INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fish preparation and maintenance
Examination of neuromasts in zebrafish
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay
Scanning electron microscopy
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
The effect of TMZ on hair cells in transgenic zebrafish treated with neomycin
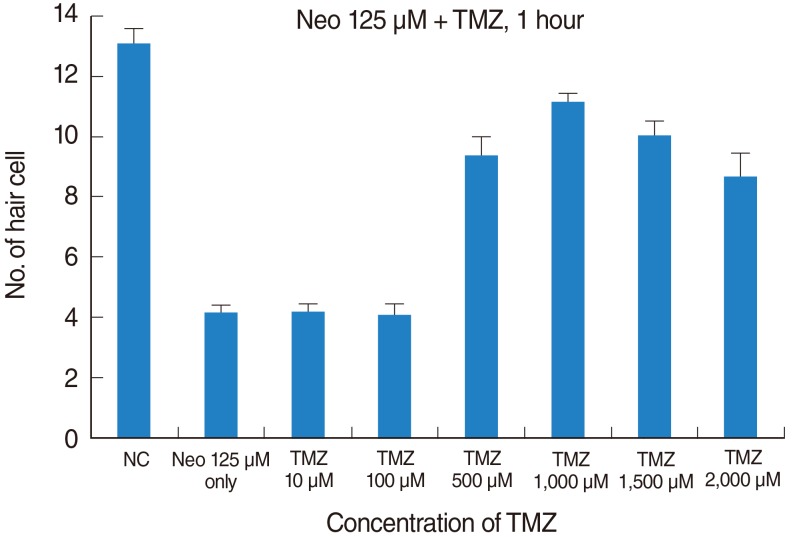 | Fig. 1Quantitative assay of neuromasts in zebrafish. Hair cells from four neuromasts (supraorbital 1, supraorbital 2, otic 1, and occipital 1 were counted. Treatment of zebrafish with 125 µM Neo for 1 hour significantly decreased the number of hair cells in the neuromasts. TMZ protected against neomycin-induced hair cell loss in neuromasts (NC, 13.1±0.9 cells; 125 µM Neo only 4.2±0.5 cells; TMZ 10 µM, 4.2±0.7 cells; TMZ 100 µM, 4.1±0.6 cells; TMZ 500 µM, 9.4±1.1 cells; TMZ 1,000 µM, 11.2±0.4 cells; TMZ 1,500 µM, 10.0±0.7 cells; TMZ 2,000 µM, 8.7±1.7 cells; n=10; P<0.05). NC, negative control; Neo, neomycin; TMZ, trimetazidine. |
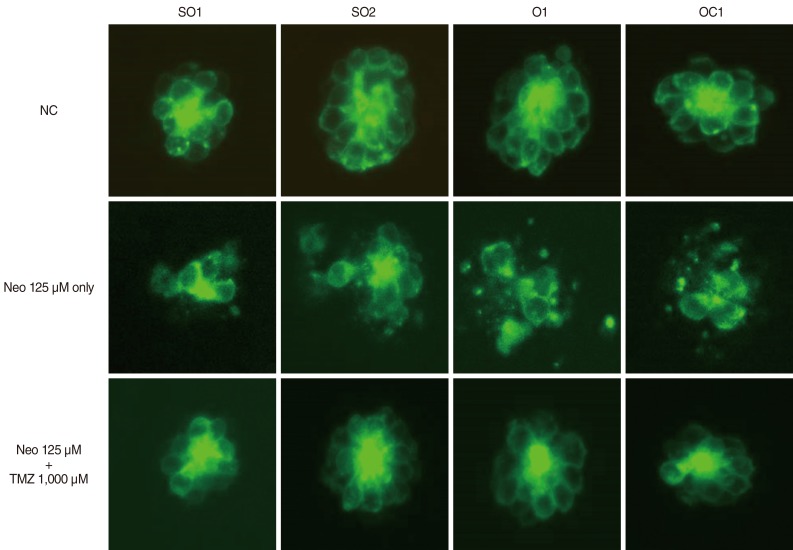 | Fig. 2Confocal microscopy (×40). The 5-dpf transgenic zebrafish were treated simultaneously with 125 µM Neo and 1,000 µM TMZ for 1 hour. Treatment with 125 µM Neo resulted in a significant decrease in the number of hair cells in the neuromasts, and TMZ protected against this neomycin-induced hair cell damage. TMZ, trimetazidine; SO1, supraorbital 1; SO2, supraorbital 2; O1, otic 1; OC1, occipital 1; NC, negative control; Neo, neomycin. |
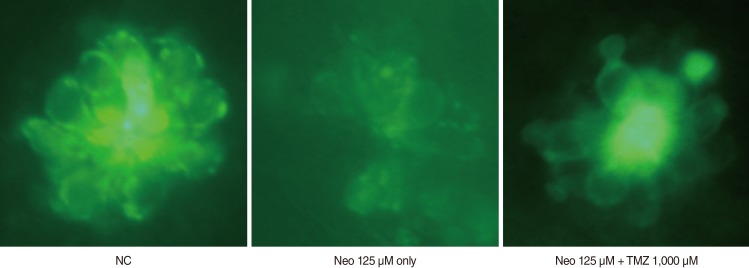 | Fig. 3Evaluation of mitochondrial damage with DASPEI (fluorescent microscopy, O1, ×40). The 5-dpf wild-type zebrafish were treated with 125 µM Neo and 1,000 µM TMZ for 1 hour. Treatment with 125 µM Neo resulted in a significant decrease in mitochondrial staining with DASPEI, and this mitochondrial damage was prevented by TMZ. NC, negative control; Neo, neomycin; TMZ, trimetazidine; O1, otic. |
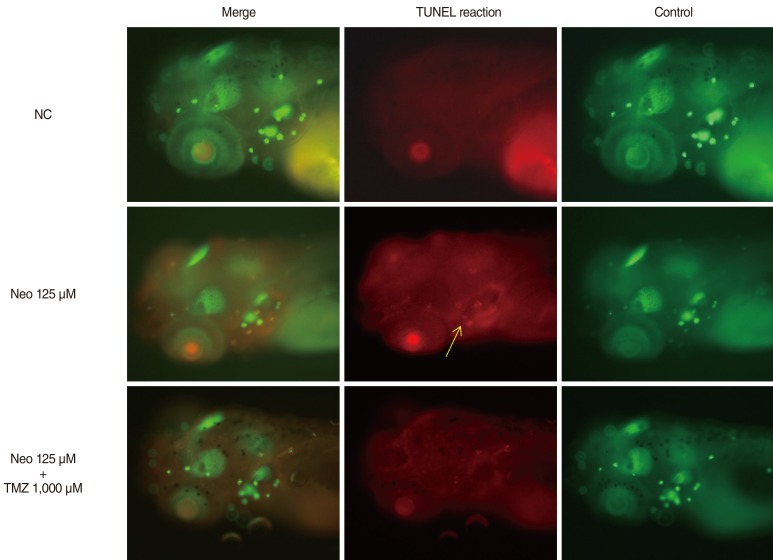 | Fig. 4Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay (fluorescent microscope, ×10). Neo-induced apoptotic cells were confirmed by the TUNEL assay. Apoptotic cells are marked as light red dots in red-colored fish after the TUNEL reaction under a fluorescent microscope (arrow indicates TUNEL-positive cells). No light-red dots were found in the NC group. A comparison of the color intensity between the group treated with 125 µM Neo and the group treated with 1,000 µM TMZ for 1 hour showed that TMZ significantly decreased the number of TUNEL-positive cells and protected against Neo-induced apoptotic cell death of the neuromast hair cells (green-colored fish of right column, control for TUNEL reaction; red-colored fish of middle column, TUNEL reaction; green- and red-colored fish of left column, combination of control and TUNEL reaction). NC, negative control; Neo, neomycin; TMZ, trimetazidine. |
TMZ protects stereocilia and kinocillium in transgenic zebrafish treated with neomycin
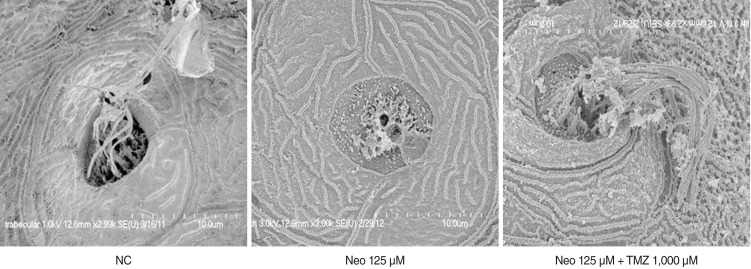 | Fig. 5Scanning electron microscopy (SEM; O1, ×3,000). Compared to control neuromasts, neuromasts in zebrafish treated with 125 µM Neo for 1 hour showed severe morphological damage to stereocilia and kinocilium under SEM. However, this damage was prevented by TMZ. NC, negative control; Neo, neomycin; TMZ, trimetazidine, O1, otic. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download