Abstract
Intrathecal drug delivery is an effective and safe option for the treatment of chronic pathology refractory to conventional pain therapies. Typical intrathecal administered drugs are opioids, baclofen, local anesthetics and adjuvant medications. Although knowledge about mechanisms of action of intrathecal drugs are every day more clear many doubt remain respect the correct location of intrathecal catheter in order to achieve the best therapeutic result. We analyze the factors that can affect drug distribution within the cerebrospinal fluid. Three categories of variables were identified: drug features, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) dynamics and patients features. First category includes physicochemical properties and pharmacological features of intrathecal administered drugs with special attention to drug lipophilicity. In the second category, the variables in CSF flow, are considered that can modify the drug distribution within the CSF with special attention to the new theories of liquoral circulation. Last category try to explain inter-individual difference in baclofen response with difference that are specific for each patients such as the anatomical area to treat, patient posture or reaction to inflammatory stimulus. We conclude that a comprehensive evaluation of the patients, including imaging techniques to study the anatomy and physiology of intrathecal environment and CSF dynamics, could become essential in the future to the purpose of optimize the clinical outcome of intrathecal therapy.
Go to : 
Intrathecal drugs delivery (IDD) is an effective and safe option for the treatment of chronic conditions that are refractory to conventional therapies such as chronic cancer and non-cancer pain, and chronic spasticity [1-9].
IDD enables to achieve adequate symptoms control in patients suffering from symptoms that are not effectively controlled by pharmacotherapy, or in patients that develop intolerable side effects at the effective oral dose [1-8]; this purpose is achieved, because IDD allows administrating medications, to bypass the blood-brain barrier, being the deposit of the medication directly in the intrathecal space, around the target, and resulting in a reduction of drugs systemic effects (Fig. 1) [8,10-13].
Drugs usually administered trough IDD systems belong to heterogeneous pharmacological class and have different features and mechanisms of action [2,6,12,13].
The trial intrathecal injection of medications, is usually performed in order to verify efficacy and side effects before to implant an IDD system [1,2,4,6,10,14]. Unfortunately not all patients with a positive trial response show a proportionate effect when IDD starts with a very large range of dosage [1,5,6,15,16]. In addition some patients who show a good clinical result during first stage of intrathecal administration, develop a progressive need to increase daily dose to maintain an adequate symptoms control [1,2,5,6,16].
Although many steps forward were made in the comprehension of mechanisms of action of intrathecally administered drugs, many doubts remain respect the correct location of intrathecal catheter in order to achieve the best therapeutic result. On the basis of published data [17,18], one of the reasons why catheter tip position assumes a pivotal importance is its relationship between drug delivery and CSF dynamics, in order to reach the best clinical outcome and avoid side effects and complications.
Any factor, or mechanical obstruction, that alter the drug spread within the CSF hampering to drug to get its site of action may be able to cause a clinical failure, side effects or complications [19-21].
In this review article, we analyze the factors that can affect drug distribution within the CSF fluid, and the variables that can influence the choice to where place an intrathecal catheter.
Go to : 
The PUBMED/MEDLINE and Cochrane databases were searched for all reports on IDD and catheter related morbidity, published in any language. The key words included "ntrathecal", "baclofen", "chronic pain", "intrathecal drug delivery", "opioids", "spasticity", catheter, and "granuloma" and all related publications between the earliest available date and August (week 1) of 2013 were searched.
Since 1979, when Wang et al. demonstrated the efficacy of intrathecal morphine administration for the treatment of chronic pain [22], diffusion of IDD as an additional way to treat pain conditions refractory to conventional handling is increased.
Different opioids have been considered for their use, positioning, both based on their physicochemical properties, level of evidence in clinical practice, and versatility of presentations, for intrathecal use.
Other than opioids, various molecules with heterogeneous physicochemical properties are administered through intrathecal delivery system [6] and with different aims [6,7]. Drugs such as local anesthetics (LA) and ziconotide are effective to treat chronic pain whereas baclofen is administered for spasticity treatment and in lesser extent for pain treatment [1-4,6,11,13].
The causes of lost of effectiveness of an intrathecal administered drug are various. One of these causes is the appearance of tolerance during intrathecal administration [1-3,5,6,11,21]. Tolerance is defined by an increase in the required doses that does not result in any technical problem [5]. Diagnosis of tolerance should be based on the exclusion of other causes of ineffectiveness and exclusion of device malfunction [5,21].
IDD administration allows to leave medications directly in the cerebrospinal fluid; the assumption that drugs left in situ will spread by liquoral circulation up to reach their site of action is outdated and a more elaborate pattern of interaction between CSF dynamics, drugs and patients features has to be considered; a complete understanding of these mechanisms is of primary importance to provide a more accurate therapeutic plan and to avoid complications related with IDD.
Cerebrospinal fluid flow dynamics within the spinal canal along with the physical, chemical, and immunological properties of intrathecal medications have been suggested to be responsible for the growth of inflammatory mass lesions at the tips of intrathecal drug delivery catheters [6,15,23-29]. The formation of granulomas in intrathecal catheters has been reported to have a 0.04% occurrence rate two years after insertion of the catheter and 1.15% six years after insertion [24]. Overall incidence has been reported to be less than 1% but probably the incidence of this complication is underreported in literature [21,24].
Etiology of the masses is not well-know; hypothesis include chemical-physical features of infused drugs, impurities and contamination of the infused solutions, bacterial infection, pyrogens and endotoxins, catheter features, effects of catheter implantation procedures, catheter position and CSF volume [6,16,24-29].
Intrathecal catheter tip granuloma typically occurs in the thoracic region; particularly, in patients receiving high doses or high concentrations of intrathecal drug infusions. Recent studies emphasize the role of opioids and in particular the role of high morphine concentrations [14,18,21]. Intrathecal morphine infusion produces a dose-dependent local inflammatory reaction at the catheter tip in the dog model that can lead to inflammatory mass formations [24,27]; this don't seems related with a direct mu-receptor action but seem to be due to its capacity to induce inflammatory mediator release from meningeal mast cells that could stimulate the diapedesis of inflammatory cells trough meningeal vessels [27]. Michael et al. [30] have pointed to the same risks factors and have observed no granuloma development with the use of baclofen and no differences in the development of granuloma with the implanted intrathecal catheter versus the infusion pump.
In a case report that prove the possibility of recurrence of intrathecal granuloma, also after a very brief period of time from granuloma removal, De Andres et al. [28] suppose that exist patients more prone to develop intrathecal inflammatory mass, and hypothesize that the more time required for the development of the last granuloma was due to the new thoracic-location of the catheter-tip, a level with faster CSF flow. This could have permit a greater dilution of morphine delaying the immunologic activation responsible for granuloma development.
In a very recent paper published by Narouze et al. [29], the possible role of previous spine surgery or spinal injury, is analyzed regarding granuloma formation. There is an increased risk of development of granuloma in patients who have had previous spine surgery or spinal injury (68%) than in a general cohort of patients (48%), with an IDD pump.
Regarding the prevention of the development of granulomas, an expert panel of clinicians [31] referred to a number of recommendations and established a diagnostic-therapeutic decision algorithm focusing on the importance of imaging in the detection of these masses (MRI or computed tomography myelogram) and the assessment of neurological signs and symptoms shown by patients when deciding to remove IT catheters or not.
Inflammatory mass formation and loss of effectiveness of intrathecal administered drugs therefore seem to be two phenomenons closely related with drug spread within the CSF fluid. Therefore, comprehension of mechanism that regulate drug distribution. including drugs features, drugs pharmacology, patients features and position of catheter tip, can improve the clinical approach to this field of pain treatment.
Go to : 
Lipid solubility can play an important role in pharmacokinetic of lipophilic drugs administered intrathecally and in the animal models the spinal bioavailability of lipid-soluble opioids is diminished by their sequestration in hydrophobic environments, their relatively rapid clearance into plasma and their rapid elimination from CSF [17].
A recent study has demonstrated a clear changes in LA pharmacokinetic during continuous epidural administration when compared with single administration [31], this could be due, at least in part, to the drug sequestration by epidural fat, as hypothesized by Reina et al. [32].
We can imagine that, considered that epidural space is one of the major way of elimination for intrathecal administered opioids [33], epidural fat can exert an important influence on intrathecally administered drugs in relation with they lipophicility. Specifically, the clearance of intrathecal drugs into epidural fat could determine the liquoral concentration of drugs; unfortunately, this action of epidural fat would be favorable in order to prevent inflammatory mass formation concurring with the "high concentration" hypothesis, but at the same time make unavailable for clinical action part of the drug.
In another study performed to investigate the distribution and clearance of intrathecal administered opioids. Ummenhofer et al. [33] showed that cephalic spread of opioids within the CSF is a very slow process and that is the slowest for the more lipophilic opioids. On the contrary, the low spinal cord distribution volume of morhine, is related with slow clearance into plasma The integral exposure of the spinal cord to the other opioids was relatively low, but for different reasons: alfentanil has a high clearance from spinal cord into plasma, fentanyl distributes rapidly into the epidural space and fat, and sufentanil has a high spinal cord volume of distribution [33]. The most lipid-soluble drugs, fentanyl and sufentanil, undergo the most limited rostral spread, but their very high volumes of distribution in the spinal cord, epidural space, and epidural fat result in very low integral exposure within the extracellular fluid space of the spinal cord Morphine reaches the highest concentration in the spinal cord extracellular fluid space and is cleared slowly. This, although allows to morphine molecules to reach in the right amount its site of action, could facilitate the activation of immune cells and release of inflammatory mediator as indicated in previous studies [16,24,27].
Furthermore, duramater veins are an important site of clearance of epidurally-administered opioids [17]. Multiple clinical studies that have demonstrated that the analgesic effect of spinally administered lipid-soluble opioids is due in part, if not exclusively, to uptake into plasma and distribution to brainstem opioid receptors. If this evidence was true even for the intrathecally-administered drugs, we might hypothesize that a blood flow increase in the duramater veins, for example due to a localized inflammatory reaction, might clear more drugs, even though less lipophilic, and more rapidly from the CSF, causing a reduced drug concentration in cerebrospinal fluid.
Opioids are one of the most common drugs used for spinal administration. Different opioids have been considered for IDD, positioning, both based on their physicochemical properties, level of evidence in clinical practice, and versatility of their presentations, for intrathecal use.
They are recommended to treat chronic pain trough spinal administration alone or in association with other drugs [6].
Although all opioids molecules have similar mechanism of action that consist in an analgesic effect mediated by µ-opioid receptor [34], chemical-physical features of their molecule can influence considerably their pharmacokinetic when administrated within the CSF.
The most important chemical aspect is the opioids lipophicility. In fact it affects the spread of the opioids within the cerebrospinal fluid, the onset time and the drug clearance from CSF towards blood stream [17,33,35]. Moreover, all these variables determine opioids concentration within the CSF, one of the most suspected cause of inflammatory mass formation.
Intrathecal morphine is the first line, therapy in treating patients with neuropathic and nociceptive chronic pain, including both cancer and non-cancer pain types [6,7,36].
Morphine is a pure µ-receptor agonist that acts binding opioid receptors situated in the substantial gelatinosa of the spinal cord and at brain level [6,37]. It is the least lipophilic opioid and this has important implications for its pharmacokinetics: morphine penetrate biologic membrane more slowly than lipophilic opioids and its accumulation in fatty tissues is less than other more lipophilic opioids [34].
Hydromorphone is a semi-synthetic hydrogenated ketone of morphine, it's an analgesic molecule 5-7 times more potent [38] and more rapid than morphine [6].
Fentanyl and sufentanil are selective µ-opioid receptor agonists and have a higher intrinsic activity than morphine. They produce dose-dependent analgesia acting at spinal cord dorsal horn activating fewer receptors than morphine to induce an equivalent analgesia whereupon they produce less tolerance [40].
Fentanyl and sufentanil are more lipophilic molecules than morphine and have a rapid diffusion in fatty tissues [40] with an higher volume of distribution [34].
Both drugs are recommended for intrathecal administration; fentanyl as first choice for line 3 drug, sufentanil is suggested as primary line 4 drug if line 3 approaches are ineffective. As a novelty in cases of nociceptive pain, fentanyl has been upgraded to first line because of a long-term positive safety profile [6].
Bupivacaine and Ropivacaine are two amino-amide LA that act causing a reversible block of voltage-gated sodium channels in axons [41].
Lipid solubility of these drugs increase with the increasing of the molecular weight accordingly with the R- substitution in their molecule. For this reason bupivacaine is a more liphophilic molecule than ropivacaine [41].
Bupivacaine allow to achieve adequate analgesia without significant motor blockade [41]. Even though ropivacaine has a clinical profile similar to bupivacaine it's a less potent and short-acting agent in term of motor fiber blockade [41]. This differential blockade of sensory and motor fibers is the basis for the widespread use of these LAs for the treatment of chronic pain.
Bupivacaine is recommended in combination therapy for treatment of patients with mixed and neuropathic pains, whereas ropivacaine is a line 5 drug which use is recommended with caution because of little information about safety and efficacy during long-term intrathecal administration [6].
Although LAs don't seem to be related to inflammatory mass formations, LA lipophilicity is important to determine drug pharmacokinetic conduct and thus LA concentration and spread within CSF, and CSF clearance.
Baclofen is a structural analogue of gamma-aminobutiryc acid (GABA), the most important inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. It binds GABA-receptor, both presynaptically and postsynaptically, causing inhibition of monosynaptic and polysynaptic spinal reflexes [12,42]. Exert its action at spinal cord level inhibiting calcium uptake thus impeding the release of excitatory neurotransmitters that cause spasticity [2,12,13].
Unfortunately baclofen has a poor lipid solubility and does not cross the blood-brain barrier effectively [1,11-13]. Even at large oral doses, baclofen reaches relatively low levels at its site of action in the CSF while reach high plasma levels that can cause unwanted side effects [2,11,13].
On the contrary, baclofen infused intrathecally reaches a higher concentration at its sites of action in spinal cord and provide safe and effective treatment to reduce spasticity and spasms with a small doses compared with oral administration [11-13]. It is known to exert its effect at spinal level penetrating the superficial layer of spinal cord and binding GABA B receptor sites [13].
Regarding the use of baclofen in progressive and severe spasticity refractory to medical therapy, authors such as Natale et al. [43] or Uchiyama et al. [44] consider it to be a good treatment option, in keeping with the available literature. In 2012, successful use of ITB has been reported in patients with dystonia [45,46], myoclonus [47], dysautonomia and hypertonia following severe traumatic brain injury [48]. In patients with complex regional pain syndromes with dystonia, Van der Plas et al. [49] demonstrated a significant improvement in global intense pain, sharp pain, dull pain, and deep pain during the first 6 months. After this period, the scores leveled off despite further improvement of dystonia and continued ITB dose escalation.
Despite its effectiveness is known from approximately twenty-five years [4], the role of catheter position in treatment of spasticity is still controversial and in 2007 first three case of baclofen related inflammatory masses was reported in literature [23], bringing to light a matter until then believed to belong to the opioids.
It is the synthetic form of the hydrophilic peptide ω-MVIIA from the venom of a marine snail, it binds reversibly and with high affinity to a subset of voltage-sensitive calcium channels, the N-type channels, whereas other types of voltage-sensitive calcium channels are not affected by Ziconotide [50]. A clinical vial for IDD infusion contains ziconotide acetate, with L-methionine (0.05 mg/ml) and sodium chloride as excipients at pH 4.0 to 5.0 (Prialt®; Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc.). It is a non-opioid molecule with a higher hydrophilicity that is nearly exclusively distributed in the CSF [6].
N-type voltagesensitive calcium channels (NVSCCs), abundantly present in the superficial lamina of the spinalcord dorsal horn, were identified as its target site [50]. NVSCCs are found exclusively in presynaptic neurons, and their inhibition results in blocking the release of presynaptic algesic neurotransmitters into the synapse, which subsequently control a variety of calcium-dependent processes. NVSCCs, have an important role in the spinal processing of nociceptive afferent activity. These calcium-channels are also present in CNS and are responsible for supraspinal neurological side effects of ziconotide [50].
Ziconotide is a non-opioid level one drug recommended in intrathecal therapy with morphine and Hydromorphone [6].
In its consensus paper, the PACC 2012 reviewed the available literature on the use of ziconotide, reflecting latest data on its long-term efficacy in monotherapy or combination therapy, safety, use in IT morphine detoxification and trialing of IT [6,14]. Alicino et al. [51] also recognize the success of ziconotide plus morphine in chronic cancer pain patients.
Dupoiron et al. [52] conducted an observational study in which they observed that a low starting dosage of ziconotide, followed by slow titration, decreases the incidence of major adverse events, but moderate adverse events occurred at rates similar to those reported previously.
This relatively new drug, present an advantage of primary importance in the management of IDD, spinal catheter-tip granulomas that might arise during intrathecal opioids treatment have not yet been recorded for ziconotide [50].
Go to : 
It's known that time course and extent of analgesia depend from drug movement in the CSF and from drug penetration in the spinal cord tissue [35]. In addition, it is necessary to understand CSF flow kinetics and drug distribution for IDD [53]. Wallace et al. [54] conducted a study on steady state morphine and morphine metabolite concentrations in the CSF and peripheral circulation and the effects upon CSF chemistry (protein, glucose, white blood cells) after long-term spinal infusion. The chronic delivery of intrathecal morphine has no prominent effects on CSF chemistry. The study also presents an interesting case of the changes in CSF morphine concentrations that occur in the presence of a granuloma. The authors support the concept described by Bernards [55] about rostrocaudal gradients with low-rate chronic infusion.
Doubts concerning the correct intrathecal catheter location in order to obtain the best clinical outcome rose from the start of IDD administration. In the case of baclofen one of the first attempt to solve the problem indicated as major determinant of drug rostral spread the cerebrospinal flow pattern [56]. Today this concept of CSF circulatory system that provide an homogeneous drug spread is no longer correct.
Several studies show that drug spread within the CSF is very limited and that cerebrospinal spread are of small extent and not homogeneous within the spinal canal [35,57,58].
Flack et al. [57] in 2010 performed an animal study to evaluate the effect of position and baricity on drug spread within the liquoral space during the very slow infusion rates typically used for chronic IDD administration. The drugs used in this study were baclofen and bupivacaine, an example of hydrophilic and lipophilic drug respectively. The study shows significant differences in drugs distribution according to animal position and a limited spread of bupivacaine probably due to a more rapid clearance from the CSF. They conclude that drug disposition within the CSF and spinal cord are affected by baricity and by posture highlighting the substantial difference between slow intrathecal infusion and intrathecal bolus. With particular reference to baclofen they found that these findings might explain that percentage of patients that, after a significant improvement after an intrathecal trial bolus, failed to improve with intrathecal baclofen infusion despite progressive dose augmentation; this also might explain the extreme dose variability to achieve spasticity control in patient that showed a similar response after a intrathecal trial bolus. On the light of these results he also state that "...the location of the intrathecal catheter tip relative to the targeted spinal cord segment(s) is a potentially important determinant of efficacy" [57].
Regarding the CSF movements a research conducted to study the opioids distribution after intrathecal injection observed that despite injection of identical volume at a fixed rate using a slightly hypobaric solution, a remarkable heterogeneity in time pattern of drug concentrations was present in the CSF in more rostral sampling sites. The authors explained these differences by variation of the pharmacokinetic mixing parameter Kmix. This variable describe the rapidity of the CSF mixing movement. The authors hypothesize an individual variability of this parameter with some areas of intrathecal space characterized by rapid mixing and other by slow mixing.
Although physiological basis from Kmix variation is unknown, it could reflect the local anatomy of the site of drug injection, where some sites might be in a channel of rapid CSF movements whereas nearly adjacent sites are in relatively quiet movements of CSF [35].
To apply this findings to IDD, characterized by very slow infusion rate, it's possible to imagine the continuous infusion as a sequence of uninterrupted micro-bolus. In this way, if the catheter tip lie in a rapid mixing channel, the drug spread will be greater than in case of a catheter tip lying in a slow mixing channel, causing great difference in drug mixing and spread. Another hypothesis, that should be investigated, is that the catheter itself might alter the CSF dynamic modifying the Kmix of the area where lie.
Another study that investigate the origin of subarachnoid pulsations identify three dynamic channels along the spinal axis and state that CSF spinal pulsation are heterogeneous in their configuration and in their propagation [58]. Interestingly, one of the variables that influence this heterogeneity is spinal compliance that depends, in some measure, also from the presence of epidural veins and epidural fat.
Hsu et al. [59] have proposed image-based computational fluid dynamics (miCFD) for investigating IDD. The novel miCFD method combines quantitative medical imaging and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to generate patient-specific computational models in order to explain the cause of high variability in drug distribution in the spine. Patient physiological variables such as heart rate and CSF stroke volume are considered to be key factors in drug biodistribution [60]. An interesting study on CSF in the lumbosacral dural sac at various vertebral levels was conducted by Prats-Galino et al. [61], who showed, using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a mean CSF volume of 34.3 ± 5.1 ml (mean CSF volume per vertebral segment ranged from 4.3 ± 0.7 ml at L5 and 5.8 ± 2.5 ml at L1 with high inter-individual variability).
This to highlight the fact that two determinant of pharmacokinetic of intrathecal drugs exert they influence even on CSF dynamics and suggest that a pre-implant anatomical study performed with imaging technique, in the future, might play an important role in the evaluation of a candidate for IDD [61].
Go to : 
Our experience suggest that a comprehensive evaluation of the patient candidate to IDD assume a pivotal role to choose the best catheter position.
In the specific case of baclofen intrathecal infusion, to this day, it isn't possible define an univocal site where place the catheter-tip.
With the classical lumbar approach the catheter tip is usually placed in the intrathecal space between approximately T10 and L2 [3,4,10] but literature report effective case of more rostral placement.
There are many concerns about cervical catheter tip position because of the risk of major side effects related to baclofen overdose such as sedation, convulsion, respiratory depression and coma. Plassat in his review show that severe side effects, present in 12% of patients, are directly related to errors occur in pump refill procedure in 80% of the case [5]. This fact offer a wide margin to reduce severe side effects and make IDD a more safe technique.
Better control of upper-extremity spasticity was found to be associated with mid-thoracic tip placement in children with spastic quadriparesis [61] and no adverse events was related to the more rostral location of the catheter [61,62]. More recent literature confirm these findings, stating that the cervical positioning of the catheter is feasible and safe and that side effects due to baclofen are comparable with other studies with catheter-tip in conventional position [63].
Although these studies show result from a non-homogeneous population and from a child population they suggest that upper-extremity spasticity benefit from a more rostral administration of baclofen. Baclofen despite his hydrophilicity, present a limited spread within the CSF showing a lumbar-to-cisternal gradient of 4:1, moreover, factors as baricity of compounded solution and patient bearing can limit further the cephalic spread of baclofen causing an ineffective drug concentration in the upper intrathecal space segments, just where baclofen exert its action in a patient with upper-extremity spasticity.
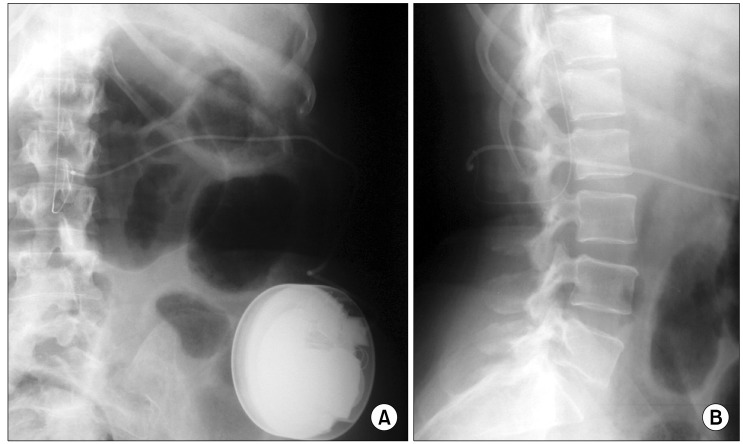
In our specific case we hypothesize that baclofen also has an action at supramedullary level and that inflammatory reaction at cervical site has played an important role hampering to baclofen to get its site of action.
To the direct surgical visualization, the cervical spinal area appeared totally surrounded by an abundant amount of fibrotic tissue that imprinted the dural sac in the cervical segment corresponding to the catheter position. Our hypothesis is that fibrotic scar, conditioning a canal stenosis documented also by magnetic resonance, can function as a mechanical barrier creating a partitioning within the intrathecal space. This partitioning could be responsible for an alteration of CSF dynamics creating a two connected liquoral space but with a clear separation of CSF movements. For this reason we can imagine a liquoral compartment below the fibrotic scar with higher baclofen concentration but that can't reach its receptor target and a liquoral compartment upon the fibrotic scar with an ineffective low baclofen concentration. This hypothesis is reinforced by a recent research performed by Kumru et al., to evaluate the contribution to baclofen effects from CNS regions above the spinal cord. Neurophysiological results showed in their study confirm that baclofen have, at least in part, an action at brainstem level [42].
Go to : 
IDD is a proven and effective tool in the hands of pain specialists to treat chronic intractable cancer and non-cancer pains.
In the last decade the common effort brought to shared guide-lines for a more rational use of IDD [6]. Nevertheless exist a certain number of cases of failure if IDD despite a positive trial and case of loss of effectiveness during the treatment; in addition, exist a broad range variability in drug dosage to obtain the same clinical effect.
We have identified some factors that should be considered when a patient is candidate for an intrathecal drug infusion, they can be included as follows: drug features, CSF dynamics and patients features. This subdivision has only a didactic meaning because the three categories are tightly related influencing each other.
The case of baclofen, recently associated with the onset of intrathecal inflammatory mass, is an example of complexity of interaction between these factors.
Some authors have reconsider the role of baclofen in the development of intrathecal masses leaning towards a concentration-related baclofen precipitate rather than concentration-related immune reaction [64]. This theory, even though explain the different mechanism of mass formation between opioids and baclofen, emphasize even more (maybe more than for the opioids related inflammatory masses) the importance of catheter tip position.
Hence, although there is the need to know more about mechanisms influencing drugs action within the CSF, our knowledge are enough to state that decision of catheter-tip position can't be left to chance. All the factors formerly listed should be carefully examined before to start an intrathecal infusion and periodically revised particular in case of acute events affecting the "spinal environment" such as spinal surgery or IDD system revision.
Go to : 
References
1. Ochs G, Naumann C, Dimitrijevic M, Sindou M. Intrathecal baclofen therapy for spinal origin spasticity: spinal cord injury, spinal cord disease, and multiple sclerosis. Neuromodulation. 1999; 2:108–119. PMID: 22151114.

2. Avellino AM, Loeser JD. Intrathecal baclofen for the treatment of intractable spasticity of spine or brain etiology. Neuromodulation. 2000; 3:75–81. PMID: 22151402.

3. Burns AS, Meythaler JM. Intrathecal baclofen in tetraplegia of spinal origin: efficacy for upper extremity hypertonia. Spinal Cord. 2001; 39:413–419. PMID: 11512071.

4. Penn RD, Savoy SM, Corcos D, Latash M, Gottlieb G, Parke B, et al. Intrathecal baclofen for severe spinal spasticity. N Engl J Med. 1989; 320:1517–1521. PMID: 2657424.

5. Plassat R, Perrouin Verbe B, Menei P, Menegalli D, Mathé JF, Richard I. Treatment of spasticity with intrathecal Baclofen administration: long-term follow-up, review of 40 patients. Spinal Cord. 2004; 42:686–693. PMID: 15303111.

6. Deer TR, Prager J, Levy R, Rathmell J, Buchser E, Burton A, et al. Polyanalgesic Consensus Conference 2012: recommendations for the management of pain by intrathecal (intraspinal) drug delivery: report of an interdisciplinary expert panel. Neuromodulation. 2012; 15:436–464. PMID: 22748024.

7. Hayek SM, Deer TR, Pope JE, Panchal SJ, Patel VB. Intrathecal therapy for cancer and non-cancer pain. Pain Physician. 2011; 14:219–248. PMID: 21587327.
8. De Andres J, Asensio-Samper JM, Fabregat-Cid G. Advances in intrathecal drug delivery. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2013; [in press].

9. Kim JH, Jung JY, Cho MS. Continuous intrathecal morphine administration for cancer pain management using an intrathecal catheter connected to a subcutaneous injection port: a retrospective analysis of 22 terminal cancer patients in Korean population. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:32–38. PMID: 23342205.

11. Loubser PG, Narayan RK, Sandin KJ, Donovan WH, Russell KD. Continuous infusion of intrathecal baclofen: long-term effects on spasticity in spinal cord injury. Paraplegia. 1991; 29:48–64. PMID: 2023770.

12. Dario A, Tomei G. A benefit-risk assessment of baclofen in severe spinal spasticity. Drug Saf. 2004; 27:799–818. PMID: 15350152.

13. Francisco GE. The role of intrathecal baclofen therapy in the upper motor neuron syndrome. Eura Medicophys. 2004; 40:131–143. PMID: 16046935.
14. Deer TR, Prager J, Levy R, Burton A, Buchser E, Caraway D, et al. Polyanalgesic Consensus Conference--2012: recommendations on trialing for intrathecal (intraspinal) drug delivery: report of an interdisciplinary expert panel. Neuromodulation. 2012; 15:420–435. PMID: 22494357.

15. Albright AL, Thompson K, Carlos S, Minnigh MB. Cerebrospinal fluid baclofen concentrations in patients undergoing continuous intrathecal baclofen therapy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007; 49:423–425. PMID: 17518926.

16. Miele VJ, Price KO, Bloomfield S, Hogg J, Bailes JE. A review of intrathecal morphine therapy related granulomas. Eur J Pain. 2006; 10:251–261. PMID: 15964775.

17. Bernards CM. Recent insights into the pharmacokinetics of spinal opioids and the relevance to opioid selection. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2004; 17:441–447. PMID: 17023903.

18. Flack SH, Anderson CM, Bernards C. Morphine distribution in the spinal cord after chronic infusion in pigs. Anesth Analg. 2011; 112:460–464. PMID: 21212256.

19. Rhee SM, Choi EJ, Lee PB, Nahm FS. Catheter obstruction of intrathecal drug administration system -a case report-. Korean J Pain. 2012; 25:47–51. PMID: 22259717.

20. Hassenbusch S, Burchiel K, Coffey RJ, Cousins MJ, Deer T, Hahn MB, et al. Management of intrathecal catheter-tip inflammatory masses: a consensus statement. Pain Med. 2002; 3:313–323. PMID: 15099236.

21. Deer TR, Levy R, Prager J, Buchser E, Burton A, Caraway D, et al. Polyanalgesic Consensus Conference--2012: recommendations to reduce morbidity and mortality in intrathecal drug delivery in the treatment of chronic pain. Neuromodulation. 2012; 15:467–482. PMID: 22849581.

22. Wang JK, Nauss LA, Thomas JE. Pain relief by intrathecally applied morphine in man. Anesthesiology. 1979; 50:149–151. PMID: 373503.

23. Deer TR, Raso LJ, Garten TG. Inflammatory mass of an intrathecal catheter in patients receiving baclofen as a sole agent: a report of two cases and a review of the identification and treatment of the complication. Pain Med. 2007; 8:259–262. PMID: 17371413.

24. Yaksh TL, Hassenbusch S, Burchiel K, Hildebrand KR, Page LM, Coffey RJ. Inflammatory masses associated with intrathecal drug infusion: a review of preclinical evidence and human data. Pain Med. 2002; 3:300–312. PMID: 15099235.

25. De Andrés J, Tatay Vivò J, Palmisani S, Villanueva Pérez VL, Mínguez A. Intrathecal granuloma formation in a patient receiving long-term spinal infusion of tramadol. Pain Med. 2010; 11:1059–1062. PMID: 20642731.

26. Peng P, Massicotte EM. Spinal cord compression from intrathecal catheter-tip inflammatory mass: case report and a review of etiology. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2004; 29:237–242. PMID: 15138910.

27. Allen JW, Horais KA, Tozier NA, Yaksh TL. Opiate pharmacology of intrathecal granulomas. Anesthesiology. 2006; 105:590–598. PMID: 16931994.

28. De Andrés J, Palmisani S, Villanueva Pérez VL, Asensio J, López-Alarcón MD. Can an intrathecal, catheter-tip-associated inflammatory mass reoccur? Clin J Pain. 2010; 26:631–634. PMID: 20639731.

29. Narouze SN, Casanova J, Souzdalnitski D. Patients with a history of spine surgery or spinal injury may have a higher chance of intrathecal catheter granuloma formation. Pain Pract. 2013; [in press].

30. Michael A, Buffen E, Rauck R, Anderson W, McGirt M, Mendenhall HV. An in vivo canine study to assess granulomatous responses in the MedStream Programmable Infusion System (TM) and the SynchroMed II Infusion System(R). Pain Med. 2012; 13:175–184. PMID: 22239738.

31. Cusato M, Allegri M, Niebel T, Ingelmo P, Broglia M, Braschi A, et al. Flip-flop kinetics of ropivacaine during continuous epidural infusion influences its accumulation rate. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011; 67:399–406. PMID: 21079936.

32. Reina MA, Franco CD, López A, Dé Andrés JA, van Zundert A. Clinical implications of epidural fat in the spinal canal. A scanning electron microscopic study. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2009; 60:7–17. PMID: 19459550.
33. Ummenhofer WC, Arends RH, Shen DD, Bernards CM. Comparative spinal distribution and clearance kinetics of intrathecally administered morphine, fentanyl, alfentanil, and sufentanil. Anesthesiology. 2000; 92:739–753. PMID: 10719953.

34. Rosow CE, Dershwitz M. Pharmacology of opioid analgesics. In : Longnecker DE, Brown DL, Newman MF, Zapol WM, editors. Anesthesiology. New York (NY): McGraw-Hill;2008. p. 869–896.
35. Eisenach JC, Hood DD, Curry R, Shafer SL. Cephalad movement of morphine and fentanyl in humans after intrathecal injection. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:166–173. PMID: 12826857.

36. Gogia V, Chaudhary P, Ahmed A, Khurana D, Mishra S, Bhatnagar S. Intrathecal morphine pump for neuropathic cancer pain: a case report. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2012; 29:409–411. PMID: 21868426.

37. Goodchild CS, Nadeson R, Cohen E. Supraspinal and spinal cord opioid receptors are responsible for antinociception following intrathecal morphine injections. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2004; 21:179–185. PMID: 15055889.

38. Deer TR, Prager J, Levy R, Rathmell J, Buchser E, Burton A, et al. Polyanalgesic Consensus Conference--2012: consensus on diagnosis, detection, and treatment of catheter-tip granulomas (inflammatory masses). Neuromodulation. 2012; 15:483–495. PMID: 22494332.

39. Georges P, Lavand'homme P. Intrathecal hydromorphone instead of the old intrathecal morphine: the best is the enemy of the good? Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2012; 29:3–4. PMID: 22127266.
40. Waara-Wolleat KL, Hildebrand KR, Stewart GR. A review of intrathecal fentanyl and sufentanil for the treatment of chronic pain. Pain Med. 2006; 7:251–259. PMID: 16712626.

41. Heavner JE. Pharmacology of local anesthetics. In : Longnecker DE, Brown DL, Newman MF, Zapol WM, editors. Anesthesiology. New York (NY): McGraw-Hill;2008. p. 954–973.
42. Kumru H, Stetkarova I, Schindler C, Vidal J, Kofler M. Neurophysiological evidence for muscle tone reduction by intrathecal baclofen at the brainstem level. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011; 122:1229–1237. PMID: 20889372.

43. Natale M, Mirone G, Rotondo M, Moraci A. Intrathecal baclofen therapy for severe spasticity: analysis on a series of 112 consecutive patients and future prospectives. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012; 114:321–325. PMID: 22104692.

44. Uchiyama T, Nakanishi K, Fukawa N, Yoshioka H, Murakami S, Nakano N, et al. Neuromodulation using intrathecal baclofen therapy for spasticity and dystonia. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2012; 52:463–469. PMID: 22850493.

45. Bahl A, Tripathi C, McMullan J, Goddard J. Novel use of intrathecal baclofen drug delivery system for periodic focal dystonia in a teenager. Neuromodulation. 2013; 16:273–275. PMID: 23009035.

46. Turner M, Nguyen HS, Cohen-Gadol AA. Intraventricular baclofen as an alternative to intrathecal baclofen for intractable spasticity or dystonia: outcomes and technical considerations. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2012; 10:315–319. PMID: 22861196.

47. Chiodo AE, Saval A. Intrathecal baclofen for the treatment of spinal myoclonus: a case series. J Spinal Cord Med. 2012; 35:64–67. PMID: 22330193.

48. Hoarau X, Richer E, Dehail P, Cuny E. A 10-year follow-up study of patients with severe traumatic brain injury and dysautonomia treated with intrathecal baclofen therapy. Brain Inj. 2012; 26:927–940. PMID: 22668125.

49. van der Plas AA, van Rijn MA, Marinus J, Putter H, van Hilten JJ. Efficacy of intrathecal baclofen on different pain qualities in complex regional pain syndrome. Anesth Analg. 2013; 116:211–215. PMID: 23223108.

50. Schmidtko A, Lötsch J, Freynhagen R, Geisslinger G. Ziconotide for treatment of severe chronic pain. Lancet. 2010; 375:1569–1577. PMID: 20413151.

51. Alicino I, Giglio M, Manca F, Bruno F, Puntillo F. Intrathecal combination of ziconotide and morphine for refractory cancer pain: a rapidly acting and effective choice. Pain. 2012; 153:245–249. PMID: 22082570.

52. Dupoiron D, Bore F, Lefebvre-Kuntz D, Brenet O, Debourmont S, Dixmerias F, et al. Ziconotide adverse events in patients with cancer pain: a multicenter observational study of a slow titration, multidrug protocol. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:395–403. PMID: 22996851.
53. Lawson EF, Wallace MS. Advances in intrathecal drug delivery. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2012; 25:572–576. PMID: 22825049.

54. Wallace M, Yaksh TL. Characteristics of distribution of morphine and metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma with chronic intrathecal morphine infusion in humans. Anesth Analg. 2012; 115:797–804. PMID: 22822192.

55. Bernards CM. Cerebrospinal fluid and spinal cord distribution of baclofen and bupivacaine during slow intrathecal infusion in pigs. Anesthesiology. 2006; 105:169–178. PMID: 16810009.

56. Loubser PG, Narayan RK. Effect of subarachnoid catheter position on the efficacy of intrathecal baclofen for spinal spasticity. Anesthesiology. 1993; 79:611–614. PMID: 8363090.

57. Flack SH, Bernards CM. Cerebrospinal fluid and spinal cord distribution of hyperbaric bupivacaine and baclofen during slow intrathecal infusion in pigs. Anesthesiology. 2010; 112:165–173. PMID: 19996952.

58. Henry-Feugeas MC, Idy-Peretti I, Baledent O, Poncelet-Didon A, Zannoli G, Bittoun J, et al. Origin of subarachnoid cerebrospinal fluid pulsations: a phase-contrast MR analysis. Magn Reson Imaging. 2000; 18:387–395. PMID: 10788715.

59. Hsu Y, Hettiarachchi HD, Zhu DC, Linninger AA. The frequency and magnitude of cerebrospinal fluid pulsations influence intrathecal drug distribution: key factors for interpatient variability. Anesth Analg. 2012; 115:386–394. PMID: 22523420.

60. Martin BA, Reymond P, Novy J, Balédent O, Stergiopulos N. A coupled hydrodynamic model of the cardiovascular and cerebrospinal fluid system. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012; 302:H1492–H1509. PMID: 22268106.

61. Prats-Galino A, Reina MA, Puigdellívol-Sánchez A, Juanes Méndez JA, De Andrés JA, Collier CB. Cerebrospinal fluid volume and nerve root vulnerability during lumbar puncture or spinal anaesthesia at different vertebral levels. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2012; 40:643–647. PMID: 22813492.

62. Sivakumar G, Yap Y, Tsegaye M, Vloeberghs M. Intrathecal baclofen therapy for spasticity of cerebral origin--does the position of the intrathecal catheter matter? Childs Nerv Syst. 2010; 26:1097–1102. PMID: 20306056.

63. McCall TD, MacDonald JD. Cervical catheter tip placement for intrathecal baclofen administration. Neurosurgery. 2006; 59:634–640. PMID: 16955045.

64. Deer TR, Raso LJ, Coffey RJ, Allen JW. Intrathecal baclofen and catheter tip inflammatory mass lesions (granulomas): a reevaluation of case reports and imaging findings in light of experimental, clinicopathological, and radiological evidence. Pain Med. 2008; 9:391–395. PMID: 18489628.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download