INTRODUCTION
CASE REPORT
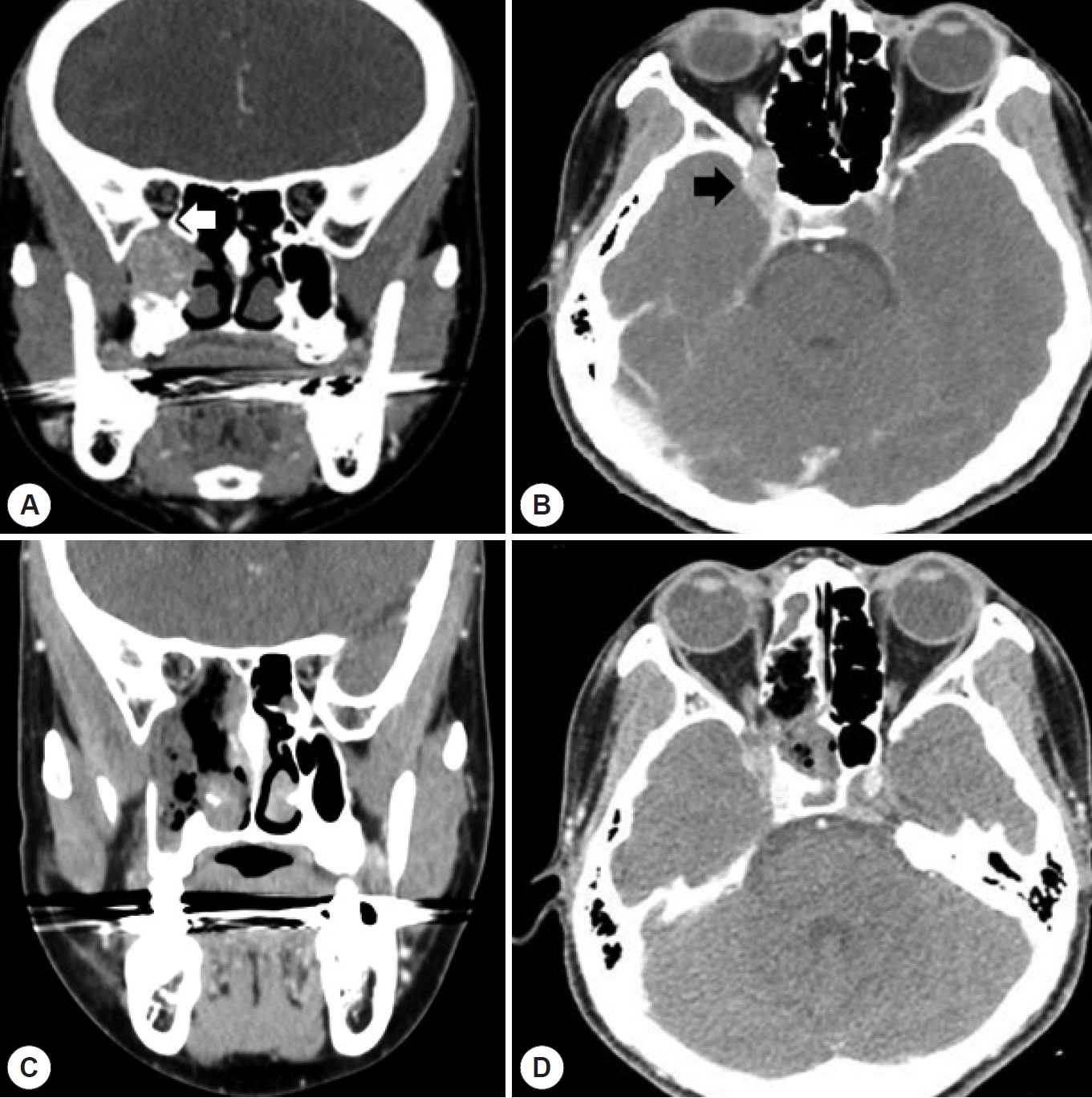 | Fig. 1.A: Coronal view of contrast CT scan represents about 2-cm sized round enhancing mass in the right pterygopalatine fossa. The tumor causes widening of adjacent bony structure with extension to inferior orbital fissure (white arrow). B: Axial view of contrast CT represents that the tumor was adjacent to the cavernous sinus superiorly (black arrow) and the sphenoid lateral recess posteriorly. C, D: Immediate post-operative CT scan demonstrated no definite residual mass in pterygopalatine fossa. |
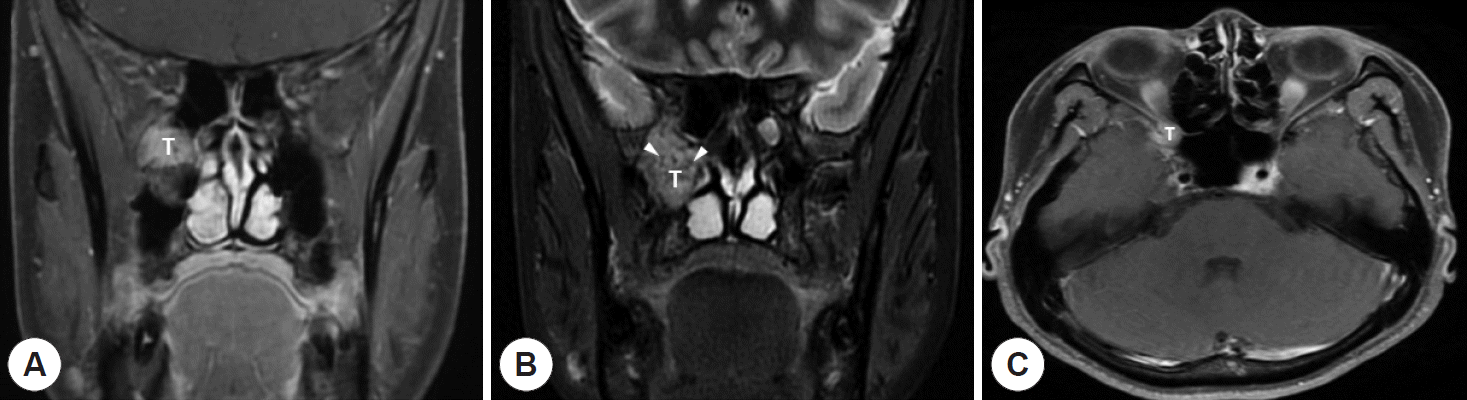 | Fig. 2.A: In contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI scan, tumor (T) showed high signal intensity comparing to muscle. B: In T2-weighted MRI scan, the tumor (T) showed heterogeneous signal intensity and there are flow voids (white arrow heads) within the tumor caused by rapid vascular flow, which is a typical radiological finding in paraganglioma called “salt-and-pepper pattern.” C: Axial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI scan. Though cavernous sinus invasion was suspected in CT scan, no definite cavernous sinus invasion was seen in MRI scan. |
Table 1.
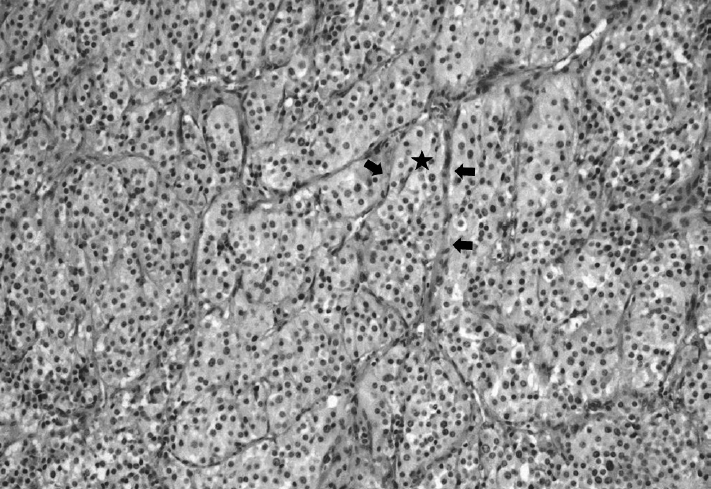 | Fig. 3.Histopathologic examinations. The tumor shows typical Zellballen cluster formation (star) with prominent vascular network (black arrows) separating clusters of endocrine cells (H & E, ×100). In Zellballen cluster, the endocrine cells with round nuclei containing abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm are observed. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download