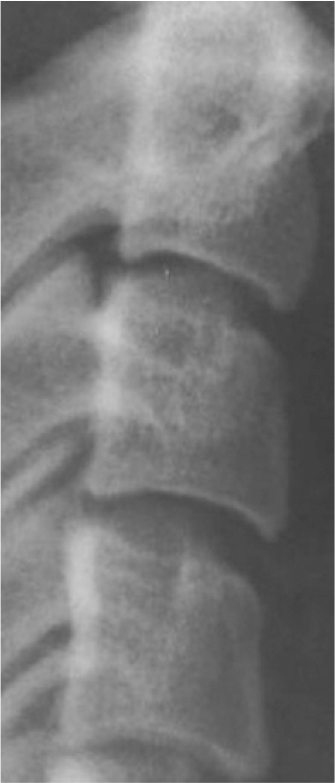
1. Baccetti T, Franchi L, McNamara JA Jr. 2005; The cervical vertebral maturation (CVM) method for the assessment of optimal treatment timing in dentofacial orthopedics. Semin Orthod. 11:119–29. DOI:
10.1053/j.sodo.2005.04.005.

4. Franchi L, Baccetti T, De Toffol L, Polimeni A, Cozza P. 2008; Phases of the dentition for the assessment of skeletal maturity: a diagnostic performance study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 133:395–400. quiz 476.e1–2. DOI:
10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.02.040. PMID:
18331939.

6. Zhao XG, Lin J, Jiang JH, Wang Q, Ng SH. 2012; Validity and reliability of a method for assessment of cervical vertebral maturation. Angle Orthod. 82:229–34. DOI:
10.2319/051511-333.1. PMID:
21875315. PMCID:
PMC8867953.

7. Nestman TS, Marshall SD, Qian F, Holton N, Franciscus RG, Southard TE. 2011; Cervical vertebrae maturation method morphologic criteria: poor reproducibility. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 140:182–8. DOI:
10.1016/j.ajodo.2011.04.013. PMID:
21803255.

8. Makaremi M, Lacaule C, Mohammad-Djafari A. 2019; Deep learning and artificial intelligence for the determination of the cervical vertebra maturation degree from lateral radiography. Entropy. 21:1222. DOI:
10.3390/e21121222. PMCID:
PMC7514567.

9. Khanagar SB, Al-Ehaideb A, Maganur PC, Vishwanathaiah S, Patil S, Baeshen HA, et al. 2021; Developments, application, and performance of artificial intelligence in dentistry - a systematic review. J Dent Sci. 16:508–22. DOI:
10.1016/j.jds.2020.06.019. PMID:
33384840. PMCID:
PMC7770297.

10. Amasya H, Yildirim D, Aydogan T, Kemaloglu N, Orhan K. 2020; Cervical vertebral maturation assessment on lateral cephalometric radiographs using artificial intelligence: comparison of machine learning classifier models. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 49:20190441. DOI:
10.1259/dmfr.20190441. PMID:
32105499. PMCID:
PMC7333473.

14. Mohammad-Rahimi H, Nadimi M, Rohban MH, Shamsoddin E, Lee VY, Motamedian SR. 2021; Machine learning and orthodontics, current trends and the future opportunities: a scoping review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 160:170–92.e4. DOI:
10.1016/j.ajodo.2021.02.013. PMID:
34103190.

15. Ravishankar H, Sudhakar P, Venkataramani R, Thiruvenkadam S, Annangi P, Babu N, et al. 2016. Understanding the mechanisms of deep transfer learning for medical images. Springer International Publishing;Cham: p. 188–96. DOI:
10.1007/978-3-319-46976-8_20.
17. Mongan J, Moy L, Kahn CE Jr. 2020; Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM): a guide for authors and reviewers. Radiol Artif Intell. 2:e200029. DOI:
10.1148/ryai.2020200029. PMID:
33937821. PMCID:
PMC8017414.

18. Wang CW, Huang CT, Lee JH, Li CH, Chang SW, Siao MJ, et al. 2016; A benchmark for comparison of dental radiography analysis algorithms. Med Image Anal. 31:63–76. DOI:
10.1016/j.media.2016.02.004. PMID:
26974042.

19. Landis JR, Koch GG. 1977; The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 33:159–74. DOI:
10.2307/2529310. PMID:
843571.

20. Tajmir SH, Lee H, Shailam R, Gale HI, Nguyen JC, Westra SJ, et al. 2019; Artificial intelligence-assisted interpretation of bone age radiographs improves accuracy and decreases variability. Skeletal Radiol. 48:275–83. DOI:
10.1007/s00256-018-3033-2. PMID:
30069585.

21. Graber LW, Vanarsdall RL Jr, Vig KWL, Huang GJ. 2016. Orthodontics: current principles and techniques. 6th ed. Elsevier;St. Louis:
22. Yu HJ, Cho SR, Kim MJ, Kim WH, Kim JW, Choi J. 2020; Automated skeletal classification with lateral cephalometry based on artificial intelligence. J Dent Res. 99:249–56. DOI:
10.1177/0022034520901715. PMID:
31977286.

23. Amasya H, Cesur E, Yıldırım D, Orhan K. 2020; Validation of cervical vertebral maturation stages: artificial intelligence vs human observer visual analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 158:e173–9. DOI:
10.1016/j.ajodo.2020.08.014. PMID:
33250108.

24. Yu Y, Lin H, Meng J, Wei X, Guo H, Zhao Z. 2017; Deep transfer learning for modality classification of medical images. Information. 8:91. DOI:
10.3390/info8030091.

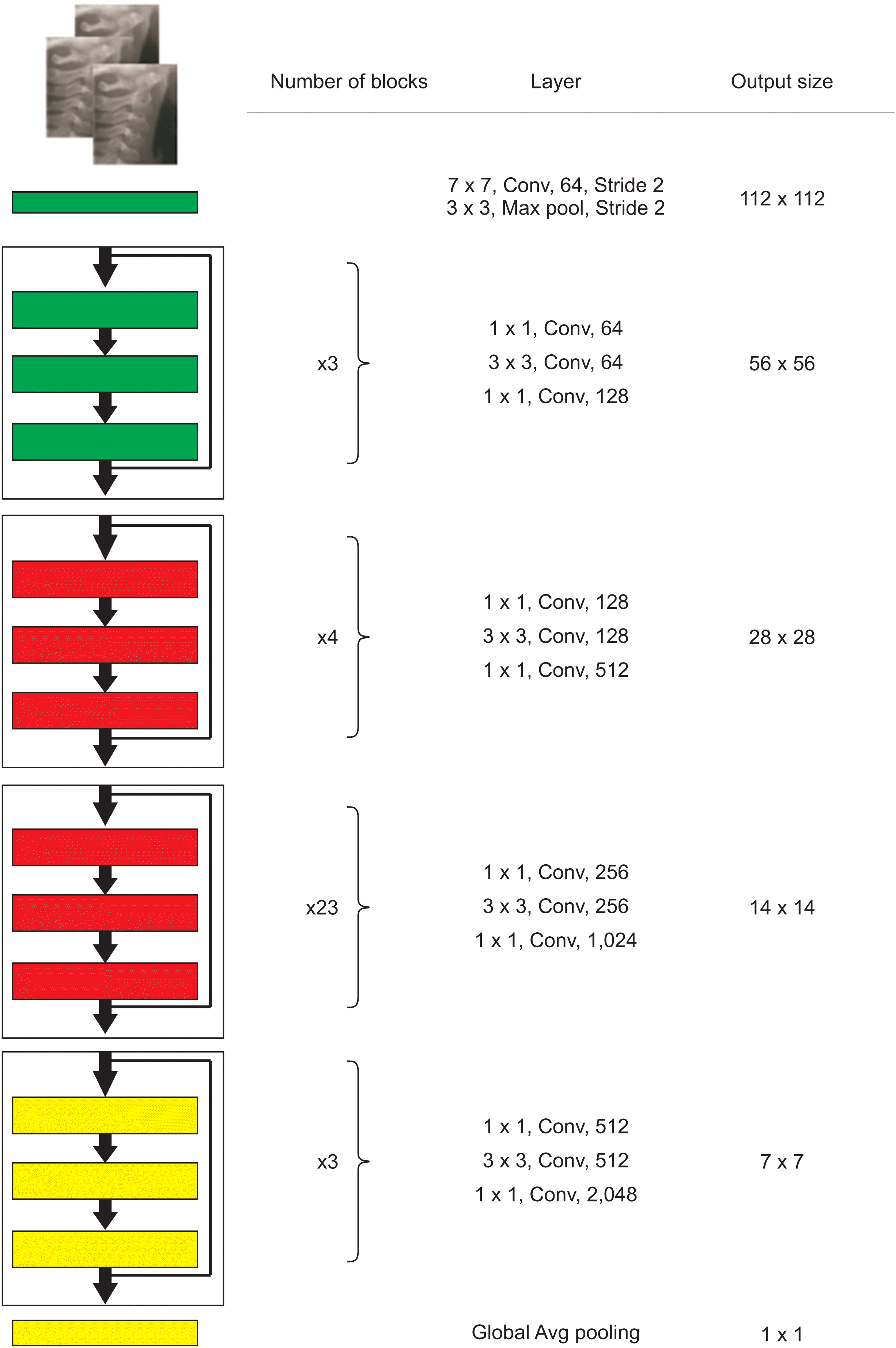
25. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition. Paper presented at: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016 Jun 27-30; Las Vegas, USA. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers;Piscataway: p. 770–8. DOI:
10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. PMID:
26180094.

26. Wang W, Liang D, Chen Q, Iwamoto Y, Han XH, Zhang Q, et al. Chen YW, Jain LC, editors. 2020. Medical image classification using deep learning. Deep learning in healthcare: paradigms and applications. Springer;Cham: p. 33–51. DOI:
10.1007/978-3-030-32606-7_3.

27. Shin HC, Tenenholtz NA, Rogers JK, Schwarz CG, Senjem ML, Gunter JL, et al. 2018. Medical image synthesis for data augmentation and anonymization using generative adversarial networks. Springer International Publishing;Cham: p. 1–11. DOI:
10.1007/978-3-030-00536-8_1.
29. Ramentol E, Caballero Y, Bello R, Herrera F. 2012; SMOTE-RS
B*: a hybrid preprocessing approach based on oversampling and undersampling for high imbalanced data-sets using SMOTE and rough sets theory. Knowl Inf Syst. 33:245–65. DOI:
10.1007/s10115-011-0465-6.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download