Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Conclusions
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: Geonhyeong Bae, Yunhee Lim. Data curation: Geonhyeong Bae, Sangseok Lee, Woo Yong Lee, Yunhee Lim. Formal analysis: Geonhyeong Bae, Yunhee Lim. Funding acquisition: Yunhee Lim. Writing - original draft: Geonhyeong Bae, Yunhee Lim. Writing - review & editing: Suyeon Kim, Sangseok Lee, Woo Yong Lee, Yunhee Lim. Supervision: Yunhee Lim.
REFERENCES
Fig. 2.
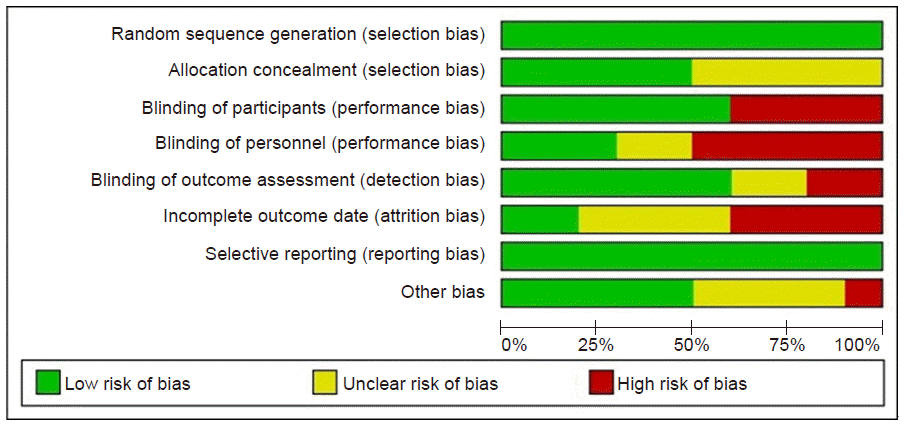
Fig. 3.
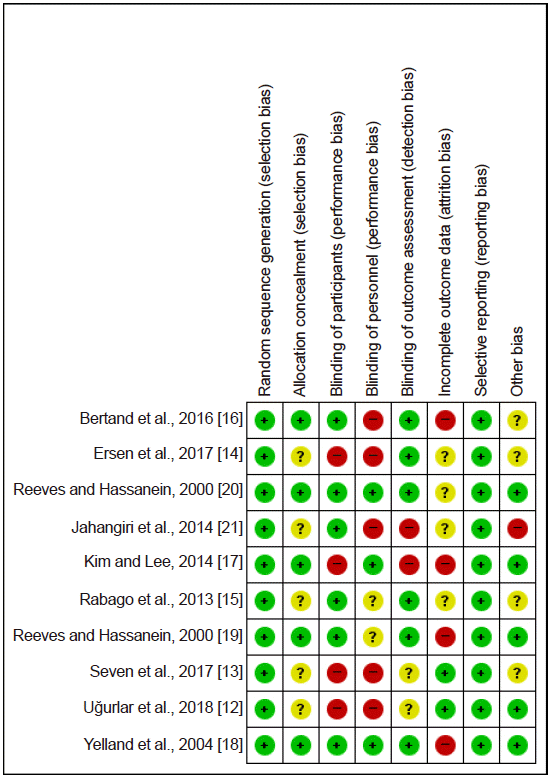
Fig. 4.
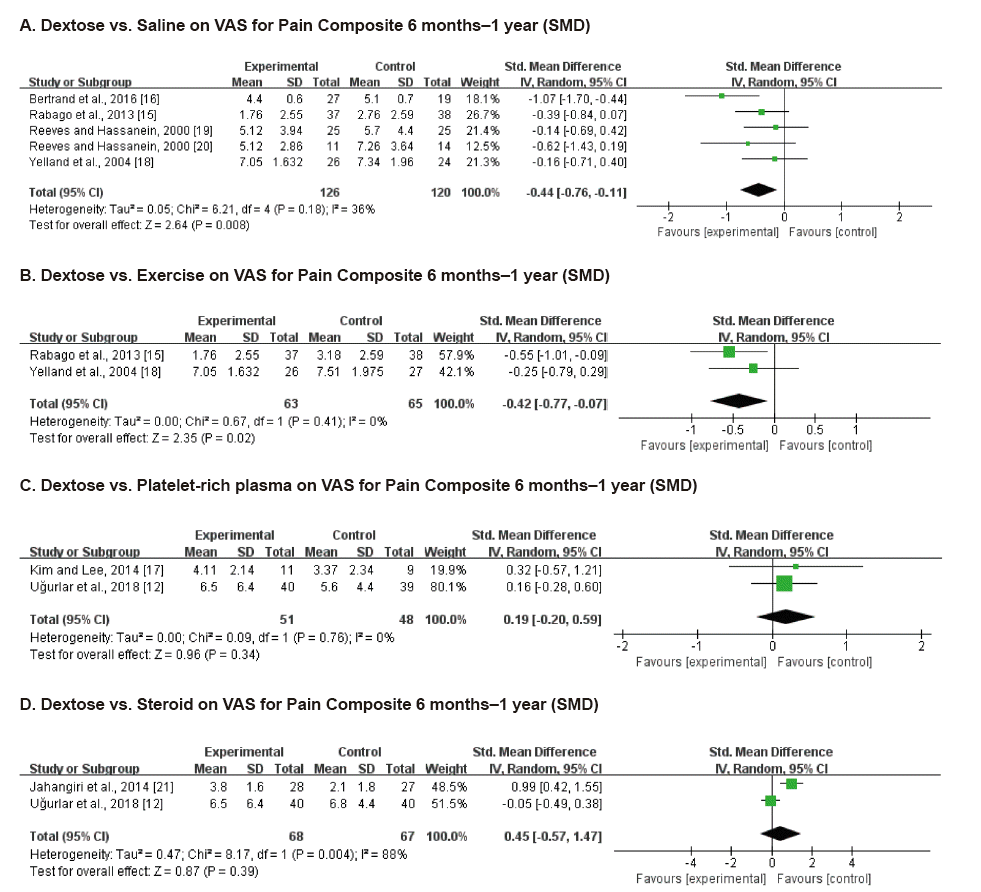
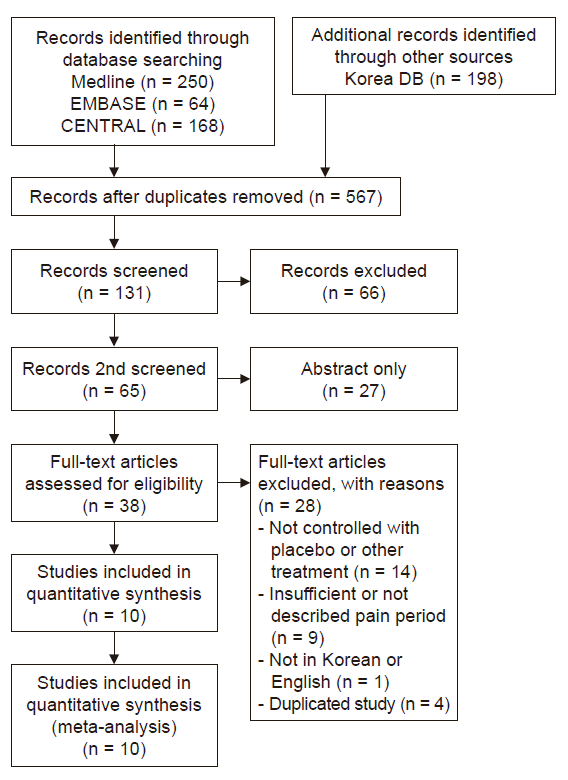
Table 1.
Table 2.
| Study | Disease | Intervention (number of patients) | Average age (yr)* | Outcome measure (s) | Follow-up timing | Total number of prolotherapy injection & interval | Prolotherapy regimen | Prolotherapy volume per dose | Prolotherapy injection technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabago et al., 2013 [15] | Knee OA | Dextrose (30) | Dextrose 56.8 ± 7.9 | WOMAC | Baseline, 5, 9, 12, 24, 52 weeks | 3 (1, 5, 9 weeks. 3 basic doses but additional injections were allowed at 13, 17 weeks) | Intra-articular 25% dextrose 10 ml: 5 ml 50% dextrose + 5 ml 1% lidocaine | 6 ml | 6.0 ml was injected using an inferomedial approach |
| Saline (29) | Saline 56.8 ± 6.7 | KPS | |||||||
| Exercise (31) | Exercise 56.4 ± 7.0 | Extra-articular 15% dextrose 22.5 ml: 6.75 ml 50% dextrose + 4.5 ml 1% lidocaine + 11.25 ml saline | per 0.5 ml, up to 22.5 ml | Palpation at major tender tendon and ligament insertions through up to 15 skin punctures using a peppering technique, placing a possible total 22.5 ml of solution | |||||
| Bertrand et al., 2016 [16] | Rotator cuff tendinopathy | Enthesis dextrose (27) | Enthesis dextrose 53.8 ± 13.5 | VAS | For VAS at baseline, 3, 9 months | 3 (0, 1, 2 months) | 25% dextrose/0.1% lidocaine/saline | 1 to 3 ml at primary injection site | The supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor insertions, insertions on the coracoid process, were injected with the shoulder in neutral rotation. |
| Enthesis saline (27) | Enthesis saline 51.1 ± 9.2 | USPRS | 0.5 ml at adjacent to primary injection area at 1 cm intervals | The biceps long head, subscapularis insertion, and inferior glenohumeral ligament were injected with the shoulder in various degrees of external rotation and abduction/adduction. | |||||
| Superficial saline (27) | Superfic saline 49.0 ± 11.9 | Satisfaction measure (0–10 scale) | For USPRS & Satisfaction measure at baseline, 9 months | Origins of the teres minor, teres major, and the posterior inferior glenohumeral ligament were injected posteriorly | |||||
| Seven et al., 2017 [13] | Rotator cuff tendinopathy | Dextrose (60) | Dextrose 50.19 ± 12.13 | VAS | Baseline, 3, 6, 12 weeks, and final follow up examination minimum of 1 year | N/A | 3.6 ml 25% dextrose + 0.4 ml lidocaine | 4 ml to the subacromial bursa | Shoulder in postero lateral aspect of the acromion using 27 G needle |
| Exercise (60) | Exercise 46.31 ± 10.6 | SPADI | Maximum 6 rounds of injections | 18 ml 15% dextrose + 2 ml lidocaine | Maximum 20 ml to | Shoulder in neutral rotation using 27 G needle | |||
| WORC | 1. Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor insertions, pectoralis minor, coracobrachialis and biceps brachii insertions | ||||||||
| Shoulder range of motion | 2. Biceps long head, subscapularis, inferior glenohumeral ligament insertions | Shoulder in external rotation and abduction/adduction using 27 G needle | |||||||
| 3. Origins of the teres minor, teres major, and posterior inferior glenohumeral ligament | Injected posteriorly using 27 G needle | ||||||||
| Ersen et al., 2017 [14] | Chronic plantar fasciitis | Dextrose (26) | Dextrose 45.1 ± 6.7 | VAS | Baseline, 21, 42, 90, 360 days | 3 (every 21 days) | 3.6 ml 15% dextrose + 0.4 ml lidocaine | 4 ml | Up to five different points, medial side of the heel and advanced under continuous ultrasound guidance into the proximal plantar fascia |
| Stretching exercise (24) | Exercise 46.3 ± 7.6 | FAOS | |||||||
| FFI | |||||||||
| Yelland et al., 2004 [18] | Chronic low back pain | Dextrose + Exercise (28) | Dextrose + exercise 51.5 ± 10.6 | VAS | Baseline, 2.5, 4, 6, 12, 24 months | 6 (every 2 weeks until six treatments, and additional injections were allowed at 4, 6 months) | 20% glucose + 0.2% lidocaine | 3 ml at each site and a maximum of 10 sites | Injection site was tenderness in ligaments and broad tendinous attachments of lumbosacral spine and pelvic girdle |
| Dextrose + normal activity (26) | Dextrose + normal activity 49.4 ± 10.4 | Disability scores (Roland-Morris) | Primary outcome at 12 month | ||||||
| Saline + exercise (27) | Saline + exercise 50.0 ± 9.8 | VAS, disability scores (Roland-Morris) | Secondary outcome at 24 month | ||||||
| Saline + normal activity (29) | Saline + normal activity 50.9±11.2 | ||||||||
| Kim and Lee, 2014 [17] | Chronic plantar fasciitis | Dextrose (11) | Dextrose 37.8 | FFI | Baseline, 2, 10, 28 weeks | 2 (interval 2 weeks) | 20% dextrose 1.5 ml + 0.5% lidocaine 0.5 ml | 2 ml | Under US guidance, abnormal hypoechoic areas in the thickened proximal plantar fascia were targeted and the needle was inserted through the medial heel along the long-axis view (in-plane technique) toward the target area. Then, 2 ml of dextrose solution was injected using a peppering technique, which involved a single skin portal followed by 5 penetration of the fascia |
| PRP (10) | PRP 36.2 | 1. Total | |||||||
| 2. Pain subscale scores | |||||||||
| 3. Disability subscale scores | |||||||||
| 4. Activity limitation subscale scores | |||||||||
| Reeves and Hassanein, 2000 [20] | Knee OA | Total 111 knees in 68 patients. | N/A | VAS (at rest, with walking, with stair use) | Baseline, 6, 12 months | 3 (every 2 months, and additional injections were allowed for dextrose group at 6, 8, 10 months) | 10% dextrose + 0.75% lidocaine | 9 ml | Using 27 G needle via an inferomedial approach, tibiofemoral injection |
| Dextrose | Swelling | ||||||||
| Bacteriostatic water | Buckling episodes | ||||||||
| Knee flexion range | |||||||||
| Reeves and Hassanein, 2000 [19] | OA in thumb and finger | Dextrose (11) | Dextrose 64.5 ± 9.2 | VAS | Baseline, 6 months | 3 (every 2 months) | 10% dextrose + 0.075% xylocaine in bacteriostatic water | 0.5 ml at each site | Using 27 G needle, All symptomatic DIP, PIP, thumb CMC joints were injected at the joint line laterally and medially until firm resistance was felt |
| Bacteriostatic water (14) | Control 63.9 ± 9.4 | 1. Rest pain | |||||||
| 2. Movement | |||||||||
| 3. Grip pain | |||||||||
| Goniometric measurements of joint flexion for PIP and DIP | |||||||||
| Uğurlar et al., 2018 [12] | Chronic plantar fasciitis | ESWT (39) | ESWT 39.2 | VAS (at the first step in the morning) | Baseline, 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, 36 months | 3 (every 1 week) | 1 ml bupivacaine 5 mg/ml + 5% dextrose 3 ml + 0.9% normal saline 6 ml bupivacaine 5 mg/ml | N/A | Under US guidance, injection was done into the site of maximal tenderness |
| Dextrose (40) | Dextrose 37.5 | Revised FFI | |||||||
| PRP(39) | PRP 38.4 | ||||||||
| Steroid(40) | Corticosteroid 40.1 | ||||||||
| Jahangiri et al., 2014 [21] | OA in the first carpometacarpal | Dextrose (30) | Dextrose 63.9 ± 9.4 | VAS (pain intensity of tenderness, pain on joint movement) | Baseline, 1, 2, 6 months | 3 (every 1 months) | 20% dextrose 0.5 ml + 2% lidocaine 0.5 ml | 1 ml | A 25 G needle was inserted toward the ulnar side of the extensor pollicis brevis and just proximal to the base of the first metacarpal in the snuffbox |
| Corticosteroid (30) | Corticosteroid 63.3 ± 10.1 | Hand function (self-administered questionnaire HAQ-DI about eating, gripping, dressing) | |||||||
| Strength (lateral pinch grip) |
OA: Osteoarthritis, PRP: platelet-rich plasma, N/A: Not available , ESWT: extracorporeal shock wave therapy, WOMAC: Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index, KPS: knee pain scale, VAS: Visual Analog Scale, USPRS: ultrasound shoulder pathology rating scale, SPADI: shoulder pain and disability, WORC: Western Ontario Rotator Cuff, FAOS: Foot and Ankle Outcome Score, FFI: foot function index, PIP: Proximal interphalangeal joints, DIP: Distal interphalangeal joints, HAQ-DI: Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index, CMC: Carpometacarpal.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download