Introduction
Materials and Methods
Animals
Experimental design
Peripheral blood
Mice sacrifice and isolation of bone marrow cells (BMCs)
Flowcytometric analysis of sca-1+c-kit+ hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)
Short term adherent cell (STAC) culture
Studies on cell mediated immune (CMI) parameters
Statistical analysis
Results
Peripheral blood
Table 1.
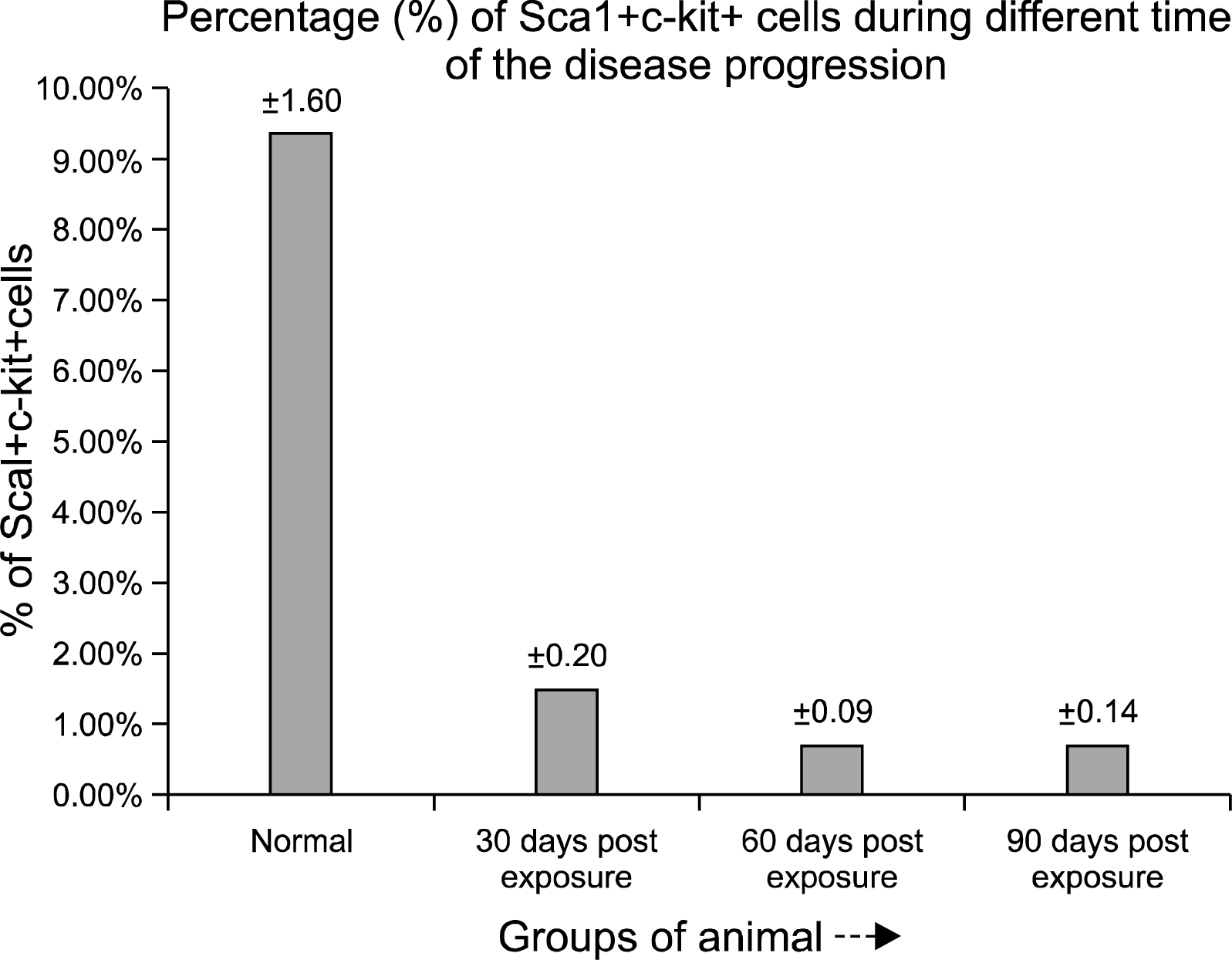
Flowcytometric characterization of sca-1+c-kit+ cells
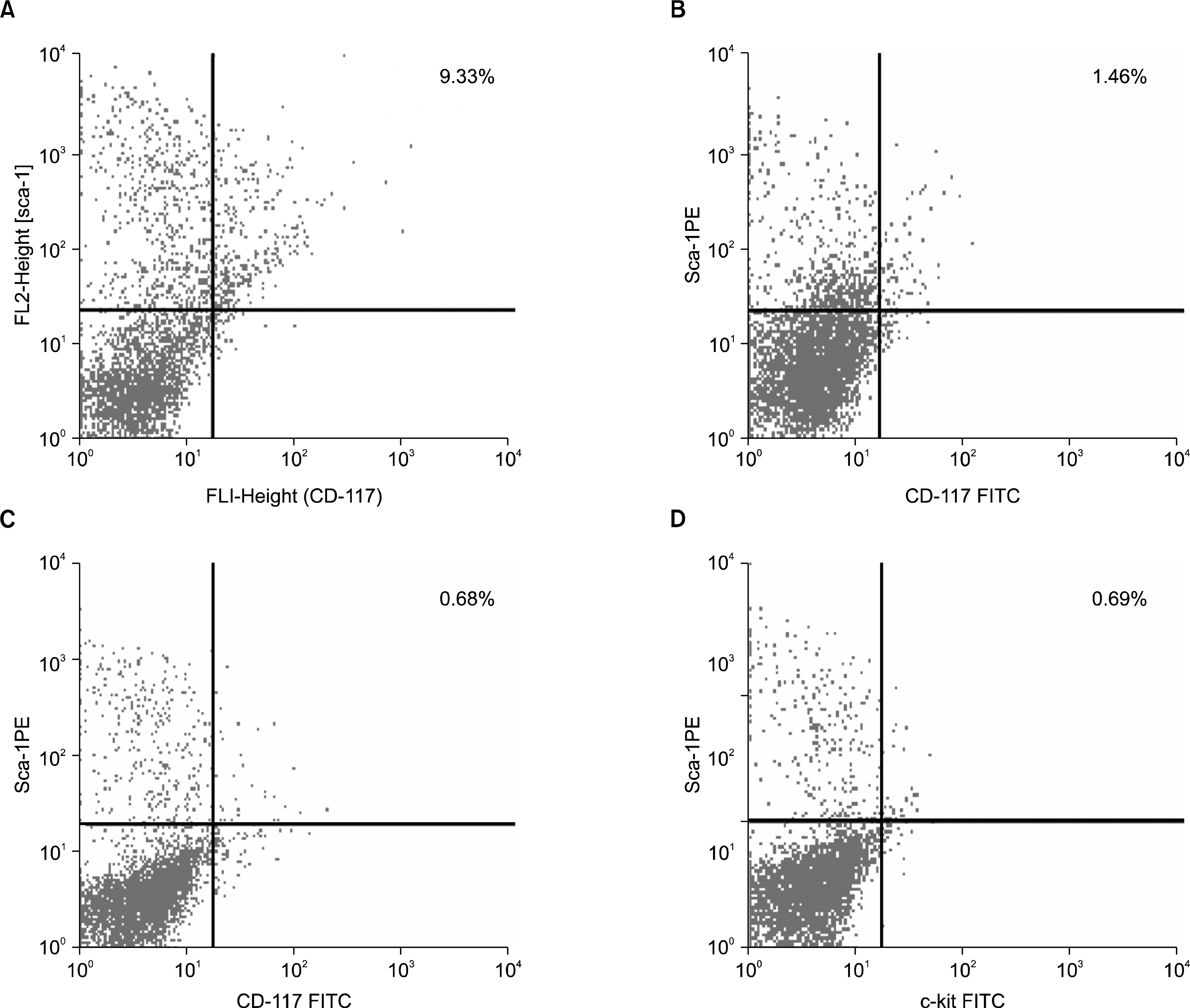 | Fig. 3.(A) Phenotypic characterization of Sca-1 and c-kit receptor expression from the normal mouse bone marrow cells. The normal bone marrow contains 9.33% dual positive (Sca1+c-kit+) cells. (B) Phenotypic characterization of Sca-1 and c-kit expression by the bone marrow cells from 30 days post pesticide exposed group of mice. Severe reduction in the percentage of Sca1+c-kit+ (1.46%) cells has been observed in this group of animals. (C) Phenotypic characterization of Sca-1 and c-kit receptor expression by the bone marrow cells from 60 days post pesticide exposed group of mice. The bone marrow from this group of animals showed further decrease in the Sca1+c-kit+ (0.68%) population. (D) Phenotypic characterization of Sca-1 and c-kit receptor expression by the bone marrow cells from 90 days post pesticide exposed group of mice. Severe reduction in the percentage of Sca1+c-kit+ (0.69%) cells resembled the previous group. |
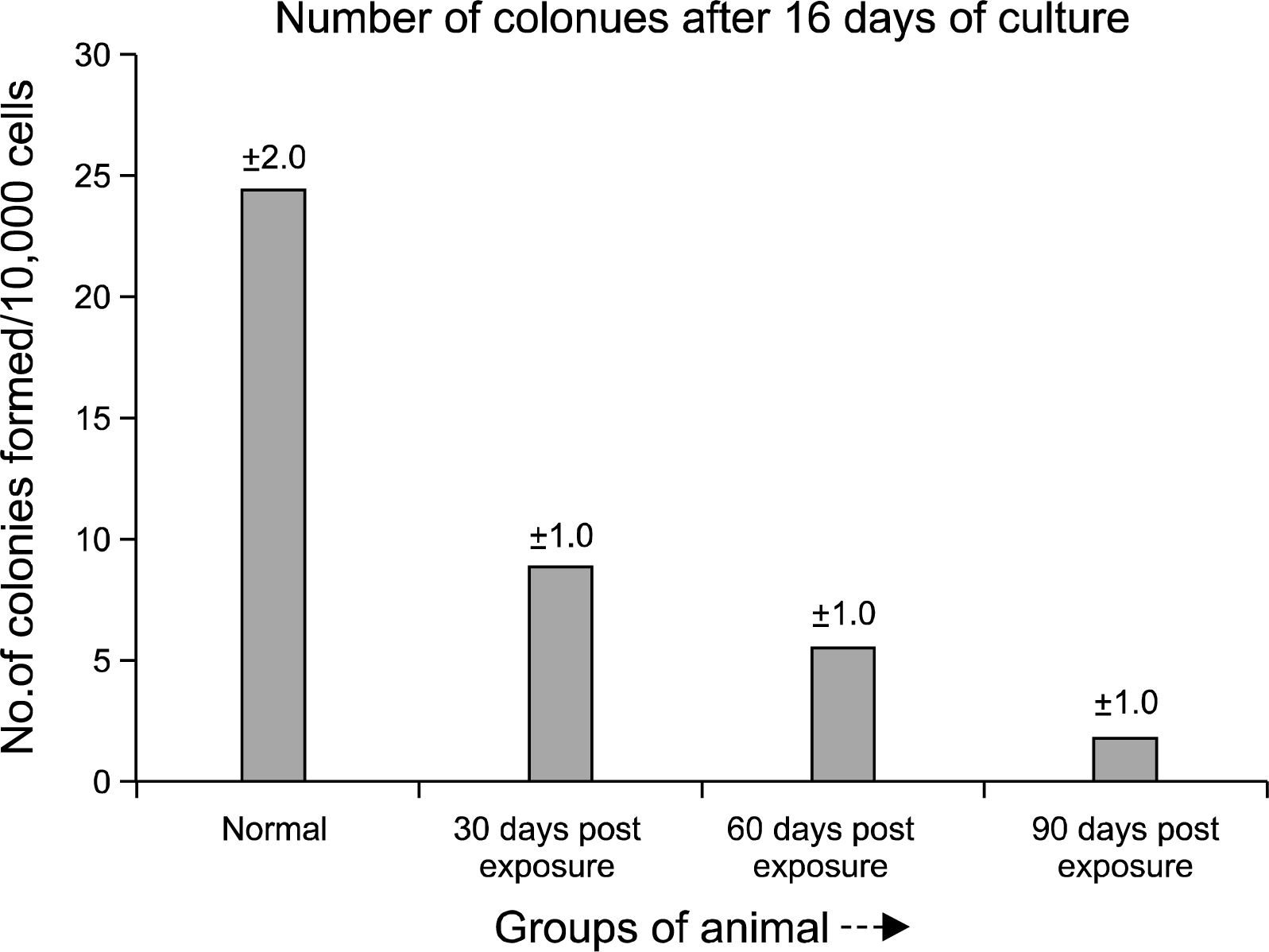
Short term adherent cell colony (STACC) forming assay
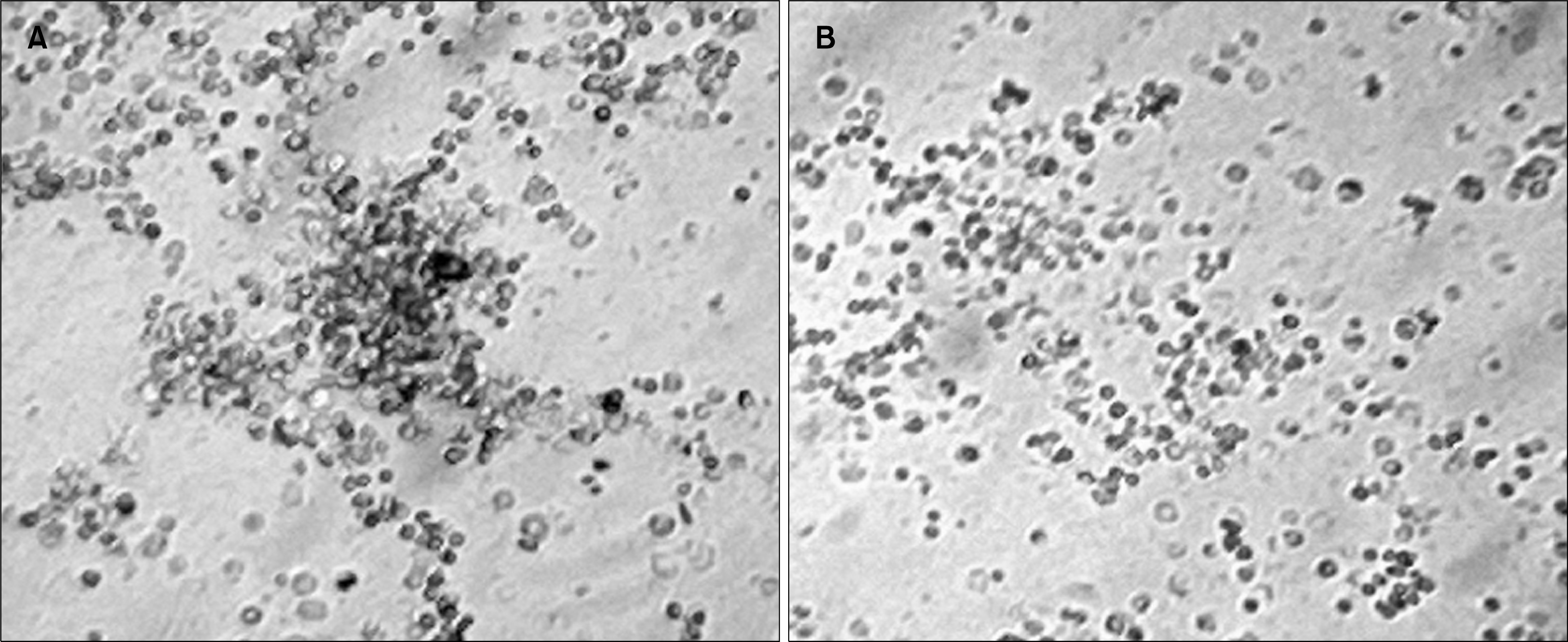 | Fig. 5.(A) The short term adherent cell colony (STACC) derived from normal bone marrow adherent cell culture at day 16. Colonies were colorless and compact. (B) Absence of prominent adherent cell colony after 16 days of bone marrow adherent cell culture from the pesticide exposed group of mice. This image has been taken from the 90 days post pesticide exposed group of mice. However very low number of small colonies can be identified in that group. |
Immune functional efficacy of the bone marrow derived cells
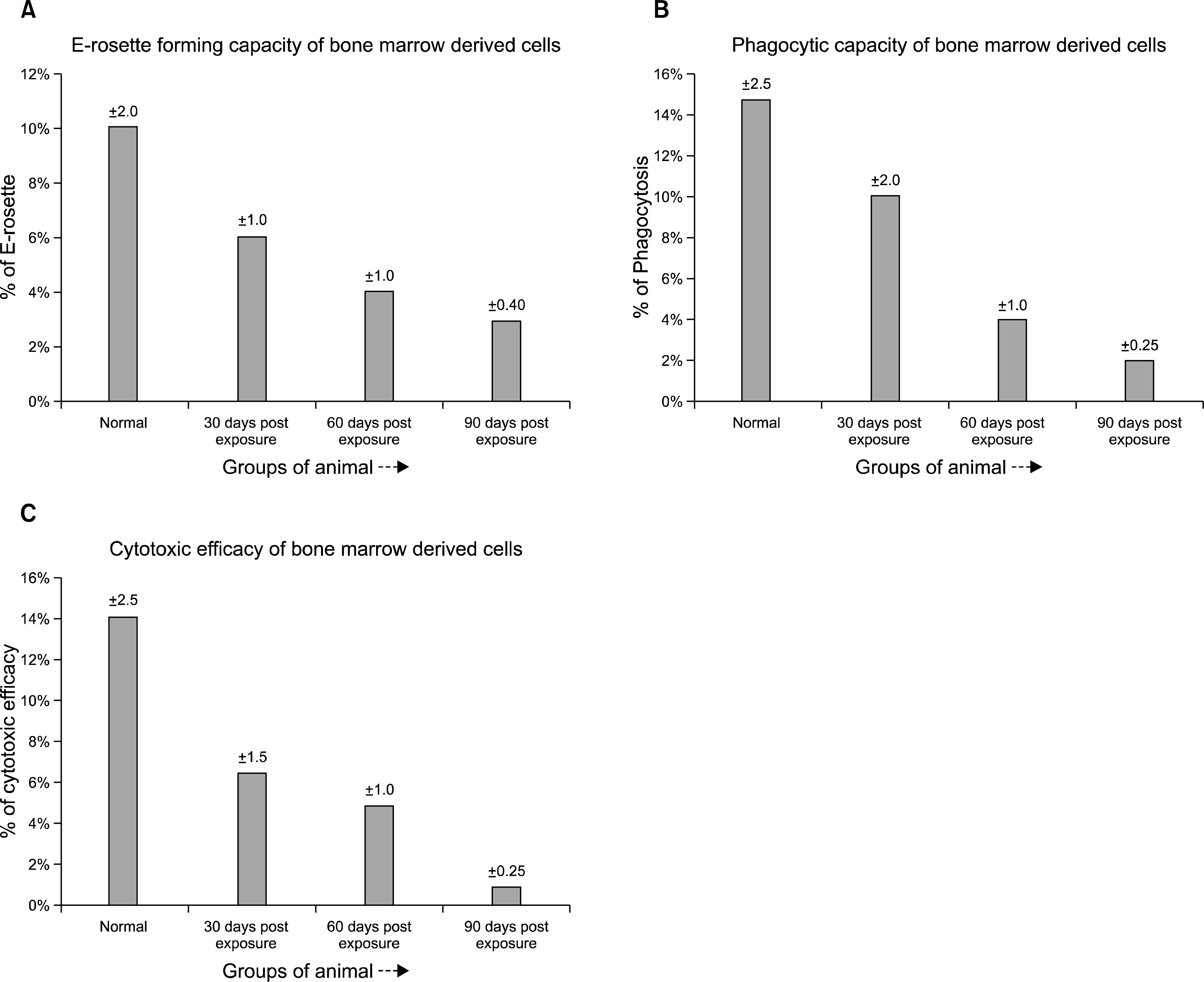 | Fig. 7.(A) Spontaneous E-rosette forming capacity of bone marrow derived cells (BMC) from the different pesticide exposed groups of mice compared with the normal. The pesticide exposed groups suffered a significant decrease in the E-rosette forming capacity compared to the normal. The 90 days post pesticide exposed group suffered maximum damage to the immune cells in terms of E-rosette forming ability. (B) The phagocytic capacity of the bone marrow derived cells (BMC) from different pesticide exposed groups of animals compared to the normal. The pesticide exposed groups showed a significant reduction in the phagocytic capacity compared to the normal control group. (C) Cytotoxic efficacy of the bone marrow derived cells (BMC) from different pesticide exposed groups of animals compared with the normal. The pesticide exposed groups showed a significant reduction in the cytotoxic efficacy compared to the normal healthy group. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download