Abstract
Background
This study used bibliometric analysis of articles published about the topic of regional anesthesia from 1980-2019 with the aim of determining which countries, organizations, and authors were effective, engaged in international cooperation, and had the most cited articles and journals.
Methods
All articles published from 1980-2019 included in the Web of Science database and found using the keywords regional anesthesia/anaesthesia, spinal anesthesia/anaesthesia, epidural anesthesia/anaesthesia, neuraxial anesthesia/anaesthesia, combined spinal-epidural, and peripheral nerve block in the title section had bibliometric analysis performed. Correlations between the number of publications from a country with gross domestic product (GDP), gross domestic product (at purchasing power parity) per capita (GDP PPP), and human development index (HDI) values were investigated with the Spearman correlation coefficient. The number of articles that will be published in the future was estimated with linear regression analysis.
Results
Literature screening found 11,156 publications. Of these publications, 6,452 were articles. The top 4 countries producing articles were United States of America (n = 1,583), Germany (585), United Kingdom (510), and Turkey (386). There was a significant positive correlation found between the GDP, GDP PPP, and HDI markers for global countries with publication productivity (r = 0.644, P < 0.001; r = 0.623, P < 0.001, r = 0.542, P < 0.001). The most productive organizations were Harvard University and the University of Toronto.
Go to : 
Regional anesthesia is defined as a temporary removal of nerve conduction and pain senses in certain regions of the body with local anesthetic medications without causing loss of consciousness [1]. When regional anesthesia is compared with general anesthesia, the frequency of use is increasing, due to early mobilization, high analgesia level, shortened hospital stay, and lower postoperative nausea and vomiting [2]. Additionally, due to the increase in the use of ultrasonography, currently, regional anesthesia techniques are performed more reliably and effectively [3]. Though it is commonly believed that regional anesthesia is more reliable than general anesthesia, especially among elderly patients, no significant difference has been demonstrated between the two anesthesia types in terms of mortality and morbidity [4].
Bibliometric analysis is a method used to analyze the effect of research outputs like articles and book using quantitative measurements [5-8]. Bibliometric analyses may determine potential research cooperation between countries, organizations or authors in new and developing research areas [9-11]. Citation analysis analyzes how many times articles belonging to an author, country or journal are cited by others and reveals the effect of a certain author, country or journal in a certain field [12,13]. With the increase in publication numbers in recent times, many bibliometric analyses have been performed in the health field [5-13]. Articles included in common bibliometric analyses in these unique studies in the literature generally are found using databases like Web of Science, but also PubMed and Scopus.
Though the frequency of use of regional anesthesia, instead of general anesthesia, has been increasing in recent years, there is still no comprehensive bibliometric research about this topic in the literature. This study aimed to perform bibliometric analysis of articles published from 1980-2019 about the topic of regional anesthesia, to determine which countries, organizations, and authors are effective, international cooperation and most cited articles and journals in this field. Additionally, correlation analyses aimed to reveal factors affecting publication productivity. Keywords analysis aimed to determine current research areas and trends in relation to this topic.
Go to : 
Literature scanning was performed with the Web of Science (WoS: by Clavariate Analytics) database (access date: 23.08.2020). All articles containing the search keywords in the ‘Title’ section, published from 1980-2019 in the WoS database, had bibliometric analysis performed. The search keywords used the following codes: “regional anesthesia” or “regional anaesthesia” or “spinal anesthesia” or “spinal anaesthesia” or “epidural anesthesia” or “epidural anaesthesia” or “neuraxial anesthesia” or “neuraxial anaesthesia” or “combined spinal epidural” or “combined spinal and epidural” or “peripheral nerve block” Timespan: 1980-2019. Indexes: SCI-Expanded, SSCI, A&HCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH, BKCI-S, BKCI-SSH, ESCI. For bibliometric network visualization, the VOSviewer (version 1.6.13) program was used [14].
Statistical analyses used the SPSS version 22.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY) program. Normal distribution of data was tested with the Shapiro–Wilk test. The correlation analyses between the number of articles produced by countries with economic and development markers of gross domestic product (GDP), gross domestic product purchasing power parity (GDP PPP), and human development index (HDI) used the Spearman correlation analysis suitable for data distribution. Linear regression analysis was used to predict the number of publications in future years. P < 0.05 was accepted as statistically significant.
Go to : 
Literature screening found a total of 11,156 published items. Of these items, 6,452 were articles, 1,947 were letters, 1,372 were meeting abstracts, 505 were proceedings papers, 490 were reviews, and the remaining were other types of publication (390 publications; editorial materials, notes, corrections, book chapters, early access, news items, biographical items, book reviews, correction additions, retracted publications, books, discussions, reprints, retractions, items about an individual, data papers, and software reviews).
The research only performed bibliometric analysis of the 6,452 published articles. Of the 6,452 articles, there were a total of 107,533 citations (85,550 without self-citations), and the h-index of articles was 108, with average citations per item 16.67. Of the articles, 90% (5,815) were published in the English language. The remaining 10% were published in other languages (German [380], French [140], Portuguese [32], Russian [23], Spanish [21], Turkish [20], Czech [9], Korean [5], Dutch [2], Serbian [2], Chinese [1], Japanese [1], and Slovenian [1]).
The top 15 research areas for the published articles were anesthesiology (4,120, 63.9%), general internal medicine (525, 8.1%), surgery (470, 7.3%), obstetrics and gynecology (380, 5.9%), critical care medicine (289, 4.5%), experimental medical research (177, 2.7%), veterinary sciences (176, 2.7%), orthopedics (166, 2.6%), clinical neurology (141, 2.2%), pediatrics (140, 2.2%), pharmacology/pharmacy (130, 2.0%), peripheral vascular disease (110, 1.7%), cardiac cardiovascular systems (97, 1.5%), urology nephrology (78, 1.2%), and neurosciences (74, 1.1%).
The distribution of articles according to countries in the world is shown in Fig. 2. The active countries producing more than 100 articles were the United States of America (USA) (1,583), Germany (585), the United Kingdom (510), Turkey (386), Canada (338), India (315), Japan (307), France (298), China (289), Sweden (162), Australia (158), Italy (155), Finland (143), South Korea (130), Switzerland (130), Iran (129), Austria (110), and the Netherlands (103), in order. A total of 119 countries produced 6,452 articles. Of these countries, the network map showing international cooperation between the 50 countries with at least 10 articles is shown in Fig. 3.
There were statistically significant level correlations found between the number of articles produced by countries on the topic of regional anesthesia with GDP, GDP PPP, and HDI (r = 0.644, P < 0.001; r = 0.623, P < 0.001, r = 0.542, P = 0.001).
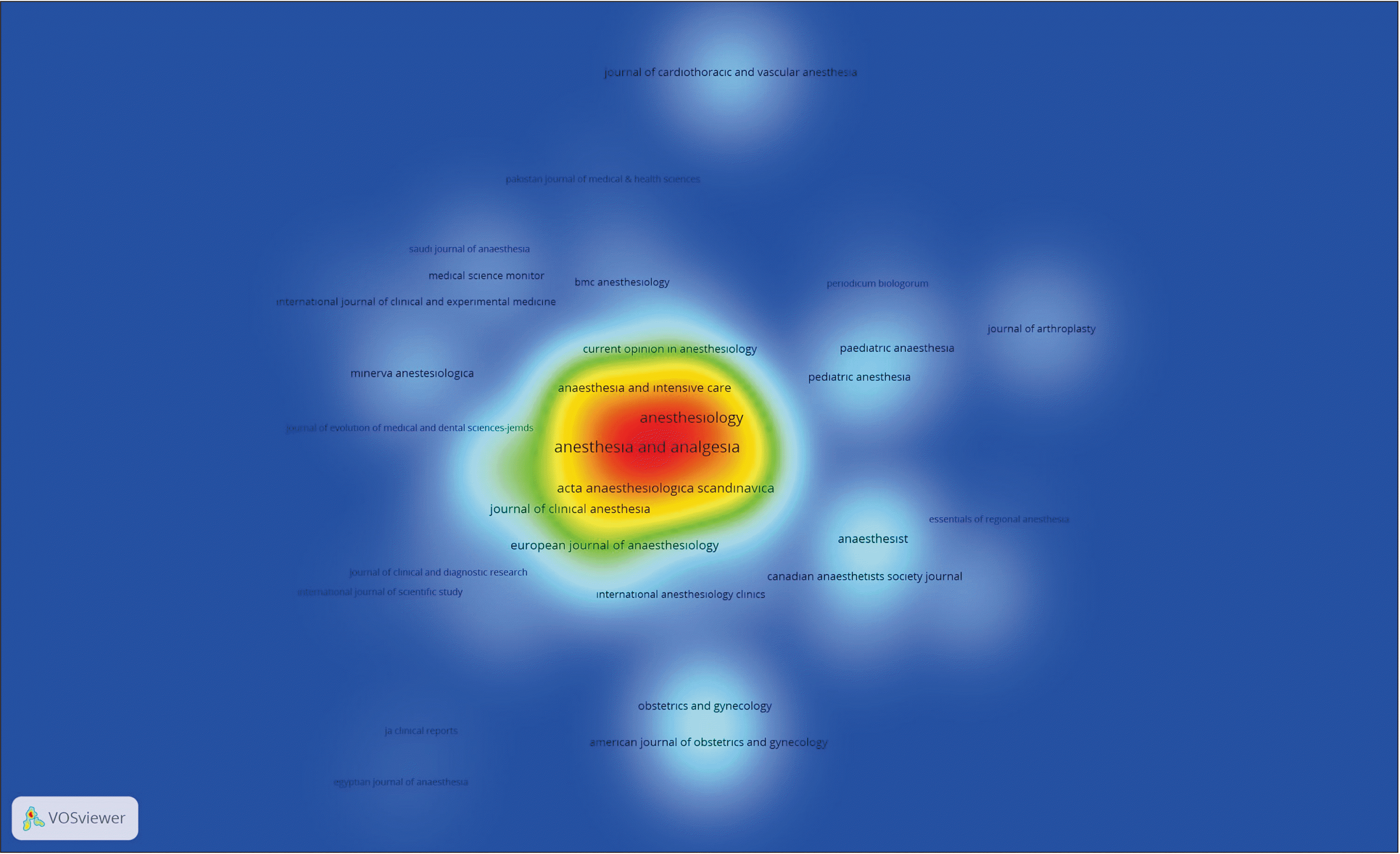
The 6,452 articles were published in a total of 1,015 journals. Among these journals, there were 50 with at least 15 articles about the topic. The top 50 journals produced most of the articles shown in Table 1. Additionally, the final column of the table shows the total citation numbers received by the journals and the mean citation number per article. The citation density map between these journals is shown in Fig. 4.
Active journals on regional anesthesia
The top 25 organizations and enhanced organizations producing articles are shown in Table 2.
Active organization and organizations-enhanced on regional anesthesia
The top 16 authors producing most articles were Rosenberg PH (49), Wulf H (29), Chan VWS (28), Neal JM (28), Horlocker TT (27), Sessler DI (25), Van Aken H (25), Kee WDN (23), Sharrock NE (23), Datta S (22), Hebl JR (22), Khaw KS (22), Nolte H (22), Saito Y (22), Standl T (22), and Tuominen M (22), in descending order.
According to total citation numbers, the top 20 articles receiving most citations from past to present are presented in Table 3. The final column of the table additionally gives the number of citations per year for the article.
The 15 most cited manuscripts on regional anesthesia
The reference sections of 6,452 articles cited 69,813 publications. Among these publications there are 8 with more than 100 citations. These publications receiving most citations are, in order, Rodgers et al. (2000) (Number of citations: 168), Auroy et al. (1997) (160), Carpenter et al. (1992) (124), Bromage (1965) (110), Rigler et al. (1991) (110), Moen et al. (2004) (108), Vandermeulen et al. (1994) (105), and Greene (1985) (104) [15-22].
In the 6,452 articles, a total of 6,551 different keywords were used. The network map related to the results of cluster analysis of 88 of these keywords, used in at least 20 different articles, is shown in Fig. 5, with the network map, related to trend word analysis, shown in Fig. 6. The most used medication in articles published about the topic of regional anesthesia were bupivacaine (199), dexmedetomidine (108), lidocaine (100), ropivacaine (91), fentanyl (69), levobupivacaine (56), clonidine (51), propofol (41), ketamine (34), and phenylephrine (33) (Table 4).
The first trend keywords on regional anesthesia
Go to : 
According to our research findings, a significant increasing trend was found for the number of articles about the topic of regional anesthesia. Initially there were low numbers of articles (a mean of 50 articles per year), with the annual mean rising to 107-215 articles from 1988-2015, before reaching over 300 articles annually from 2015 to the present date. When regression analysis results are assessed, it appears the increasing trend for articles will continue.
When the article distribution by country was investigated, it was observed that developed countries [23] had effective article production (the USA, Germany, the United Kingdom, Canada, Japan, France, Sweden, Australia, Italy, Finland, South Korea, Switzerland, Austria, and the Netherlands). However, developing countries, led by Turkey, such as India, China, and Iran had a notable effect on article productivity. Some bibliometric research in the literature determined that the economic size of a country, or development level, had a significant effect on academic publication productivity [5,13-22,24]. In our study, the significant correlation results found between the number of articles produced by countries and certain development indicators confirm the results of the literature. When the common authorship cooperation of countries is evaluated, clusters like Denmark-Sweden-Finland, or Germany-Switzerland, or Australia-New Zealand show that neighboring geographic region was the most important factor for cooperation.
When the analyzed articles were assessed according to total citation numbers received, the study with the most citations in total was determined to be the study published in the Journal of Pain in 2016 by Chou et al. [25]. After this study, the study with most total citations was the study published in Anesthesiology in 1997 by Auroy et al. [16]. In third place for citations was a study by Yeager et al. (1987) published in Anesthesiology [26]. When evaluated according to annual mean citation numbers, the most effective article was the study by Chou et al. (2016) in the Journal of Pain, with a mean of 111.4 citations [25]. The next most effective study after this was by Davidson et al. (2016) published in the Lancet [27]. According to co-citation analysis findings, all articles commonly cited studies by Rodgers et al. (2000), Auroy et al. (1997), Carpenter et al. (1992), Bromage (1965), Rigler et al. (1991), Moen et al. (2004), Vandermeulen et al. (1994), and Greene (1985) [15-22]. It is recommended that researchers interested in this topic initially read the studies determined by citation and co-citation analyses in this study.
The most active journals producing more than 200 articles were Anesthesia and Analgesia, Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, Anesthesiology, Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, the British Journal of Anaesthesia, Anaesthesist, and Anaesthesia. Authors wishing to produce articles about this topic may initially pay attention to these journals. When the top 50 journals producing the most articles are assessed according to citation numbers per article, the results according to analysis of the citation network map found the journals Anesthesiology, Obstetrics and Gynecology, Anesthesia and Analgesia, British Journal of Anaesthesia, the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine received the most citations. Researchers wishing to gain more citations for their articles on this topic may submit to these journals.
When keyword analysis results are assessed, according to trend analysis results in the early years, topics like shivering, anxiety, and caesarean section were followed by dexmedetomidine in order of frequency. In later years, trends in topics studied were determined to be dexamethasone, postoperative analgesia, ketamine, hemodynamics, spinal anesthesia, bupivacaine, and hypotension.
As a result of literature screening, we encountered only 1 study similar to the bibliometric study of our research. Fathi et al. (2015) performed bibliometric research for epidural anesthesia [28]. Firstly, our study is more comprehensive in terms of topic, year interval, and article numbers than this study. The study determined the top 10 authors, organizations, and countries in the distribution of publications about the topic of epidural anesthesia from 1990 to 2013. Our study includes keywords not included in that study, and we also performed citation analysis for journals and articles, and determined international cooperation. Our study is the most comprehensive research analyzing the highest number of articles about this topic.
A limitation of our study is that only the WoS database was used for literature scanning. Databases like PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus were not used, because the WoS database indexes articles published in journals with a higher impact factor compared to the other databases [5,24]. Additionally, in situations where more than one database is used for bibliometric studies analyzing large numbers of articles, the inclusion of the same article more than once in the analysis may affect the reliability of the results. Another limitation is; it may be that while using the “peripheral nerve block” as a search word, we did not include variations of this technique for example, brachial plexus block, femoral nerve block, sciatic nerve block, etc.
In conclusion, we presented a summary of 6,452 studies that were in the article category among the studies on regional anesthesia between 1980-2019. This summary will allow an anesthesiologist or other researcher to see the most effective articles, most cited articles, and perhaps the articles that should initially be read in relation to this topic. Observing which journals which produce the most articles in this field, and which journals contain articles receiving most citations, will allow easy assessment of current data. This study may provide an idea about which topics were studied according to year, an investigation of the trending topics, and an identification of new research topics. Additionally, researchers can see the impact level of countries and organizations in relation to this topic. This article will be a beneficial guide for clinicians and scientists about the global output in the field of regional anesthesia.
Go to : 
Notes
Author contributions: Selcuk Kayir: Writing/manuscript preparation; Alperen Kisa: Writing/manuscript preparation.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Stoelting RK, Miller RD. Akkaya ÖT, Ateş Y, Batislam Y, editors. 2010. Rejyonel anestezi. In: Temel anestezi. 5th ed. Güneş Tıp Kitabevleri;Ankara: p. 136–60. Turkish.
2. Çiftçi F, Altan Y. 2019; Comparing effects of midazolam and dexmedetomidine sedation on ultrasound guided infraclavicular nerve block for upper extremity orthopedic surgeries. Turkiye Klinikleri J Anest Reanim. 17:8–15. DOI: 10.5336/anesthe.2019-64922.

3. Potter JF, Kleiman AM, Myers EG, Herberg TJ, Bechtel AJ, Forkin KT, et al. 2019; Generative retrieval does not improve long-term retention of regional anesthesia ultrasound anatomy in unengaged learners. J Educ Perioper Med. 21:E623. DOI: 10.46374/volxxi-issue2-potter. PMID: 31988984. PMCID: PMC6972972.
4. Roy RC. 2000; Choosing general versus regional anesthesia for the elderly. Anesthesiol Clin North Am. 18:91–104. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-8537(05)70151-6. PMID: 10935002.

5. Demir E, Yaşar E, Özkoçak V, Yıldırım E. 2020; The evolution of the field of legal medicine: a holistic investigation of global outputs with bibliometric analysis. J Forensic Leg Med. 69:101885. DOI: 10.1016/j.jflm.2019.101885. PMID: 31733463.

6. Demir E, Comba A. 2020; The evolution of celiac disease publications: a holistic approach with bibliometric analysis. Ir J Med Sci. 189:267–76. DOI: 10.1007/s11845-019-02080-x. PMID: 31422546.

7. Doğan G, Kayır S. 2020; Global scientific outputs of brain death publications and evaluation according to the religions of countries. J Relig Health. 59:96–112. DOI: 10.1007/s10943-019-00886-8. PMID: 31317465.

8. Doğan G. 2020; The effect of religious beliefs on the publication productivity of countries in circumcision: a comprehensive bibliometric view. J Relig Health. 59:1126–36. DOI: 10.1007/s10943-020-00985-x. PMID: 31960357.

9. Demir E. 2019; The evolution of spirituality, religion and health publications: yesterday, today and tomorrow. J Relig Health. 58:1–13. DOI: 10.1007/s10943-018-00739-w. PMID: 30523486.

10. Muslu Ü, Demir E. 2019; Development of rhinoplasty: yesterday and today. Med Sci. 23:294–301.
11. Doğan G, İpek H. 2020; The development of necrotizing enterocolitis publications: a holistic evolution of global literature with bibliometric analysis. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 30:293–303. DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-3400514. PMID: 31777031.

12. Yıldırım E, Demir E. 2019; Comparative bibliometric analysis of fertility preservation. Ann Med Res. 26:1622–8. DOI: 10.5455/annalsmedres.2019.06.339.

13. Kiraz M, Demir E. 2020; A bibliometric analysis of publications on spinal cord injury during 1980-2018. World Neurosurg. 136:e504–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.01.064. PMID: 31954906.

14. van Eck NJ, Waltman L. 2010; Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 84:523–38. DOI: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3. PMID: 20585380. PMCID: PMC2883932.

15. Rodgers A, Walker N, Schug S, McKee A, Kehlet H, van Zundert A, et al. 2000; Reduction of postoperative mortality and morbidity with epidural or spinal anaesthesia: results from overview of randomised trials. BMJ. 321:1493. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.321.7275.1493. PMID: 11118174. PMCID: PMC27550.

16. Auroy Y, Narchi P, Messiah A, Litt L, Rouvier B, Samii K. 1997; Serious complications related to regional anesthesia: results of a prospective survey in France. Anesthesiology. 87:479–86. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199709000-00005. PMID: 9316950.
17. Carpenter RL, Caplan RA, Brown DL, Stephenson C, Wu R. 1992; Incidence and risk factors for side effects of spinal anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 76:906–16. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199206000-00006. PMID: 1599111.

18. Bromage PR. 1965; A comparison of the hydrochloride and carbon dioxide salts of lidocaine and prilocaine in epidural analgesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 16:55–69. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1965.tb00523.x. PMID: 5322004.

19. Rigler ML, Drasner K, Krejcie TC, Yelich SJ, Scholnick FT, DeFontes J, et al. 1991; Cauda equina syndrome after continuous spinal anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 72:275–81. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-199103000-00001. PMID: 1994754.

20. Moen V, Dahlgren N, Irestedt L. 2004; Severe neurological complications after central neuraxial blockades in Sweden 1990-1999. Anesthesiology. 101:950–9. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200410000-00021. PMID: 15448529.

21. Vandermeulen EP, Van Aken H, Vermylen J. 1994; Anticoagulants and spinal-epidural anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 79:1165–77. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-199412000-00024. PMID: 7978443.

22. Greene NM. 1985; Distribution of local anesthetic solutions within the subarachnoid space. Anesth Analg. 64:715–30. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-198507000-00012. PMID: 3893222.

23. United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). 2019. Human Development Report 2019. Beyond income, beyond averages, beyond today: inequalities in human development in the 21st century [Internet]. UNDP;New York: Available at: http://hdr.undp.org/en/2019-report/download.
24. Ozsoy Z, Demir E. 2018; The evolution of bariatric surgery publications and global productivity: a bibliometric analysis. Obes Surg. 28:1117–29. DOI: 10.1007/s11695-017-2982-1. PMID: 29086169.

25. Chou R, Gordon DB, de Leon-Casasola OA, Rosenberg JM, Bickler S, Brennan T, et al. 2016; Management of postoperative pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American Pain Society, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, and the American Society of Anesthesiologists' Committee on Regional Anesthesia, executive committee, and administrative council. J Pain. 17:131–57. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2015.12.008. PMID: 26827847.

26. Yeager MP, Glass DD, Neff RK, Brinck-Johnsen T. 1987; Epidural anesthesia and analgesia in high-risk surgical patients. Anesthesiology. 66:729–36. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-198706000-00004. PMID: 3296854.

27. Davidson AJ, Disma N, de Graaff JC, Withington DE, Dorris L, Bell G, et al. 2016; Neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years of age after general anaesthesia and awake-regional anaesthesia in infancy (GAS): an international multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 387:239–50. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00608-X. PMID: 26507180. PMCID: PMC5023520.

28. Fathi M, Joudi M, Habibi G, Javid S, Mardani A, Aghasizadeh M. 2015; A bibliometric study of epidural anesthesia: a 24-year review. Kuwait Med J. 47:118–21.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print








 XML Download
XML Download