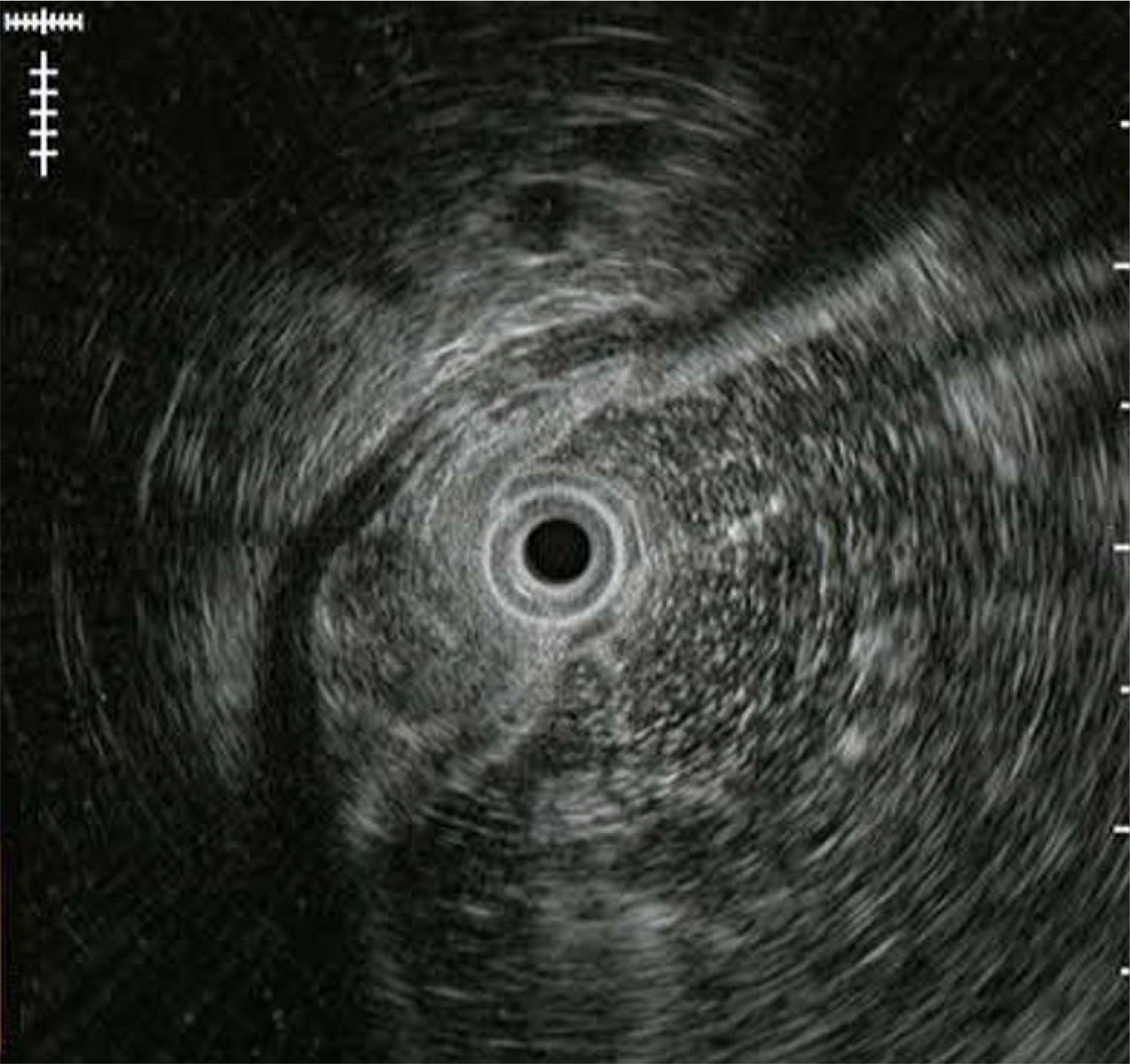
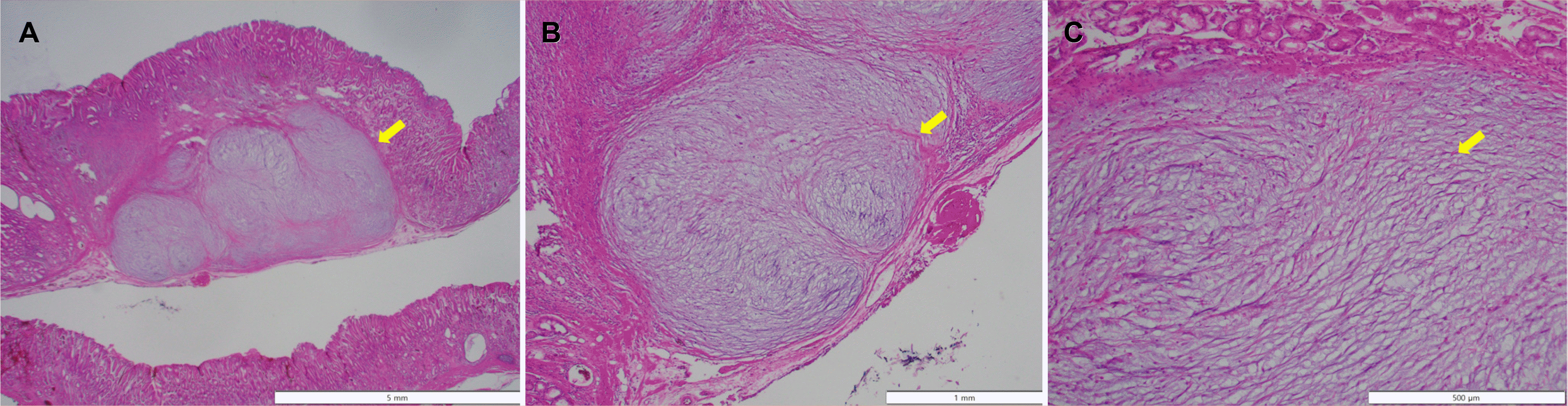
증례: 56세 여자 환자가 건강검진 목적으로 시행한 식도위십이지장내시경(esophagogastroduodenoscopy) 검사에서 발견된 전정부 후벽의 약 1 cm 크기 융기 병변에 대한 내시경적 절제를 위해 의뢰되었다. 환자는 증상을 호소하지 않았고 혈액검사에서도 이상 소견을 보이지 않았다. 병변의 표면은 정상 점막으로 덮여 있었고 조직검사 겸자를 이용하여 눌러보았을 때 단단하게 느껴졌으며, rolling sign을 보여 상피하병변으로 진단하였다(Fig. 1). 초음파 내시경(endoscopic ultrasound) 검사에서 점막하층(submucosal layer)에 국한된 원형의 불균일한 저에코 병변(heterogenous hypoechoic lesion)으로 관찰되었다(Fig. 2). 내시경점막하박리절제술(endoscopic submucosal dissection)을 시행하여 절제하였다(Fig. 3). 병리검사에서 점막하층에 국한된 병변의 완전 절제를 확인하였으며, 풍부한 점액성 기질(myxoid stroma) 내에 방추 세포(spindle cell)가 섞인 다결절성(multinodular) 총상(叢狀, plexiform)의 증식을 보였다(Fig. 4). 면역화학염색검사에서 C-kit와 S100에 염색이 되지 않아 총상(얼기 모양) 섬유점액종(plexiform fibromyxoma)으로 진단하였다(Fig. 5).
진단: 상피하병변 형태로 발견된 위의 총상 섬유점액종
위에서 발견되는 상피하병변 중 대부분의 중간엽 종양(mesenchymal tumor)은 위장관 기질종양(gastrointestinal stromal tumor)이다. 총상 섬유점액종은 과거 plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor 또는 plexiform angiomyxoid tumor로 명명되었으며, 2007년에 최초 보고된 이후로 비교적 최근에 그 특징에 대해 알려졌다.1-3 총상 섬유점액종은 매우 드문 양성 중간엽 신생물(mesenchymal neoplasm)로 위장관 기질종양으로 의심되는 병변의 1-2% 정도가 plexiform fibromyxoma일 것으로 추정된다.1,2 소아와 성인을 포함한 다양한 연령에서 보고되고 있으며 크기 또한 1 cm에서 15 cm까지 다양하다.4-6 대부분 위 전정부에서 발견되나 일부는 위 체부나 저부에서 발견되며, 드물게 위벽 외연부조직(extragastric soft tissue)이나 십이지장 구부(duodenal bulb)를 침범하기도 한다.4-6 내시경 검사에서 상피하병변의 형태로 나타나기도 하지만 위벽 전체를 침범하는 종양(transmural mass)으로 발견되기도 한다.6 가장 흔한 임상증상은 복통으로, 약 20%의 환자들이 복통을 호소하였고 일부에서는 궤양이나 출혈, 천공 등의 합병증을 동반하기도 하며 10%에서는 증상 없이 우연히 발견되었다. 위장관 기질종양에 동반되는 증상 중 복통이 두 번째로 흔하고, 약 37%의 환자는 우연히 발견되는 것을 고려하면 임상 증상으로 위장관 기질종양과 plexiform fibromyxoma를 감별하기는 어렵다.2,6
상피하병변 형태로 발현된 총상 섬유점액종은 위장관 기질종양, 근종(leiomyoma), 신경초종(schwannoma), 신경내분비종양(endocrine tumor), 이소성 췌장(ectopic pancreas), 염증성 섬유양 용종(inflammatory fibroid polyp) 등과 감별이 필요하다.6 총상 섬유점액종의 영상검사 소견은 일관되지않으며 컴퓨터단층촬영(CT)에서 종양이 조영증강을 보이기도 하고 그렇지 않은 경우도 있어 감별에 제한이 있다.6 내시경 초음파에서는 점막하층에 위치한 원형의 불균일한 저에코병변으로 관찰된다.6,7 내시경이나 영상검사만으로는 감별이어렵지만 조직학적으로 감별이 가능하다.
총상 섬유점액종은 조직학적으로 근섬유아세포(myofibroblast)에서 기원하고 평활근 세포로 분화가 가능한 중간엽 종양이다.6 특징적으로 다발성의 결절이 확인되는데, 내부에 점액성(myxoid), 교원성(collagenous) 또는 섬유점액성 신생물질(fibromyxoid neoplastic cell) 기질(stroma)과 방추세포가 포함되어 있고 mitotic activity는 낮은 것으로 알려져 있다.5 위장관 기질종양은 총상의 벽내 증식을 보이지 않고 총상 섬유점액종이 위장관 기질종양에 비해 호산구성 세포질(eosinophilic cytoplasm)을 덜 보인다는 점이 조직학적 감별점이다.6 또한 점액양 위장관 기질종양(myxoid gastrointestinal stromal tumor)과도 감별이 필요한데, 총상 섬유점액종은 C-kit와 platelet-derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRA) 유전자 변이를 보이지 않아 위장관 기질종양과 다른 종류의 중간엽 종양임을 시사한다.1 총상 섬유점액종의 일부에서 glioma-associated oncogene homologue 1 (GLI1)이나 metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) 변이 또는 GLI1 다염색체성(polysomy)을 보인다는 보고가 있다.1,6,8
총상 섬유점액종은 면역화학염색에서 α-smooth muscle actin이나 Alcian blue 염색에 양성이고 C-kit (CD117), S100, CD34, desmin 등에 음성인 것으로 알려져 있다.5,6 이는 위장관 기질종양이 C-kit (CD117) 또는 CD34에 양성인 것이나 근종이 α-smooth muscle actin, desmin 또는 CD34에 양성인 것, 신경초종이 S100에 양성인 것과 구별되는 또 다른 감별점이다.6
본 증례는 내시경 검사를 통해 우연히 발견된 위 전정부의 상피하병변을 내시경적 절제술로 제거한 후 최종 병리검사에서 총상 섬유점액종으로 진단되었다. 추적검사에서 3년간 재발을 보이지 않고 있다. 현재까지 보고된 증례들은 대부분 양성 경과를 보였으나1,2 일부에서는 위벽 전체를 침범하는 종괴 형태로 나타나 위 절제술 후 진단되기도 하였다.5,6 다양한 연령에서 다양한 크기로 발견되며 영상의학적 검사 또는 내시경 초음파 검사 소견만으로 위에서 발견되는 다른 상피하병변과 감별하는 데 제한이 있으므로 주의가 필요하다. 특히 위궤양이나 위출혈 소견 또한 동반되는 것으로 알려져 있어 가장 흔한 중간엽 종양인 위장관 기질종양과의 감별 진단이 필요하다.
REFERENCES
1. Arslan ME, Li H, Jennings TA, Lee EC, Nigam A, Lee H. 2020; Frequency of plexiform fibromyxoma relative to gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a single center study. Ann Diagn Pathol. 48:151568. DOI: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2020.151568. PMID: 32717659.

2. Miettinen M, Fletcher CDM, Kindblom LG, Tsui WMS. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND, editors. 2010. Mesenchymal tumors of the stomach. WHO classification of tumors of the digestive system. 4th ed. IARC;Lyon: p. 74–79.
3. Takahashi Y, Shimizu S, Ishida T, et al. 2007; Plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor of the stomach. Am J Surg Pathol. 31:724–728. DOI: 10.1097/01.pas.0000213448.54643.2f. PMID: 17460456.

4. Miettinen M, Makhlouf HR, Sobin LH, Lasota J. 2009; Plexiform fibromyxoma: a distinctive benign gastric antral neoplasm not to be confused with a myxoid GIST. Am J Surg Pathol. 33:1624–1632. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181ae666a. PMID: 19675452.
5. Baek SH, Yoon JH, Kim JY. 2014; Plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor of the stomach: report of a case and review of the literature. J Korean Soc Radiol. 70:47–52. DOI: 10.3348/jksr.2014.70.1.47.

6. Su HA, Yen HH, Chen CJ. 2019; An update on clinicopathological and molecular features of plexiform fibromyxoma. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019:3960920. DOI: 10.1155/2019/3960920. PMID: 31360694. PMCID: PMC6642755.

7. Akai H, Kiryu S, Shinozaki M, et al. 2017; Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of a plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor: a case report. BMC Med Imaging. 17:7. DOI: 10.1186/s12880-017-0180-1. PMID: 28103839. PMCID: PMC5244533.

8. Spans L, Fletcher CD, Antonescu CR, et al. 2016; Recurrent MALAT1-GLI1 oncogenic fusion and GLI1 up-regulation define a subset of plexiform fibromyxoma. J Pathol. 239:335–343. DOI: 10.1002/path.4730. PMID: 27101025. PMCID: PMC5586099.

Fig. 1
Findings of esophagogastroduodenoscopy. About 1 cm sized subepithelial lesion was noted on the posterior wall of the gastric antrum.
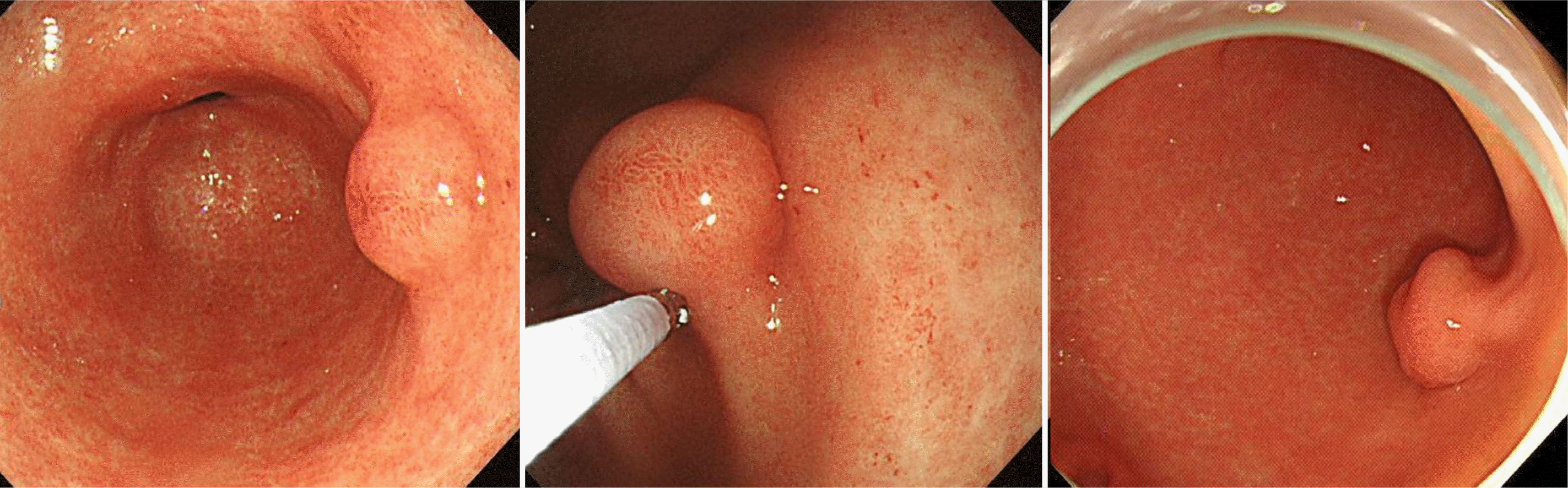
Fig. 2
On endoscopic ultrasonography, a heterogenous hypoechoic lesion with a size of 10 mm localized in the submucosal layer is observed.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download