INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Genetic screening
Genomic DNA isolation
Polymerase chain reaction amplification and sequence analysis of ENG and ACVRL1
Clinical analysis
Fig. 1.
RESULTS
Gene variant analyses of Korean patients with suspected HHT
Table 1.
| Gene | No. of families | No. of tested family members | No. of members with genetic variants |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENG | 12 | 35 | 26 |
| ACVRL1 | 12 | 19 | 16 |
| Total | 24 | 54 | 42 |
Table 2.
| Family no. | Variant location | Variant type | Nucleotide changea) | Protein changea) | Classificationb) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intron 3 | Substitution/splicing defect | c.360+1G>A | p.? | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP1, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 2 | 5′-UTR | Substitution/translation defect | c.1-127C>T | New upstream translation start codon | Likely pathogenic (PS3, PM2, PP1, PP4) | [12] |
| 8 | Exon 13 | Deletion/frameshift | c.1687del | p.Glu563Lysfs*10 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 18 | Exon 13 | Deletion/frameshift | c.1687del | p.Glu563Lysfs*10 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 20 | Intron 3 | Substitution/splicing defect | c.360+1G>A | p.? | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP1, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 21 | Exon 7 | Substitution/missense | c.821C>T | p.Thr274Ile | Uncertain significance (PM2, PP4) | [10] |
| 22 | Exon 1 | Deletion/frameshift | c.63del | p.Thr22Glnfs*21 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP1, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 24 | Exon 3 | Deletion-insertion/nonsense | c.276_277delinsAT | p.Arg93* | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP4) | This study |
| 26 | Intron 3 | Substitution/splicing defect | c.360+1G>A | p.? | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP1, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 31 | Exon 13 | Duplication/frameshift | c.1690_1693dup | p.His565Argfs*3 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP4) | This study |
| 33 | Exon 7 | Deletion-insertion/frameshift | c.857_858delinsG | p.Asn286Argfs*73 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP4) | This study |
| 34 | Exon 11 | Duplication/frameshift | c.1342dup | p.Leu338Profs*53 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP4) | This study |
HHT, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia; p.?, an effect on the protein level is expected, but it is not possible to give a reliable prediction of the consequences; PVS, pathogenic very strong; PM, pathogenic moderate; PP, pathogenic supporting; PS, pathogenic strong; *, termination by nonsense mutation.
a) The reference sequences to describe variants were NC_000009.12 (genomic DNA), NM_000118.3 (coding DNA), and NP_000109.1 (protein).
b) The classification was based on the Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology [17].
Table 3.
| Family No. | Variant location | Variant type | Nucleotide changea) | Protein changea) | Classificationb) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Exon 3 | Duplication/frameshift | c.252dup | p.Val85Argfs*84 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP1, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 6 | Exon 3 | Substitution/missense | c.199C>T | p.Arg67Trp | Likely pathogenic (PM2c), PP1, PP3, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 10 | Exon 7 | Substitution/missense | c.925G>A | p.Gly309Ser | Likely pathogenic (PM2, PP1, PP3, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 12 | Exon 7 | Substitution/missense | c.781G>C | p.Ala261Pro | Uncertain significance (PM2, PP3, PM4) | This study |
| 16 | Exon 10 | Substitution/nonsense | c.1435C>T | p.Arg479* | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP1, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 17 | Exon 8 | Deletion/frameshift | c.1118del | p.Lys373Serfs*42 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP1, PP4, PP5) | [10] |
| 28 | Exon 3 | Duplication/frameshift | c.121dup | p.Cys41Leufs*128 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP4) | This study |
| 30 | Exon 5 | Substitution/missense | c.605T>G | p.Val202Gly | Uncertain significance (PM2, PP3, PP4) | This study |
| 32 | Exon 8 | Substitution/missense | c.1124A>G | p.Tyr375Cys | Uncertain significance (PM2, PP3, PP4) | [10] |
| 35 | Exon 9 | Deletion/frameshift | c.1311_1315del | p.Asp437Glufs*15 | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP4) | This study |
| 38 | Exon 7 | Substitution/missense | c.1005T>G | p.Asn335Lys | Uncertain significance (PM2, PP3, PP4) | This study |
| 40 | Intron 7 | Substitution/splicing defect | c.1048+5G>A | p.? | Likely pathogenic (PS3, PM2, PP4) | [9,20] |
HHT, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia; *, termination by nonsense mutation; PVS, pathogenic very strong; PM, pathogenic moderate; PP, pathogenic supporting; p.?, an effect on the protein level is expected, but it is not possible to give a reliable prediction of the consequences; PS, pathogenic strong.
a) The reference sequences to describe variants are NC_000012.12 (genomic DNA), NM_000020.3 (coding DNA), and NP_000011.2 (protein).
b) The classification was based on the Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology [17].
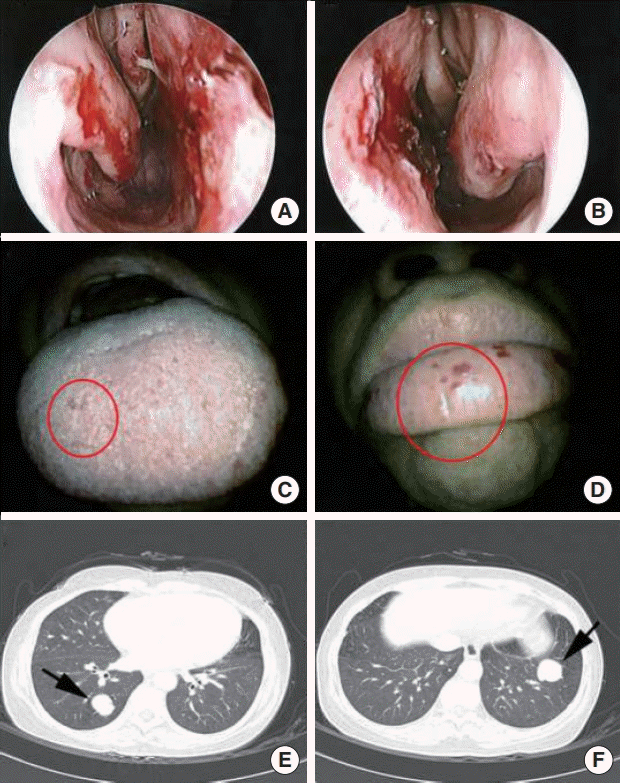
Clinical characteristics of Korean patients with HHT
Table 4.
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 23 (55) |
| Female | 19 (45) |
| Age (yr) | 53.9 |
| Genotype | |
| ENG | 26 (62) |
| ACVRL1 | 16 (38) |
| Clinical presentation | |
| Epistaxis | 38 (90) |
| Telangiectasia | 21 (50) |
| Family history | 37 (88) |
| AVM | 24 (57) |
| Pulmonary | 12 (29) |
| Cerebral | 6 (14) |
| Hepatic | 4 (10) |
| Gastrointestinal | 2 (5) |
| Curaçao criteriaa) | |
| Definite | 24 (57) |
| Probable | 17 (41) |
| Unlikely | 1 (2) |
Table 5.
| Clinical characteristics | ENG (n=26) | ACVRL1 (n=16) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (yr) | 55.3 | 53.4 | - |
| Curaçao criteriaa) | - | ||
| Definite | 17 (65) | 7 (44) | |
| Probable | 9 (35) | 8 (50) | |
| Unlikely | 0 | 1 (6) | |
| Clinical presentation | |||
| Epistaxis | 24 (92) | 14 (88) | 0.628 |
| Telangiectasia | 12 (46) | 9 (56) | 0.751 |
| Family history | 25 (96) | 12 (75) | 0.061 |
| AVM | 18 (42) | 9 (56) | 0.511 |
| Pulmonary | 12 (46) | 0 | <0.001 |
| Cerebral | 3 (12) | 4 (25) | 0.397 |
| Hepatic | 1 (4) | 3 (19) | 0.146 |
| Gastrointestinal | 2 (8) | 2 (13) | 0.628 |
Table 6.
| Curaçao criteriaa) | No. of members (%) |
|---|---|
| Definite | 6 (20) |
| Probable | 0 |
| Unlikely | 24 (80) |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download