Volunteers were monitored using end-tidal carbon dioxide partial pressure and fraction of inspired oxygen by using Carescape
® B850 (GE Healthcare, USA). Each volunteer was placed in a semi-Fowler’s position and connected to a breathing circuit to administer the nitrogen-air-carbon dioxide mixtures. A nose clip was applied to prevent breathing of room air. For frequent blood sampling, an arterial cannula was placed in the radial artery of each volunteer. Seven pulse oximeter probes were simultaneously attached to each volunteer’s fingers. The following models were used in this study: (1) WA-100 reusable finger probe (MEDNIS Co., Ltd., Korea), (2) MDNA disposable finger probe (MEDNIS Co., Ltd.), (3) IS-1011 disposable finger probe (Insung Medical Co., Ltd., Korea), (4) CJ340NA disposable finger probe (CHUN JI IN Medical Co., Ltd., Korea), (5) Nellcor
TM OxiMax DS-100A reusable finger probe (Medtronic, USA), (6) Nellcor
TM OxiMax MAX-N disposable finger probe (Medtronic), and (7) OXI-PRO DA disposable finger probe (Bio-Protech Inc., Korea). The same reusable probes were used for all volunteers, and a new disposable probe was used for each volunteer. To minimize light interference from outside, both hands were covered with a blanket. An air warmer (Bair Hugger™, 3M™, USA) was applied to the hands to prevent hypoperfusion. To obtain the SpO
2 value to be referenced when determining the target plateau, a reusable pulse oximeter finger probe (OxiMax
® N-600x, Medtronic) was also used. The probes were placed on the fingers of the hand with the arterial catheter as follows: CJ340NA disposable finger probe (thumb), MDNA disposable finger probe (index finger), OXI-PRO DA disposable finger probe (middle finger), Nellcor
TM OxiMax MAX-N disposable finger probe (ring finger). The probes were placed on the fingers of the other hand as follows: IS-1011 disposable finger probe (thumb), OxiMax
® N-600x (index finger), WA-100 reusable finger probe (middle finger), Nellcor
TM OxiMax DS-100A reusable finger probe (ring finger). Each volunteer was exposed to various levels of induced hypoxia from 70-100% of SaO
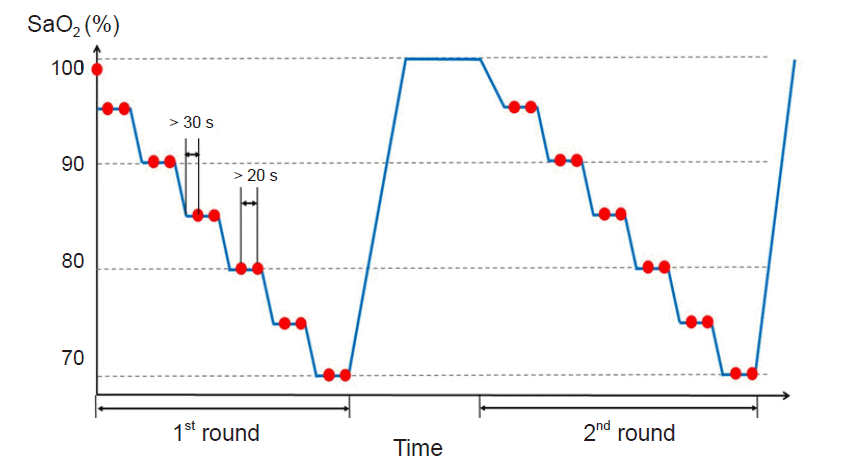
2. Each plateau of oxygen saturation was maintained for at least 30 s until stabilization, after which 1 ml of arterial blood was drawn into a heparinized syringe (
Fig. 1). The study period consisted of two rounds of hypoxia, and the volunteers were maintained on room air between each round. SaO
2 measurements using a CO-oximeter (ABL90 FLEX, Radiometer Medical A/S, Denmark) were used as a reference for the SpO
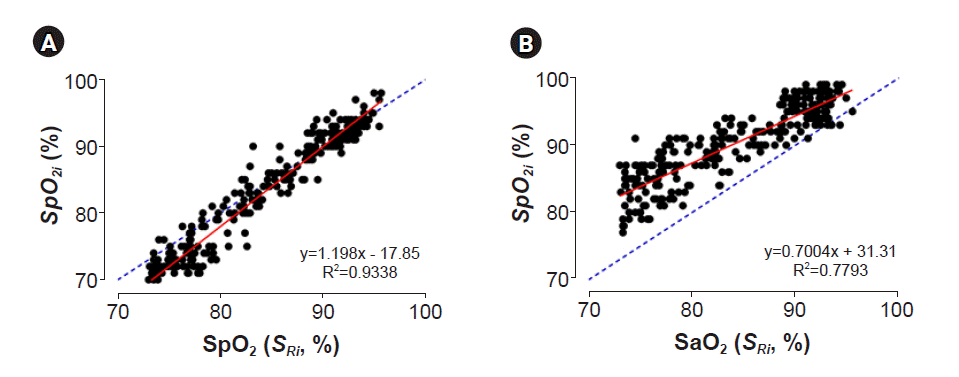
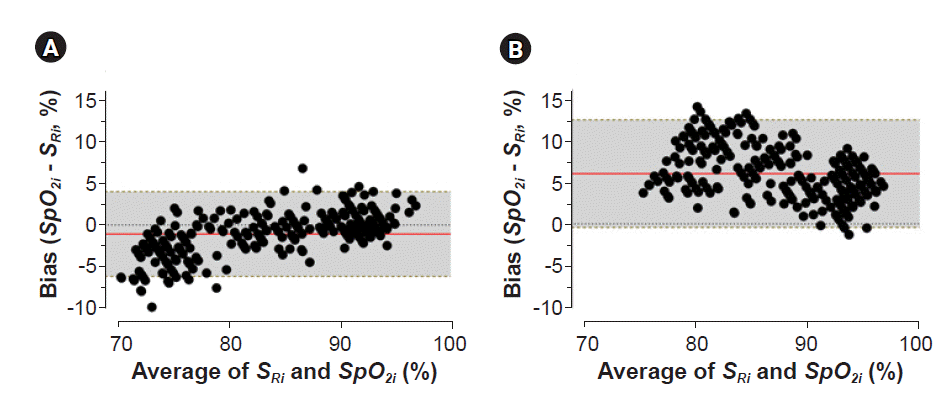
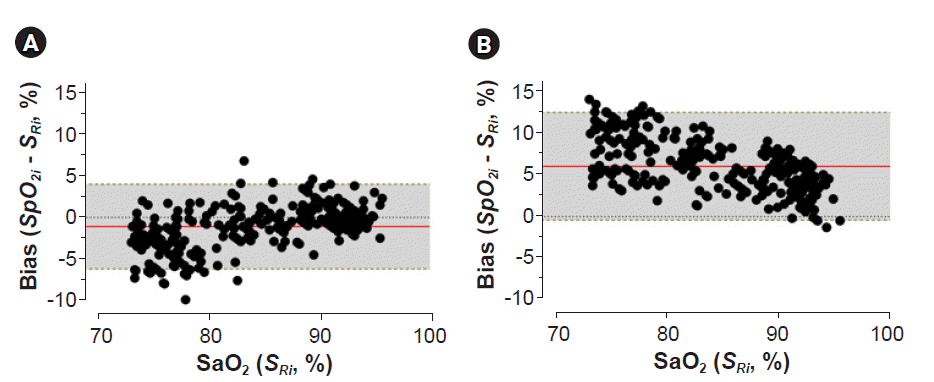
2 accuracy.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download