INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Cell culture and treatment
Real-time PCR analysis of MUC5B and MMP-9 mRNA expression
Immunoassay for MUC5B protein
Gelatin zymography assay of MMP-9 protein activity
Western blot analysis of p38 MAPK, ERK1/2 MAPK, and MMP-9
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
The effect of EGCG on PMA-induced MUC5B expression
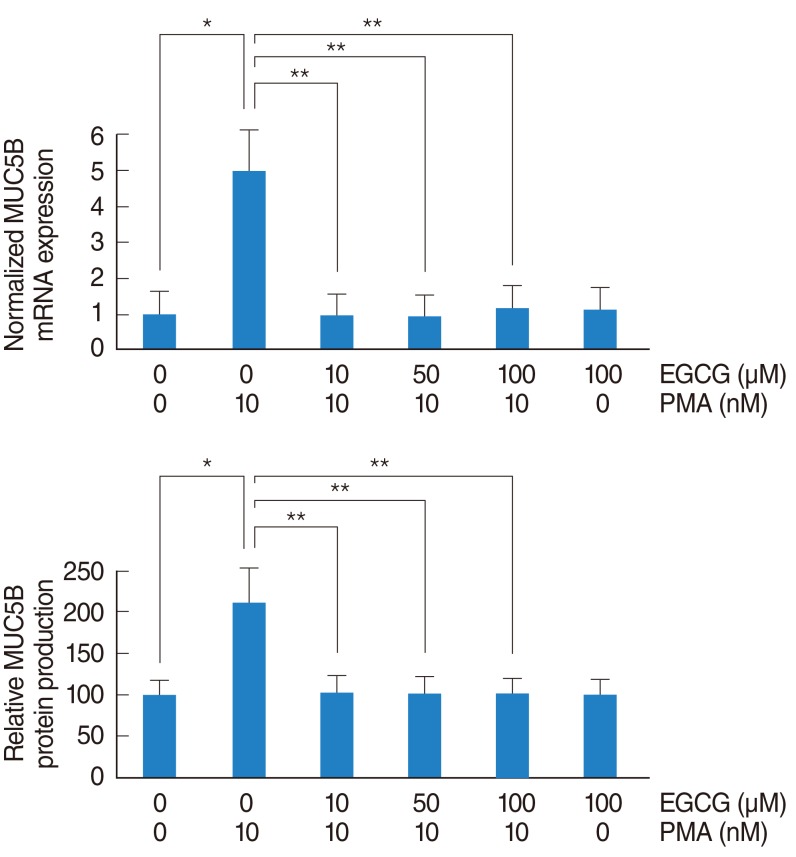 | Fig. 1The effect of EGCG on PMA-induced MUC5B expression. To investigate the effect of EGCG on PMA-induced MUC5B expression, NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were incubated with PMA in the absence or presence of EGCG. (A) Real-time PCR and (B) ELISA showed that PMA induced MUC5B mRNA expression and protein production, which were significantly decreased by pretreatment with EGCG. EGCG, epigallocatechin-3-gallate; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. *P<0.05 compared with zero value. **P<0.05 compared with PMA alone. |
The effect of EGCG on PMA-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK
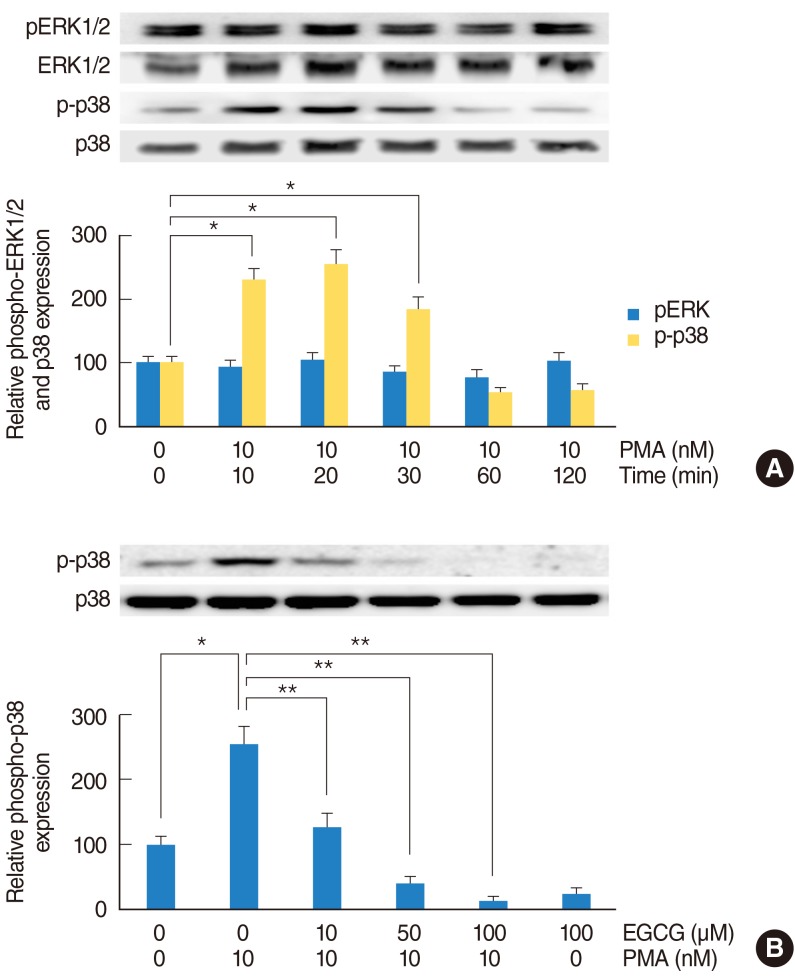 | Fig. 2The effect of EGCG on PMA-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK. To investigate the MAPK signaling pathway of PMA-induced MUC5B expression, NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were incubated with PMA in the absence or presence of EGCG and phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK were analyzed by Western blot. (A) As time elapsed, phosphorylation of p38 MAPK was significantly increased: phosphorylation of p38 MAPK peaked at 20 minutes after treatment with PMA, but phosphorylation of ERK1/2 did not increase. (B) EGCG significantly decreased PMA-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK. EGCG, epigallocatechin-3-gallate; ERK1/2, extracellular signal related kinase 1/2; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. *P<0.05 compared with zero value. **P<0.05 compared with PMA alone. |
The effect of EGCG on PMA-induced MMP-9 expression
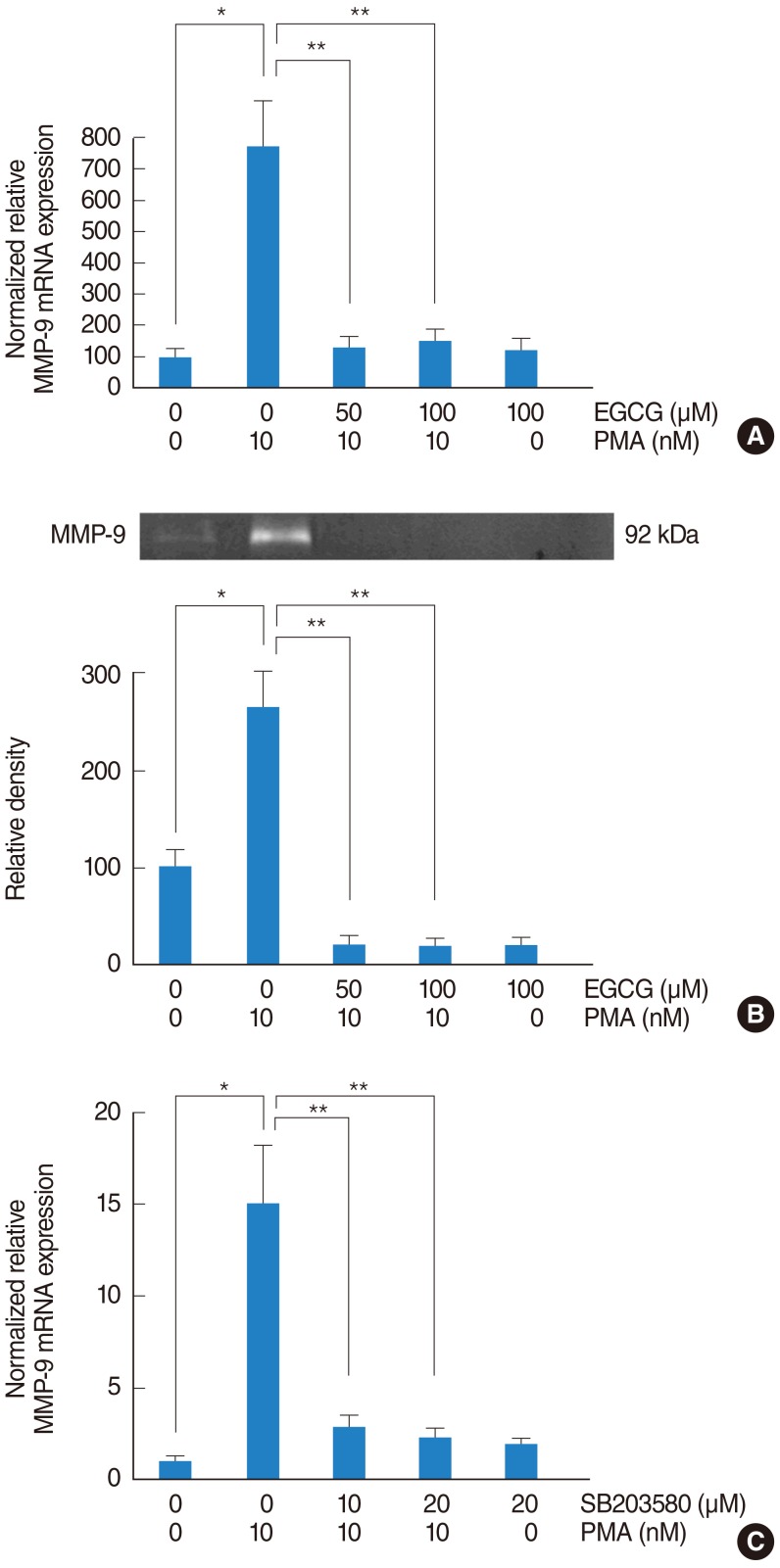 | Fig. 3The effect of EGCG on PMA-induced MMP-9 expression. To investigate the signaling pathway associated with MMP-9, NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were incubated with PMA in the absence or presence of EGCG. (A) Real-time PCR showed that PMA induced MMP-9 mRNA expression and EGCG significantly decreased PMA-induced MMP-9 mRNA expression. (B) Gelatin zymography showed that EGCG inhibited PMA-induced MMP-9 protein activity. To investigate the correlation between MMP-9 and p38 MAPK, NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were pretreated with SB203580 before being exposed to PMA. (C) Real-time PCR showed that SB203580 significantly decreased PMA-induced MMP-9 mRNA expression. EGCG, epigallocatechin-3-gallate; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase-9; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. *P<0.05 compared with zero value. **P<0.05 compared with PMA alone. |
The signaling pathway of EGCG on PMA-induced MUC5B expression
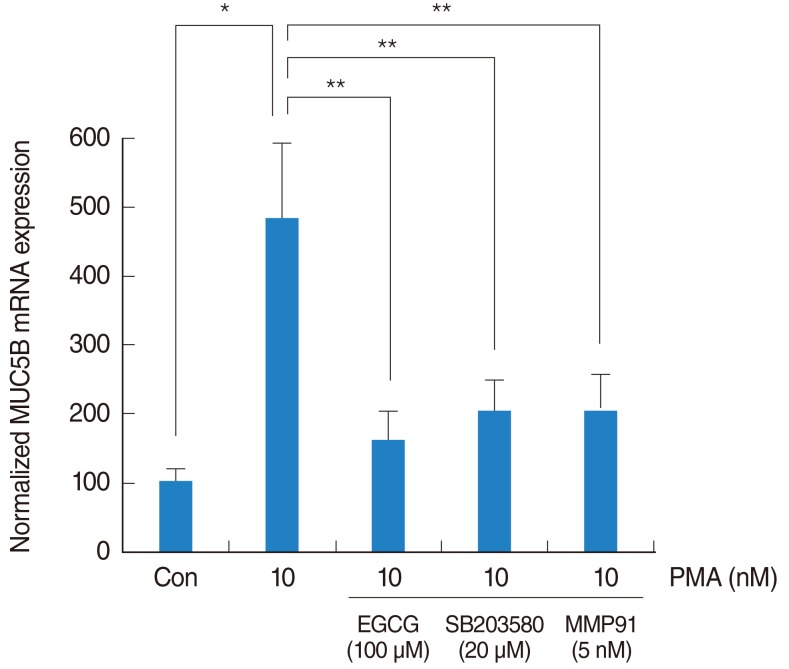 | Fig. 4The signaling pathway of EGCG on PMA-induced MUC5B expression. To investigate the brief signaling pathway of EGCG on PMA-induced MUC5B expression, NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were pretreated with SB203580 as a p38 MAPK inhibitor or MMP-9 I as a MMP-9 inhibitor before being exposed to PMA. Real-time PCR showed that SB203580 and MMP-9 I significantly decreased PMA-induced MUC5B mRNA expression. EGCG, epigallocatechin-3-gallate; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMP-9 I, matrix metalloproteinase-9 inhibitor; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. *P<0.05 compared with zero value. **P<0.05 compared with PMA alone. |
DISCUSSION
 | Fig. 5The schematic signaling pathway of EGCG on PMA-induced MUC5B expression. EGCG can down-regulate PMA-induced MUC5B expression, which is associated with p38 MAPK dependent MMP-9 signaling pathway. PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate; EGCG, epigallocatechin-3-gallate; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase-9. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download