Abstract
The advent of human intestinal organoid systems has revolutionized the way we understand the interactions between the human gut and microorganisms given the host tropism of human microorganisms. The gut microorganisms have regionality (i.e., small versus large intestine) and the expression of various virulence factors in pathogens is influenced by the gut milieu. However, the culture conditions, optimized for human intestinal organoids, often do not fully support the proliferation and functionality of gut microorganisms. In addition, the regional identity of human intestinal organoids has not been considered to study specific microorganisms with regional preference. In this review we provide an overview of current efforts to understand the role of microorganisms in human intestinal organoids. Specifically, we will emphasize the importance of matching the regional preference of microorganisms in the gut and tailoring the appropriate luminal environmental conditions (i.e., oxygen, pH, and biochemical levels) for modeling real interactions between the gut and the microorganisms with human intestinal organoids.
With its diverse genetic and metabolic potential, the gut microbiota has a substantial influence on our health and disease (1). Beyond genetics, environmental factors predominantly shape the microbial composition (2), alteration of which is associated with various human diseases (3). Human microbiota transplantation to germ-free animals has revealed a causal role of the disease-associated human microbiota, moving from its associative role (4-9). This might suggest that the gut microbiota (i.e., human origin) can easily adapt to its surrogate host (i.e., mouse). However, microbial composition between the human donors and the recipient animals colonized with the human microbiota can be substantially different (10-12). Differences in the gut milieu such as dietary components, bile acid profiles, and anatomical and cellular differences in the intestine (13-16) might contribute to failure of the microbiota in colonizing different host species.
These specificities in choice referred to as host tropism limit our understanding of the pathologies of human pathogens. Traditionally, mouse models have been widely used to reveal pathological roles of virulence factors of human pathogens (17, 18). However, the inability of the human pathogens to colonize in non-human animal models often leads to the failure of replication of their pathologies. This includes several enteric pathogenic bacteria (i.e., Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica, Shigella flexneri) and enteric viruses (i.e., human noroviruses, human rotaviruses) (19, 20). To overcome the host tropism, immortalized human cell lines have been used to model interactions between pathogens and the host. However, immortalized cell lines usually originate from a cancerous clone and tend to lose their original characteristics. Another drawback of immortalized cell lines is the lack of interactions among different cell types and extracellular environments, which can reduce cell or tissue-specific functions (21-23). Thus, modeling the role of pathogens in immortalized cell lines has not been optimal so far. The production of human organoids, the self-organizing, stem cell-based 3D culture systems have combated the issues of immortalized cell lines and non-human animal models since they resemble the in vivo organ architecture and landscape (24, 25).
In this review, we will describe current efforts to use human organoids to model the interactions between commensal microorganisms or pathogens and the host. Since many reviews have already described extensively the various organoids in the context of pathogen interactions (26-29), we will focus on the interactions between enteric microorganisms and gut epithelium with specific emphasis on the gut milieu.
Since the term organoid was first used in 1987 and the discovery of leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-cou-pled receptor 5 (Lgr5) as a marker for crypt-base columnal stem cells in 2007, Sato, Clevers, and colleagues have identified the key niche factors for the long-term culture of mouse small intestinal organoids, derived from intestinal stem cells (30, 31). These niche factors include epidermal growth factor (EGF), Noggin (a BMP signaling inhibitor), R-spondin (a Wnt signaling activator), often referred to collectively as ENR. Establishing various organoids derived from different tissues of mouse or human origin has become possible by modifying the ENR conditions (i.e., adding Wnt, a TGFβ signaling inhibitor, and a p38α MAPK signaling inhibitor for human intestinal organoids) (24, 32).
Two types of cell sources are used to establish human intestinal organoids, inducible pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) or adult stem cells (AdSCs). These two types of organoids have their respective advantages and limitations. Establishing iPSCs-derived intestinal organoids does not require human intestinal biopsies. The iPSCs are generated from reprogramming of somatic cells (i.e., fibroblasts) by forced expression of pluripotency factors such as OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and Myc (33). The iPSCs then need to undergo directed differentiation processes such as germ-layer specification towards endoderm, induction, and maturation into an intestinal organ type, which takes weeks to months (34). However, pluripotency factors are oncogenic or potentially oncogenic and reprogramming is often inefficient, thus leaving an epigenetic memory of somatic tissue of origin (35). In addition, the cell state of the iPSCs-derived organoids remains immature and generally lacks function (36). Similarly, these organoids do not reflect the region of interest in the intestine and also can contain mesenchymal cells as a byproduct of their differentiation (24, 37). In addition, iPSCs-derived intestinal organoids used in the most studies show small intestinal properties (38, 39). A recent study has applied the protocol inducing colonic organoids from hESCs in iPSCs derived from patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP-iPSCs) harboring APC mutations (40). This study showed that FAP-iPSCs intestinal organoids have enhanced proliferation and Wnt activity, similar to those in colorectal cancers (40).
The AdSCs-derived intestinal organoids can be directly generated from human intestinal biopsies, which do not require endoderm specification (24). In addition, they retain intestinal regional identities due to the maintenance of stable epigenetic signatures such as DNA methylation throughout long-term culture (41). Thus, colon organoids can be established directly from colon tissues, different from iPSCs-derived small intestinal organoids (32). The AdSCs-derived organoids only have epithelial cell types, simplifying disease modeling but instead limiting its usage to model complex interactions among cells originated from different germ layers. Another drawback is inaccessibility to human tissues. Nevertheless, as the number and accessibility of biobanks increases, it will become easier to obtain human tissues for AdSCs-derived organoids (42).
The intestinal organoids have closed 3D structures where the apical surface of the epithelium is located inside the organoids, thus limiting the epithelial interactions with luminal contents (43). Therefore, microinjection is required to induce contacts between the microorganisms and the apical surface of the intestinal epithelium while mimicking in vivo physiology. This technique has led to support luminal growth of facultative or obligate anaerobic bacteria, such as E. coli, Clostridium difficile, or fecal matter containing complex microbiota (44-47). C. difficile, a leading cause of nosocomial antibiotic-associated diarrhea, is an obligate anaerobic bacterium in its vegetative form but oxygen tolerant via dormant spore formation (44, 48). Microinjection of anaerobic C. difficile into the lumen of intestinal organoids has been successful (45, 49). This suggests the hypoxic environment of the organoids with a sealed lumen and a mucus layer (29). However, given that the lumen of organoids is not in a perfect hypoxic state, it is difficult to sustain a stable co-culture with obligate anaerobic bacteria for a long period (43). In addition, it is hard to perform high-throughput experiment with the manually performed microinjection method; however, the recently reported system would allow us to approach high-throughput experiments (44, 50).
Co and colleagues have described a method to face the apical surface of the epithelium outside the organoids, referred to as reversed polarity while maintaining a 3D organoid structure (51). Upon removal of extracellular matrix proteins and subsequent continuous suspension culture, reversed polarity can be induced, enabling easy access to the apical side of the epithelium in the organoids (51). Moreover, these apical-out organoids can differentiate into the major intestinal epithelial cell types. Modeling infections of enteric pathogens such as Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes, and transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) have been successful with the apical-out intestinal organoids (51, 52). Compared to laborious microinjection, this technique is relatively easy to demonstrate interactions with pathogens or bacterial metabolites (43, 51). With this approach, differential preference of each pathogen towards a polarized epithelium was identified (i.e., S. Typhimurium on the apical side, L. monocytogenes on the basal side) (51). However, it is questionable whether the reversed organoids in suspension were tolerable to study long-term interactions with pathogens. In addition, investigating anaerobes in the apical-out intestinal organoids is not feasible due to the oxygen-rich environment.
3D organoids can be used to generate monolayers with the apical side facing upward (43, 53). Briefly, dissociated 3D organoids are plated as monolayers in a transwell, which enables separation between the apical and basal compartment where we can easily introduce microorgani-sms in the apical side (43, 54). However, this system is not optimal for culturing both obligate anaerobes and oxygen-requiring epithelial cells (43). To overcome this limitation, an anaerobic transwell system has been developed in which the apical chamber is anaerobic while the basal chamber is in aerobic conditions. Briefly, an anaerobic environment is generated by sealing the apical chamber with a plug and thus the epithelial monolayer could be co-cultured with obligate anaerobes such as Bifidobacteria, Clostiridium, and Akkermansia (55). However, the long-term culture of organoids as 2D monolayers generates low oxygen tension, causing cellular stress and reduced cell differentiation (56).
Oxygenation at the apical side in 2D monolayers can be improved by removing the medium from the upper chamber while keeping the basal side submerged in the medium (57). This air-liquid interface (ALI) method can supply oxygen and thus healthy epithelial monolayers can be maintained for a long period by reducing oxygen stress. Moreover, incorporating underlying stromal elements into the ALI is possible, thus preserving the epithelial-mesenchymal interactions (58). The ALI culture system provides an accessible model to study long-term host-pathogen interactions, as evidenced by robust growth and complete development of the gastrointestinal parasite Cryptosporidium with this system (59). However, the ALI system does not form a physiological lumen (60) and to culture obligate anaerobes in the ALI culture system, the apical compartment needs to be anoxic while host cells need to be oxygenated basolaterally.
Escherichia coli is one of the most well-known bacterial species, which is a member of the intestinal microbiome. Non-pathogenic E. coli produces vitamin K and B12 which provide benefits to the host, but certain pathogenic E. coli strains cause diseases (46). Co-culture of non-pathogenic E. coli with human intestinal organoids via microinjection has shown to induce hypoxia in the intestinal lumen, leading to maturation of the mucus layer, antimicrobial peptide production, and improved barrier function (47, 61). Pathogenic E. coli strains have been also applied to the human intestinal organoids, which includes enterohemorr-hagic E. coli (EHEC), a foodborne pathogen that causes bloody diarrhea and hemolytic uremic syndrome and enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC), the most common cause of children’s and traveler’s diarrhea in the developing countries (62, 63). Infecting pathogenic EHEC into 3D human intestinal organoids caused hypoxia and intestinal maturity, like those infected with non-pathogenic E. coli (61). However, unlike non-pathogenic E. coli, EHEC severely destroyed the epithelial barrier, induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and initiated inflammatory responses (61). Infecting pathogenic E. coli including EHEC and ETEC in 2D intestinal organoid monolayers confirmed that E. coli infection occurred on the apical surface of the intestinal epithelium (54, 64). In addition, with 2D human colonoid monolayers, EHEC-induced early molecular events such as mucin layer reduction and microvillar effacement have been identified (54). Furthermore, a human enteroid-macrophage co-culture system has revealed that macrophages facing the basal side can kill luminal pathogens such as ETEC attached to the apical side across the intestinal monolayer (65).
Shigella, an intracellular pathogen, causes intense inflammation in the colonic and rectal epithelium (66). In human intestinal organoid monolayers derived from the small intestine and colon, basolateral infection and intracellular replication of S. flexneri have been recapitulated (67, 68). S. flexneri invasion in monolayers increased NF-κB-mediated inflammation signaling pathway and production of MUC2 (26, 67, 68). However, the apical invasion of S. flexneri can be increased by M cell induction or tight junction disruption in monolayers (67, 68).
Salmonella, a major foodborne pathogen, causes enteric fever and acute self-limiting gastroenteritis (69). Apical infection preference of S. Typhimurium has been demonstrated in the reversed epithelial polarity organoids (51). S. Typhimurium was able to invade the epithelial barriers and increase the expression of innate immune responses, inflammation, and cytokine-mediated signals upon apical infection via microinjection (70). In addition, infection of S. Typhimurium in 2D monolayers induces transdifferen-tiation of enterocytes into functional M cells (71). However, basolateral infection of S. Typhimurium seemed to be effective in disrupting tight junctions and enhancing NF‐κB signaling in 3D murine intestinal organoids (72). Infection of another serovar strain of Salmonella enterica, S. Typhi in human intestinal organoid-derived monolayers has shown to reproduce phenotypes observed in the infected tissue such as microvilli destruction, cytoskeleton rearrangement, and vesicle-contained bacteria (69, 73).
Vibrio cholerae causes human diarrheal pandemic disease cholera. V. cholerae has two major virulence factors, Cholerae toxin (CT) and toxin-coregulated pili (TCP) (74). CT is sufficient to induce severe diarrhea, which is caused by CT-induced electrolyte imbalance (75). Specifically, CT binding to GM1 receptors induces the entry of CT into the epithelium and after the activation of several signal transduction pathways, cAMP levels are increased. Increased cAMP then leads to increased chloride secretion into the lumen via the activation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane receptor (CFTR) and reduced sodium uptake via the inhibition of sodium-hydrogen exchanger 3 (NHE3). This net electrolyte imbalance leads to watery diarrhea characteristic of cholera (76, 77). Therefore, as a strategy to prevent diarrhea caused by CT, blocking of GM1 binding using random polymers carrying galactose and fucose has been reported in the human enteroids (78). In vivo pathology of CT has shown to be recapitulated in human organoids such as GM1 or NHE3-dependent CT-induced swelling of organoids (79, 80). Moreover, intestinal organoids derived from O-blood group and A-blood group provided a direct clue as to why O-blood group is associated with more severe cholera infections (81).
Clostridium difficile, the cause of severe diarrhea and colitis, can spread via the fecal-oral route (82). The pathogenicity of C. difficile is mediated by two exotoxins, TcdA and TcdB, which disrupt the cytoskeletal structure and the tight junction of the intestinal epithelium (83). In vivo pathologies of C. difficile such as epithelial barrier disruption were recapitulated in the human intestinal organoids infected with C. difficile, or injected with TcdA (44, 48). In the human jejunal enteroids, TcdA receptor levels were higher than TcdB receptors (84). Similarly, TcdA was 10-fold more effective in disrupting cytoskeletal rearrangement than TcdB in the 2D jejunal enteroid monolayers. Moreover, bacitracin, an antibiotic known to inhibit the cell wall synthesis of gram-positive bacteria, can protect human intestinal organoids from C. difficile-induced destruction of F-actin (85). This suggests that the human enteroid system is a great tool to investigate the clinical efficacy of drugs against C. difficile infections.
Human norovirus, the most common causative agent of acute gastroenteritis, causes vomiting and diarrhea worldwide (86). Since the discovery of norovirus, many resear-chers have attempted to cultivate human norovirus in vitro, but most efforts were unsuccessful (87, 88). Interestingly, however, norovirus can be replicated when co-cultured with human small intestinal organoid-derived monolayers (89). Moreover, human intestinal organoids are effective to identify norovirus inactivation factors (89, 90).
Rotavirus is the leading cause of serious gastroenteritis in young children worldwide (91). The growth of human rotavirus is limited in most transformed cell lines and animal models. However, rotavirus can also be cultured in human and murine intestinal organoids (92, 93). Further-more, organoids infected with rotavirus can produce virus particles, and the viral replication in organoids was inhibited by interferon-alpha and ribavirin treatment (92). Importantly, human intestinal organoids were more permissive to human rotavirus infection than mouse intestinal organoids, demonstrating host specificity of human rotavirus (93).
Since the human microbiome project began, important roles of commensal bacteria in the gut homeostasis, such as the supply of essential nutrients, metabolism of indigestible compounds, and stimulation of the immune system have been emphasized (94, 95). For example, Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Akkermansia, and Eubacterium spp. have been suggested to be associated with good intestinal health (96-98). Lactobacillus spp. such as L. rhamnosus, L. reuteri, and L. plantarum have been shown to enhance maturation, proliferation, and barrier function of the intestinal organoids (99-101). In addition, Lactobacillus spp. growth was more supported by mature human intestinal organoids than immature human intestinal organoids (101). This suggests that intestinal organoids can be used to investigate host effects towards microorganisms as well as the effects of microorganisms on the intestinal epithelium.
Compared to Lactobacillus spp, facultative anaerobes, obligate anaerobic bacteria such as Bifidobacterium, Akkermansia, and Eubacterium, the dominant species in the large intestine require a hypoxic environment. Co-culture of B. adolescentis and E. hallii with Caco-2 cells has shown to be successful with the anoxic-oxic interface-on-a-chip for up to 1 week (102). However, the co-culture of human colonic organoids with obligate anaerobes has been challenging until Sasaki and colleagues established the 2D-intestinal hemi-anaerobic coculture system (iHACS), consisting of a hypoxia apical chamber and a normoxic basal chamber (55). In this iHACS system, B. adolescentis significantly increased the expression of markers for goblet and stem cells. Unlike B. adolescentis, A. muciniphila uses mucin as a carbon source instead of glucose. Differentiated human colonic organoids but not undifferentiated organoids can support the growth of A. muciniphila, which supports the role of goblet cell-derived mucin as a carbon source for this bacterium (55). This indicates that proper use of organoid systems would enable us to model competitive or beneficial interactions between human epithelium and commensals.
Microorganisms including pathogens often have a tissue tropism (i.e., small intestine versus large intestine) (Table 1, Fig. 1). As mentioned earlier, the AdSCs-derived intestinal organoids retain their own highly stable gut segment-specific epigenetic regional identities (41). However, the iPSCs-derived intestinal organoids might retain epigenetic memory of non-intestinal tissue of origin and showed small intestine properties in the most studies (35, 38, 39). Thus, it is necessary to choose proper intestinal organoid systems based on the regionality of microorganisms (Table 1, Fig. 1). For example, Shigella, S. Typhi, and C. difficile show the highest adhesion to the large intestine (68, 103, 104). However, some in vitro models of these pathogen infections have been established in organoids with small intestinal properties (39, 48, 68, 73, 84, 85). On the other hand, in some cases, pathogens with a preference towards the small intestine are studied in the large intestine-derived organoids (79, 81, 92, 99). If the tissue tropism of microorganisms is not considered, it might lead to wrong interpretation. For example, pathogenic enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) with preference towards the large intestine increased expression of Muc2 and tight junction proteins in the hESCs-derived small intestinal organoids whereas it reduced Muc2 expression and integrity of tight junction in human colonoids (54, 61). Similarly, EHEC infection in vivo redistributed the tight junction protein (105). Therefore, for better modeling of the interactions between human intestinal epithelium and microorganisms, the tissue tropism of microorganisms and it’s matched organoid systems should be considered.
Although there has been enormous progress in the use of human intestinal organoids for modeling interactions with microorganisms, it is still at an immature stage in applying various gut environmental factors other than anaerobic conditions. Here, we will describe various gut milieu (Fig. 1), which needs to be considered in future intestinal organoid research.
Microbial fermentation activity in the gut can influence oxygen levels and pH. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate are products of microbial fermentation of dietary fibers (106). Primarily, SCFAs are used as energy substrates in oxidative phospho-rylation, where oxygen is consumed to produce ATP. For example, microbial butyrate limits the bioavailability of oxygen and maintains intestinal homeostasis via PPARγ-mediated β oxidation of butyrate or hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) stabilization (107, 108). Without microbial butyrate, oxygen levels were high in the intestinal epithelium in germ-free mice, whereas butyrate supplementation restored oxygen levels in antibiotics-treated mice (108, 109). Different from epithelial oxygen levels, luminal oxygen levels in germ-free mice and conventional mice were nearly identical along the intestinal tract (110). This suggests the existence of a host-derived oxygen consumption mechanism (i.e., lipid oxidation) other than microbial respiration although the oxygen consumption rate was slower in the germ-free mice than conventionally-raised mice (110).
In addition, the oxygen concentrations of the intestine need to be considered in two directions - longitudinal and cross-sectional. First, there is a longitudinal steep decrease in the oxygen gradient from the proximal small intestine to the distal colon. Luminal pO2 in the small intestine is about 10 mmHg (∼2% O2), which decreases rapidly along the gut axis and reaches less than 3 mmHg in the sigmoid colon (∼0.4% O2) (111). Second, there is a steep decrease in the oxygen from the base of the epithelium to the lumen. In the small intestine, pO2 at the intestinal barrier is about 59 mmHg (∼8% O2), about 22 mmHg (∼3% O2) at the tip of the villus, and less than 10 mmHg (∼2% O2) in the lumen (111). In the large intestine, pO2 of the colonic muscle wall is around 42∼71 mmHg (∼6-9% O2), about 42 mmHg (∼6% O2) in the vascularized submucosa, 5∼10 mmHg (∼0.6-1.3% O2) at the crypt-lumen interface, and less than 3 mmHg (∼0.4% O2) in the lumen of the sigmoid colon (111, 112). Therefore, strict anaerobes could grow in this anaerobic environment in the large intestine (111).
Microbial fermentative products, SCFAs, also affect pH in the colon, sharply dropping to 6 in the cecum and rising back to 6.7 in the rectum (113-115). The pH of the small intestine can be affected by stomach acid (pH 1.4) and pancreatic juice (pH 8.6). The pH of the duodenum is about 6.0, which becomes 7.1 in the jejunum and 7.4 in the ileum (116, 117). The intestinal pH can be altered by intake of food or water, and these variations in pH affect microbial community and metabolism (118).
Beyond SCFAs, the gut microbiota can metabolize primary bile acids, synthesized in the liver, into secondary bile acids and the amino acid tryptophan into indole-containing compounds (119). Despite the successful replication of previously non-cultivatable human noroviruses in human organoids, not every norovirus strain can replicate. Interestingly, bile acids have been shown to induce strain-dependent norovirus replication such as GI.1, GII.3, GII.17 and enhance infectivity (89, 90, 120). In addition, microbial indole-3-propionic acid and indole-3-al-dehyde have been shown to increase the expression of IL-10 receptor ligand-binding subunit, mediating anti-inflammatory IL-10 action in human intestinal organoids (121, 122). These suggest that microbial metabolites need to be considered as important gut milieu to better mimic in vivo gut, in addition to oxygen and pH.
Another important gut milieu to consider is immune cells interacting with the intestinal epithelium and the microbiota. Immune cells such as T cells, innate lymphoid cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages have shown to affect differentiation and barrier function of the intestinal epithelium, which in turn can prevent infections (123, 124) and might affect microbial composition (125). Intestinal dendritic cells have suggested to compartmentalize the commensal microbiota via sampling of the gut bacteria for antigen presentation (126). Moreover, the immune system maintains a homeostatic relationship with microbiota by a mucosal firewall, a structural and immunological component made in cooperation with mucosal cells, IgA, antibacterial peptides, and immune cells (127). For example, a diversified and selected IgA has suggested to maintain balanced microbiome and to prevent inflammation (126). Thus, immune cells are important gut milieu when modelling the real interactions between the intestinal epithelium and commensals or pathogens.
Human intestinal organoids have made it possible to establish models that mimic actual organs (50). Hence, it can overcome the limitations of intrinsic anatomical and cellular differences in the intestine between human and animal models and is a promising human-microorganism interaction model. However, culture conditions for intestinal organoid establishment may not match the environment for the survival of microorganisms in the gut (50, 128).
The oxygen concentration is one of the representative mismatched conditions. Intestinal oxygen concentration is controlled by microbial and epithelial oxygen consumption. In the human newborn intestine, the facultative bacteria such as Escherichia, Streptococcus, and Enterobacteriaceae, colonizing during the first 2 weeks, can consume oxygen and lower the redox potential to negative values (129, 130). This enables colonization of the obligate anaerobes such as Bifidobacterium, Clostridia, and Bacteroides (130, 131). Subsequently, saccharolytic bacterial fermentation activity of normal intestinal microbiota generates beneficial SCFAs, lowering pH. Specifically, butyrate reduces epithelial oxygenation levels via β-oxidation of butyrate and thus prevents dysbiotic expansion of aerotolerant pathogens such as V. cholerae, S. enterica, and S. flexneri (26, 132, 133).
Intestinal organoid culture conditions in vitro, however, are enriched with high glucose, but devoid of butyrate. Colonocytes in vivo use butyrate as a primary energy source, but energy sources can be converted into glucose when butyrate is depleted (107, 134). Thus, even if we add butyrate as an alternative energy source in the presence of high levels of glucose in intestinal organoid cultures, glycolysis will occur more predominantly than oxidative phosphorylation. This can lead to the accumulation of butyrate, enough to act as a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor (106, 133, 135). Indeed, butyrate and valproic acid, structurally similar to butyrate, have been shown to affect intestinal organoid stem cell function via HDAC inhibition under the typical intestinal organoid culture conditions (136, 137). Therefore, optimizing glucose and butyrate concentrations would be required to induce β-oxida-tion of butyrate and, as well as sustain functional intestinal organoid cultures where subsequently induced physiological hypoxia would generate a suitable environment for microorganisms-intestinal epithelium interactions.
Given that the gut milieu such as oxygen, pH, metabolites, and immune cells are regulated by the interaction of gut microbiota and intestinal epithelial cells, the gut microbiota transplantation into intestinal organoids may help to simulate actual intestinal physiological activity (45). However, intestinal organoid culture conditions in vitro are also enriched with amino acids, but devoid of fibers. Under the traditional organoid culture conditions, ssacharolytic bacteria cannot ferment fibers but assacharolytic bacteria can use amino acids as their carbon source, which potentially generates toxic metabolites (138, 139). It would thus be critical to use physiologically relevant culture conditions to maintain transplanted microbiota in intestinal organoids.
From the perspective of pathogens, changes in environmental signals during host infection can trigger an adaptive response to survive and affect the expression of virulence genes (140). For instance, anaerobic conditions can enhance S. flexneri invasion by the activation of the type 3 secretion system (141). Bile acids can increase the survivability and pathogenicity of some enteric pathogens (142, 143). To sum up, when studying host-pathogen interaction, efforts should be made to generate an environment in which pathogenicity can be expressed for each pathogen by reflecting the actual environment as much as possible.
Acknowledgments
This paper is supported by Basic Science Research Institute Fund, whose NRF grant number is 2021R1A6A1 A10042944 and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2020R1C1C1003241), and by POSCO Science Fellowship of POSCO TJ Park Foundation. This work is also supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2021R 1A6A3A01086599 to N.Y.P).
References
1. Guinane CM, Cotter PD. 2013; Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 6:295–308. DOI: 10.1177/1756283X13482996. PMID: 23814609. PMCID: PMC3667473.

2. Rothschild D, Weissbrod O, Barkan E, Kurilshikov A, Korem T, Zeevi D, Costea PI, Godneva A, Kalka IN, Bar N, Shilo S, Lador D, Vila AV, Zmora N, Pevsner-Fischer M, Israeli D, Kosower N, Malka G, Wolf BC, Avnit-Sagi T, Lotan-Pompan M, Weinberger A, Halpern Z, Carmi S, Fu J, Wijmenga C, Zhernakova A, Elinav E, Segal E. 2018; Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature. 555:210–215. DOI: 10.1038/nature25973. PMID: 29489753.

3. Schroeder BO, Bäckhed F. 2016; Signals from the gut microbiota to distant organs in physiology and disease. Nat Med. 22:1079–1089. DOI: 10.1038/nm.4185. PMID: 27711063.

4. Turnbaugh PJ, Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Knight R, Gordon JI. 2009; The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome: a metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci Transl Med. 1:6ra14. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000322. PMID: 20368178. PMCID: PMC2894525.

5. Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Cheng J, Duncan AE, Kau AL, Griffin NW, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Ilkayeva O, Semenkovich CF, Funai K, Hayashi DK, Lyle BJ, Martini MC, Ursell LK, Clemente JC, Van Treuren W, Walters WA, Knight R, Newgard CB, Heath AC, Gordon JI. 2013; Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science. 341:1241214. DOI: 10.1126/science.1241214. PMID: 24009397. PMCID: PMC3829625.

6. Arrieta MC, Walter J, Finlay BB. 2016; Human microbiota-associated mice: a model with challenges. Cell Host Microbe. 19:575–578. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.04.014. PMID: 27173924.

7. Britton GJ, Contijoch EJ, Mogno I, Vennaro OH, Llewellyn SR, Ng R, Li Z, Mortha A, Merad M, Das A, Gevers D, McGovern DPB, Singh N, Braun J, Jacobs JP, Clemente JC, Grinspan A, Sands BE, Colombel JF, Dubinsky MC, Faith JJ. 2019; Microbiotas from humans with inflammatory bowel disease alter the balance of gut Th17 and RORγt+ regulatory T cells and exacerbate colitis in mice. Immunity. 50:212–224.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.015. PMID: 30650377. PMCID: PMC6512335.

8. Sampson TR, Debelius JW, Thron T, Janssen S, Shastri GG, Ilhan ZE, Challis C, Schretter CE, Rocha S, Gradinaru V, Chesselet MF, Keshavarzian A, Shannon KM, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Wittung-Stafshede P, Knight R, Mazmanian SK. 2016; Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson's disease. Cell. 167:1469–1480.e12. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.018. PMID: 27912057. PMCID: PMC5718049.

9. Sharon G, Cruz NJ, Kang DW, Gandal MJ, Wang B, Kim YM, Zink EM, Casey CP, Taylor BC, Lane CJ, Bramer LM, Isern NG, Hoyt DW, Noecker C, Sweredoski MJ, Moradian A, Borenstein E, Jansson JK, Knight R, Metz TO, Lois C, Geschwind DH, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Mazmanian SK. 2019; Human gut microbiota from autism spectrum disorder promote behavioral symptoms in mice. Cell. 177:1600–1618.e17. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.004. PMID: 31150625. PMCID: PMC6993574.

10. Staley C, Kaiser T, Beura LK, Hamilton MJ, Weingarden AR, Bobr A, Kang J, Masopust D, Sadowsky MJ, Khoruts A. 2017; Stable engraftment of human microbiota into mice with a single oral gavage following antibiotic conditioning. Microbiome. 5:87. DOI: 10.1186/s40168-017-0306-2. PMID: 28760163. PMCID: PMC5537947.

11. Hintze KJ, Cox JE, Rompato G, Benninghoff AD, Ward RE, Broadbent J, Lefevre M. 2014; Broad scope method for creating humanized animal models for animal health and disease research through antibiotic treatment and human fecal transfer. Gut Microbes. 5:183–191. DOI: 10.4161/gmic.28403. PMID: 24637796. PMCID: PMC4063843.

12. Cox LM, Yamanishi S, Sohn J, Alekseyenko AV, Leung JM, Cho I, Kim SG, Li H, Gao Z, Mahana D, Zárate Rodriguez JG, Rogers AB, Robine N, Loke P, Blaser MJ. 2014; Altering the intestinal microbiota during a critical developmental window has lasting metabolic consequences. Cell. 158:705–721. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.052. PMID: 25126780. PMCID: PMC4134513.

13. Nguyen TL, Vieira-Silva S, Liston A, Raes J. 2015; How informative is the mouse for human gut microbiota research? Dis Model Mech. 8:1–16. DOI: 10.1242/dmm.017400. PMID: 25561744. PMCID: PMC4283646.

14. Chung H, Pamp SJ, Hill JA, Surana NK, Edelman SM, Troy EB, Reading NC, Villablanca EJ, Wang S, Mora JR, Umesaki Y, Mathis D, Benoist C, Relman DA, Kasper DL. 2012; Gut immune maturation depends on colonization with a host-specific microbiota. Cell. 149:1578–1593. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.037. PMID: 22726443. PMCID: PMC3442780.

15. Winston JA, Theriot CM. 2020; Diversification of host bile acids by members of the gut microbiota. Gut Microbes. 11:158–171. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2019.1674124. PMID: 31595814. PMCID: PMC7053883. PMID: 2d1d8891264645709fb6e93bb37d99c1.

16. Spor A, Koren O, Ley R. 2011; Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 9:279–290. DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2540. PMID: 21407244.

17. Casadevall A, Pirofski LA. 2009; Virulence factors and their mechanisms of action: the view from a damage-response framework. J Water Health. 7 Suppl 1:S2–S18. DOI: 10.2166/wh.2009.036. PMID: 19717929.

18. Sarkar S, Heise MT. 2019; Mouse models as resources for studying infectious diseases. Clin Ther. 41:1912–1922. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.08.010. PMID: 31540729. PMCID: PMC7112552.

19. Swearengen JR. 2018; Choosing the right animal model for infectious disease research. Animal Model Exp Med. 1:100–108. DOI: 10.1002/ame2.12020. PMID: 30891554. PMCID: PMC6388060.

20. Kolawole AO, Wobus CE. 2020; Gastrointestinal organoid technology advances studies of enteric virus biology. PLoS Pathog. 16:e1008212. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008212. PMID: 31999791. PMCID: PMC6991956. PMID: a7c35bb50e8c418e90dc62abc9c630e8.

21. Baker BM, Chen CS. 2012; Deconstructing the third dimension: how 3D culture microenvironments alter cellular cues. J Cell Sci. 125(Pt 13):3015–3024. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.079509. PMID: 22797912. PMCID: PMC3434846.
22. Kapałczyńska M, Kolenda T, Przybyła W, Zajączkowska M, Teresiak A, Filas V, Ibbs M, Bliźniak R, Łuczewski Ł, Lamperska K. 2018; 2D and 3D cell cultures - a comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch Med Sci. 14:910–919. DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2016.63743. PMID: 30002710. PMCID: PMC6040128.

23. Pampaloni F, Reynaud EG, Stelzer EH. 2007; The third dimension bridges the gap between cell culture and live tissue. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:839–845. DOI: 10.1038/nrm2236. PMID: 17684528.

24. Kim J, Koo BK, Knoblich JA. 2020; Human organoids: model systems for human biology and medicine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:571–584. DOI: 10.1038/s41580-020-0259-3. PMID: 32636524. PMCID: PMC7339799.

25. Angus HC, Butt AG, Schultz M, Kemp RA. 2020; Intestinal organoids as a tool for inflammatory bowel disease research. Front Med (Lausanne). 6:334. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00334. PMID: 32010704. PMCID: PMC6978713. PMID: fbe13b4e28064edb9a11b5e5f9534012.

26. Hentschel V, Arnold F, Seufferlein T, Azoitei N, Kleger A, Müller M. 2021; Enteropathogenic infections: organoids go bacterial. Stem Cells Int. 2021:8847804. DOI: 10.1155/2021/8847804. PMID: 33505475. PMCID: PMC7810537.

27. Min S, Kim S, Cho SW. 2020; Gastrointestinal tract modeling using organoids engineered with cellular and microbiota niches. Exp Mol Med. 52:227–237. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-020-0386-0. PMID: 32103122. PMCID: PMC7062772. PMID: 2bb77a6b61684d79a3525dbeddc5abb9.

28. Allam-Ndoul B, Castonguay-Paradis S, Veilleux A. 2020; Gut microbiota and intestinal trans-epithelial permeability. Int J Mol Sci. 21:6402. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21176402. PMID: 32899147. PMCID: PMC7503654. PMID: 79676aa3a9344219b2be8bbbb2766a65.

29. Bartfeld S. 2016; Modeling infectious diseases and host-microbe interactions in gastrointestinal organoids. Dev Biol. 420:262–270. DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.09.014. PMID: 27640087.

30. Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ, Clevers H. 2007; Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 449:1003–1007. DOI: 10.1038/nature06196. PMID: 17934449.

31. Sato T, Vries RG, Snippert HJ, van de Wetering M, Barker N, Stange DE, van Es JH, Abo A, Kujala P, Peters PJ, Clevers H. 2009; Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature. 459:262–265. DOI: 10.1038/nature07935. PMID: 19329995.

32. Sato T, Stange DE, Ferrante M, Vries RG, Van Es JH, Van den Brink S, Van Houdt WJ, Pronk A, Van Gorp J, Siersema PD, Clevers H. 2011; Long-term expansion of epithelial organoids from human colon, adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and Barrett's epithelium. Gastroenterology. 141:1762–1772. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.050. PMID: 21889923.

33. Trillhaase A, Maertens M, Aherrahrou Z, Erdmann J. 2021; Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in vascular research: from two-to three-dimensional organoids. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 17:1741–1753. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-021-10149-3. PMID: 33738695. PMCID: PMC7972819.

34. Tsuruta S, Uchida H, Akutsu H. 2020; Intestinal organoids generated from human pluripotent stem cells. JMA J. 3:9–19. DOI: 10.31662/jmaj.2019-0027. PMID: 33324771. PMCID: PMC7733741.

35. Kim K, Doi A, Wen B, Ng K, Zhao R, Cahan P, Kim J, Aryee MJ, Ji H, Ehrlich LI, Yabuuchi A, Takeuchi A, Cunniff KC, Hongguang H, McKinney-Freeman S, Naveiras O, Yoon TJ, Irizarry RA, Jung N, Seita J, Hanna J, Murakami P, Jaenisch R, Weissleder R, Orkin SH, Weissman IL, Feinberg AP, Daley GQ. 2010; Epigenetic memory in induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 467:285–290. DOI: 10.1038/nature09342. PMID: 20644535. PMCID: PMC3150836.

36. Watanabe N, Santostefano KE, Yachnis AT, Terada N. 2017; A pathologist's perspective on induced pluripotent stem cells. Lab Invest. 97:1126–1132. DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2017.81. PMID: 28759008. PMCID: PMC5918271.

37. Spence JR, Mayhew CN, Rankin SA, Kuhar MF, Vallance JE, Tolle K, Hoskins EE, Kalinichenko VV, Wells SI, Zorn AM, Shroyer NF, Wells JM. 2011; Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intestinal tissue in vitro. Nature. 470:105–109. DOI: 10.1038/nature09691. PMID: 21151107. PMCID: PMC3033971.

38. Sommer CA, Capilla A, Molina-Estevez FJ, Gianotti-Sommer A, Skvir N, Caballero I, Chowdhury S, Mostoslavsky G. 2018; Modeling APC mutagenesis and familial adenomatous polyposis using human iPS cells. PLoS One. 13:e0200657. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200657. PMID: 30024920. PMCID: PMC6053155.

39. Takahashi Y, Sato S, Kurashima Y, Yamamoto T, Kurokawa S, Yuki Y, Takemura N, Uematsu S, Lai CY, Otsu M, Matsuno H, Osawa H, Mizushima T, Nishimura J, Hayashi M, Yamaguchi T, Kiyono H. 2018; A refined culture system for human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived intestinal epithelial organoids. Stem Cell Reports. 10:314–328. DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.11.004. PMID: 29233552. PMCID: PMC5768885. PMID: c4006f10f2d34228a3837a3832bd0c9b.

40. Crespo M, Vilar E, Tsai SY, Chang K, Amin S, Srinivasan T, Zhang T, Pipalia NH, Chen HJ, Witherspoon M, Gordillo M, Xiang JZ, Maxfield FR, Lipkin S, Evans T, Chen S. 2017; Colonic organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells for modeling colorectal cancer and drug testing. Nat Med. 23:878–884. Erratum in: Nat Med 2018;24:526. DOI: 10.1038/nm0418-526a. PMID: 29634683.

41. Kraiczy J, Nayak KM, Howell KJ, Ross A, Forbester J, Salvestrini C, Mustata R, Perkins S, Andersson-Rolf A, Leenen E, Liebert A, Vallier L, Rosenstiel PC, Stegle O, Dougan G, Heuschkel R, Koo BK, Zilbauer M. 2019; DNA methylation defines regional identity of human intestinal epithelial organoids and undergoes dynamic changes during development. Gut. 68:49–61. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314817. PMID: 29141958. PMCID: PMC6839835.

42. Han X, Mslati MA, Davies E, Chen Y, Allaire JM, Vallance BA. 2021; Creating a more perfect union: modeling intestinal bacteria-epithelial interactions using organoids. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:769–782. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.04.010. PMID: 33895425. PMCID: PMC8273413.

43. Poletti M, Arnauts K, Ferrante M, Korcsmaros T. 2021; Organoid-based models to study the role of host-microbiota interactions in IBD. J Crohns Colitis. 15:1222–1235. DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa257. PMID: 33341879. PMCID: PMC8256633.

44. Williamson IA, Arnold JW, Samsa LA, Gaynor L, DiSalvo M, Cocchiaro JL, Carroll I, Azcarate-Peril MA, Rawls JF, Allbritton NL, Magness ST. 2018; A high-throughput organoid microinjection platform to study gastrointestinal microbiota and luminal physiology. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:301–319. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.05.004. PMID: 30123820. PMCID: PMC6092482.

45. Leslie JL, Huang S, Opp JS, Nagy MS, Kobayashi M, Young VB, Spence JR. 2015; Persistence and toxin production by Clostridium difficile within human intestinal organoids result in disruption of epithelial paracellular barrier function. Infect Immun. 83:138–145. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.02561-14. PMID: 25312952. PMCID: PMC4288864.

46. Blount ZD. 2015; The unexhausted potential of E. coli. Elife. 4:e05826. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.05826. PMID: 25807083. PMCID: PMC4373459. PMID: 0dec92df648d4db59dd563d07a49a524.

47. Hill DR, Huang S, Nagy MS, Yadagiri VK, Fields C, Mukherjee D, Bons B, Dedhia PH, Chin AM, Tsai YH, Thodla S, Schmidt TM, Walk S, Young VB, Spence JR. 2017; Bacterial colonization stimulates a complex physiological response in the immature human intestinal epithelium. Elife. 6:e29132. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.29132. PMID: 29110754. PMCID: PMC5711377. PMID: 4f3e225ce6c5433682f7583fb2e61dd3.

48. Jump RL, Pultz MJ, Donskey CJ. 2007; Vegetative Clostridium difficile survives in room air on moist surfaces and in gastric contents with reduced acidity: a potential mechanism to explain the association between proton pump inhibitors and C. difficile-associated diarrhea? Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 51:2883–2887. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01443-06. PMID: 17562803. PMCID: PMC1932506.

49. Engevik MA, Yacyshyn MB, Engevik KA, Wang J, Darien B, Hassett DJ, Yacyshyn BR, Worrell RT. 2015; Human Clostridium difficile infection: altered mucus production and composition. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 308:G510–G524. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00091.2014. PMID: 25552581. PMCID: PMC4422372.
50. Puschhof J, Pleguezuelos-Manzano C, Martinez-Silgado A, Akkerman N, Saftien A, Boot C, de Waal A, Beumer J, Dutta D, Heo I, Clevers H. 2021; Intestinal organoid cocultures with microbes. Nat Protoc. 16:4633–4649. DOI: 10.1038/s41596-021-00589-z. PMID: 34381208.

51. Co JY, Margalef-Català M, Li X, Mah AT, Kuo CJ, Monack DM, Amieva MR. 2019; Controlling epithelial polarity: a human enteroid model for host-pathogen interactions. Cell Rep. 26:2509–2520.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.108. PMID: 30811997. PMCID: PMC6391775.

52. Li Y, Yang N, Chen J, Huang X, Zhang N, Yang S, Liu G, Liu G. 2020; Next-generation porcine intestinal organoids: an apical-out organoid model for swine enteric virus infection and immune response investigations. J Virol. 94:e01006–20. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01006-20. PMID: 32796075. PMCID: PMC7565635.

53. Thorne CA, Chen IW, Sanman LE, Cobb MH, Wu LF, Altschuler SJ. 2018; Enteroid monolayers reveal an autonomous WNT and BMP circuit controlling intestinal epithelial growth and organization. Dev Cell. 44:624–633.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.01.024. PMID: 29503158. PMCID: PMC5849535.

54. In J, Foulke-Abel J, Zachos NC, Hansen AM, Kaper JB, Bernstein HD, Halushka M, Blutt S, Estes MK, Donowitz M, Kovbasnjuk O. 2016; Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli reduce mucus and intermicrovillar bridges in human stem cell-derived colonoids. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2:48–62.e3. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2015.10.001. PMID: 26855967. PMCID: PMC4740923.
55. Sasaki N, Miyamoto K, Maslowski KM, Ohno H, Kanai T, Sato T. 2020; Development of a scalable coculture system for gut anaerobes and human colon epithelium. Gastroenterology. 159:388–390.e5. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.021. PMID: 32199883.

56. Wang Y, Chiang IL, Ohara TE, Fujii S, Cheng J, Muegge BD, Ver Heul A, Han ND, Lu Q, Xiong S, Chen F, Lai CW, Janova H, Wu R, Whitehurst CE, VanDussen KL, Liu TC, Gordon JI, Sibley LD, Stappenbeck TS. 2019; Long-term culture captures injury-repair cycles of colonic stem cells. Cell. 179:1144–1159.e15. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.015. PMID: 31708126. PMCID: PMC6904908.

57. Nossol C, Diesing AK, Walk N, Faber-Zuschratter H, Hartig R, Post A, Kluess J, Rothkötter HJ, Kahlert S. 2011; Air-liquid interface cultures enhance the oxygen supply and trigger the structural and functional differentiation of intestinal porcine epithelial cells (IPEC). Histochem Cell Biol. 136:103–115. DOI: 10.1007/s00418-011-0826-y. PMID: 21681518. PMCID: PMC3132278.

58. Ootani A, Li X, Sangiorgi E, Ho QT, Ueno H, Toda S, Sugihara H, Fujimoto K, Weissman IL, Capecchi MR, Kuo CJ. 2009; Sustained in vitro intestinal epithelial culture within a Wnt-dependent stem cell niche. Nat Med. 15:701–706. DOI: 10.1038/nm.1951. PMID: 19398967. PMCID: PMC2919216.

59. Wilke G, Funkhouser-Jones LJ, Wang Y, Ravindran S, Wang Q, Beatty WL, Baldridge MT, VanDussen KL, Shen B, Kuhlenschmidt MS, Kuhlenschmidt TB, Witola WH, Stappenbeck TS, Sibley LD. 2019; A stem-cell-derived platform enables complete Cryptosporidium development in vitro and genetic tractability. Cell Host Microbe. 26:123–134.e8. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.05.007. PMID: 31231046. PMCID: PMC6617391.
60. Choi KG, Wu BC, Lee AH, Baquir B, Hancock REW. 2020; Utilizing organoid and air-liquid interface models as a screening method in the development of new host defense peptides. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 10:228. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00228. PMID: 32509598. PMCID: PMC7251080. PMID: 8f772fa5525f461285d39a5ba67b128d.

61. Karve SS, Pradhan S, Ward DV, Weiss AA. 2017; Intestinal organoids model human responses to infection by commensal and Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli. PLoS One. 12:e0178966. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178966. PMID: 28614372. PMCID: PMC5470682.

62. Park SH, Seung HJ, Jeong HW, Park SY, Jung JH, Jin YH, Han SH, Kim HS, Kim JS, Park JH, Gong YJ, Hong CK, Lee JH, Kim IY, Jung K. 2018; Molecular characterization of enterotoxigenic escherichia coli in foodborne outbreak. J Bacteriol Virol. 48:113–120. DOI: 10.4167/jbv.2018.48.4.113.

63. Pacheco AR, Sperandio V. 2012; Shiga toxin in enterohemorrhagic E.coli: regulation and novel anti-virulence strategies. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2:81. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00081. PMID: 22919672. PMCID: PMC3417539.

64. Vermeire B, Gonzalez LM, Jansens RJJ, Cox E, Devriendt B. 2021; Porcine small intestinal organoids as a model to explore ETEC-host interactions in the gut. Vet Res. 52:94. Erratum in: Vet Res 2021;52:107. DOI: 10.1186/s13567-021-00961-7. PMID: 34174960. PMCID: PMC8235647. PMID: 8d83712726cf4c89819507d8bd9e82b1.

65. Noel G, Baetz NW, Staab JF, Donowitz M, Kovbasnjuk O, Pasetti MF, Zachos NC. 2017; A primary human macrophage-enteroid co-culture model to investigate mucosal gut physiology and host-pathogen interactions. Sci Rep. 7:45270. Erratum in: Sci Rep 2017;7:46790. DOI: 10.1038/srep46790. PMID: 28467395. PMCID: PMC5414479.

66. Zaidi MB, Estrada-García T. 2014; Shigella: a highly virulent and elusive pathogen. Curr Trop Med Rep. 1:81–87. DOI: 10.1007/s40475-014-0019-6. PMID: 25110633. PMCID: PMC4126259.

67. Ranganathan S, Doucet M, Grassel CL, Delaine-Elias B, Zachos NC, Barry EM. 2019; Evaluating shigella flexneri pathogenesis in the human enteroid model. Infect Immun. 87:e00740–18. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00740-18. PMID: 30642900. PMCID: PMC6434113.

68. Koestler BJ, Ward CM, Fisher CR, Rajan A, Maresso AW, Payne SM. 2019; Human intestinal enteroids as a model system of Shigella pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 87:e00733–18. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00733-18. PMID: 30642906. PMCID: PMC6434139.
69. Verma S, Senger S, Cherayil BJ, Faherty CS. 2020; Spheres of influence: insights into Salmonella pathogenesis from intestinal organoids. Microorganisms. 8:504. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8040504. PMID: 32244707. PMCID: PMC7232497. PMID: f11e35ed31c244bb86ef4b3a7eb2e513.

70. Forbester JL, Goulding D, Vallier L, Hannan N, Hale C, Pickard D, Mukhopadhyay S, Dougan G. 2015; Interaction of salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium with intestinal organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Infect Immun. 83:2926–2934. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00161-15. PMID: 25964470. PMCID: PMC4468523.

71. Rouch JD, Scott A, Lei NY, Solorzano-Vargas RS, Wang J, Hanson EM, Kobayashi M, Lewis M, Stelzner MG, Dunn JC, Eckmann L, Martín MG. 2016; Development of functional microfold (M) cells from intestinal stem cells in primary human enteroids. PLoS One. 11:e0148216. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148216. PMID: 26820624. PMCID: PMC4731053.

72. Zhang YG, Wu S, Xia Y, Sun J. 2014; Salmonella-infected crypt-derived intestinal organoid culture system for host-bacterial interactions. Physiol Rep. 2:e12147. DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12147. PMID: 25214524. PMCID: PMC4270227.

73. Nickerson KP, Senger S, Zhang Y, Lima R, Patel S, Ingano L, Flavahan WA, Kumar DKV, Fraser CM, Faherty CS, Sztein MB, Fiorentino M, Fasano A. 2018; Salmonella typhi colonization provokes extensive transcriptional changes aimed at evading host mucosal immune defense during early infection of human intestinal tissue. EBioMedicine. 31:92–109. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.04.005. PMID: 29735417. PMCID: PMC6013756.

74. Silva AJ, Benitez JA. 2016; Vibrio cholerae biofilms and cholera pathogenesis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 10:e0004330. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004330. PMID: 26845681. PMCID: PMC4741415.

75. Bharati K, Ganguly NK. 2011; Cholera toxin: a paradigm of a multifunctional protein. Indian J Med Res. 133:179–187. PMID: 21415492. PMCID: PMC3089049.
76. Subramanya SB, Rajendran VM, Srinivasan P, Nanda Kumar NS, Ramakrishna BS, Binder HJ. 2007; Differential regulation of cholera toxin-inhibited Na-H exchange isoforms by butyrate in rat ileum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 293:G857–G863. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00462.2006. PMID: 17690171.

77. Cervin J, Wands AM, Casselbrant A, Wu H, Krishnamurthy S, Cvjetkovic A, Estelius J, Dedic B, Sethi A, Wallom KL, Riise R, Bäckström M, Wallenius V, Platt FM, Lebens M, Teneberg S, Fändriks L, Kohler JJ, Yrlid U. 2018; GM1 ganglioside-independent intoxication by Cholera toxin. PLoS Pathog. 14:e1006862. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006862. PMID: 29432456. PMCID: PMC5825173. PMID: f798db5d3c714c6f9abd3318d6d329e7.

78. Cervin J, Boucher A, Youn G, Björklund P, Wallenius V, Mottram L, Sampson NS, Yrlid U. 2020; Fucose-galactose polymers inhibit cholera toxin binding to fucosylated structures and galactose-dependent intoxication of human enteroids. ACS Infect Dis. 6:1192–1203. DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00009. PMID: 32134631. PMCID: PMC7227030.

79. Zomer-van Ommen DD, Pukin AV, Fu O, Quarles van Ufford LH, Janssens HM, Beekman JM, Pieters RJ. 2016; Functional characterization of cholera toxin inhibitors using human intestinal organoids. J Med Chem. 59:6968–6972. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00770. PMID: 27347611.

80. Foulke-Abel J, In J, Kovbasnjuk O, Zachos NC, Ettayebi K, Blutt SE, Hyser JM, Zeng XL, Crawford SE, Broughman JR, Estes MK, Donowitz M. 2014; Human enteroids as an ex-vivo model of host-pathogen interactions in the gastrointestinal tract. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 239:1124–1134. DOI: 10.1177/1535370214529398. PMID: 24719375. PMCID: PMC4380516.

81. Kuhlmann FM, Santhanam S, Kumar P, Luo Q, Ciorba MA, Fleckenstein JM. 2016; Blood group O-dependent cellular responses to cholera toxin: parallel clinical and epidemiological links to severe cholera. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 95:440–443. DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0161. PMID: 27162272. PMCID: PMC4973196.

82. Fekety R. 1997; Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea and colitis. American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. Am J Gastroenterol. 92:739–750. PMID: 9149180.
83. Di Bella S, Ascenzi P, Siarakas S, Petrosillo N, di Masi A. 2016; Clostridium difficile toxins A and B: insights into pathogenic properties and extraintestinal effects. Toxins (Basel). 8:134. DOI: 10.3390/toxins8050134. PMID: 27153087. PMCID: PMC4885049.

84. Engevik MA, Danhof HA, Chang-Graham AL, Spinler JK, Engevik KA, Herrmann B, Endres BT, Garey KW, Hyser JM, Britton RA, Versalovic J. 2020; Human intestinal enteroids as a model of Clostridioides difficile-induced enteritis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 318:G870–G888. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00045.2020. PMID: 32223302. PMCID: PMC7272722.
85. Zhu Z, Schnell L, Müller B, Müller M, Papatheodorou P, Barth H. 2019; The antibiotic bacitracin protects human intestinal epithelial cells and stem cell-derived intestinal organoids from Clostridium difficile toxin TcdB. Stem Cells Int. 2019:4149762. DOI: 10.1155/2019/4149762. PMID: 31467562. PMCID: PMC6701344.
86. Ramani S, Atmar RL, Estes MK. 2014; Epidemiology of human noroviruses and updates on vaccine development. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 30:25–33. DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000022. PMID: 24232370. PMCID: PMC3955997.

87. Duizer E, Schwab KJ, Neill FH, Atmar RL, Koopmans MPG, Estes MK. 2004; Laboratory efforts to cultivate noroviruses. J Gen Virol. 85(Pt 1):79–87. DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.19478-0. PMID: 14718622.

88. Takanashi S, Saif LJ, Hughes JH, Meulia T, Jung K, Scheuer KA, Wang Q. 2014; Failure of propagation of human norovirus in intestinal epithelial cells with microvilli grown in three-dimensional cultures. Arch Virol. 159:257–266. DOI: 10.1007/s00705-013-1806-4. PMID: 23974469. PMCID: PMC3946686.

89. Ettayebi K, Crawford SE, Murakami K, Broughman JR, Karandikar U, Tenge VR, Neill FH, Blutt SE, Zeng XL, Qu L, Kou B, Opekun AR, Burrin D, Graham DY, Ramani S, Atmar RL, Estes MK. 2016; Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science. 353:1387–1393. DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf5211. PMID: 27562956. PMCID: PMC5305121.

90. Costantini V, Morantz EK, Browne H, Ettayebi K, Zeng XL, Atmar RL, Estes MK, Vinjé J. 2018; Human norovirus replication in human intestinal enteroids as model to evaluate virus inactivation. Emerg Infect Dis. 24:1453–1464. DOI: 10.3201/eid2408.180126. PMID: 30014841. PMCID: PMC6056096.

91. Arnold MM, Sen A, Greenberg HB, Patton JT. 2013; The battle between rotavirus and its host for control of the interferon signaling pathway. PLoS Pathog. 9:e1003064. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003064. PMID: 23359266. PMCID: PMC3554623. PMID: 6ad866c212a5451092ec18ad334c112d.

92. Yin Y, Bijvelds M, Dang W, Xu L, van der Eijk AA, Knipping K, Tuysuz N, Dekkers JF, Wang Y, de Jonge J, Sprengers D, van der Laan LJ, Beekman JM, Ten Berge D, Metselaar HJ, de Jonge H, Koopmans MP, Peppelenbosch MP, Pan Q. 2015; Modeling rotavirus infection and antiviral therapy using primary intestinal organoids. Antiviral Res. 123:120–131. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.09.010. PMID: 26408355.

93. Saxena K, Blutt SE, Ettayebi K, Zeng XL, Broughman JR, Crawford SE, Karandikar UC, Sastri NP, Conner ME, Opekun AR, Graham DY, Qureshi W, Sherman V, Foulke-Abel J, In J, Kovbasnjuk O, Zachos NC, Donowitz M, Estes MK. 2015; Human intestinal enteroids: a new model to study human rotavirus infection, host restriction, and pathophysiology. J Virol. 90:43–56. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01930-15. PMID: 26446608. PMCID: PMC4702582.

94. Khan R, Petersen FC, Shekhar S. 2019; Commensal bacteria: an emerging player in defense against respiratory pathogens. Front Immunol. 10:1203. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01203. PMID: 31214175. PMCID: PMC6554327.

95. Martín R, Miquel S, Ulmer J, Kechaou N, Langella P, Bermúdez-Humarán LG. 2013; Role of commensal and probiotic bacteria in human health: a focus on inflammatory bowel disease. Microb Cell Fact. 12:71. DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-12-71. PMID: 23876056. PMCID: PMC3726476.

96. Heeney DD, Gareau MG, Marco ML. 2018; Intestinal Lactobacillus in health and disease, a driver or just along for the ride? Curr Opin Biotechnol. 49:140–147. DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2017.08.004. PMID: 28866243. PMCID: PMC5808898.

97. Rinninella E, Raoul P, Cintoni M, Franceschi F, Miggiano GAD, Gasbarrini A, Mele MC. 2019; What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms. 7:14. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms7010014. PMID: 30634578. PMCID: PMC6351938.

98. Lordan C, Thapa D, Ross RP, Cotter PD. 2020; Potential for enriching next-generation health-promoting gut bacteria through prebiotics and other dietary components. Gut Microbes. 11:1–20. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2019.1613124. PMID: 31116628. PMCID: PMC6973326. PMID: 86c9abd4fe1e41118035d35a7711d4cc.

99. Han X, Lee A, Huang S, Gao J, Spence JR, Owyang C. 2019; Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents epithelial barrier dysfunction induced by interferon-gamma and fecal supernatants from irritable bowel syndrome patients in human intestinal enteroids and colonoids. Gut Microbes. 10:59–76. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2018.1479625. PMID: 30040527. PMCID: PMC6363076.

100. Wu H, Xie S, Miao J, Li Y, Wang Z, Wang M, Yu Q. 2020; Lactobacillus reuteri maintains intestinal epithelial regeneration and repairs damaged intestinal mucosa. Gut Microbes. 11:997–1014. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1734423. PMID: 32138622. PMCID: PMC7524370.

101. Son YS, Ki SJ, Thanavel R, Kim JJ, Lee MO, Kim J, Jung CR, Han TS, Cho HS, Ryu CM, Kim SH, Park DS, Son MY. 2020; Maturation of human intestinal organoids in vitro facilitates colonization by commensal lactobacilli by reinforcing the mucus layer. FASEB J. 34:9899–9910. DOI: 10.1096/fj.202000063R. PMID: 32602623.

102. Shin W, Wu A, Massidda MW, Foster C, Thomas N, Lee DW, Koh H, Ju Y, Kim J, Kim HJ. 2019; A robust longitudinal co-culture of obligate anaerobic gut microbiome with human intestinal epithelium in an anoxic-oxic interface-on-a-chip. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 7:13. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00013. PMID: 30792981. PMCID: PMC6374617.

103. Nickerson KP, Llanos-Chea A, Ingano L, Serena G, Miranda-Ribera A, Perlman M, Lima R, Sztein MB, Fasano A, Senger S, Faherty CS. 2021; A versatile human intestinal organoid-derived epithelial monolayer model for the study of enteric pathogens. Microbiol Spectr. 9:e0000321. DOI: 10.1128/Spectrum.00003-21. PMID: 34106568. PMCID: PMC8552518. PMID: 72c9a39e47f844738b9c99362443b4b3.

104. Kelly CP, LaMont JT. 1998; Clostridium difficile infection. Annu Rev Med. 49:375–390. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.med.49.1.375. PMID: 9509270.

105. Roxas JL, Koutsouris A, Bellmeyer A, Tesfay S, Royan S, Falzari K, Harris A, Cheng H, Rhee KJ, Hecht G. 2010; Enterohemorrhagic E. coli alters murine intestinal epithelial tight junction protein expression and barrier function in a Shiga toxin independent manner. Lab Invest. 90:1152–1168. DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.91. PMID: 20479715. PMCID: PMC2912457.

106. Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Bäckhed F. 2016; From dietary fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell. 165:1332–1345. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041. PMID: 27259147.

107. Byndloss MX, Olsan EE, Rivera-Chávez F, Tiffany CR, Cevallos SA, Lokken KL, Torres TP, Byndloss AJ, Faber F, Gao Y, Litvak Y, Lopez CA, Xu G, Napoli E, Giulivi C, Tsolis RM, Revzin A, Lebrilla CB, Bäumler AJ. 2017; Microbiota-activated PPAR-γ signaling inhibits dysbiotic Enterobacteriaceae expansion. Science. 357:570–575. DOI: 10.1126/science.aam9949. PMID: 28798125. PMCID: PMC5642957.

108. Kelly CJ, Zheng L, Campbell EL, Saeedi B, Scholz CC, Bayless AJ, Wilson KE, Glover LE, Kominsky DJ, Magnuson A, Weir TL, Ehrentraut SF, Pickel C, Kuhn KA, Lanis JM, Nguyen V, Taylor CT, Colgan SP. 2015; Crosstalk between microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and intestinal epithelial HIF augments tissue barrier function. Cell Host Microbe. 17:662–671. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.03.005. PMID: 25865369. PMCID: PMC4433427.

109. Konjar Š, Pavšič M, Veldhoen M. 2021; Regulation of oxygen homeostasis at the intestinal epithelial barrier site. Int J Mol Sci. 22:9170. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179170. PMID: 34502078. PMCID: PMC8431628. PMID: 74fd954f471649d896c2fbf200a92149.

110. Friedman ES, Bittinger K, Esipova TV, Hou L, Chau L, Jiang J, Mesaros C, Lund PJ, Liang X, FitzGerald GA, Goulian M, Lee D, Garcia BA, Blair IA, Vinogradov SA, Wu GD. 2018; Microbes vs. chemistry in the origin of the anaerobic gut lumen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 115:4170–4175. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1718635115. PMID: 29610310. PMCID: PMC5910840.

111. Singhal R, Shah YM. 2020; Oxygen battle in the gut: hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in metabolic and inflammatory responses in the intestine. J Biol Chem. 295:10493–10505. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011188. PMID: 32503843. PMCID: PMC7383395.

112. Lind Due V, Bonde J, Kann T, Perner A. 2003; Extremely low oxygen tension in the rectal lumen of human subjects. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 47:372. DOI: 10.1034/j.1399-6576.2003.00542.x. PMID: 12648210.

113. Walker AW, Duncan SH, McWilliam Leitch EC, Child MW, Flint HJ. 2005; pH and peptide supply can radically alter bacterial populations and short-chain fatty acid ratios within microbial communities from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 71:3692–3700. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.7.3692-3700.2005. PMID: 16000778. PMCID: PMC1169066.

114. Evans DF, Pye G, Bramley R, Clark AG, Dyson TJ, Hardcastle JD. 1988; Measurement of gastrointestinal pH profiles in normal ambulant human subjects. Gut. 29:1035–1041. DOI: 10.1136/gut.29.8.1035. PMID: 3410329. PMCID: PMC1433896.

115. Jubelin G, Desvaux M, Schüller S, Etienne-Mesmin L, Muniesa M, Blanquet-Diot S. 2018; Modulation of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli survival and virulence in the human gastrointestinal tract. Microorganisms. 6:115. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms6040115. PMID: 30463258. PMCID: PMC6313751.

116. Fallingborg J, Pedersen P, Jacobsen BA. 1998; Small intestinal transit time and intraluminal pH in ileocecal resected patients with Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 43:702–705. DOI: 10.1023/A:1018893409596. PMID: 9558022.
117. Takeshima T, Adler M, Nacchiero M, Rudick J, Dreiling DA. 1977; Effects of duodenal alkalinization on pancreatic secretion. Am J Gastroenterol. 67:54–62. PMID: 851106.
118. Duncan SH, Louis P, Thomson JM, Flint HJ. 2009; The role of pH in determining the species composition of the human colonic microbiota. Environ Microbiol. 11:2112–2122. DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01931.x. PMID: 19397676.

119. Koh A, Bäckhed F. 2020; From association to causality: the role of the gut microbiota and its functional products on host metabolism. Mol Cell. 78:584–596. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.03.005. PMID: 32234490.

120. Williams AN, Sherman MB, Smith HQ, Taube S, Pettitt BM, Wobus CE, Smith TJ. 2021; A norovirus uses bile salts to escape antibody recognition while enhancing receptor binding. J Virol. 95:e0017621. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00176-21. PMID: 33827952. PMCID: PMC8315966.

121. Liu JR, Miao H, Deng DQ, Vaziri ND, Li P, Zhao YY. 2021; Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolism mediates renal fibrosis by aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling activation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:909–922. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-020-03645-1. PMID: 32965514.

122. Alexeev EE, Lanis JM, Kao DJ, Campbell EL, Kelly CJ, Battista KD, Gerich ME, Jenkins BR, Walk ST, Kominsky DJ, Colgan SP. 2018; Microbiota-derived indole metabolites promote human and murine intestinal homeostasis through regulation of interleukin-10 receptor. Am J Pathol. 188:1183–1194. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.01.011. PMID: 29454749. PMCID: PMC5906738.

123. Viggiano D, Ianiro G, Vanella G, Bibbò S, Bruno G, Simeone G, Mele G. 2015; Gut barrier in health and disease: focus on childhood. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:1077–1085. PMID: 25855935.
124. Hou Q, Huang J, Ayansola H, Masatoshi H, Zhang B. 2021; Intestinal stem cells and immune cell relationships: potential therapeutic targets for inflammatory bowel diseases. Front Immunol. 11:623691. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.623691. PMID: 33584726. PMCID: PMC7874163. PMID: f735b04a2411496d816b623782d98dbb.

125. Fulde M, Sommer F, Chassaing B, van Vorst K, Dupont A, Hensel M, Basic M, Klopfleisch R, Rosenstiel P, Bleich A, Bäckhed F, Gewirtz AT, Hornef MW. 2018; Neonatal selection by Toll-like receptor 5 influences long-term gut microbiota composition. Nature. 560:489–493. Erratum in: Nature 2018;563:E25. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0395-5. PMID: 30089902.

126. Zheng D, Liwinski T, Elinav E. 2020; Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 30:492–506. DOI: 10.1038/s41422-020-0332-7. PMID: 32433595. PMCID: PMC7264227.

127. Belkaid Y, Hand TW. 2014; Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell. 157:121–141. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.011. PMID: 24679531. PMCID: PMC4056765.

128. Okkelman IA, Foley T, Papkovsky DB, Dmitriev RI. 2017; Live cell imaging of mouse intestinal organoids reveals heterogeneity in their oxygenation. Biomaterials. 146:86–96. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.08.043. PMID: 28898760.

129. Bezirtzoglou E. 1997; The intestinal microflora during the first weeks of life. Anaerobe. 3:173–177. DOI: 10.1006/anae.1997.0102. PMID: 16887585.

130. Adlerberth I. Hanson LA, Yolken RH, editors. 1999. Establishment of a normal intestinal microflora in the newborn infant. Probiotics, other nutritional factors, and intestinal microflora. Lippincott-Raven;Philadelphia: p. 63–78.
131. Moore TA, Hanson CK, Anderson-Berry A. 2011; Colonization of the gastrointestinal tract in neonates: a review. Infant Child Adolesc Nutr. 3:291–295. DOI: 10.1177/1941406411421629.
132. Schaffer K, Taylor CT. 2015; The impact of hypoxia on bacterial infection. FEBS J. 282:2260–2266. DOI: 10.1111/febs.13270. PMID: 25786849.

133. Salvi PS, Cowles RA. 2021; Butyrate and the intestinal epithelium: modulation of proliferation and inflammation in homeostasis and disease. Cells. 10:1775. DOI: 10.3390/cells10071775. PMID: 34359944. PMCID: PMC8304699. PMID: 473f2cbe475a4a28a4005e46d618255d.

134. Bultman SJ. 2016; Butyrate consumption of differentiated colonocytes in the upper crypt promotes homeostatic proliferation of stem and progenitor cells near the crypt base. Transl Cancer Res. 5(Suppl 3):S526–S528. DOI: 10.21037/tcr.2016.08.36. PMID: 30568890. PMCID: PMC6296489.

135. Singh B, Halestrap AP, Paraskeva C. 1997; Butyrate can act as a stimulator of growth or inducer of apoptosis in human colonic epithelial cell lines depending on the presence of alternative energy sources. Carcinogenesis. 18:1265–1270. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/18.6.1265. PMID: 9214612.

136. Yin X, Farin HF, van Es JH, Clevers H, Langer R, Karp JM. 2014; Niche-independent high-purity cultures of Lgr5+ intestinal stem cells and their progeny. Nat Methods. 11:106–112. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.2737. PMID: 24292484. PMCID: PMC3951815.

137. Gurvich N, Tsygankova OM, Meinkoth JL, Klein PS. 2004; Histone deacetylase is a target of valproic acid-mediated cellular differentiation. Cancer Res. 64:1079–1086. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-0799. PMID: 14871841.

138. Amaretti A, Gozzoli C, Simone M, Raimondi S, Righini L, Pérez-Brocal V, García-López R, Moya A, Rossi M. 2019; Profiling of protein degraders in cultures of human gut microbiota. Front Microbiol. 10:2614. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02614. PMID: 31803157. PMCID: PMC6874058.

139. den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK, Venema K, Reijngoud DJ, Bakker BM. 2013; The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J Lipid Res. 54:2325–2340. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R036012. PMID: 23821742. PMCID: PMC3735932.

140. Fang FC, Frawley ER, Tapscott T, Vázquez-Torres A. 2016; Bacterial stress responses during host infection. Cell Host Microbe. 20:133–143. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.07.009. PMID: 27512901. PMCID: PMC4985009.

141. Marteyn B, West NP, Browning DF, Cole JA, Shaw JG, Palm F, Mounier J, Prévost MC, Sansonetti P, Tang CM. 2010; Modulation of Shigella virulence in response to available oxygen in vivo. Nature. 465:355–358. DOI: 10.1038/nature08970. PMID: 20436458. PMCID: PMC3750455.

142. Nickerson KP, Faherty CS. 2018; Bile salt-induced biofilm formation in enteric pathogens: techniques for identification and quantification. J Vis Exp. (135):57322. DOI: 10.3791/57322. PMID: 29781989. PMCID: PMC6101122.

143. Nickerson KP, Chanin RB, Sistrunk JR, Rasko DA, Fink PJ, Barry EM, Nataro JP, Faherty CS. 2017; Analysis of Shigella flexneri resistance, biofilm formation, and transcriptional profile in response to bile salts. Infect Immun. 85:e01067–16. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01067-16. PMID: 28348056. PMCID: PMC5442615.

Fig. 1
A schematic depiction of the gut milieu in which the interaction between hosts and microorganisms occurs. Enteric microorganisms have different regional preferences along the length of the intestine with different biochemical environments such as oxygen and pH. Interactions between the intestinal epithelium and microorganisms affect these biochemical environments. For example, microbial fermentation of dietary fibers produces SCFAs, reducing pH, while butyrate utilization in the colonocytes consumes oxygen, lowering oxygen concentrations and thus allowing for the growth of strict anaerobes. Microbial growth, viability, and virulence expressions are affected by the surrounding environment. Moreover, intestinal homeostasis is maintained by the interaction between intestinal microbiota and immune cells. Given that iPSCs-derived organoids retain small intestinal properties, caution is needed when studying commensals with preference to the large intestine in iPSCs-derived organoids. For better modeling interactions between the gut and microorganisms using intestinal organoids, it would be necessary to consider various gut environments (i.e., pH, oxygen, microbial metabolites, glucose, immune cells) as well as the regional preference of the microorganisms. AdSCs: Adult stem cells, iPSCs: inducible pluripotent stem cells.
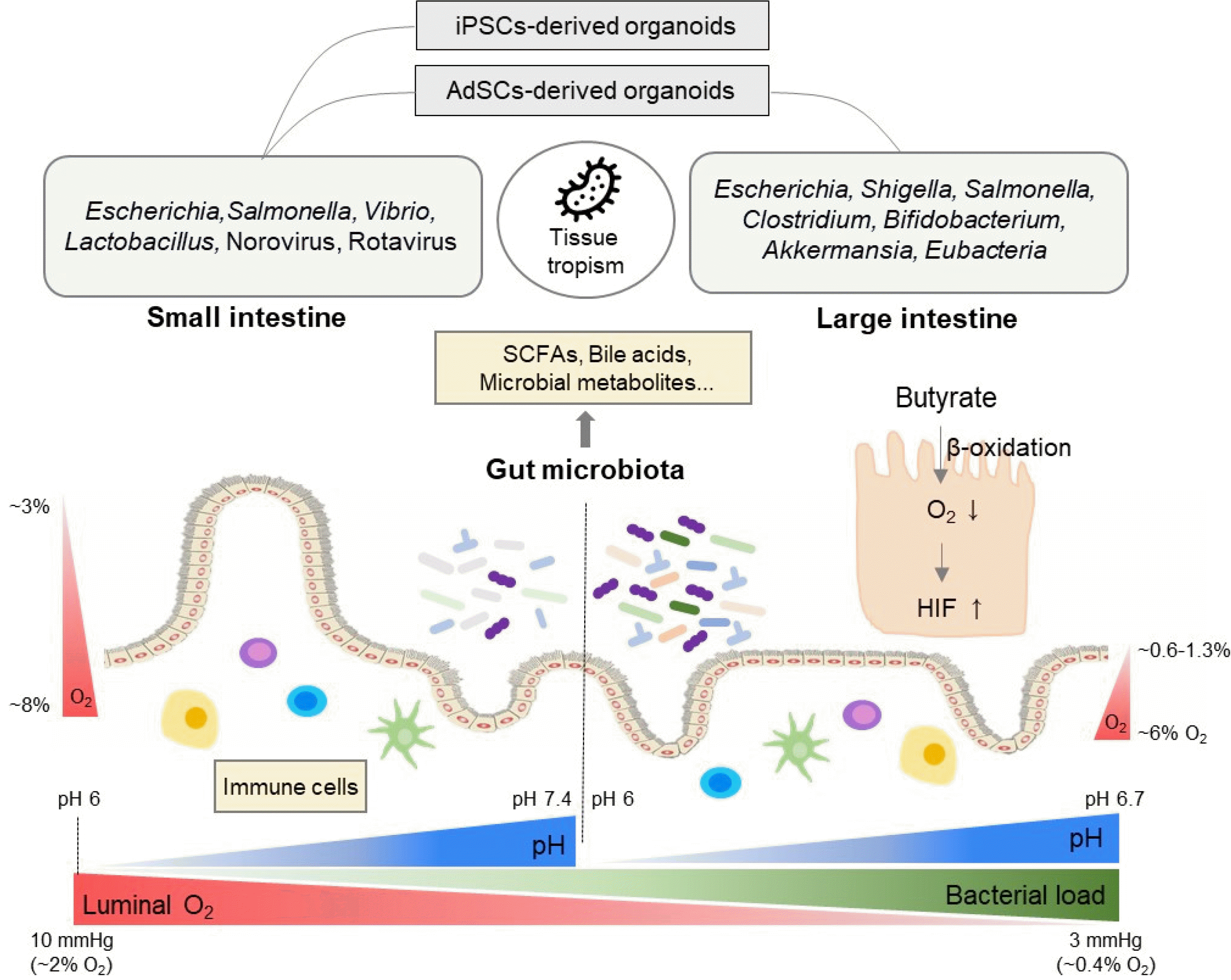
Table 1
Studies reporting host-microorganism interactions using human intestinal organoids
| Microorganism | Tissue tropism | Systems used | Infection method | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonpathogenic E. coli | Large intestine | Human ESC | 3D-Microinjection | (47, 61) | |
| Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) | Large intestine | Human ESC | 3D-Microinjection | (54, 61) | |
| Human colon* | 2D-Monolayer transwell | ||||
| Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) | Small intestine | Human duodenum*, jejunum* and proximal colon | 2D-Monolayer transwell | (65) | |
| Shigella flexneri | Large intestine | Human duodenum, ileum, cecum* and colon* | 2D-Monolayer transwell | (67, 68) | |
| Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium | Small intestine (ileum) | Human iPSC* | 3D-Microinjection | (51, 70, 71) | |
| Human small intestine* | 2D-Monolayer | ||||
| Human ileum* | 2D-Suspension culture | ||||
| Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi | Large intestine (cecum) | Human ileum | 2D-Monolayer transwell | (73) | |
| Vibrio cholerae | Small intestine | Human duodenum* and rectum | 3D-Enteroids treated with cholerae toxin | (78-81) | |
| Human ileum* and colon | 2D-Monolayer transwell | ||||
| Human jejunum* | |||||
| Clostridium difficile | Large intestine | Human ESC | 3D-Microinjection | (45, 49, 84, 85) | |
| Human jejunum | 2D-Monolayer transwell | ||||
| Human iPSC | 3D-Microinjection | ||||
| 3D-Organoids treated with toxin | |||||
| Norovirus | Small intestine | Human ESC | 2D-Monolayer | (89, 90) | |
| Human jejunum* | 2D-Monolayer transwell | ||||
| Rotavirus | Small intestine | 3D-Organoid treated with rotavirus | (92, 93) | ||
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus reuteri Lactobacillus plantarum | Small intestine | Human small intestine* and colon | 3D-Microinjection | (99, 101) | |
| Human ESC | |||||
| Bifidobacterium adolescentis | Large intestine | Human colon* | (55, 102) | ||
| Human intestinal epithelial Caco-2BBE cells* | |||||
| Akkermansia muciniphila | Large intestine | Human colon* | 2D-iHACS | Only differentiated human colonic organoids can support the growth of A. muciniphila | (55) |
| Eubacterium | Large intestine | Human intestinal epithelial Caco-2BBE cells* | AOI chip | Co-cultured with epithelial cells in the AOI Chip for up to a week | (102) |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download