1. Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. 2006; Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. DOI:
10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024. PMID:
16904174.

2. Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, Nie J, Jonsdottir GA, Ruotti V, Stewart R, Slukvin II, Thomson JA. 2007; Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 318:1917–1920. DOI:
10.1126/science.1151526. PMID:
18029452.

3. Ezashi T, Telugu BP, Alexenko AP, Sachdev S, Sinha S, Roberts RM. 2009; Derivation of induced pluripotent stem cells from pig somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 106:10993–10998. DOI:
10.1073/pnas.0905284106. PMID:
19541600. PMCID:
PMC2698893.

4. Han X, Han J, Ding F, Cao S, Lim SS, Dai Y, Zhang R, Zhang Y, Lim B, Li N. 2011; Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from bovine embryonic fibroblast cells. Cell Res. 21:1509–1512. DOI:
10.1038/cr.2011.125. PMID:
21826109. PMCID:
PMC3193448.

5. Liao J, Cui C, Chen S, Ren J, Chen J, Gao Y, Li H, Jia N, Cheng L, Xiao H, Xiao L. 2009; Generation of induced pluripotent stem cell lines from adult rat cells. Cell Stem Cell. 4:11–15. DOI:
10.1016/j.stem.2008.11.013. PMID:
19097959.

6. Nagy K, Sung HK, Zhang P, Laflamme S, Vincent P, Agha-Mohammadi S, Woltjen K, Monetti C, Michael IP, Smith LC, Nagy A. 2011; Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from equine fibroblasts. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 7:693–702. DOI:
10.1007/s12015-011-9239-5. PMID:
21347602. PMCID:
PMC3137777.

7. Liu J, Balehosur D, Murray B, Kelly JM, Sumer H, Verma PJ. 2012; Generation and characterization of reprogrammed sheep induced pluripotent stem cells. Theriogenology. 77:338–346.e1. DOI:
10.1016/j.theriogenology.2011.08.006. PMID:
21958637.

8. Liu H, Zhu F, Yong J, Zhang P, Hou P, Li H, Jiang W, Cai J, Liu M, Cui K, Qu X, Xiang T, Lu D, Chi X, Gao G, Ji W, Ding M, Deng H. 2008; Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from adult rhesus monkey fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell. 3:587–590. DOI:
10.1016/j.stem.2008.10.014. PMID:
19041774.

9. Buehr M, Meek S, Blair K, Yang J, Ure J, Silva J, McLay R, Hall J, Ying QL, Smith A. 2008; Capture of authentic embryonic stem cells from rat blastocysts. Cell. 135:1287–1298. DOI:
10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.007. PMID:
19109897.

10. Li P, Tong C, Mehrian-Shai R, Jia L, Wu N, Yan Y, Maxson RE, Schulze EN, Song H, Hsieh CL, Pera MF, Ying QL. 2008; Germline competent embryonic stem cells derived from rat blastocysts. Cell. 135:1299–1310. DOI:
10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.006. PMID:
19109898. PMCID:
PMC2735113.

11. Tulgat R, Schaller GB. 1992; Status and distribution of wild Bactrian camels Camelus bactrianus ferus. Biol Conserv. 62:11–19. DOI:
10.1016/0006-3207(92)91147-K.

12. Peters J, Driesch Avd. 1997; The two-humped camel (Camelus bactrianus): new light on its distribution, management and medical treatment in the past. J Zool. 242:651–679. DOI:
10.1111/j.1469-7998.1997.tb05819.x.

13. Gurvich N, Tsygankova OM, Meinkoth JL, Klein PS. 2004; Histone deacetylase is a target of valproic acid-mediated cellular differentiation. Cancer Res. 64:1079–1086. DOI:
10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-0799. PMID:
14871841.

14. Phiel CJ, Zhang F, Huang EY, Guenther MG, Lazar MA, Klein PS. 2001; Histone deacetylase is a direct target of valproic acid, a potent anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, and terato-gen. J Biol Chem. 276:36734–36741. DOI:
10.1074/jbc.M101287200. PMID:
11473107.

15. Huangfu D, Maehr R, Guo W, Eijkelenboom A, Snitow M, Chen AE, Melton DA. 2008; Induction of pluripotent stem cells by defined factors is greatly improved by small-molecule compounds. Nat Biotechnol. 26:795–797. DOI:
10.1038/nbt1418. PMID:
18568017. PMCID:
PMC6334647.

16. Giorgetti A, Montserrat N, Aasen T, Gonzalez F, Rodríguez-Pizà I, Vassena R, Raya A, Boué S, Barrero MJ, Corbella BA, Torrabadella M, Veiga A, Izpisua Belmonte JC. 2009; Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human cord blood using OCT4 and SOX2. Cell Stem Cell. 5:353–357. DOI:
10.1016/j.stem.2009.09.008. PMID:
19796614. PMCID:
PMC2779776.

17. Chen X, Zhai Y, Yu D, Cui J, Hu JF, Li W. 2016; Valproic acid enhances iPSC induction from human bone marrow-derived cells through the suppression of reprogramming-in-duced senescence. J Cell Physiol. 231:1719–1727. DOI:
10.1002/jcp.25270. PMID:
26620855.

18. Frank DA. 1984; Culture of animal cells: a manual of basic technique. Yale J Biol Med. 57:247–248.
19. Chen M, Zhang H, Wu J, Xu L, Xu D, Sun J, He Y, Zhou X, Wang Z, Wu L, Xu S, Wang J, Jiang S, Zhou X, Hoffman AR, Hu X, Hu J, Li T. 2012; Promotion of the induction of cell pluripotency through metabolic remodeling by thyroid hormone triiodothyronine-activated PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Biomaterials. 33:5514–5523. DOI:
10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.04.001. PMID:
22575839. PMCID:
PMC3358472.

20. Zhang H, Jiao W, Sun L, Fan J, Chen M, Wang H, Xu X, Shen A, Li T, Niu B, Ge S, Li W, Cui J, Wang G, Sun J, Fan X, Hu X, Mrsny RJ, Hoffman AR, Hu JF. 2013; Intrachromosomal looping is required for activation of endogenous pluripotency genes during reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 13:30–35. DOI:
10.1016/j.stem.2013.05.012. PMID:
23747202.

22. Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL. 2015; HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods. 12:357–360. DOI:
10.1038/nmeth.3317. PMID:
25751142. PMCID:
PMC4655817.

24. Sun J, Li W, Sun Y, Yu D, Wen X, Wang H, Cui J, Wang G, Hoffman AR, Hu JF. 2014; A novel antisense long noncoding RNA within the IGF1R gene locus is imprinted in hematopoietic malignancies. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:9588–9601. DOI:
10.1093/nar/gku549. PMID:
25092925. PMCID:
PMC4150754.
25. Wiame I, Remy S, Swennen R, Sági L. 2000; Irreversible heat inactivation of DNase I without RNA degradation. Biotech-niques. 29:252–254. 256DOI:
10.2144/00292bm11. PMID:
10948426.

26. Huangfu D, Osafune K, Maehr R, Guo W, Eijkelenboom A, Chen S, Muhlestein W, Melton DA. 2008; Induction of pluripotent stem cells from primary human fibroblasts with only Oct4 and Sox2. Nat Biotechnol. 26:1269–1275. DOI:
10.1038/nbt.1502. PMID:
18849973.

27. Moschidou D, Mukherjee S, Blundell MP, Drews K, Jones GN, Abdulrazzak H, Nowakowska B, Phoolchund A, Lay K, Ramasamy TS, Cananzi M, Nettersheim D, Sullivan M, Frost J, Moore G, Vermeesch JR, Fisk NM, Thrasher AJ, Atala A, Adjaye J, Schorle H, De Coppi P, Guillot PV. 2012; Valproic acid confers functional pluripotency to human amniotic fluid stem cells in a transgene-free approach. Mol Ther. 20:1953–1967. DOI:
10.1038/mt.2012.117. PMID:
22760542. PMCID:
PMC3464631.

28. Ben-Nun IF, Montague SC, Houck ML, Tran HT, Garitaonandia I, Leonardo TR, Wang YC, Charter SJ, Laurent LC, Ryder OA, Loring JF. 2011; Induced pluripotent stem cells from highly endangered species. Nat Methods. 8:829–831. DOI:
10.1038/nmeth.1706. PMID:
21892153.

29. Lluis F, Pedone E, Pepe S, Cosma MP. 2008; Periodic activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling enhances somatic cell reprogramming mediated by cell fusion. Cell Stem Cell. 3:493–507. DOI:
10.1016/j.stem.2008.08.017. PMID:
18983965.

30. Yang Y, Liu B, Xu J, Wang J, Wu J, Shi C, Xu Y, Dong J, Wang C, Lai W, Zhu J, Xiong L, Zhu D, Li X, Yang W, Yamauchi T, Sugawara A, Li Z, Sun F, Li X, Li C, He A, Du Y, Wang T, Zhao C, Li H, Chi X, Zhang H, Liu Y, Li C, Duo S, Yin M, Shen H, Belmonte JCI, Deng H. 2017; Derivation of pluripotent stem cells with in vivo embryonic and extraembryonic potency. Cell. 169:243–257. e25. DOI:
10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.005. PMID:
28388409. PMCID:
PMC5679268.

31. Hou P, Li Y, Zhang X, Liu C, Guan J, Li H, Zhao T, Ye J, Yang W, Liu K, Ge J, Xu J, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Deng H. 2013; Pluripotent stem cells induced from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule compounds. Science. 341:651–654. DOI:
10.1126/science.1239278. PMID:
23868920.

32. Zhao Y, Zhao T, Guan J, Zhang X, Fu Y, Ye J, Zhu J, Meng G, Ge J, Yang S, Cheng L, Du Y, Zhao C, Wang T, Su L, Yang W, Deng H. 2015; A XEN-like state bridges somatic cells to pluripotency during chemical reprogramming. Cell. 163:1678–1691. DOI:
10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.017. PMID:
26686652.

33. Cao S, Yu S, Li D, Ye J, Yang X, Li C, Wang X, Mai Y, Qin Y, Wu J, He J, Zhou C, Liu H, Zhao B, Shu X, Wu C, Chen R, Chan W, Pan G, Chen J, Liu J, Pei D. 2018; Chromatin accessibility dynamics during chemical induction of pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell. 22:529–542.e5. DOI:
10.1016/j.stem.2018.03.005. PMID:
29625068.

34. Armstrong L, Hughes O, Yung S, Hyslop L, Stewart R, Wappler I, Peters H, Walter T, Stojkovic P, Evans J, Stojkovic M, Lako M. 2006; The role of PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK and NFkappabeta signalling in the maintenance of human embryonic stem cell pluripotency and viability highlighted by transcriptional profiling and functional analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 15:1894–1913. DOI:
10.1093/hmg/ddl112. PMID:
16644866.

35. Hong H, Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, Aoi T, Kanagawa O, Nakagawa M, Okita K, Yamanaka S. 2009; Suppression of induced pluripotent stem cell generation by the p53-p21 pathway. Nature. 460:1132–1135. DOI:
10.1038/nature08235. PMID:
19668191. PMCID:
PMC2917235.

36. Rasmussen MA, Holst B, Tümer Z, Johnsen MG, Zhou S, Stummann TC, Hyttel P, Clausen C. 2014; Transient p53 suppression increases reprogramming of human fibroblasts without affecting apoptosis and DNA damage. Stem Cell Reports. 3:404–413. DOI:
10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.07.006. PMID:
25241739. PMCID:
PMC4266010.

37. Soufi A, Donahue G, Zaret KS. 2012; Facilitators and impediments of the pluripotency reprogramming factors' initial engagement with the genome. Cell. 151:994–1004. DOI:
10.1016/j.cell.2012.09.045. PMID:
23159369. PMCID:
PMC3508134.

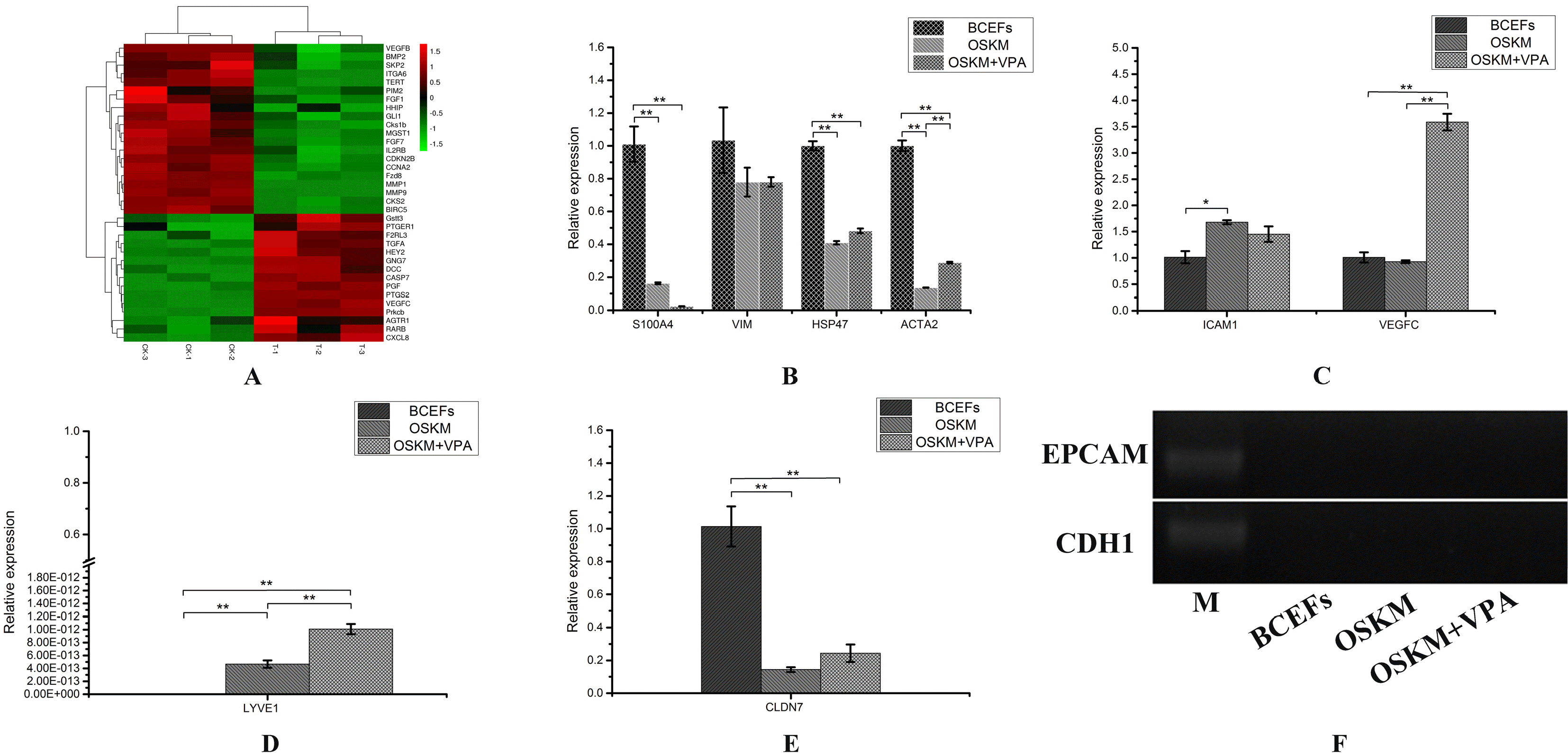




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


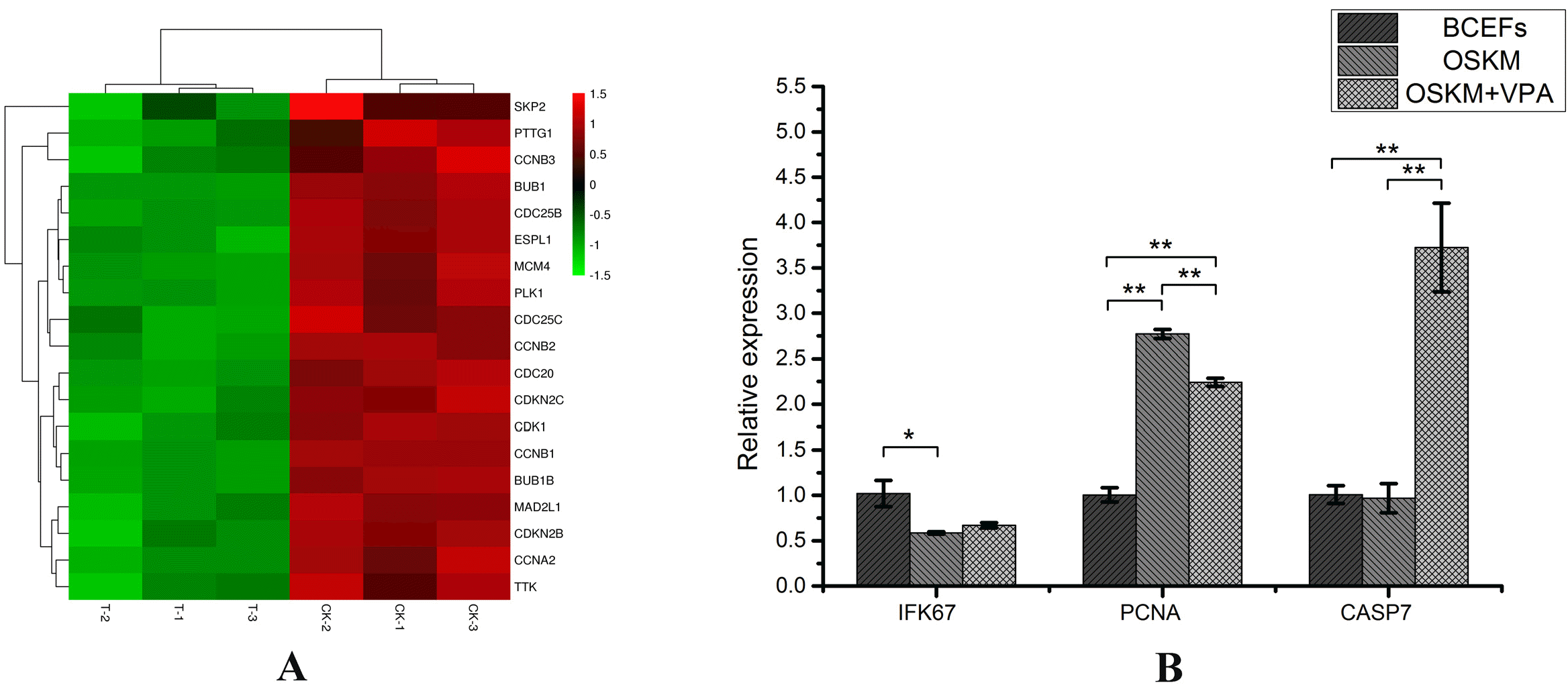
 XML Download
XML Download