1. Coia LR. The role of radiation therapy in the treatment of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992; 23:229–38.

2. Agboola O, Benoit B, Cross P, Da Silva V, Esche B, Lesiuk H, et al. Prognostic factors derived from recursive partition analysis (RPA) of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials applied to surgically resected and irradiated brain metastatic cases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998; 42:155–9.

3. Aupérin A, Arriagada R, Pignon JP, Le Péchoux C, Gregor A, Stephens RJ, et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:476–84.

4. Gaspar LE, Scott C, Murray K, Curran W. Validation of the RTOG recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) classification for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000; 47:1001–6.

5. Shaw EG, Su JQ, Eagan RT, Jett JR, Maksymiuk AW, Deigert FA. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in complete responders with small-cell lung cancer: analysis of the Mayo Clinic and North Central Cancer Treatment Group data bases. J Clin Oncol. 1994; 12:2327–32.

6. Zhang W, Jiang W, Luan L, Wang L, Zheng X, Wang G. Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:793.

7. Bang A, Kendal WS, Laurie SA, Cook G, MacRae RM. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive stage small cell lung cancer: outcomes at a comprehensive cancer centre. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018; 101:1133–40.

8. Rohan EA, Miller N, Bonner F 3rd, Fultz-Butts K, Pratt-Chapman ML, Alfano CM, et al. Comprehensive cancer control: promoting survivor health and wellness. Cancer Causes Control. 2018; 29:1277–85.

9. Poppe E. Experimental investigations on cataract formation following whole-body roentgen irradiation. Acta radiol. 1957; 47:138–48.

10. Rose-Ped AM, Bellm LA, Epstein JB, Trotti A, Gwede C, Fuchs HJ. Complications of radiation therapy for head and neck cancers. The patient's perspective. Cancer Nurs. 2002; 25:461–7.
11. Deasy JO, Moiseenko V, Marks L, Chao KS, Nam J, Eisbruch A. Radiotherapy dose-volume effects on salivary gland function. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 76(3 Suppl):S58–63.

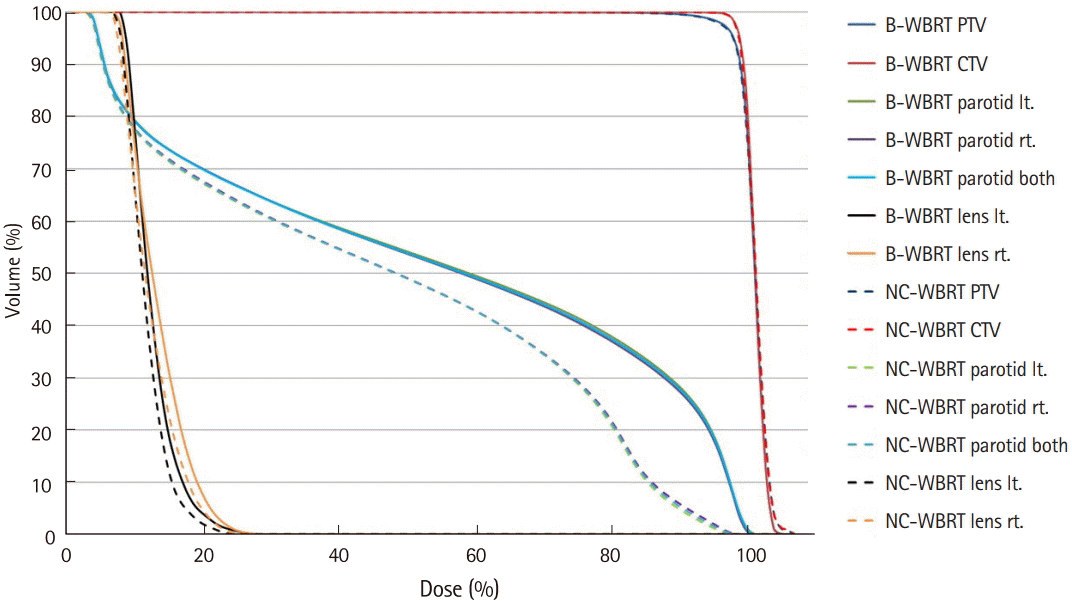
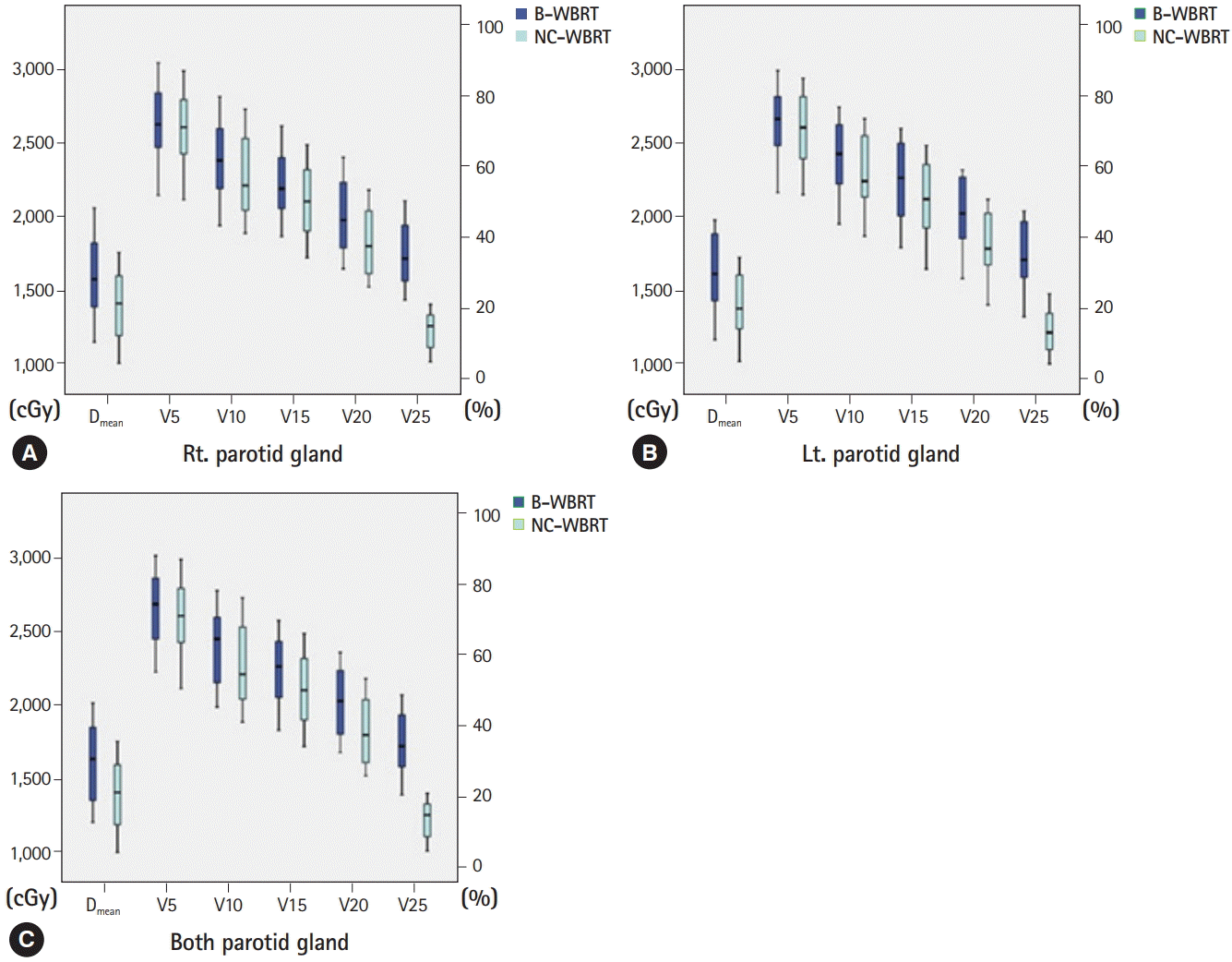
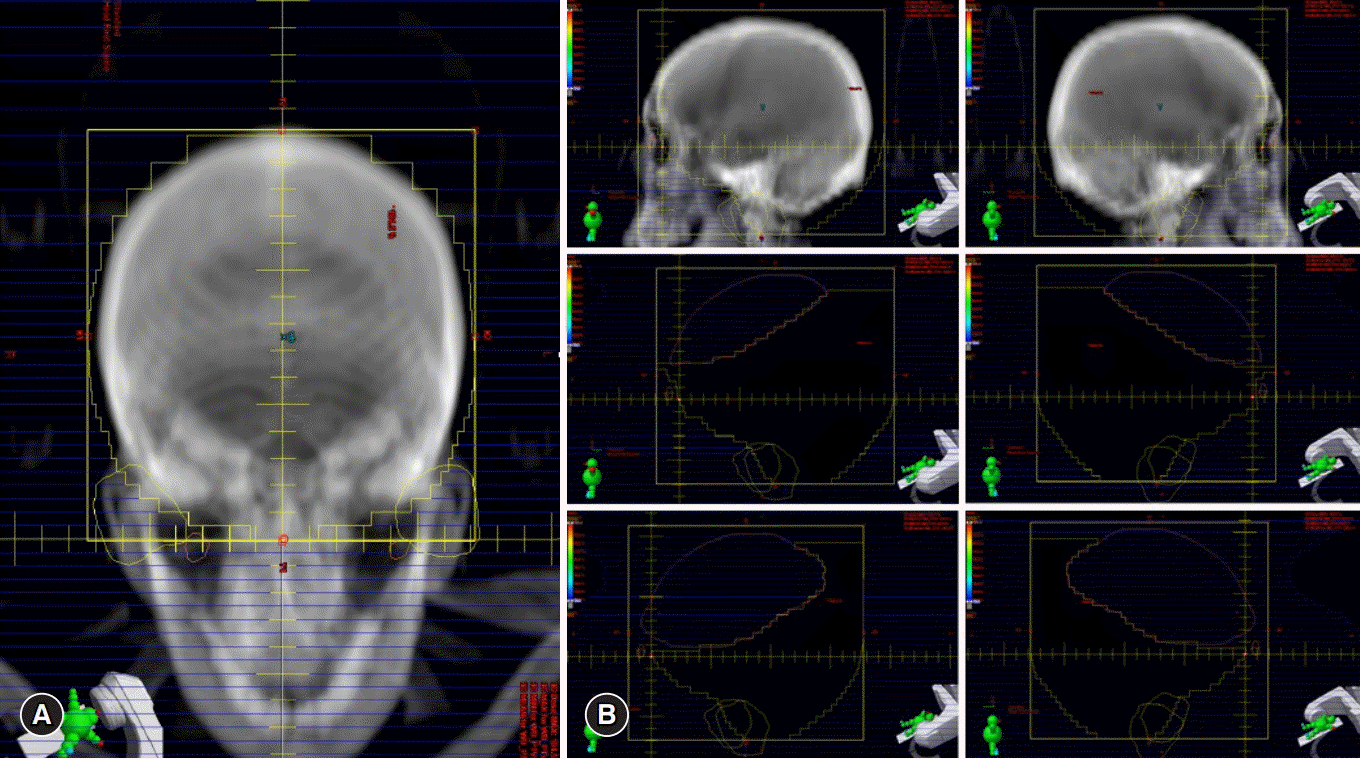
12. Trignani M, Genovesi D, Vinciguerra A, Di Pilla A, Augurio A, Di Tommaso M, et al. Parotid glands in whole-brain radiotherapy: 2D versus 3D technique for no sparing or sparing. Radiol Med. 2015; 120:324–8.

13. Noh OK, Chun M, Nam SS, Jang H, Jo S, Oh YT, et al. Parotid gland as a risk organ in whole brain radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2011; 98:223–6.

14. Cho O, Chun M, Park SH, Oh YT, Kim MH, Park HJ, et al. Parotid gland sparing effect by computed tomography-based modified lower field margin in whole brain radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol J. 2013; 31:12–7.

15. Yu JB, Shiao SL, Knisely JP. A dosimetric evaluation of conventional helmet field irradiation versus two-field intensity-modulated radiotherapy technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007; 68:621–31.

16. Kim T, Song C, Han JH, Kim IA, Kim YJ, Kim SH, et al. Epidemiology of intracranial metastases in Korea: a national cohort investigation. Cancer Res Treat. 2018; 50:164–74.

17. Bovi JA, Schultz CJ, Mehta MP, Corn BW. Consolidative whole-brain radiation therapy versus autologous stem cell transplant for primary central nervous system lymphoma: a large dose of perspective and perhaps a lower dose of radiation are in order. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018; 102:59–60.

18. Slotman B, Faivre-Finn C, Kramer G, Rankin E, Snee M, Hatton M, et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:664–72.

19. Burlage FR, Coppes RP, Meertens H, Stokman MA, Vissink A. Parotid and submandibular/sublingual salivary flow during high dose radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2001; 61:271–4.

20. Fiorentino A, Chiumento C, Caivano R, Cozzolino M, Clemente S, Pedicini P, et al. "Whole brain radiotherapy: are parotid glands organs at risk?". Radiother Oncol. 2012; 103:130–1.

21. Ship JA, Hu K. Radiotherapy-induced salivary dysfunction. Semin Oncol. 2004; 31(6 Suppl 18):29–36.

22. Chung E, Noh JM, Lee KC, Kim JH, Chung W, Suh YG, et al. Dummy run of quality assurance program before prospective study of hippocampus-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy (HS-WBRT) and simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) for multiple brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: Korean Radiation Oncology Group (KROG) 17-06 study. Cancer Res Treat. 2018; doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.415 [Epub ahead of print].
23. Gondi V, Tolakanahalli R, Mehta MP, Tewatia D, Rowley H, Kuo JS, et al. Hippocampal-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy: a "how-to" technique using helical tomotherapy and linear accelerator-based intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 78:1244–52.

24. Gupta T, Agarwal J, Jain S, Phurailatpam R, Kannan S, Ghosh-Laskar S, et al. Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) versus intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a randomized controlled trial. Radiother Oncol. 2012; 104:343–8.

25. Pow EH, Kwong DL, McMillan AS, Wong MC, Sham JS, Leung LH, et al. Xerostomia and quality of life after intensity-modulated radiotherapy vs. conventional radiotherapy for early-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma: initial report on a randomized controlled clinical trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 66:981–91.

26. Nutting CM, Morden JP, Harrington KJ, Urbano TG, Bhide SA, Clark C, et al. Parotid-sparing intensity modulated versus conventional radiotherapy in head and neck cancer (PARSPORT): a phase 3 multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:127–36.

27. Rim CH, Lee J, Kim WC, Yang D, Yoon WS, Koom WS, et al. A survey of radiation therapy utilization in Korea from 2010 to 2016: focusing on use of intensity-modulated radiation therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2018; 33:e67.

28. Henk JM, Whitelocke RA, Warrington AP, Bessell EM. Radiation dose to the lens and cataract formation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993; 25:815–20.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download