1. Fallat L, Grimm DJ, Saracco JA. 1998; Sprained ankle syndrome: prevalence and analysis of 639 acute injuries. J Foot Ankle Surg. 37:280–5. doi: 10.1016/S1067-2516(98)80063-X. DOI:
10.1016/S1067-2516(98)80063-X. PMID:
9710779.

3. Marti RK, Raaymakers EL, Nolte PA. 1990; Malunited ankle fractures. The late results of reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 72:709–13. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.72B4.2116416. DOI:
10.1302/0301-620X.72B4.2116416. PMID:
2116416.

4. Boden SD, Labropoulos PA, McCowin P, Lestini WF, Hurwitz SR. 1989; Mechanical considerations for the syndesmosis screw. A cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 71:1548–55. DOI:
10.2106/00004623-198971100-00014. PMID:
2512295.

5. Rasmussen O, Tovborg-Jensen I, Boe S. 1982; Distal tibiofibular ligaments. Analysis of function. Acta Orthop Scand. 53:681–6. doi: 10.3109/17453678208992276. DOI:
10.3109/17453678208992276. PMID:
7102288.
6. Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Reed SC, Hedman TP. 1994; Disruption of the ankle syndesmosis: biomechanical study of the ligamentous restraints. Arthroscopy. 10:558–60. doi: 10.1016/S0749-8063(05)80014-3. DOI:
10.1016/S0749-8063(05)80014-3. PMID:
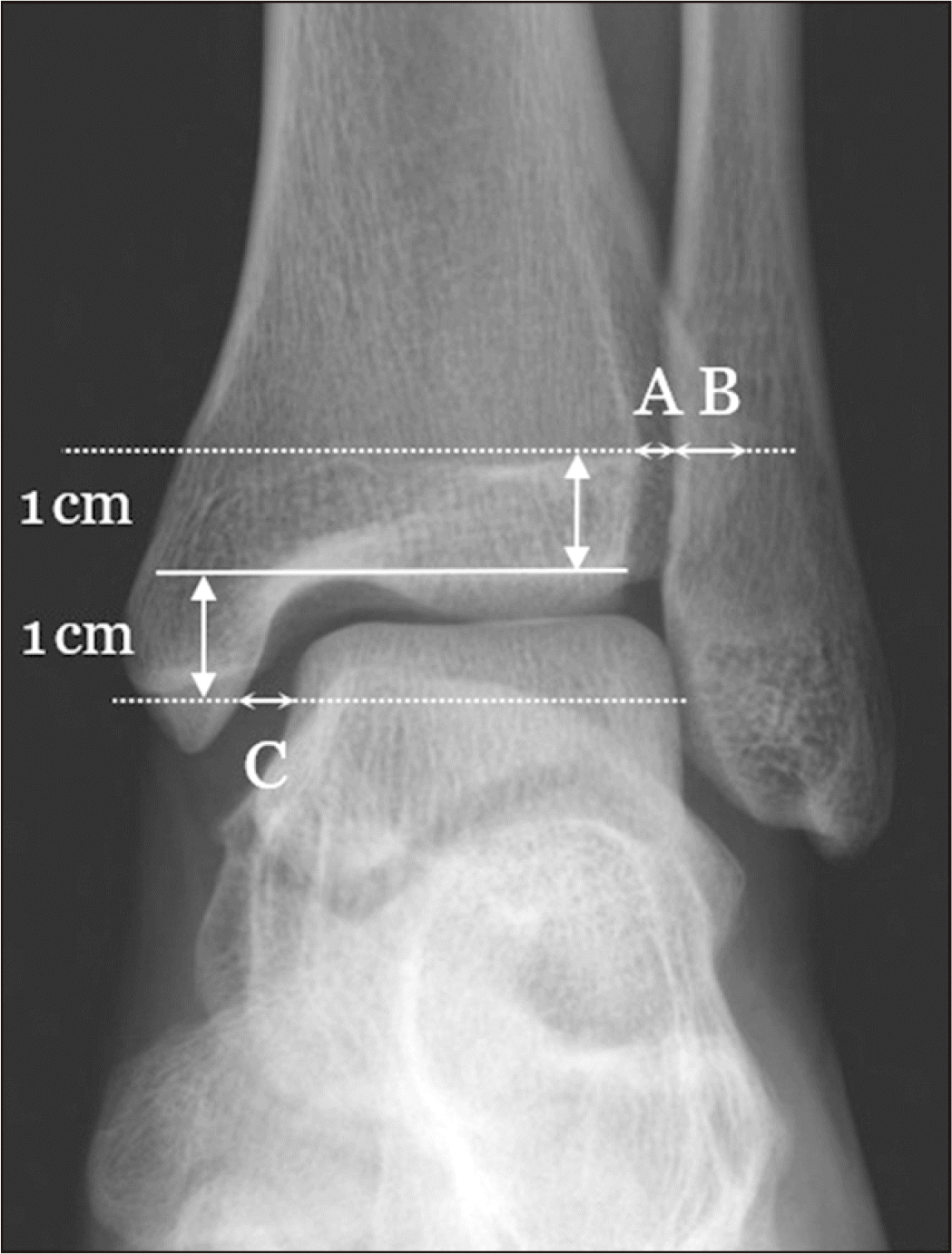
7999167.

9. van den Bekerom MP, Lamme B, Hogervorst M, Bolhuis HW. 2007; Which ankle fractures require syndesmotic stabilization? J Foot Ankle Surg. 46:456–63. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2007.08.009. DOI:
10.1053/j.jfas.2007.08.009. PMID:
17980843.

10. Jenkinson RJ, Sanders DW, Macleod MD, Domonkos A, Lydestadt J. 2005; Intraoperative diagnosis of syndesmosis injuries in external rotation ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 19:604–9. doi: 10.1097/01.bot.0000177114.13263.12. DOI:
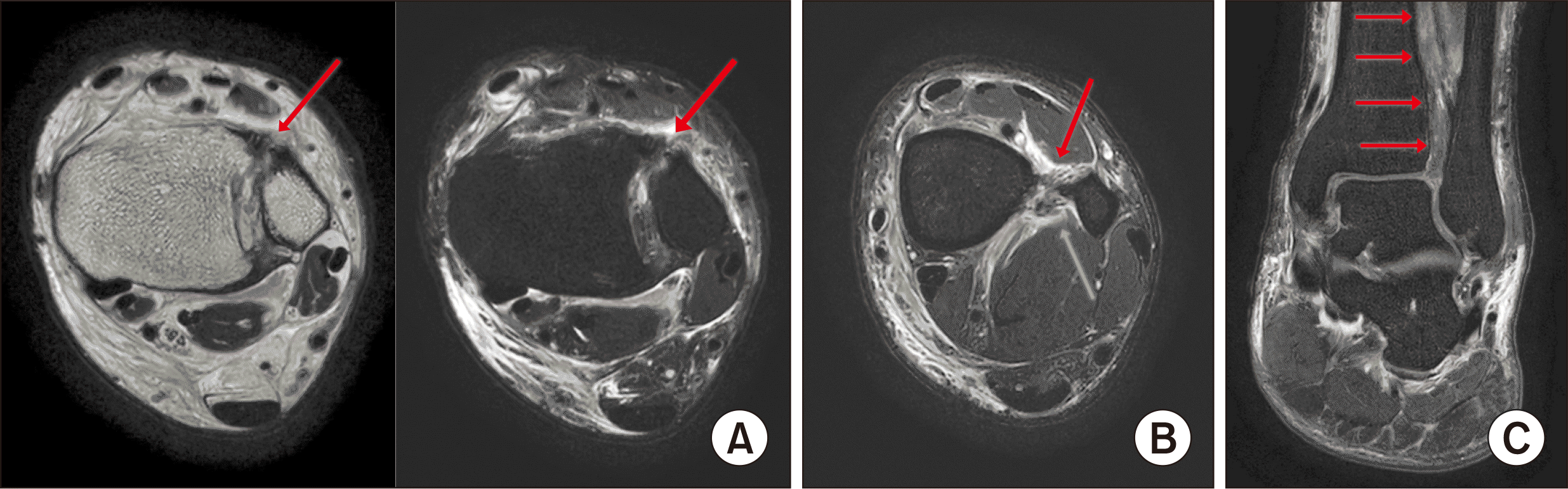
10.1097/01.bot.0000177114.13263.12. PMID:
16247304.

11. Hopkinson WJ, St Pierre P, Ryan JB, Wheeler JH. 1990; Syndesmosis sprains of the ankle. Foot Ankle. 10:325–30. doi: 10.1177/107110079001000607. DOI:
10.1177/107110079001000607. PMID:
2113510.

12. Sikka RS, Fetzer GB, Sugarman E, Wright RW, Fritts H, Boyd JL, et al. 2012; Correlating MRI findings with disability in syndesmotic sprains of NFL players. Foot Ankle Int. 33:371–8. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2012.0371. DOI:
10.3113/FAI.2012.0371. PMID:
22735278.

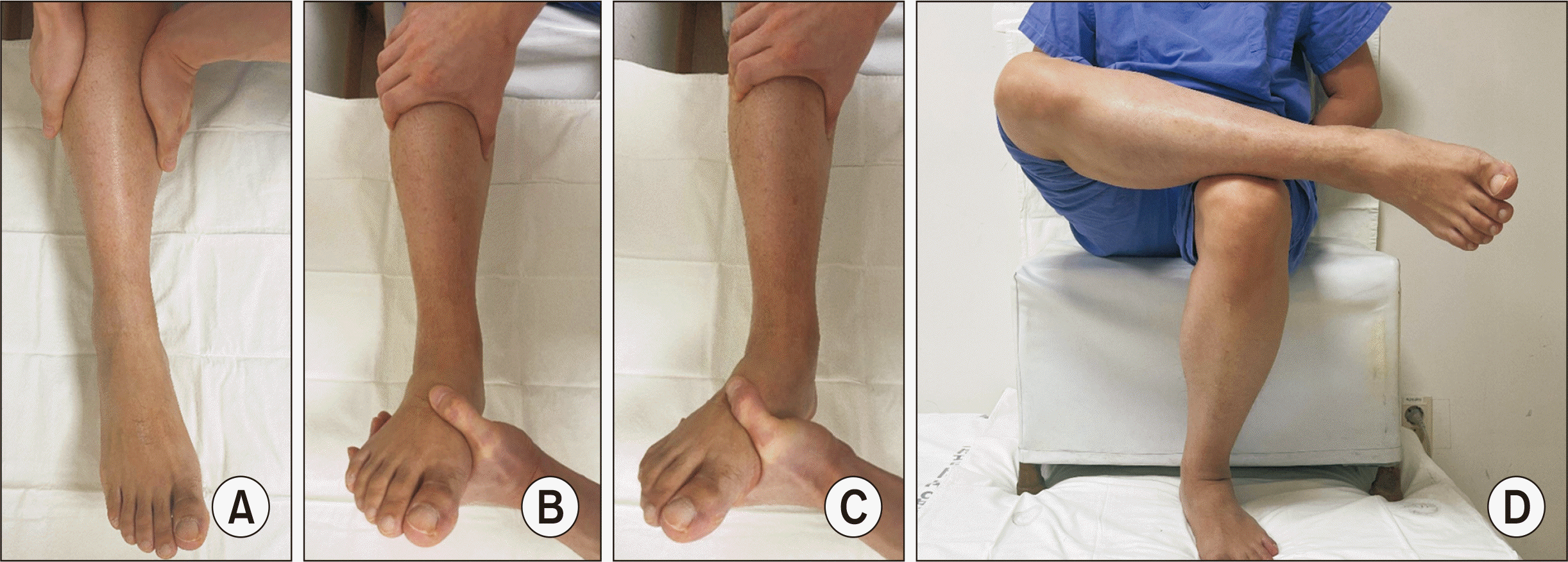
13. Kiter E, Bozkurt M. 2005; The crossed-leg test for examination of ankle syndesmosis injuries. Foot Ankle Int. 26:187–8. doi: 10.1177/107110070502600213. DOI:
10.1177/107110070502600213. PMID:
15737264.

14. Beumer A, van Hemert WL, Niesing R, Entius CA, Ginai AZ, Mulder PG, et al. Radiographic measurement of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis has limited use. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (423):227–34. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000129152.81015.ad. DOI:
10.1097/01.blo.0000129152.81015.ad. PMID:
15232454.

15. Pneumaticos SG, Noble PC, Chatziioannou SN, Trevino SG. 2002; The effects of rotation on radiographic evaluation of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int. 23:107–11. doi: 10.1177/107110070202300205. DOI:
10.1177/107110070202300205. PMID:
11858329.

16. Edwards GS Jr, DeLee JC. 1984; Ankle diastasis without fracture. Foot Ankle. 4:305–12. doi: 10.1177/107110078400400606. DOI:
10.1177/107110078400400606. PMID:
6429020.

17. Takao M, Ochi M, Oae K, Naito K, Uchio Y. 2003; Diagnosis of a tear of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. The role of arthroscopy of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 85:324–9. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.85B3.13174. DOI:
10.1302/0301-620X.85B3.13174. PMID:
12729102.
18. Vogl TJ, Hochmuth K, Diebold T, Lubrich J, Hofmann R, Stöckle U, et al. 1997; Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of acute injured distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Invest Radiol. 32:401–9. doi: 10.1097/00004424-199707000-00006. DOI:
10.1097/00004424-199707000-00006. PMID:
9228606.

19. Oae K, Takao M, Naito K, Uchio Y, Kono T, Ishida J, et al. 2003; Injury of the tibiofibular syndesmosis: value of MR imaging for diagnosis. Radiology. 227:155–61. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2271011865. DOI:
10.1148/radiol.2271011865. PMID:
12616009.

20. Ebraheim NA, Lu J, Yang H, Mekhail AO, Yeasting RA. 1997; Radiographic and CT evaluation of tibiofibular syndesmotic diastasis: a cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int. 18:693–8. doi: 10.1177/107110079701801103. DOI:
10.1177/107110079701801103. PMID:
9391813.

21. Mei-Dan O, Kots E, Barchilon V, Massarwe S, Nyska M, Mann G. 2009; A dynamic ultrasound examination for the diagnosis of ankle syndesmotic injury in professional athletes: a preliminary study. Am J Sports Med. 37:1009–16. doi: 10.1177/0363546508331202. DOI:
10.1177/0363546508331202. PMID:
19336613.
22. Espinosa N, Smerek JP, Myerson MS. 2006; Acute and chronic syndesmosis injuries: pathomechanisms, diagnosis and management. Foot Ankle Clin. 11:639–57. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2006.07.006. DOI:
10.1016/j.fcl.2006.07.006. PMID:
16971254.

23. van den Bekerom MP, de Leeuw PA, van Dijk CN. 2009; Delayed operative treatment of syndesmotic instability. Current concepts review. Injury. 40:1137–42. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2009.03.011. DOI:
10.1016/j.injury.2009.03.011. PMID:
19524232.

24. Gerber JP, Williams GN, Scoville CR, Arciero RA, Taylor DC. 1998; Persistent disability associated with ankle sprains: a prospective examination of an athletic population. Foot Ankle Int. 19:653–60. doi: 10.1177/107110079801901002. DOI:
10.1177/107110079801901002. PMID:
9801078.

25. Rammelt S, Zwipp H, Grass R. 2008; Injuries to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: an evidence-based approach to acute and chronic lesions. Foot Ankle Clin. 13:611–33. vii–viii. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2008.08.001. DOI:
10.1016/j.fcl.2008.08.001. PMID:
19013399.

26. Magan A, Golano P, Maffulli N, Khanduja V. 2014; Evaluation and management of injuries of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Br Med Bull. 111:101–15. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldu020. DOI:
10.1093/bmb/ldu020. PMID:
25190761.

27. Miller TL, Skalak T. 2014; Evaluation and treatment recommendations for acute injuries to the ankle syndesmosis without associated fracture. Sports Med. 44:179–88. doi: 10.1007/s40279-013-0106-1. DOI:
10.1007/s40279-013-0106-1. PMID:
24127279.

28. Han SH, Lee JW, Kim S, Suh JS, Choi YR. 2007; Chronic tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: the diagnostic efficiency of magnetic resonance imaging and comparative analysis of operative treatment. Foot Ankle Int. 28:336–42. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2007.0336. DOI:
10.3113/FAI.2007.0336. PMID:
17371657.

29. Ebraheim NA, Elgafy H, Padanilam T. Syndesmotic disruption in low fibular fractures associated with deltoid ligament injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (409):260–7. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000052935.71325.30. DOI:
10.1097/01.blo.0000052935.71325.30. PMID:
12671510.

30. Thompson MC, Gesink DS. 2000; Biomechanical comparison of syndesmosis fixation with 3.5- and 4.5-millimeter stainless steel screws. Foot Ankle Int. 21:736–41. doi: 10.1177/107110070002100904. DOI:
10.1177/107110070002100904. PMID:
11023220.

31. Needleman RL, Skrade DA, Stiehl JB. 1989; Effect of the syndesmotic screw on ankle motion. Foot Ankle. 10:17–24. doi: 10.1177/107110078901000104. DOI:
10.1177/107110078901000104. PMID:
2767562.

32. Heim D, Heim U, Regazzoni P. 1993; [Malleolar fractures with ankle joint instability--experience with the positioning screw]. Unfallchirurgie. 19:307–12. German doi: 10.1007/BF02588127. DOI:
10.1007/BF02588127. PMID:
8273262.
33. Tornetta P 3rd, Spoo JE, Reynolds FA, Lee C. 2001; Overtightening of the ankle syndesmosis: is it really possible? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 83:489–92. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200104000-00002. DOI:
10.2106/00004623-200104000-00002. PMID:
11315776.

34. Kukreti S, Faraj A, Miles JN. 2005; Does position of syndesmotic screw affect functional and radiological outcome in ankle fractures? Injury. 36:1121–4. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2005.01.014. DOI:
10.1016/j.injury.2005.01.014. PMID:
16051235.

35. Reckling FW, McNamara GR, DeSmet AA. 1981; Problems in the diagnosis and treatment of ankle injuries. J Trauma. 21:943–50. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198111000-00006. DOI:
10.1097/00005373-198111000-00006. PMID:
7299863.

36. Baek JH, Kim TY, Kwon YB, Jeong BO. 2018; Radiographic change of the distal tibiofibular joint following removal of transfixing screw fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 39:318–25. doi: 10.1177/1071100717745526. DOI:
10.1177/1071100717745526. PMID:
29278930.

37. Lee SY, Moon SY, Park MS, Jo BC, Jeong H, Lee KM. 2018; Syndesmosis fixation in unstable ankle fractures using a partially threaded 5.0-mm cannulated screw. J Foot Ankle Surg. 57:721–5. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2017.12.012. DOI:
10.1053/j.jfas.2017.12.012. PMID:
29705234.

38. Fites B, Kunes J, Madaleno J, Silvestri P, Johnson DL. 2006; Latent syndesmosis injuries in athletes. Orthopedics. 29:124–7. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20060201-08. DOI:
10.3928/01477447-20060201-08. PMID:
16485455.

39. Shimozono Y, Hurley ET, Myerson CL, Murawski CD, Kennedy JG. 2019; Suture button versus syndesmotic screw for syndesmosis injuries: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Sports Med. 47:2764–71. doi: 10.1177/0363546518804804. DOI:
10.1177/0363546518804804. PMID:
30475639.

40. Naqvi GA, Shafqat A, Awan N. 2012; Tightrope fixation of ankle syndesmosis injuries: clinical outcome, complications and technique modification. Injury. 43:838–42. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2011.10.002. DOI:
10.1016/j.injury.2011.10.002. PMID:
22036451.

41. Cottom JM, Hyer CF, Philbin TM, Berlet GC. 2008; Treatment of syndesmotic disruptions with the Arthrex Tightrope: a report of 25 cases. Foot Ankle Int. 29:773–80. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2008.0773. DOI:
10.3113/FAI.2008.0773. PMID:
18752774.

42. Qamar F, Kadakia A, Venkateswaran B. 2011; An anatomical way of treating ankle syndesmotic injuries. J Foot Ankle Surg. 50:762–5. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2011.07.001. DOI:
10.1053/j.jfas.2011.07.001. PMID:
21962383.

43. Naqvi GA, Cunningham P, Lynch B, Galvin R, Awan N. 2012; Fixation of ankle syndesmotic injuries: comparison of tightrope fixation and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy of syndesmotic reduction. Am J Sports Med. 40:2828–35. doi: 10.1177/0363546512461480. DOI:
10.1177/0363546512461480. PMID:
23051785.
44. Thornes B, Shannon F, Guiney AM, Hession P, Masterson E. Suture-button syndesmosis fixation: accelerated rehabilitation and improved outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; (431):207–12. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000151845.75230.a0. DOI:
10.1097/01.blo.0000151845.75230.a0. PMID:
15685077.
45. Schepers T. 2012; Acute distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: a systematic review of suture-button versus syndesmotic screw repair. Int Orthop. 36:1199–206. doi: 10.1007/s00264-012-1500-2. DOI:
10.1007/s00264-012-1500-2. PMID:
22318415. PMCID:
PMC3353089.

46. Parlamas G, Hannon CP, Murawski CD, Smyth NA, Ma Y, Kerkhoffs GM, et al. 2013; Treatment of chronic syndesmotic injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 21:1931–9. doi: 10.1007/s00167-013-2515-y. DOI:
10.1007/s00167-013-2515-y. PMID:
23620248.

47. Harper MC. 2001; Delayed reduction and stabilization of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int. 22:15–8. doi: 10.1177/107110070102200103. DOI:
10.1177/107110070102200103. PMID:
11206818.

48. Zamzami MM, Zamzam MM. 2009; Chronic isolated distal tibiofibular syndesmotic disruption: diagnosis and management. Foot Ankle Surg. 15:14–9. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2008.04.002. DOI:
10.1016/j.fas.2008.04.002. PMID:
19218059.

49. Yasui Y, Takao M, Miyamoto W, Innami K, Matsushita T. 2011; Anatomical reconstruction of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament for chronic disruption of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 19:691–5. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1311-1. DOI:
10.1007/s00167-010-1311-1. PMID:
21063681.

50. Olson KM, Dairyko GH Jr, Toolan BC. 2011; Salvage of chronic instability of the syndesmosis with distal tibiofibular arthrodesis: functional and radiographic results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 93:66–72. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00030. DOI:
10.2106/JBJS.J.00030. PMID:
21209270.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download