1. Martin BI, Deyo RA, Mirza SK, Turner JA, Comstock BA, Hollingworth W, et al. Expenditures and health status among adults with back and neck problems. JAMA. 2008; 299:656–664. PMID:
18270354.

2. US Burden of Disease Collaborators. The state of US health, 1990-2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA. 2013; 310:591–608. PMID:
23842577.
3. Freburger JK, Holmes GM, Agans RP, Jackman AM, Darter JD, Wallace AS, et al. The rising prevalence of chronic low back pain. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169:251–258. PMID:
19204216.

4. Hoy D, Brooks P, Blyth F, Buchbinder R. The epidemiology of low back pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010; 24:769–781. PMID:
21665125.

5. Leigh JP. Economic burden of occupational injury and illness in the United States. Milbank Q. 2011; 89:728–772. PMID:
22188353.

6. Manchikanti L, Abdi S, Atluri S, Benyamin RM, Boswell MV, Buenaventura RM, et al. An update of comprehensive evidence-based guidelines for interventional techniques in chronic spinal pain. Part II: guidance and recommendations. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:S49–S283. PMID:
23615883.
7. Rajaee SS, Bae HW, Kanim LE, Delamarter RB. Spinal fusion in the United States: analysis of trends from 1998 to 2008. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37:67–76. PMID:
21311399.
8. Phillips FM, Slosar PJ, Youssef JA, Andersson G, Papatheofanis F. Lumbar spine fusion for chronic low back pain due to degenerative disc disease: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:E409–E422. PMID:
23334400.
9. Bydon M, De la Garza-Ramos R, Macki M, Baker A, Gokaslan AK, Bydon A. Lumbar fusion versus nonoperative management for treatment of discogenic low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014; 27:297–304. PMID:
24346052.

10. Singh K, Nandyala SV, Marquez-Lara A, Fineberg SJ. Epidemiological trends in the utilization of bone morphogenetic protein in spinal fusions from 2002 to 2011. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39:491–496. PMID:
24365905.

11. Cervera-Irimia J, Tomé-Bermejo F. Caudal epidural steroid injection in the treatment of chronic discogenic low back pain. Comparative, prospective and randomized study. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2013; 57:324–332. PMID:
24071051.

12. Saltychev M, Eskola M, Laimi K. Lumbar fusion compared with conservative treatment in patients with chronic low back pain: a meta-analysis. Int J Rehabil Res. 2014; 37:2–8. PMID:
23820296.

13. van Middelkoop M, Rubinstein SM, Kuijpers T, Verhagen AP, Ostelo R, Koes BW, et al. A systematic review on the effectiveness of physical and rehabilitation interventions for chronic non-specific low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20:19–39. PMID:
20640863.

14. Rubinstein SM, van Middelkoop M, Assendelft WJ, de Boer MR, van Tulder MW. Spinal manipulative therapy for chronic low-back pain: an update of a Cochrane review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:E825–E846. PMID:
21593658.
15. Manchikanti L, Helm Ii S, Singh V, Hirsch JA. Accountable interventional pain management: a collaboration among practitioners, patients, payers, and government. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:E635–E670. PMID:
24284849.
16. Kuslich SD, Ulstrom CL, Michael CJ. The tissue origin of low back pain and sciatica: a report of pain response to tissue stimulation during operations on the lumbar spine using local anesthesia. Orthop Clin North Am. 1991; 22:181–187. PMID:
1826546.
17. Mixter WJ, Barr JS. Rupture of the intervertebral disc with involvement of the spinal canal. N Engl J Med. 1934; 211:210–215.

18. Mixter WJ, Ayer JB. Herniation or rupture of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal: report of thirty-four cases. N Engl J Med. 1935; 213:385–393.

19. Malik KM, Cohen SP, Walega DR, Benzon HT. Diagnostic criteria and treatment of discogenic pain: a systematic review of recent clinical literature. Spine J. 2013; 13:1675–1689. PMID:
23993035.

20. Crock HV. A reappraisal of intervertebral disc lesions. Med J Aust. 1970; 1:983–989. PMID:
5427658.

21. Bogduk N, Aprill C, Derby R. Lumbar discogenic pain: state-of-the-art review. Pain Med. 2013; 14:813–836. PMID:
23566298.

22. Peng B, Fu X, Pang X, Li D, Liu W, Gao C, et al. Prospective clinical study on natural history of discogenic low back pain at 4 years of follow-up. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:525–532. PMID:
23159971.
23. Manchikanti L, Benyamin RM, Singh V, Falco FJ, Hameed H, Derby R, et al. An update of the systematic appraisal of the accuracy and utility of lumbar discography in chronic low back pain. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:SE55–SE95. PMID:
23615887.
24. Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, Fortin J, Kine G, Bogduk N. The prevalence and clinical features of internal disc disruption in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:1878–1883. PMID:
8560335.

25. DePalma MJ, Ketchum JM, Saullo T. What is the source of chronic low back pain and does age play a role? Pain Med. 2011; 12:224–233. PMID:
21266006.

26. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Pampati V, Damron KS, Barnhill RC, Beyer C, et al. Evaluation of the relative contributions of various structures in chronic low back pain. Pain Physician. 2001; 4:308–316. PMID:
16902676.
27. Mirza SK, Deyo RA, Heagerty PJ, Turner JA, Martin BI, Comstock BA. One-year outcomes of surgical versus nonsurgical treatments for discogenic back pain: a community-based prospective cohort study. Spine J. 2013; 13:1421–1433. PMID:
23890947.

28. Lu Y, Guzman JZ, Purmessur D, Iatridis JC, Hecht AC, Qureshi SA, et al. Nonoperative management of discogenic back pain: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39:1314–1324. PMID:
24827515.
29. Deyo RA, Nachemson A, Mirza SK. Spinal-fusion surgery -the case for restraint. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:722–726. PMID:
14960750.
30. Helm Ii S, Deer TR, Manchikanti L, Datta S, Chopra P, Singh V, et al. Effectiveness of thermal annular procedures in treating discogenic low back pain. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E279–E304. PMID:
22622914.
31. LaCaille RA, DeBerard MS, Masters KS, Colledge AL, Bacon W. Presurgical biopsychosocial factors predict multidimensional patient: outcomes of interbody cage lumbar fusion. Spine J. 2005; 5:71–78. PMID:
15653087.

32. Jacobs W, Van der Gaag NA, Tuschel A, de Kleuver M, Peul W, Verbout AJ, et al. Total disc replacement for chronic back pain in the presence of disc degeneration. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 9:CD008326. PMID:
22972118.

35. Parr AT, Manchikanti L, Hameed H, Conn A, Manchikanti KN, Benyamin RM, et al. Caudal epidural injections in the management of chronic low back pain: a systematic appraisal of the literature. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E159–E198. PMID:
22622911.
36. Benyamin RM, Manchikanti L, Parr AT, Diwan S, Singh V, Falco FJ, et al. The effectiveness of lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in managing chronic low back and lower extremity pain. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E363–E404. PMID:
22828691.
37. Manchikanti L, Buenaventura RM, Manchikanti KN, Ruan X, Gupta S, Smith HS, et al. Effectiveness of therapeutic lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections in managing lumbar spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E199–E245. PMID:
22622912.
38. Manchikanti L, Pampati V, Benyamin RM, Boswell MV. Analysis of efficacy differences between caudal and lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in chronic lumbar axial discogenic pain: local anesthetic alone vs. local combined with steroids. Int J Med Sci. 2015; 12:214–222. PMID:
25678838.

39. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Pampati V, Falco FJ, Hirsch JA. Comparison of the efficacy of caudal, interlaminar, and transforaminal epidural injections in managing lumbar disc herniation: is one method superior to the other? Korean J Pain. 2015; 28:11–21. PMID:
25589942.

40. Gupta R, Singh S, Kaur S, Singh K, Aujla K. Correlation between epidurographic contrast flow patterns and clinical effectiveness in chronic lumbar discogenic radicular pain treated with epidural steroid injections via different approaches. Korean J Pain. 2014; 27:353–359. PMID:
25317285.

41. Byun JM, Park HS, Woo JH, Kim J. The effects of a forceful transforaminal epidural steroid injection on radicular pain: a preliminary study. Korean J Pain. 2014; 27:334–338. PMID:
25317282.

42. Manchikanti L, Benyamin RM, Falco FJ, Kaye AD, Hirsch JA. Do epidural injections provide short- and long-term relief for lumbar disc herniation? A systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; [in press].

43. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, Pampati V, Falco FJ. Transforaminal epidural injections in chronic lumbar disc herniation: a randomized, double-blind, active-control trial. Pain Physician. 2014; 17:E489–E501. PMID:
25054399.
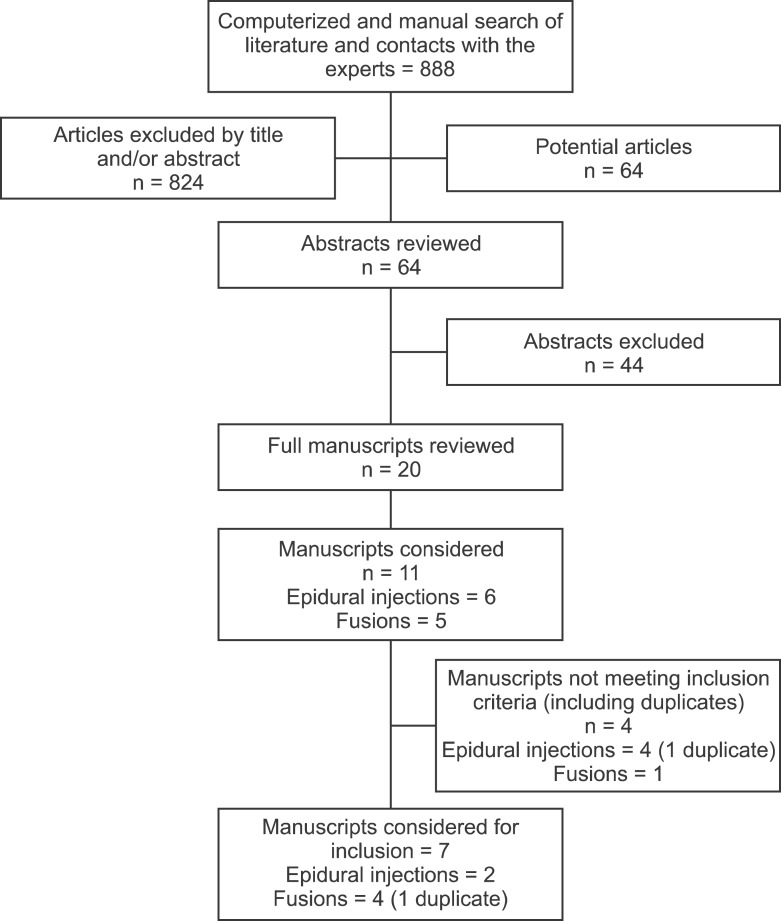
44. Furlan AD, Pennick V, Bombardier C, van Tulder M. Editorial Board. Cochrane Back Review Group. 2009 updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Back Review Group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:1929–1941. PMID:
19680101.

45. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151:W65–W94. PMID:
19622512.

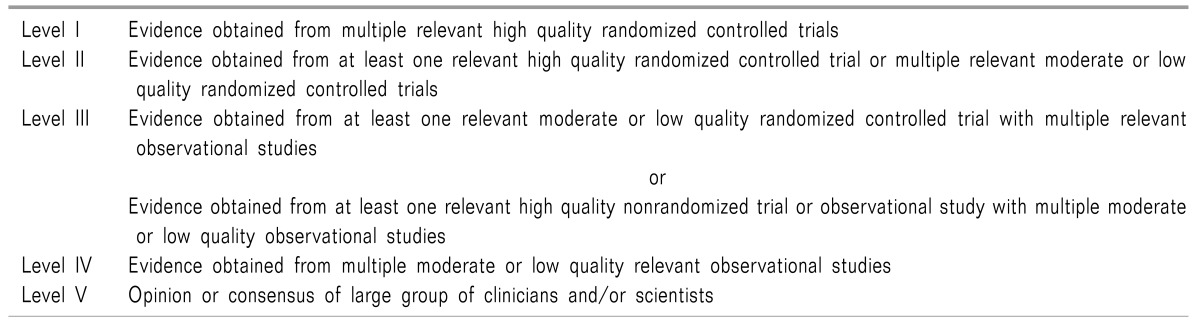
46. Manchikanti L, Falco FJ, Benyamin RM, Kaye AD, Boswell MV, Hirsch JA. A modified approach to grading of evidence. Pain Physician. 2014; 17:E319–E325. PMID:
24850113.

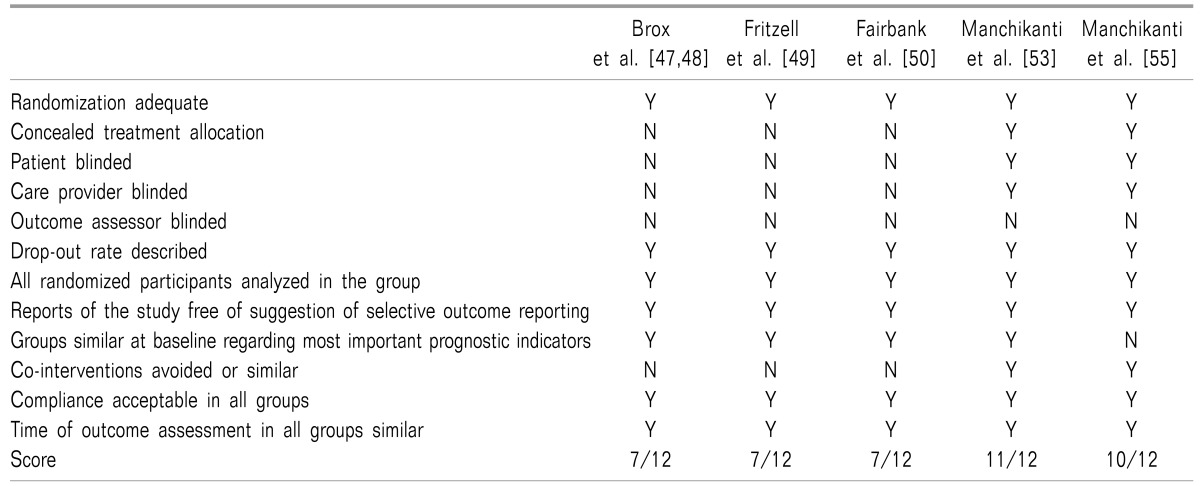
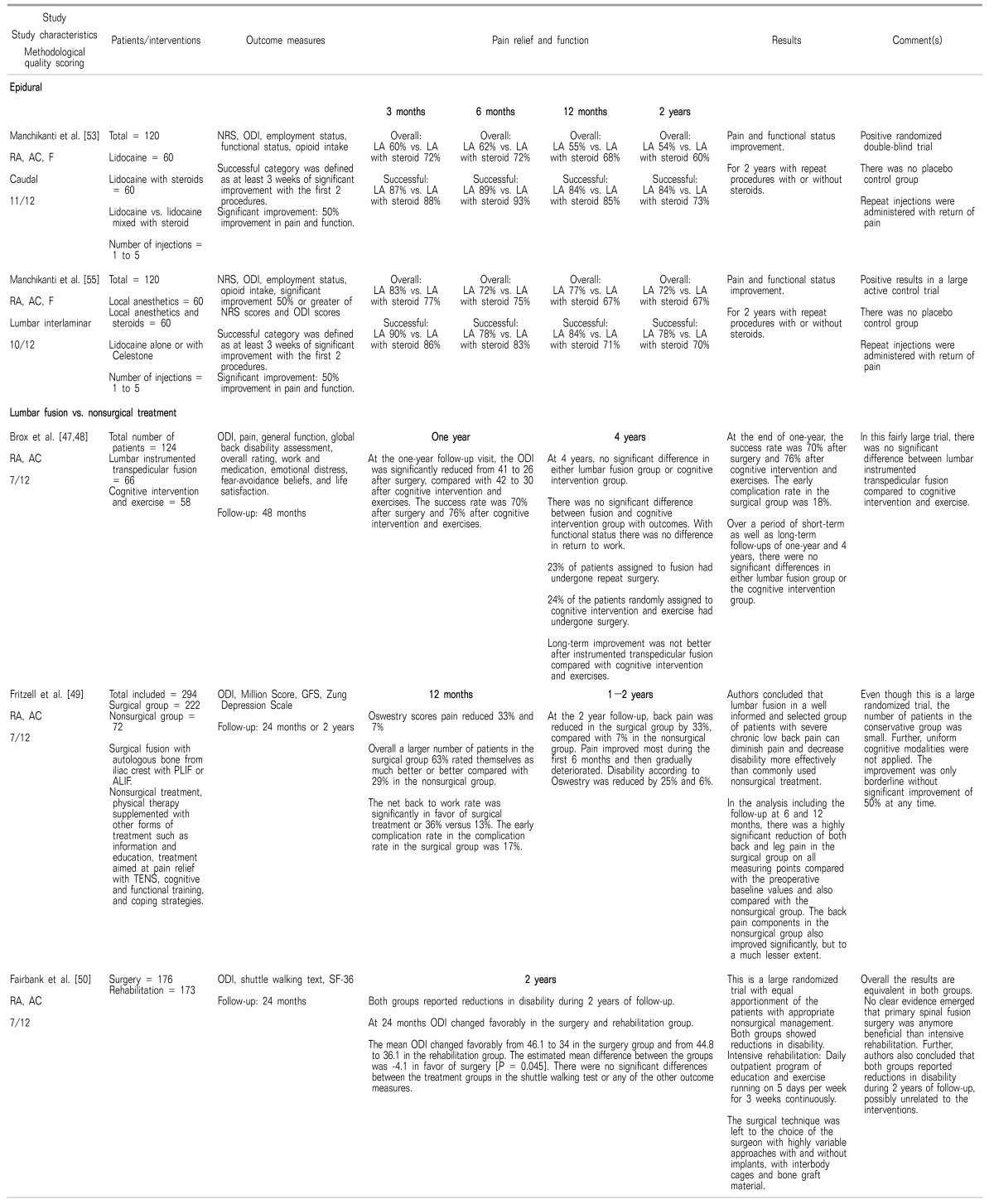
47. Brox JI, Sørensen R, Friis A, Nygaard Ø, Indahl A, Keller A, et al. Randomized clinical trial of lumbar instrumented fusion and cognitive intervention and exercises in patients with chronic low back pain and disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:1913–1921. PMID:
12973134.

48. Brox JI, Nygaard ØP, Holm I, Keller A, Ingebrigtsen T, Reikerås O. Four-year follow-up of surgical versus nonsurgical therapy for chronic low back pain. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69:1643–1648. PMID:
19635718.

49. Fritzell P, Hägg O, Wessberg P, Nordwall A. Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group. 2001 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies: lumbar fusion versus nonsurgical treatment for chronic low back pain: a multicenter randomized controlled trial from the Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:2521–2532. PMID:
11725230.

50. Fairbank J, Frost H, Wilson-MacDonald J, Yu LM, Barker K, Collins R, et al. Randomised controlled trial to compare surgical stabilisation of the lumbar spine with an intensive rehabilitation programme for patients with chronic low back pain: the MRC spine stabilisation trial. BMJ. 2005; 330:1233. PMID:
15911537.

51. Brox JI, Reikerås O, Nygaard Ø, Sørensen R, Indahl A, Holm I, et al. Lumbar instrumented fusion compared with cognitive intervention and exercises in patients with chronic back pain after previous surgery for disc herniation: a prospective randomized controlled study. Pain. 2006; 122:145–155. PMID:
16545523.

52. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Smith HS. One-year results of a randomized, double-blind, active controlled trial of fluoroscopic caudal epidural injections with or without steroids in managing chronic discogenic low back pain without disc herniation or radiculitis. Pain Physician. 2011; 14:25–36. PMID:
21267039.
53. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V. Fluoroscopic caudal epidural injections in managing chronic axial low back pain without disc herniation, radiculitis, or facet joint pain. J Pain Res. 2012; 5:381–390. PMID:
23091395.

54. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Benyamin R. Fluoroscopic lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in managing chronic lumbar axial or discogenic pain. J Pain Res. 2012; 5:301–311. PMID:
23055773.

55. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Benyamin RM. A randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial of fluoroscopic lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in chronic axial or discogenic low back pain: results of 2-year follow-up. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:E491–E504. PMID:
24077199.
56. Manchikanti L, Falco FJ, Pampati V, Cash KA, Benyamin RM, Hirsch JA. Cost utility analysis of caudal epidural injections in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation, axial or discogenic low back pain, central spinal stenosis, and post lumbar surgery syndrome. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:E129–E143. PMID:
23703415.
58. Mirza SK, Deyo RA. Systematic review of randomized trials comparing lumbar fusion surgery to nonoperative care for treatment of chronic back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:816–823. PMID:
17414918.

59. Chou R, Atlas SJ, Loeser JD, Rosenquist RW, Stanos SP. Guideline warfare over interventional therapies for low back pain: can we raise the level of discourse? J Pain. 2011; 12:833–839. PMID:
21742563.

60. Manchikanti L, Benyamin RM, Falco FJ, Caraway DL, Datta S, Hirsch JA. Guidelines warfare over interventional techniques: is there a lack of discourse or straw man? Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E1–E26. PMID:
22270745.
61. Pinto RZ, Maher CG, Ferreira ML, Hancock M, Oliveira VC, McLachlan AJ, et al. Epidural corticosteroid injections in the management of sciatica: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Ann Intern Med. 2012; 157:865–877. PMID:
23362516.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download