Introduction
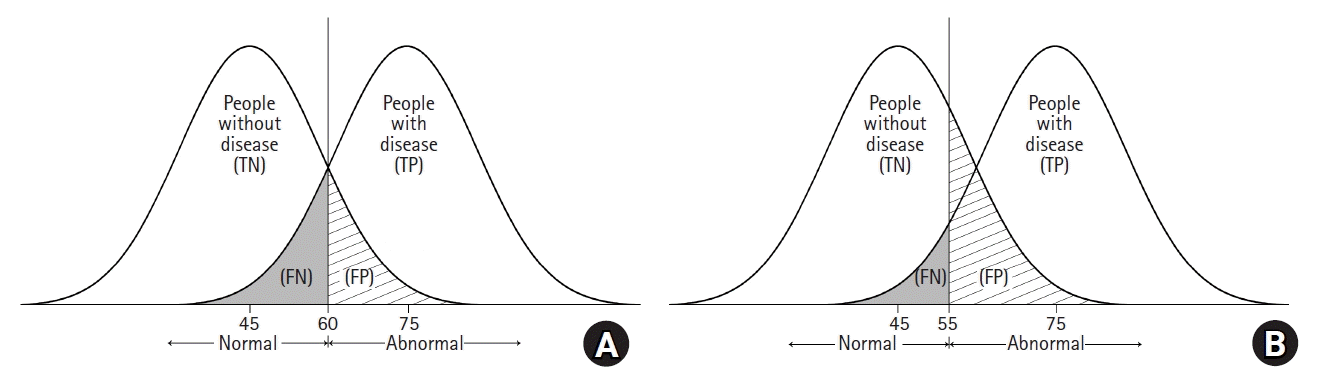
Sensitivity, specificity, false positive, and false negative
What is the ROC curve?
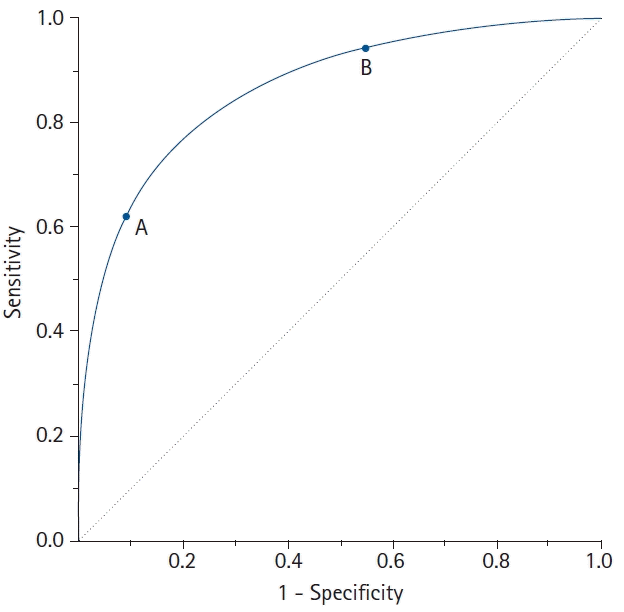 | Fig. 2.A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve connects coordinate points with 1 - specificity (= false positive rate) as the x-axis and sensitivity as the y-axis at all cut-off values measured from the test results. When a strict cut-off point (reference) value is applied, the point on the curve moves downward and to the left (Point A). When a loose cut-off point value is applied, the point moves upward and to the right (Point B). The 45° diagonal line serves as the reference line, since it is the ROC curve of random classification. |
Types of ROC curves
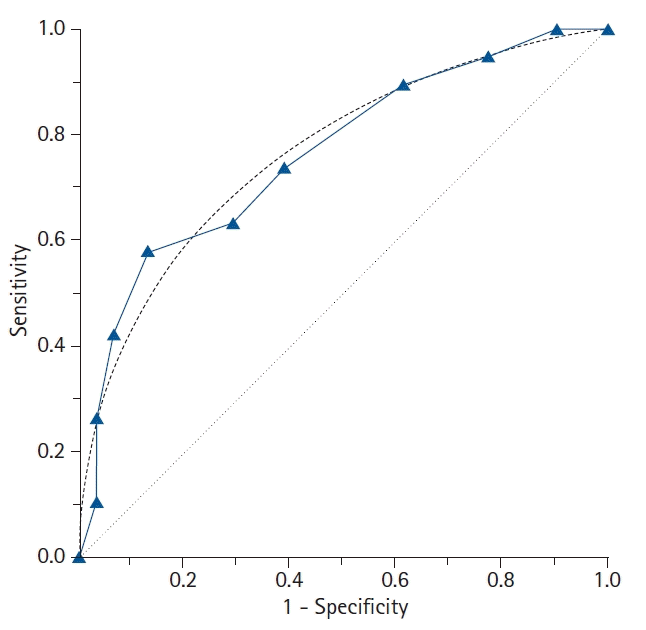 | Fig. 3.The features of the empirical (nonparametric) and binormal (parametric) receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. In contrast to the empirical ROC curve, the binormal ROC curve assumes the normal distribution of the data, resulting in a smooth curve. For estimating the binormal ROC curve, the sample mean and sample standard deviation are calculated from the disease-positive group and the disease-negative group. The 45° diagonal line serves as the reference line, since it is the ROC curve of random classification. |
Table 2.
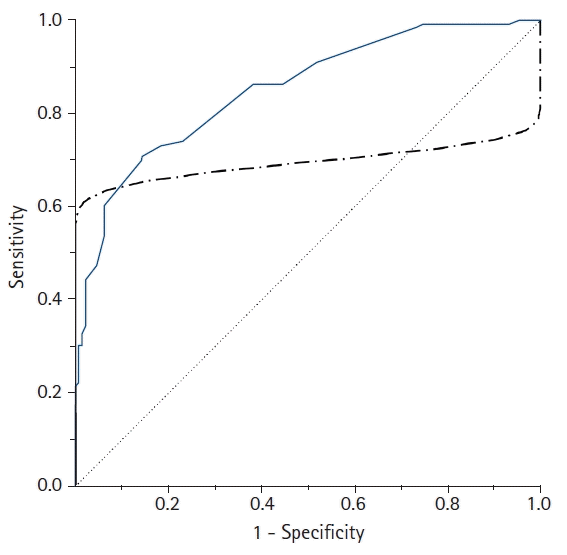 | Fig. 4.A comparison of the empirical (solid line) and parametric (dot-dashed line) receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves drawn from the same data. In contrast to the empirical ROC curve, an inappropriate parametric ROC curve can be distorted or pass through the 45° diagonal line if the data are not normally distributed or heteroscedastic. In this case, the empirical method is recommended to overcome this problem. |
How is a ROC curve drawn?
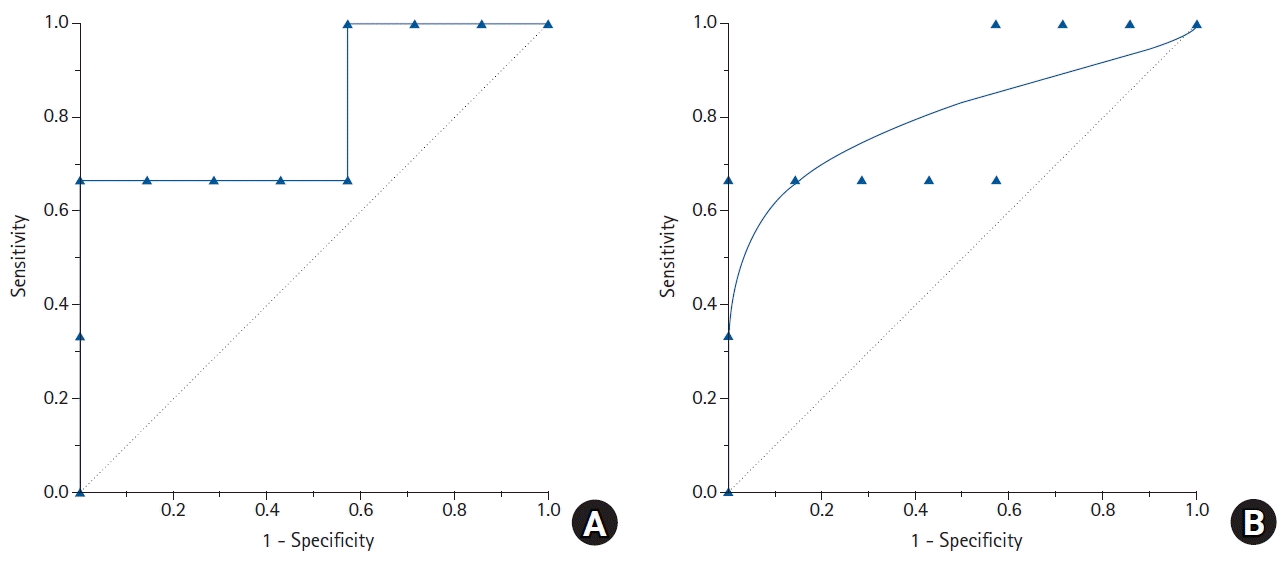 | Fig. 5.Empirical (A) and parametric (B) receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves drawn from the data in Table 3. Eleven labeled points on the empirical ROC curve correspond to each cut-off value to estimate sensitivity and specificity. A gradual increase or decrease of the cut-off values will change the proportion of disease-positive patients. Depending on the cut-off values, each sensitivity and specificity pair can be obtained. Using these calculated sensitivity and specificity pairs, a ROC curve can be obtained with “1 – specificity” as the x coordinates and “sensitivity” as the y coordinates. |
Table 3.
Suppose three patients had biopsy-confirmed cancer diagnoses. The grey-colored values refer to the cases determined to be cancer according to each cut-off value highlighted in bold. The continuous test results can be transformed into binary categories by comparing each value with the cut-off (reference) value. As the cut-off value increases, the sensitivity for cancer diagnosis decreases and the specificity increases. At each cut-off value, one pair of sensitivity and specificity values can be obtained from the 2 x 2 table.
The area under the curve (AUC)
Partial AUC (pAUC)
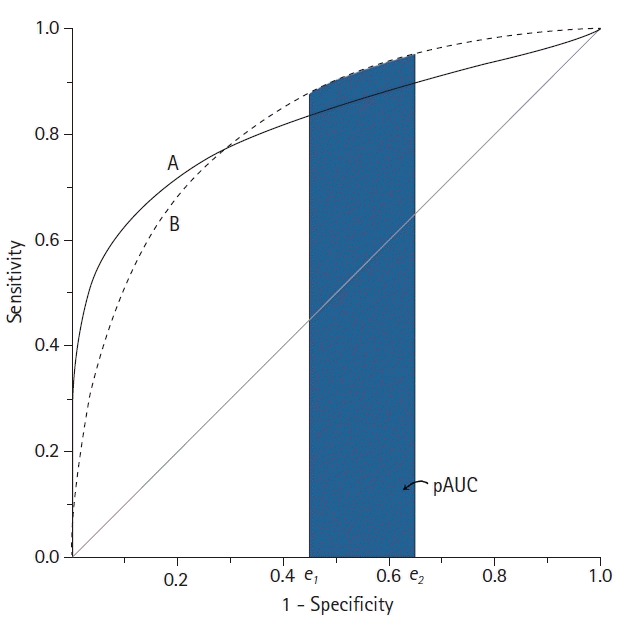 | Fig. 6.Schematic diagram of two receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves with an equal area under the ROC curve (AUC). Although the AUC is the same, the features of the ROC curves are not identical. Test B shows better performance in the high false-positive rate range than test A, whereas test A is better in the low false-positive range. In this example, the partial AUC (pAUC) can compare these two ROC curves at a specific false positive rate range. |
The sample size for the ROC curve analysis
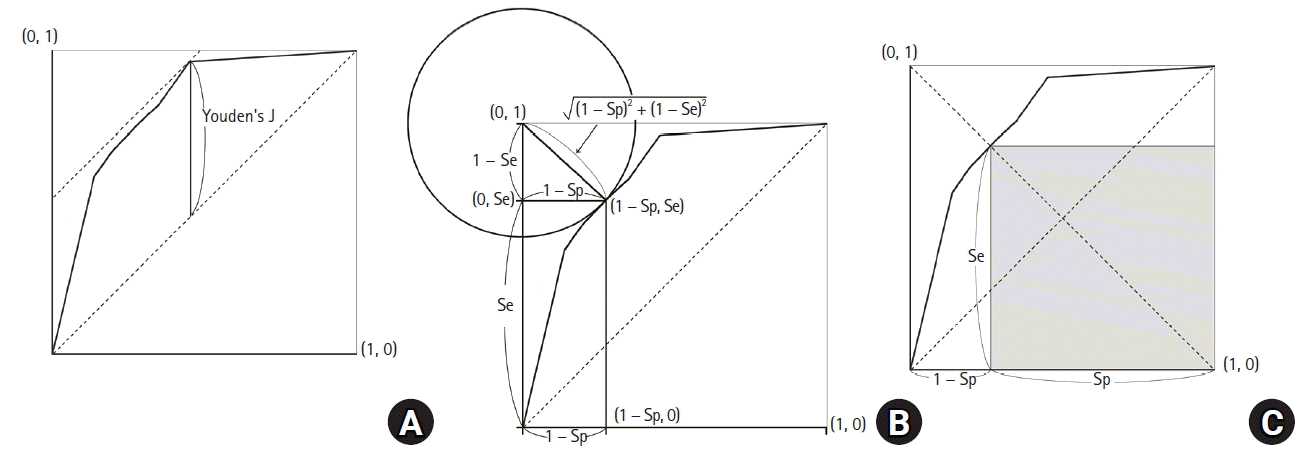
Determining the optimal cut-off value
Youden’s J statistic
Euclidean distance
Accuracy
Index of union (IU)
Cost approach
(6)
Cost = CFN (1 - Se) Pr +CFP (1 - Sp)(1 - Pr) + CTPSe Pr + CTNSp (1 - Pr)fm = Se - (1 - PrPr × CFP - CTNCFN - CTP)(1 - Sp)Positive likelihood ratio (LR+) and negative likelihood ratio (LR–)
Maximum product of sensitivity and specificity
Maximum sum of sensitivity and specificity
Number needed to misdiagnose (NNM)
Statistical program for the ROC curve analysis
Table 5.
This table was adapted and modified from Goksuluk et al. [33]. ROC: receiver operating characteristic, pAUC: partial area under the ROC curve. O: possible, X: impossible.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download