1. Paus R, Cotsarelis G. The biology of hair follicles. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:491–497.

2. Barrandon Y, Green H. Cell migration is essential for sustained growth of keratinocyte colonies: the roles of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1987. 50:1131–1137.

3. Al-Barwari SE, Potten CS. Regeneration and dose-response characteristics of irradiated mouse dorsal epidermal cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1976. 30:201–216.

4. Lavker RM, Miller S, Wilson C, Cotsarelis G, Wei ZG, Yang JS, Sun TT. Hair follicle stem cells: their location, role in hair cycle, and involvement in skin tumor formation. J Invest Dermatol. 1993. 101:16S–26S.

5. Potten CS. The epidermal proliferative unit: the possible role of the central basal cell. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1974. 7:77–88.

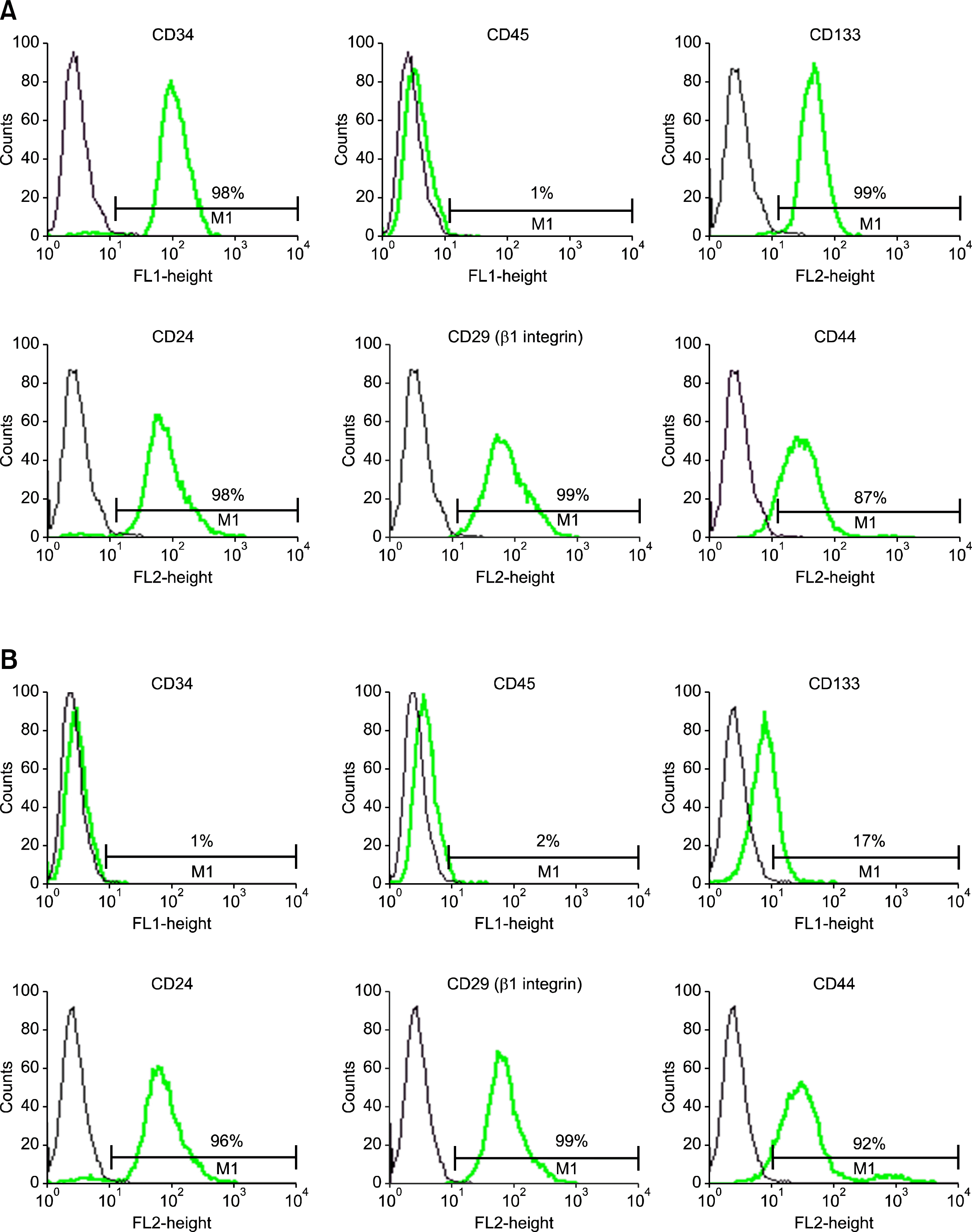
6. Li A, Simmons PJ, Kaur P. Identification and isolation of candidate human keratinocyte stem cells based on cell surface phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. 95:3902–3907.

7. Roh C, Tao Q, Photopoulos C, Lyle S. In vitro differences between keratinocyte stem cells and transit-amplifying cells of the human hair follicle. J Invest Dermatol. 2005. 125:1099–1105.

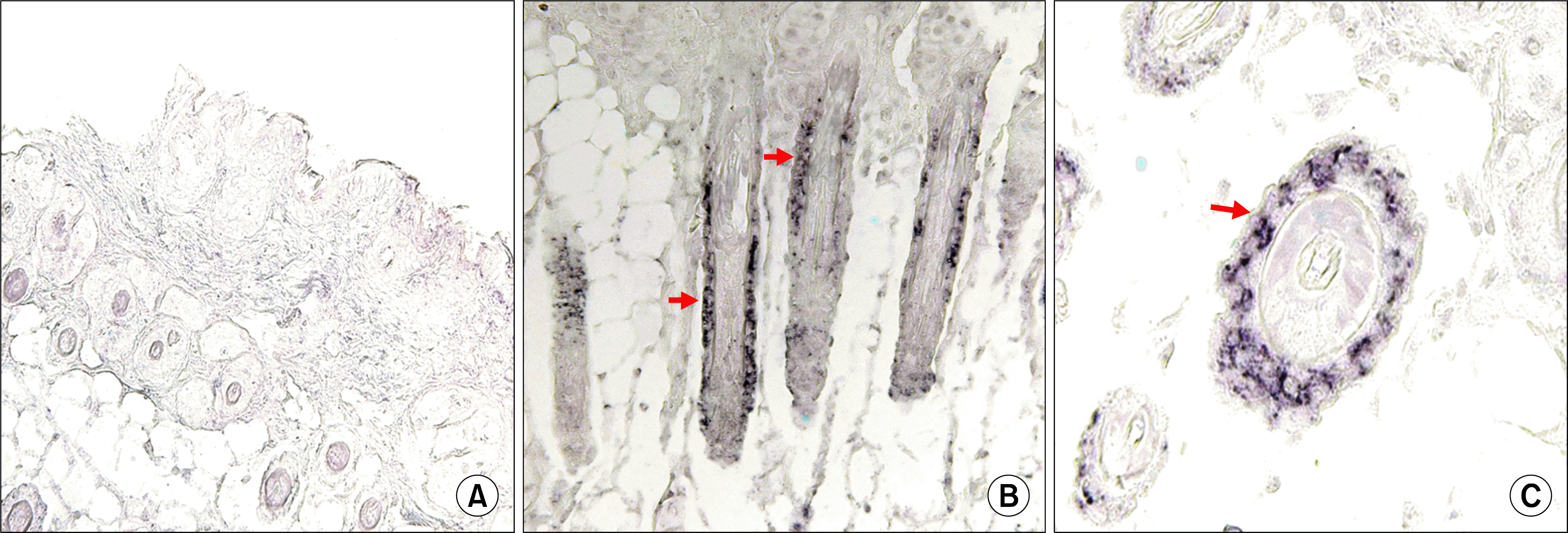
8. Liu Y, Lyle S, Yang Z, Cotsarelis G. Keratin 15 promoter targets putative epithelial stem cells in the hair follicle bulge. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. 121:963–968.

9. Commo S, Gaillard O, Bernard BA. The human hair follicle contains two distinct K19 positive compartments in the outer root sheath: a unifying hypothesis for stem cell reservoir? Differentiation. 2000. 66:157–164.

10. Pellegrini G, Dellambra E, Golisano O, Martinelli E, Fantozzi I, Bondanza S, Ponzin D, McKeon F, De Luca M. p63 identifies keratinocyte stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. 98:3156–3161.

11. Ito M, Kizawa K. Expression of calcium-binding S100 proteins A4 and A6 in regions of the epithelial sac associated with the onset of hair follicle regeneration. J Invest Dermatol. 2001. 116:956–963.

12. Selleri S, Arnaboldi F, Palazzo M, Hussein U, Balsari A, Rumio C. Caveolin-1 is expressed on multipotent cells of hair follicles and might be involved in their resistance to chemotherapy. Br J Dermatol. 2005. 153:506–513.

13. Ohyama M, Terunuma A, Tock CL, Radonovich MF, Pise-Masison CA, Hopping SB, Brady JN, Udey MC, Vogel JC. Characterization and isolation of stem cell-enriched human hair follicle bulge cells. J Clin Invest. 2006. 116:249–260.

14. Li L, Mignone J, Yang M, Matic M, Penman S, Enikolopov G, Hoffman RM. Nestin expression in hair follicle sheath progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. 100:9958–9961.

15. Tani H, Morris RJ, Kaur P. Enrichment for murine keratinocyte stem cells based on cell surface phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:10960–10965.

16. Trempus CS, Morris RJ, Bortner CD, Cotsarelis G, Faircloth RS, Reece JM, Tennant RW. Enrichment for living murine keratinocytes from the hair follicle bulge with the cell surface marker CD34. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. 120:501–511.

17. Poblet E, Jimenez-Acosta F, Rocamora A. QBEND/10 (anti-CD34 antibody) in external root sheath cells and follicular tumors. J Cutan Pathol. 1994. 21:224–228.

18. Krause DS, Ito T, Fackler MJ, Smith OM, Collector MI, Sharkis SJ, May WS. Characterization of murine CD34, a marker for hemtopoietic progenitor and stem cells. Blood. 1994. 84:691–701.

19. Lee JY, Qu-Petersen Z, Cao B, Kimura S, Jankowski R, Cummins J, Usas A, Gates C, Robbins P, Wernig A, Huard J. Clonal isolation of muscle-derived cells capable of enhancing muscle regeneration and bone healing. J Cell Biol. 2000. 150:1085–1100.

20. Vanderwinden JM, Rumessen JJ, De Laet MH, Vanderhaeghen JJ, Schiffmann SN. CD34 immunoreactivity and inter-stitial cells of Cajal in the human and mouse gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res. 2000. 302:145–153.

21. Young PE, Baumhueter S, Lasky LA. The sialomucin CD34 is expressed on hematopoietic cells and blood vessels during murine development. Blood. 1995. 85:96–105.

22. Liang L, Bickenbach JR. Somatic epidermal stem cells can produce multiple cell lineages during development. Stem Cells. 2002. 20:21–31.

23. Albert MR, Foster RA, Vogel JC. Murine epidermal label-retaining cells isolated by flow cytometry do not express the stem cell markers CD34, Sca-1, or Flk-1. J Invest Dermatol. 2001. 117:943–948.

24. Dunnwald M, Tomanek-Chalkley A, Alexandrunas D, Fishbaugh J, Bickenbach JR. Isolating a pure population of epidermal stem cells for use in tissue engineering. Exp Dermatol. 2001. 10:45–54.

25. Kariya Y, Kato K, Hayashizaki Y, Himeno S, Tarui S, Matsubara K. Revision of consensus sequence of human Alu repeats--a review. Gene. 1987. 53:1–10.

26. Rochat A, Kobayashi K, Barrandon Y. Location of stem cells of human hair follicles by clonal analysis. Cell. 1994. 76:1063–1073.

27. Lyle S, Christofidou-Solomidou M, Liu Y, Elder DE, Albelda S, Cotsarelis G. The C8/144B monoclonal antibody recognizes cytokeratin 15 and defines the location of human hair follicle stem cells. J Cell Sci. 1998. 111(Pt 21):3179–3188.

28. Ghali L, Wong ST, Tidman N, Quinn A, Philpott MP, Leigh IM. Epidermal and hair follicle progenitor cells express melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan core protein. J Invest Dermatol. 2004. 122:433–442.

29. Gallacher L, Murdoch B, Wu DM, Karanu FN, Keeney M, Bhatia M. Isolation and characterization of human CD34(−)Lin(−) and CD34(+)Lin(−) hematopoietic stem cells using cell surface markers AC133 and CD7. Blood. 2000. 95:2813–2820.

30. Uchida N, Buck DW, He D, Reitsma MJ, Masek M, Phan TV, Tsukamoto AS, Gage FH, Weissman IL. Direct isolation of human central nervous system stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:14720–14725.

31. Kaufman DS, Hanson ET, Lewis RL, Auerbach R, Thomson JA. Hematopoietic colony-forming cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. 98:10716–10721.

32. Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, Schwartz RE, Keene CD, Ortiz-Gonzalez XR, Reyes M, Lenvik T, Lund T, Blackstad M, Du J, Aldrich S, Lisberg A, Low WC, Largaespada DA, Verfaillie CM. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002. 418:41–49.

33. Hertle MD, Jones PH, Groves RW, Hudson DL, Watt FM. Integrin expression by human epidermal keratinocytes can be modulated by interferon-gamma, transforming growth factor-beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and culture on a dermal equivalent. J Invest Dermatol. 1995. 104:260–265.

34. Joannides A, Gaughwin P, Schwiening C, Majed H, Sterling J, Compston A, Chandran S. Efficient generation of neural precursors from adult human skin: astrocytes promote neurogenesis from skin-derived stem cells. Lancet. 2004. 364:172–178.

35. Adams JC, Watt FM. Fibronectin inhibits the terminal differentiation of human keratinocytes. Nature. 1989. 340:307–309.

36. Levy L, Broad S, Diekmann D, Evans RD, Watt FM. beta1 integrins regulate keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. 11:453–466.

37. Panteleyev AA, Jahoda CA, Christiano AM. Hair follicle predetermination. J Cell Sci. 2001. 114:3419–3431.

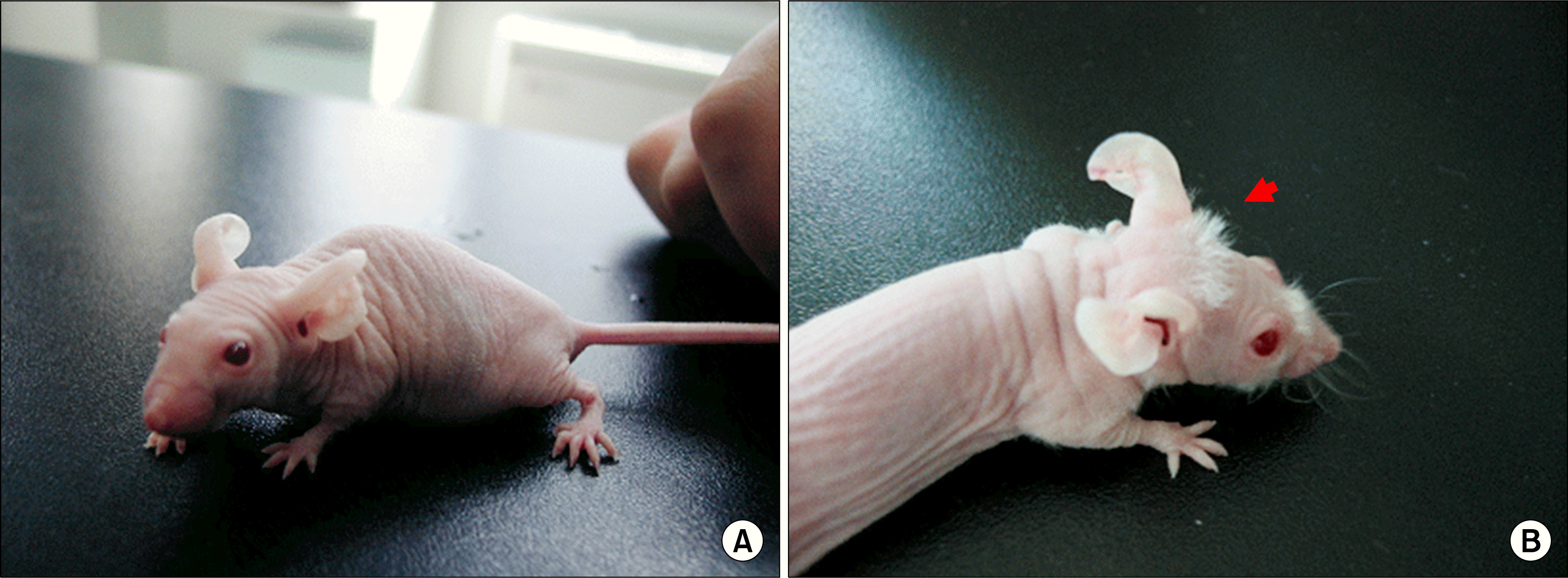
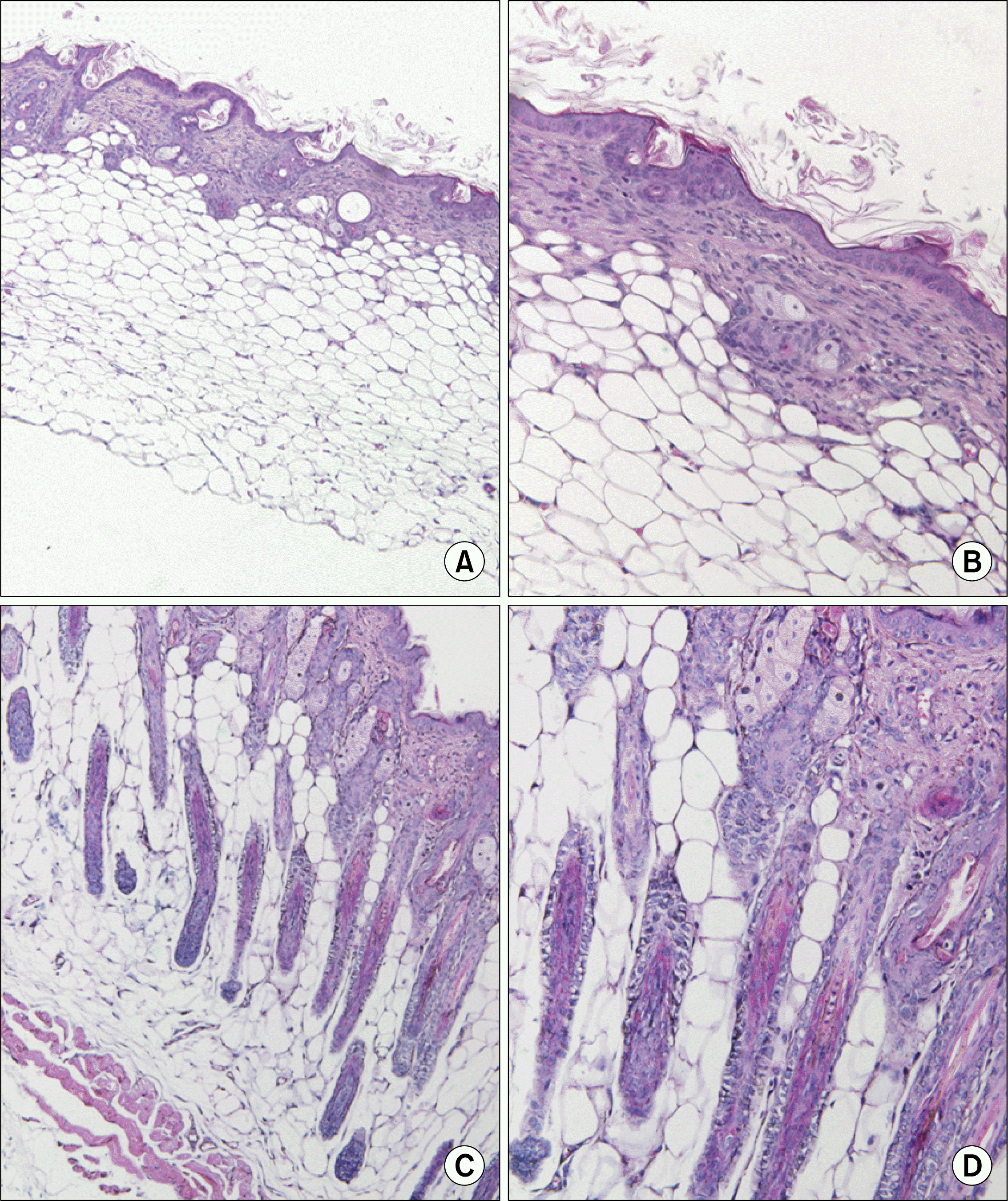
38. Tang L, Madani S, Lui H, Shapiro J. Regeneration of a new hair follicle from the upper half of a human hair follicle in a nude mouse. J Invest Dermatol. 2002. 119:983–984.

39. Gho CG, Braun JE, Tilli CM, Neumann HA, Ramaekers FC. Human follicular stem cells: their presence in plucked hair and follicular cell culture. Br J Dermatol. 2004. 150:860–868.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download