INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Participants
2. Inclusion criteria
3. Exclusion criteria
4. Randomization-sequence generation and randomization-allocation concealment
5. Blinding (masking)
6. Interventions
 | Fig. 1A schedule for the continuous infusion of nefopam with a consecutive dose reduction in hospitalized patients with postherpetic neuralgia while dose-escalating of oral medications. Each patient received a 3-day intravenous continuous infusion of either nefopam (NFP) with a consecutive dose reduction of 60, 40, and 20 mg/d or NS simultaneously while dose titrations of oral medications for neuropathic pain gradually increased every 3 days. A rescue analgesic, 10 mg of oral codeine, was given at each NPSI score VAS > 40 less than 5 times a day. The efficacy of additional NFP was evaluated by using the neuropathic pain symptom inventory (NPSI) score for 12 days. Adverse effects were also recorded. Discharge criteria after the 12-day-admission included: (1) NPSI score < 40%, (2) spontaneous pain < 3 h during the past 24 h, (3) pain attack < 5 times during the past 24 h, and (4) no serious adverse effects, including dizziness, somnolence, or ataxia. |
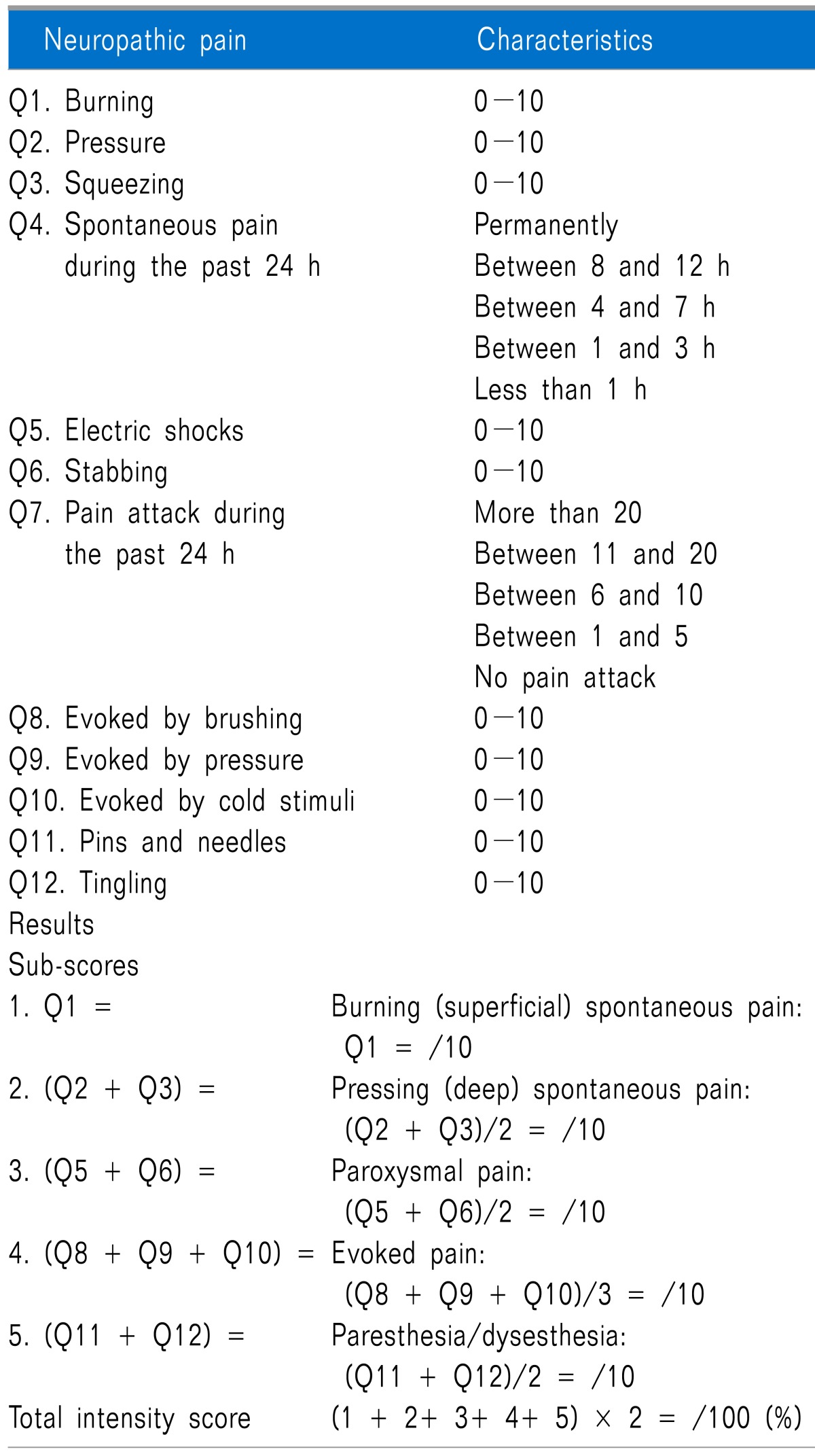
7. Outcome measures
8. Sample size
9. Statistical analysis
RESULTS
1. Patient demography and baseline data, participant flow, recruitment, and numbers analyzed
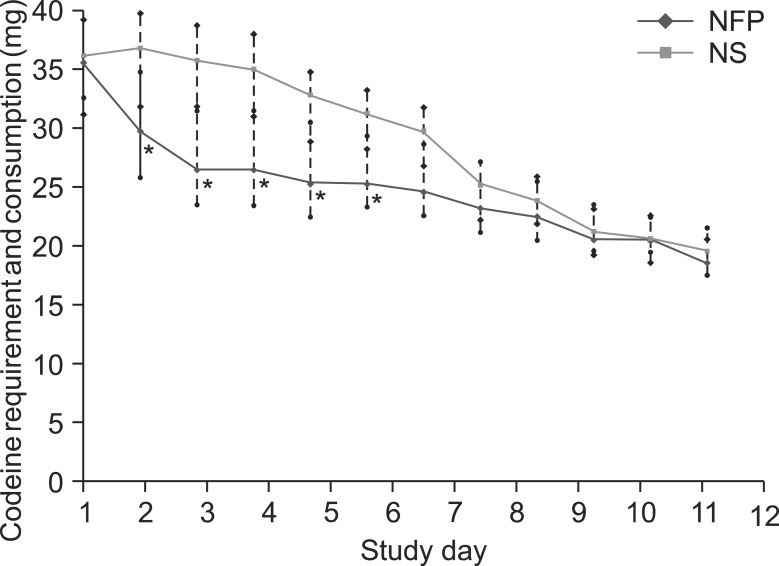
2. Outcomes and estimation
Table 3
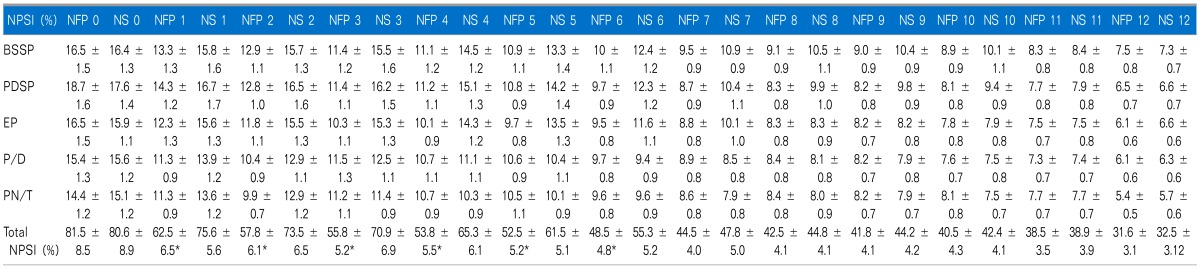
*NFP group showed significantly lower total NPSI scores from study day 1 to 6 (P < 0.05 compared to those of NS group). However, 5 each subtotal NPSI median scores did not show any statistical difference in both groups, respectively. All data are expressed SD ± error. NFP: nefopam, NS: normal saline, BSSP: burning (superficial) spontaneous pain, PDSP: pressing (deep) spontaneous pain, EP: evoked pain, PDSP: paresthesia/dysesthesia, PN/T: pIns and needles/tingling.
 | Fig. 2The median scores of the grade of duration of spontaneous pain (SP) and number of pain attack (PA) during study days. (A) *The grade by the duration of SP during the past 24 h was lower, and (B) *the grade of the number of PA during the past 24 h was lower in NFP group from the day 2 to 6 of hospitalization (P < 0.05 compared to those of NS group). All data are expressed SD ± error. NFP: nefopam, NS: normal saline. Grade by duration of SP: grade 1 (less than 1 h), grade 2 (between 1 and 3 h), grade 3 (between 4 and 7 h), grade 4 (8 and 12 h), and grade 5 (permanently). Grade by frequency of PA: grade 0 (no pain attack), grade 1 (between 1 and 5), grade 2 (between 6 and 10), grade 3 (between 11 and 20), and grade 4 (more than 20). |
3. Adverse events
 | Fig. 4Adverse effects. *Nefopam (NFP) increased the frequency of dry mouth, dizziness, nausea and ataxia, in order of frequency, during the initial period of the study days 1 to 6 (P < 0.05 compared to those of normal saline [NS] group). There was no difference between the groups in overall frequencies of occurrence for each adverse effect. Dry mouth in both groups was an intolerable adverse effect which showed a never-decreasing and even-increasing symptom till the end of the study days. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download