INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Protocol and registration
2. Search strategy
3. Inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria
1. Patients (P): all patients with acute HZ
2. Intervention (I): pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies employed to prevent PHN
3. Comparison (C): other pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies employed to prevent PHN, placebo, or no treatment
4. Outcome measurements (O): The primary outcome of this NMA was the incidence of PHN at 3 months after acute HZ. The secondary outcomes of this NMA were the incidence of PHN at 1 and 6 months after acute HZ, and severity of pain measured at 1, 3, and 6 months after acute HZ was also analyzed.
1. Review articles, case reports, case series, letters to the editor, commentaries, proceedings, laboratory science studies, and all other non-relevant studies
2. Studies that failed to report the outcomes of interest
4. Study selection
5. Data extraction
6. Risk of bias
7. Statistical analyses
8. Quality of evidence
RESULTS
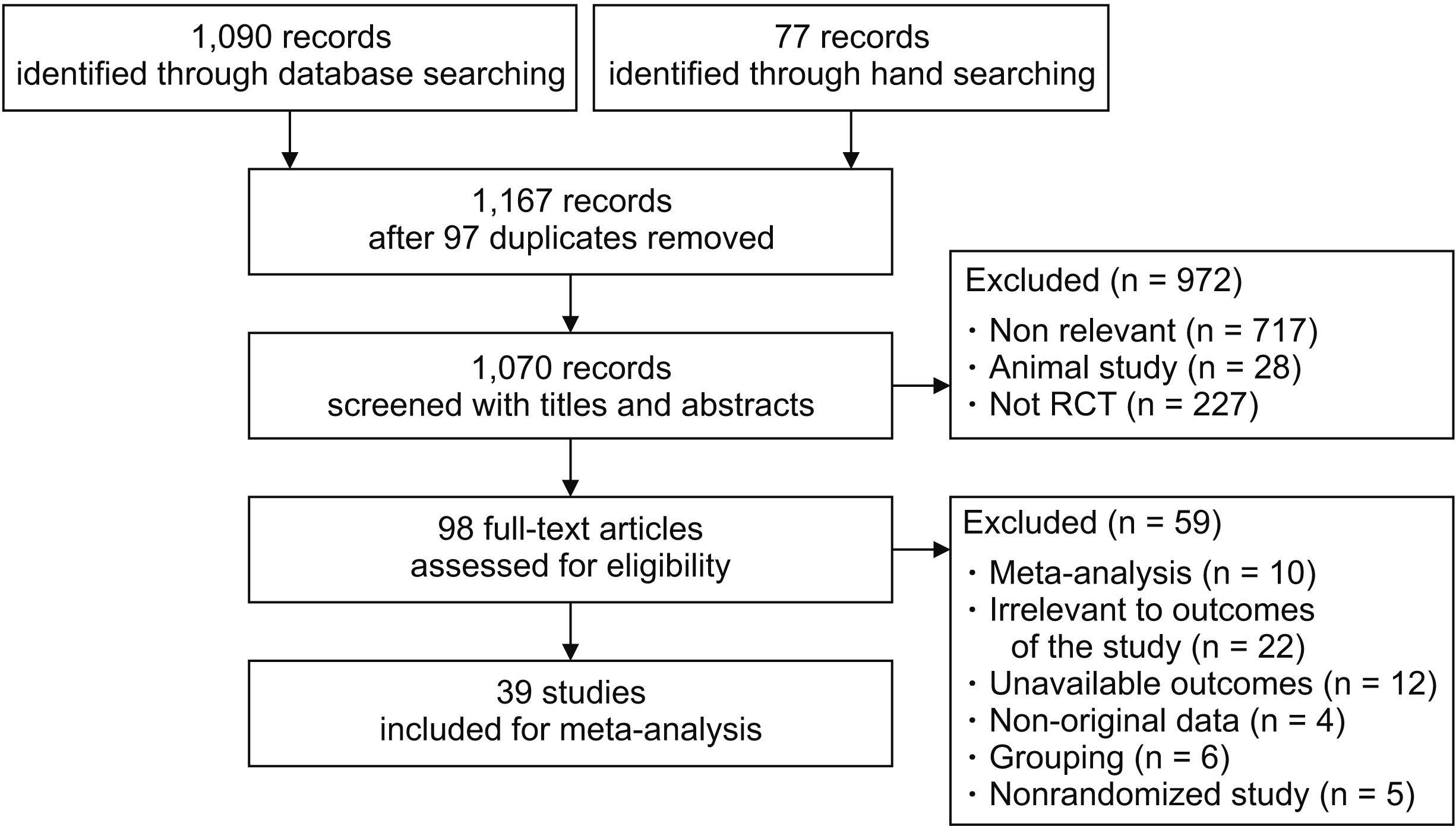
1. Study selection
2. Study characteristics
Table 1
| Author, year | Management |
Number of patients |
Age, yr | Sex, M/F |
Pain assessment tool |
Outcomes of interest | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence of PHN at 1 month | Incidence of PHN at 3 months | Incidence of PHN at 6 months | Mean pain score at 1 month | Mean pain score at 3 months | Mean pain score at 6 months | ||||||
| Bulilete et al., 2019 [108] | Valaciclovir + gabapentin | 50 | 65.1 | 20/28 | 10-point VAS | • | • | • | • | ||
| Valaciclovir + placebo | 48 | 66.0 | 18/30 | ||||||||
| Lee et al., 2016 [104] | Valaciclovir + gabapentin | 60 | 62.58 | 18/42 | 10-point Likert scale | • | • | • | • | ||
| Valaciclovir | 60 | 61.83 | 25/35 | ||||||||
| Stepanović et al., 2015 [103] | TENS | 36 | 57.3 | 14/22 | VAS | • | • | • | |||
| Symptomatic care | 38 | 59.9 | 16/22 | ||||||||
| Antiviral agent | 71 | 70.6 | 32/39 | ||||||||
| Antiviral + TENS | 77 | 65.6 | 27/50 | ||||||||
| Makharita et al., 2015 [102] | Acyclovir + pregabalin + saline (paravertebral) | 70 | 56.2 | 31/37 | VAS | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Acyclovir + pregabalin + bupivacaine + dexamethasone (paravertebral) | 73 | 56.8 | 34/36 | ||||||||
| Makharita et al., 2012 [101] | Antiviral + pregabalin + saline (SGB) | 30 | 59.6 | 14/16 | VAS | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Antiviral + pregabalin + bupivacaine + dexamethasone (SGB) | 30 | 60.6 | 13/18 | ||||||||
| Krcevski Skvarc and Kamenik, 2010 [98] | Antiviral + placebo | 15 | 63 | 4/11 | 10 point Likert scale | • | • | • | |||
| Antiviral + pregabalin | 14 | 67 | 6/8 | ||||||||
| Ji et al., 2009 [97] | Acyclovir | 64 | 68 | 28/36 | VAS | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| Acyclovir + bupivacaine + methylprednisolone (paravertebral) | 68 | 66 | 30/38 | ||||||||
| van Wijck et al., 2006 [96] | Acyclovir | 297 | 66 | 116/181 | VAS | • | • | • | • | ||
| Acyclovir + bupivacaine + methylprednisolone (epidural) | 301 | 66 | 118/183 | ||||||||
| Pasqualucci et al., 2000 [110] | Acyclovir + prednisolone | 279 | 66.9 | 125/154 | VAS | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| Bupivacaine + epinephrine + methylprednisolone via epidural catheter | 290 | 68.7 | 131/159 | ||||||||
| Ahmed et al., 1998 [94] | Famciclovir | 25 | 53 | 11/14 | VAS 100 mm | • | • | • | • | • | |
| PENS | 25 | 56 | 12/13 | ||||||||
| Bowsher, 1997 [93] | Acyclovir + amitriptyline | 9 | 71.3 | 14/24 | NR | • | • | • | |||
| Amitriptyline | 29 | ||||||||||
| Acyclovir + placebo | 17 | 72.7 | 14/20 | ||||||||
| Placebo | 17 | ||||||||||
| Harding and Porter, 1991 [114] | Acyclovir | 24 | 62.1 | 6/17 | VAS 100 mm | • | • | • | |||
| Placebo | 22 | 70.6 | 9/19 | ||||||||
| Benoldi et al., 1991 [92] | Prednisolone | 9 | 68.5 | 4/5 | NR | • | • | ||||
| RTx | 9 | 67.2 | 3/6 | ||||||||
| Acyclovir | 9 | 67.1 | 6/3 | ||||||||
| Carbamazepine | 9 | 63 | 3/6 | ||||||||
| Esmann et al., 1987 [88] | Acyclovir + prednisolone | 41 | 72.8 | 17/24 | Slight, moderate, sever, attacks per day, highest grading | • | • | ||||
| Acyclovir + placebo | 37 | 71.4 | 8/29 | ||||||||
| Cobo et al., 1986 [87] | Acyclovir | 36 | NR | 13/23 | None, mild, moderate, severe | • | |||||
| Placebo | 35 | 21/14 | |||||||||
| Balfour et al., 1983 [85] | Acyclovir | 52 | NR | 29/23 | NR | • | • | ||||
| Placebo | 42 | 25/17 | |||||||||
| Esmann et al., 1982 [84] | Acyclovir | 27 | 65.7 | 10/17 | NR | • | • | ||||
| Placebo | 29 | 68.6 | 10/19 | ||||||||
| Bean et al., 1982 [83] | Acyclovir | 19 | 53.2 | 6/13 | NR | • | • | ||||
| Placebo | 10 | 50.5 | 7/3 | ||||||||
| Keczkes and Basheer, 1980 [115] | Prednisolone | 20 | 66.4 | 14/6 | NR | • | |||||
| Carbamazepine | 20 | 68.5 | 14/6 | ||||||||
| Cui et al., 2018 [107] | Acyclovir + pregabalin + ropivacaine + methylprednisolone (intracutaneous) | 51 | 61.7 | 21/28 | VAS | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| Acyclovir + pregabalin + saline (intracutaneous) | 51 | 61.8 | 20/28 | ||||||||
| Cui et al., 2017 [105] | Acyclovir + ropivacaine + methylprednisolone (intracutaneous) | 48 | 63.7 | 21/26 | VAS | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| Acyclovir | 48 | 63.0 | 19/27 | ||||||||
| Ni et al., 2017 [106] | Acyclovir + triamcinolone + lidocaine (subcutaneous) | 50 | 63.84 | 23/27 | NRS | • | • | • | |||
| Acyclovir | 50 | 65.86 | 24/26 | ||||||||
| Zheng et al., 2019 [109] | Famciclovir + pregabalin + placebo (cervical root block) | 70 | 63.41 | 31/39 | 11 point scale | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Famciclovir + pregabalin + lidocaine + triamcinolone + cobalamine (cervical root block) | 70 | 65.84 | 29/41 | ||||||||
| Hwang et al., 1999 [79] | Acyclovir + bupivacaine + methylprednisolone (continuous epidural infusion) | 40 | 60.8 | 18/22 | VRS 0-100 | • | |||||
| Acyclovir | 35 | 56.1 | 9/26 | ||||||||
| Wan et al., 2019 [120] | Sham | 48 | 64.87 | 20/28 | VAS | • | • | • | |||
| PRF on gasserian ganglion | 48 | 66.01 | 23/25 | ||||||||
| Hügler et al., 2002 [116] | Human albumin (placebo) | 20 | 67.65 | NR | VAS | • | |||||
| VZVIG | 20 | 71.6 | |||||||||
| Cui et al., 2016 [117] | Valacyclovir + methylene blue + lidocaine (intradermal) | 32 | 69.5 | 13/19 | VAS 100 mm | • | • | • | |||
| Valacyclovir + lidocaine (intradermal) | 32 | 72.5 | 11/21 | ||||||||
| Payne et al., 1989 [91] | Placebo | 17 | 70 | 10/7 | NR | • | • | • | |||
| Isoprinosine | 21 | 70 | 10/11 | ||||||||
| Wood et al., 1994 [111] | Acyclovir 7 days | 101 | 58 | 39/62 | 0-5; non-noticeable to excruciating | • | |||||
| Acyclovir 7 days + prednisoone 21 days | 99 | 59 | 37/62 | ||||||||
| Acyclovir 21 days | 101 | 59 | 38/63 | ||||||||
| Acyclovir 21 days + prednisolone 21 days | 99 | 60 | 39/60 | ||||||||
| McGill et al., 1983 [86] | Placebo | 20 | 68.8 | 7/13 | 0-3 | • | |||||
| Acyclovir | 17 | 70.4 | 3/14 | ||||||||
| Wassilew et al., 1987 [89] | Acyclovir | 29 | 62.5 | 9/20 | 0-5 | • | • | • | |||
| Placebo | 31 | 63.4 | 6/25 | ||||||||
| Mandal et al., 1988 [90] | Acyclovir | 26 | 67.4 | 11/15 | 0-4 | • | |||||
| Placebo | 30 | 68.4 | 9/21 | ||||||||
| Lee et al., 1999 [95] | Acyclovir + mepivacaine (stellate ganglion block) | 10 | 65.0 | 3/7 | VAS 0-100 mm | • | • | ||||
| Acyclovir | 10 | 67.2 | 5/5 | ||||||||
| Harding et al., 1986 [119] | 1% lignocaine & 0.5% marcaine (stellate ganglion block) | NR | 71.5 | NR | VAS 0-100 mm | • | • | ||||
| Placebo | 72.2 | ||||||||||
| Kanodia and Singhal, 2011 [99] | Acyclovir + pregabalin | 23 | 46 | 19/4 | VAS 100 mm | • | |||||
| Acyclovir + placebo | 22 | 47 | 17/5 | ||||||||
| Kanodia et al., 2012 [100] | Acyclovir + gabapentin 300 mg/day | 15 | 64 | 11/4 | VAS 100 mm | • | |||||
| Acyclovir + gabapentin 600 mg/day | 14 | 65 | 9/5 | ||||||||
| Acyclovir + gabapentin 900 mg/day | 13 | 65 | 10/3 | ||||||||
| Placebo | 14 | 63 | 11/3 | ||||||||
| Manabe et al., 2004 [118] | Acyclovir + bupivacaine (continous epidural infusion, intermittent epidural bolus) | 29 | 67 | 9/20 | VAS | • | |||||
| Acyclovir + normal saline (continous epidural infusion) + bupivacaine (intermittent epidural bolus) | 27 | 65 | 13/14 | ||||||||
| Clemmensen and Andersen, 1984 [112] | ACTH | 17 | 55 | 10/7 | 0-4 | • | |||||
| Prednisolone | 19 | 56 | 13/6 | ||||||||
| Placebo | 19 | 56 | 10/9 | ||||||||
| Eaglstein et al., 1970 [113] | Triamcinolone | 15 | NR | NR | NR | • | |||||
| Placebo | 19 | ||||||||||
PHN: postherpetic neuralgia, TENS: transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, SGB: stellate ganglion block, PENS: percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, RTx: radiotherapy, PRF: pulsed radiofrequency, VZVIG: varicella zoster vaccine immunoglobulin, ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone, NR: not reported, VAS: visual analogue scale, NRS: numerical rating scale.
3. Risk of bias assessment
Table 2
| Study, year | Randomization process | Intended interventions | Missing outcome data |
Measurement of the outcome |
Selection of the reported result | Overall result | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulilete et al., 2019 [108] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 1/98 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Lee et al., 2016 [104] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | No specific information | Some concern | No specific information | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Stepanović et al., 2015 [103] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | Blinded only in assesor | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Makharita et al., 2015 [102] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | No exclusion | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Makharita et al., 2012 [101] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 3/64 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Krcevski Skvarc and Kamenik, 2010 [98] | High risk | No specific information | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | No exclusion | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Ji et al., 2009 [97] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | Blinded only in assesor | Low risk | 19/132 dropped, propotions existed | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| van Wijck et al., 2006 [96] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | Blinded only in assesor | Low risk | 33/598 dropped, propotions existed | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Pasqualucci et al., 2000 [110] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | Blinded only in assesor | Low risk | 31/600 dropped, protocol violation | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Ahmed et al., 1998 [94] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | Blinded only in assesor | Low risk | No exclusion | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Bowsher, 1997 [93] | Low risk | Sealed envelop | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 6/80 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Low risk |
| Harding and Porter, 1991 [114] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Some concern | Both blinded | Some concern | 8/46 dropped, no specific propotion revealed | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Benoldi et al., 1991 [92] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Some concern | Different procedure | Low risk | 1/36 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Esmann et al., 1987 [88] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Some concern | Both blinded | Low risk | No exclusion | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Cobo et al., 1986 [87] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence, basement difference existed | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | No exclusion | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Balfour et al., 1983 [85] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | No exclusion | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Esmann et al., 1982 [84] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 1/56 dropped | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Bean et al., 1982 [83] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | Both blinded | Some concern | 2/31 dropped | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Keczkes and Basheer, 1980 [115] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | No exclusion | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Cui et al., 2018 [107] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 5/102 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Cui et al., 2017 [105] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Some concern | Both blinded | Low risk | 2/96 dropped | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Ni et al., 2017 [106] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | 5/100 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Zheng et al., 2019 [109] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 13/153 dropped | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Hwang et al., 1999 [79] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | No exclusion | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Wan et al., 2019 [120] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | Both blinded | Low risk | 2/96 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Hügler et al., 2002 [116] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Some concern | Both blinded | Low risk | No exclusion | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Cui et al., 2016 [117] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | No exclusion | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Payne et al., 1989 [91] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 3/41 dropped | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Wood et al., 1994 [111] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 51/400 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| McGill et al., 1983 [86] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 3/40 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Wassilew et al., 1987 [89] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 2/60 dropped | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Mandal et al., 1988 [90] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence, basement difference existed | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 8/64 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Lee et al., 1999 [95] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence, basement difference existed | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | No exclusion | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Harding et al., 1986 [119] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment | Some concern | No specific information | Some concern | No specific information | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Kanodia and Singhal, 2011 [99] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Low risk | Both blinded | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Kanodia et al., 2012 [100] | Some concern | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Low risk | Both blinded | Some concern | No specific information | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | Some concern |
| Manabe et al., 2004 [118] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence, basement difference existed | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 3/59 dropped, unrelated to the outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Clemmensen and Andersen, 1984 [112] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence, basement difference existed | Low risk | Both blinded | Low risk | 5/60 dropped, unrelated to outcome | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
| Eaglstein et al., 1970 [113] | High risk | No statement for allocation concealment, randomization sequence | Low risk | Both blinded | Some concern | 1/35 dropped | Low risk | Blinded | Low risk | Predefined outcomes | High risk |
4. Synthesis of results
Fig. 2
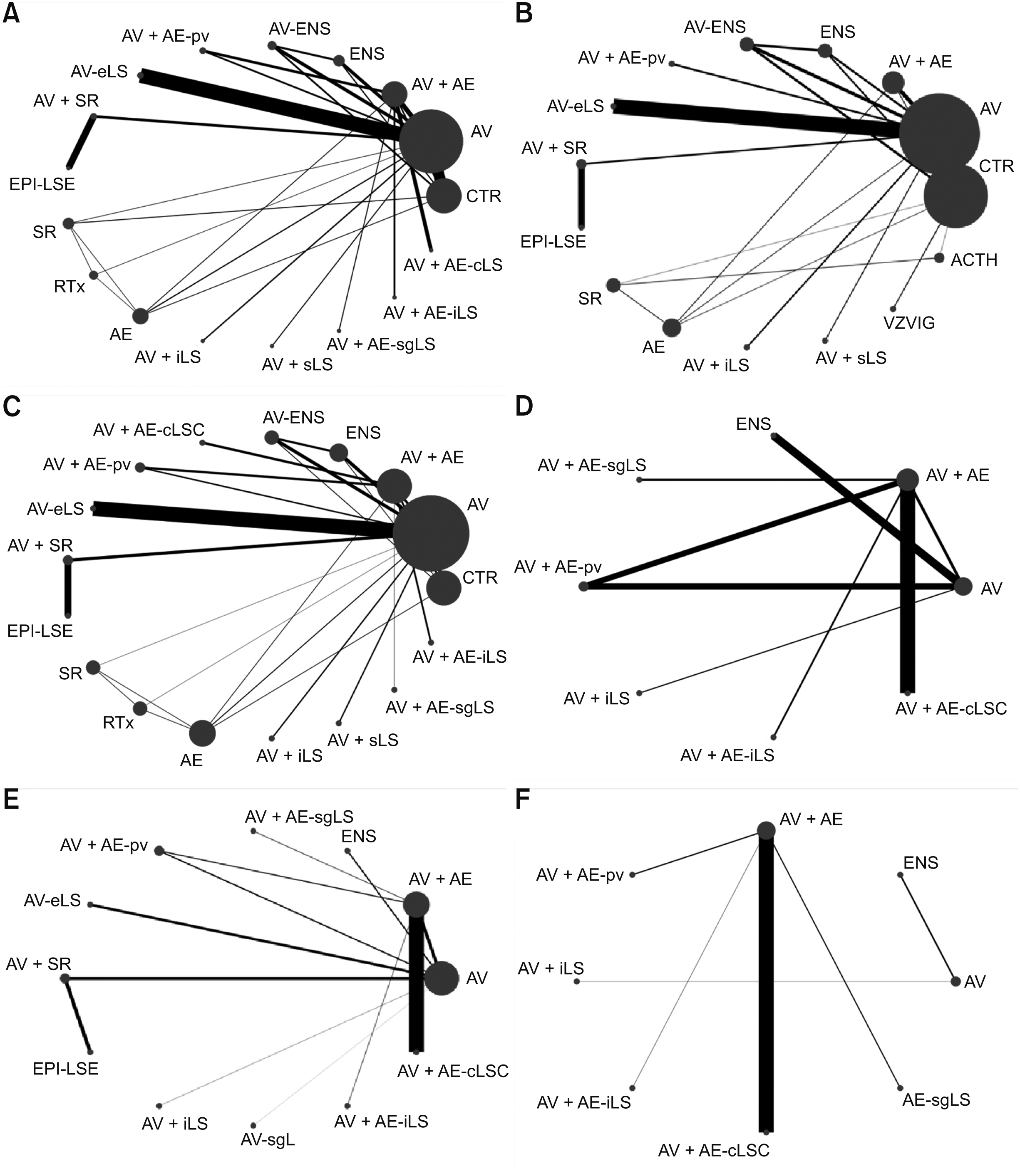
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download