INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture and treatment
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis of MUC5B and MMP-9mRNA expression
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis of MUC5B protein
Gelatin zymography assay analysis of MMP-9 protein activity
Western blot analysis of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and p38 phosphorylation
Cell transfection with small interfering RNA (siRNA) for p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Effect of PMA on MUC5B and MMP-9 mRNA expression
 | Fig. 1The effect of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) on MUC5B and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 mRNA expression. Human NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were stimulated with PMA. MUC5B and MMP-9 mRNA levels were analyzed by RT-PCR. MUC5B mRNA express ion was significantly increased at all doses of PMA and peaked at 10 nM of PMA. MMP-9 mRNA expression was significantly increased about 17 fold at 5, 10, 25, and 50 nM of PMA. *P<0.05 compared with zero value. |
Effect of MMP-9 on MUC5B mRNA expression
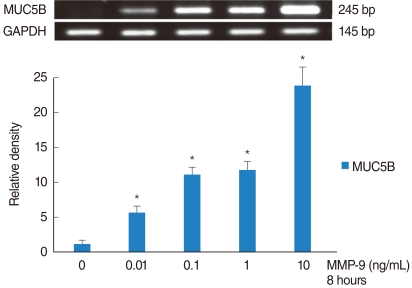 | Fig. 2The effect of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 on MUC5B mRNA expression. Human NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were stimulated with MMP-9. MUC5B mRNA levels were analyzed by RT-PCR. MUC5B mRNA expression was significantly increased in a dose-dependent manner. *P<0.05 compared with zero value. |
Phosphorylation of p38 in PMA-induced MUC5B expression
 | Fig. 3The effect of SB203580 and p38 MAPK siRNA on the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced MUC5B mRNA expression. Human NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were stimulated with SB203580 before exposure to PMA, and also were transfected with predesigned siRNA targeting p38 MAPK and a negative control siRNA for p38 MAPK before exposure to PMA. MUC5B mRNA expression was analyzed by RT-PCR. (A) SB203580 inhibited PMA-induced MUC5B expression. (B) The knockdown of p38 MAPK by p38 MAPK siRNA significantly blocked PMA-induced MUC5B mRNA expression. *P<0.05 compared with PMA alone. **P<0.05 compared with control. |
Effect of doxycycline on PMA-induced MUC5B expression and PMA-induced MMP-9 mRNA expression and protein activity
 | Fig. 4The effect of doxycycline on phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced MUC5B expression. Human NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were stimulated with doxycycline after the treatment of PMA. MUC5B RNA levels were analyzed by RT-PCR, and MUC5B protein levels of cell lysates and supernatants were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Doxycycline significantly inhibited PMA-induced MUC5B mRNA expression and protein production in a dose-dependent manner. *P<0.05 compared with PMA alone. |
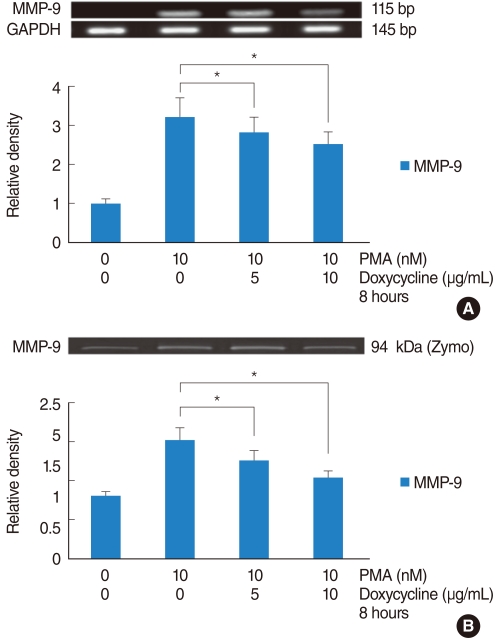 | Fig. 5The effect of doxycycline on phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 mRNA expression and protein activity. Human NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were stimulated with doxycycline after treatment with PMA. MMP-9 mRNA levels were analyzed by RT-PCR, and MMP-9 protein activity was measured by gelatin zymography. (A) Doxycycline significantly inhibited PMA-induced MMP-9 mRNA expression. (B) Doxycycline significantly inhibited PMA-induced MMP-9 protein activity. *P<0.05 compared with PMA alone. |
Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 in the effect of doxycycline after treatment with PMA or MMP-9
 | Fig. 6The effects of doxycycline on the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 after treatment with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) or matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9. Human NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells were stimulated with doxycycline after treatment with PMA or MMP-9. The phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 were detected by Western blot analysis. (A) Doxycycline inhibited PMA induced phosphorylation of p38 in a dose dependent manner, but it did not change the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 significantly. (B) Doxycycline significantly inhibited MMP-9 induced phosphorylation of p38. *P<0.05 compared with PMA alone. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download