서 론
재료 및 방법
재 료
세포 배양 및 처치
Real-time PCR 분석
면역분석법(Immunoassay)
통계적 분석
결 과
NCI-H292 세포에서 담배특이니트로사민의 세포 생존에 미치는 영향
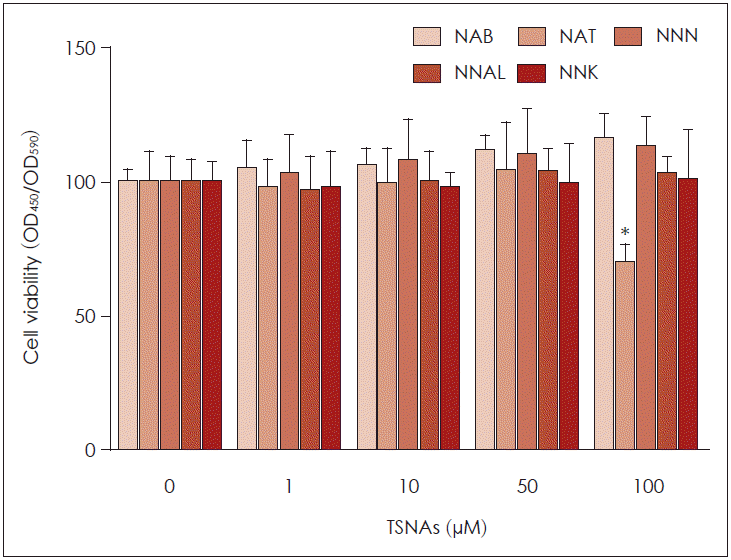 | Fig. 1.Effects of NAB, NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK on cell viability in NCI-H292 cells. WST-1 assays were performed in human airway epithelial NCI-H292 cells treated with NAB, NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK for 24 h. NAB, NNN, NNAL, and NNK did not affect cell viability up to 100 μM. However, NAT reduced cell viability at 100 μM. Bars indicate the mean±S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *: p<0.05 compared with zero value. TSNAs: Tobacco-specific nitrosamines, WST-1: water soluble tetrazolium salt-1. |
NCI-H292 세포에서 담배특이니트로사민이 MUC5AC mRNA와 단백 생성에 미치는 영향
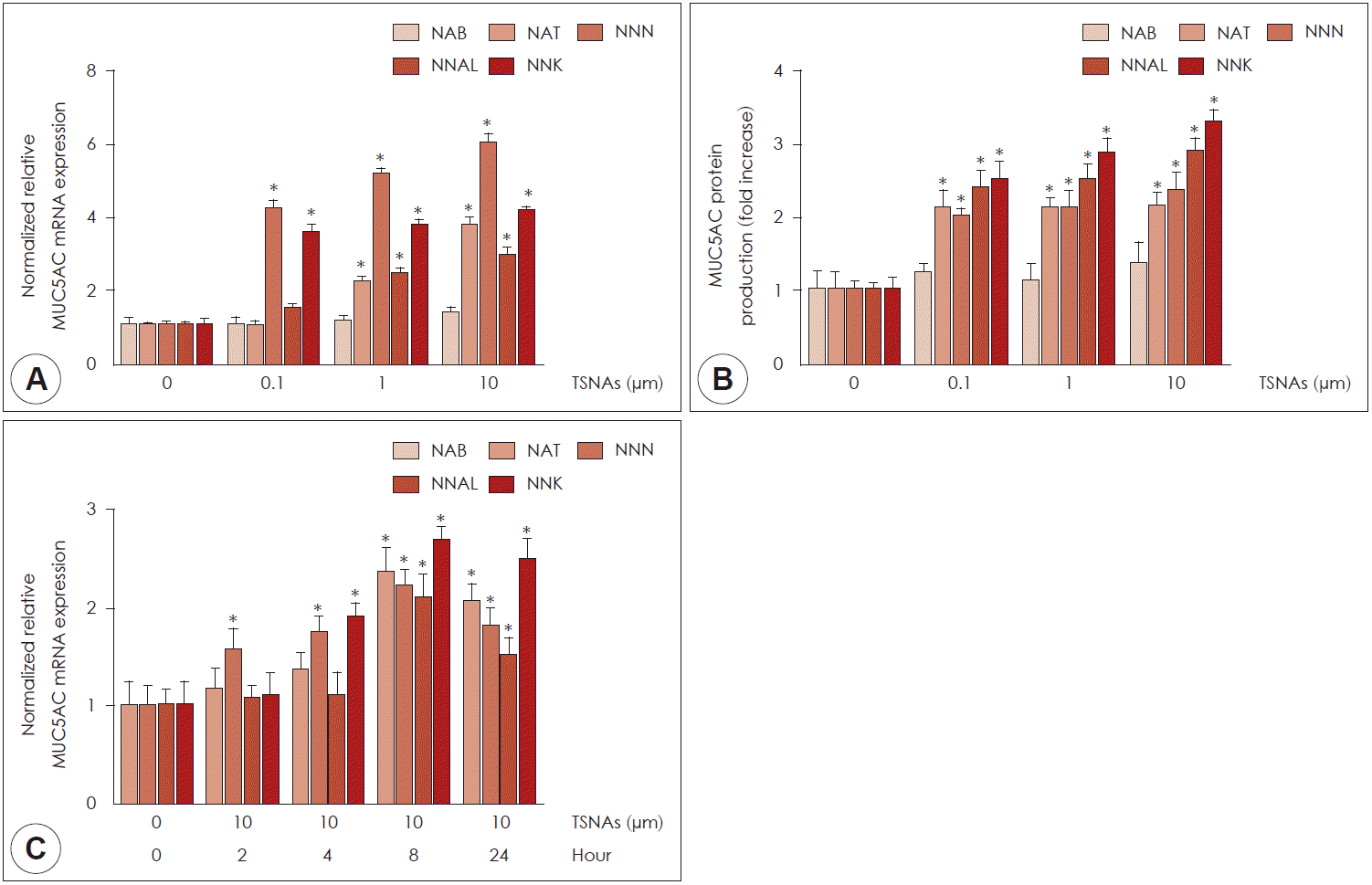 | Fig. 2.Effects of NAB, NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK on MUC5AC expression in NCI-H292 cells. NCI-H292 cells were treated with various concentration of NAB, NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK for 8 h. A, B: Real time-PCR and ELISA showed that NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK significantly induced MUC5AC gene and protein expression. However NAB did not induced MUC5AC expression. C: NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK-induced MUC5AC mRNA expression was peaked at 8 h after treatment with NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK. Bars indicate the mean±S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *: p<0.05 compared with zero value. TSNAs: Tobacco-specific nitrosamines, Real time-PCR: real time-polymerase chain reaction, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. |
NCI-H292 세포에서 담배특이니트로사민이 MUC5B mRNA와 단백 생성에 미치는 영향
 | Fig. 3.Effects of NAB, NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK on MUC5B expression in NCI-H292 cells. NCI-H292 cells were treated with various concentration of NAB, NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK for 8 h. A, B: Real time-PCR and ELISA showed that NAB, NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK did not induced MUC5B gene and protein expression. Bars indicate the mean±S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. TSNAs: Tobacco-specific nitrosamines, Real time-PCR: real time-polymerase chain reaction, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. |
NCI-H292 세포에서 NAT, NNN, NNAL, NNK이 MUC5AC mRNA와 단백 생성에 관여하는 수용체 확인
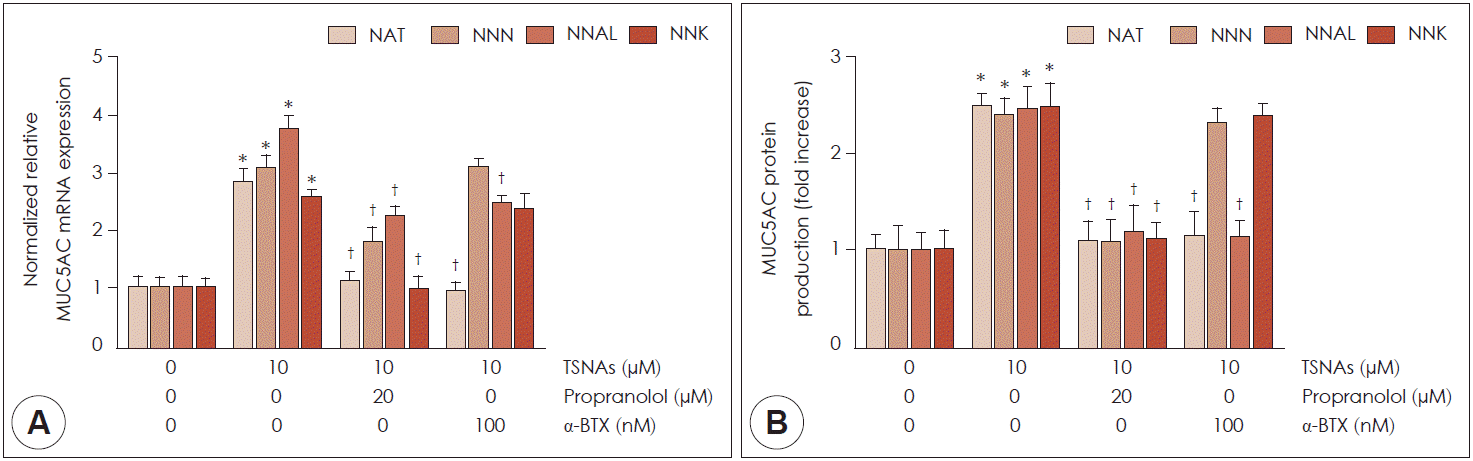 | Fig. 4.Effects of NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK on related-receptor mediated expression on MUC5AC expression in NCI-H292 cells. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with propranolol (β-adrenergic receptor inhibitor, 20 μM) or α-bungarotoxin (α-BTX, a α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor inhibitor, 100 nM) for 2 h. A, B: Real-time PCR and ELISA showed that NAT and NNAL-induced MUC5AC expression were inhibited by propranolol and α-BTX in NCI-H292 cells. NNN and NNK-induced MUC5AC were inhibited by propranolol but not α-BTX. Bars indicate the mean±S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *: p<0.05 compared with zero value. †: p<0.05 versus NAT, NNN, NNAL, and NNK (10 μM), respectively. TSNAs: Tobacco-specific nitrosamines, Real time-PCR: real time-polymerase chain reaction, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. |
고 찰
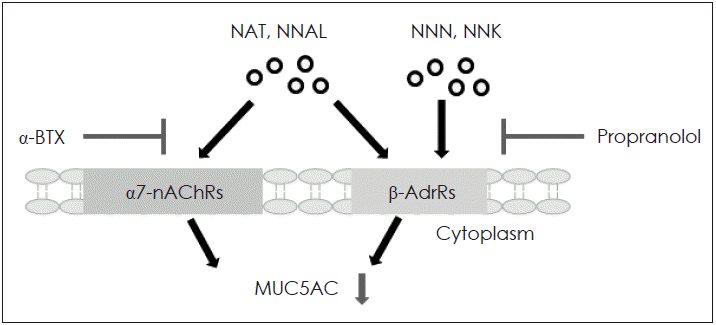 | Fig. 5.The schematic signaling pathway of TSNAs-induced MUC5AC expression. TSNAs-induced MUC5AC expression through β-adrenergic receptor and/or α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in human airway epithelial cells. TSNAs: Tobacco-specific nitrosamines, α7-nAChRs: α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, β-AdrRs: β-adrenergic receptor, α-BTX: α-bungarotoxin. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download