1. Tousoulis D, Papageorgiou N, Androulakis E, Siasos G, Latsios G, Tentolouris K, et al. Diabetes mellitus-associated vascular impairment: novel circulating biomarkers and therapeutic approaches. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; Aug. 62(8):667–76.
2. Kampoli AM, Tousoulis D, Briasoulis A, Latsios G, Papageorgiou N, Stefanadis C. Potential pathogenic inflammatory mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Pharm Des. 2011; Dec. 17(37):4147–58.

3. Asmat U, Abad K, Ismail K. Diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress-A concise review. Saudi Pharm J. 2016; Sep. 24(5):547–53.

4. Feldman EL, Nave KA, Jensen TS, Bennett DL. New horizons in diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms, bioenergetics, and pain. Neuron. 2017; Mar. 93(6):1296–313.

5. Ozougwu JC, Obimba KC, Belonwu CD, Unakalamba CB. The pathogenesis and pathophysiology of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Physiol Pathophysiol. 2013; 4(4):46–57.

6. Akinpelu OV, Ibrahim F, Waissbluth S, Daniel SJ. Histopathologic changes in the cochlea associated with diabetes mellitus: a review. Otol Neurotol. 2014; 35(5):764–74.
7. Hong BN, Kang TH. Auditory neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse. Neurosci Lett. 2008; Feb. 431(3):268–72.

8. Varkonyi T, Korei A, Putz Z, Martos T, Keresztes K, Lengyel C, et al. Advances in the management of diabetic neuropathy. Minerva Med. 2017; Oct. 108(5):419–37.

9. Hosseini A, Abdollahi M. Diabetic neuropathy and oxidative stress: therapeutic perspectives. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013; 2013:168039.

10. Han Y, Wang M, Shen J, Zhang Z, Zhao M, Huang J, et al. Differential efficacy of methylcobalamin and alpha-lipoic acid treatment on symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Minerva Endocrinol. 2018; Mar. 43(1):11–8.

11. Yilmaz M, Aktug H, Oltulu F, Erbas O. Neuroprotective effects of folic acid on experimental diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Toxicol Ind Health. 2016; May. 32(5):832–40.

12. Ganeshpurkar A, Saluja AK. The pharmacological potential of rutin. Saudi Pharm J. 2017; Feb. 25(2):149–64.

13. Ghorbani A. Mechanisms of antidiabetic effects of flavonoid rutin. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017; Dec. 96:305–12.

14. Habtemariam S, Lentini G. The therapeutic potential of rutin for diabetes: an update. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2015; 15(7):524–8.

15. Mittal R, Kumar A, Singh DP, Bishnoi M, Nag TC. Ameliorative potential of rutin in combination with nimesulide in STZ model of diabetic neuropathy: targeting Nrf2/HO-1/NF-kB and COX signalling pathway. Inflammopharmacology. 2018; Jun. 26(3):755–68.

16. Niture NT, Patil DG, Somani RS, Sahane RS. Effect of rutin on early diabetic neuropathy in experimental animals. J Nat Prod Plant Resour. 2014; 4(4):1–9.
17. Xie L, Wang M, Liao T, Tan S, Sun K, Li H, et al. The characterization of auditory brainstem response (ABR) waveforms: a study in tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri). J Otol. 2018; Sep. 13(3):85–91.

18. Norrix LW, Velenovsky D. Unraveling the mystery of auditory brainstem response corrections: the need for universal standards. J Am Acad Audiol. 2017; Nov/Dec. 28(10):950–60.

19. Helzner EP, Contrera KJ. Type 2 diabetes and hearing impairment. Curr Diab Rep. 2016; Jan. 16(1):3.

20. Wang Y, Branicky R, Noe A, Hekimi S. Superoxide dismutases: dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J Cell Biol. 2018; Jun. 217(6):1915–28.

21. Younus H. Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018; May-Jun. 12(3):88–93.
22. Islam MT. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction-linked neurodegenerative disorders. Neurol Res. 2017; Jan. 39(1):73–82.

23. Bouhajja H, Kacem FH, Abdelhedi R, Ncir M, Dimitrov JD, Marrakchi R, et al. Potential predictive role of lipid peroxidation markers for type 2 diabetes in the adult Tunisian population. Can J Diabetes. 2018; Jun. 42(3):263–71.

24. Abeeleh MA, Ismail ZA, Alzaben KR, Abu-Halaweh SA, Al-Essa MK, Abuabeeleh J, et al. Induction of diabetes mellitus in rats using intraperitoneal streptozotocin: a comparison between 2 strains of rats. Eur J Sci Res. 2009; 32(3):398–402.
25. Hernandez-Aquino E, Zarco N, Casas-Grajales S, Ramos-Tovar E, Flores-Beltran RE, Arauz J, et al. Naringenin prevents experimental liver fibrosis by blocking TGFβ-Smad3 and JNK-Smad3 pathways. World J Gastroenterol. 2017; Jun. 23(24):4354–68.
26. Kuse H, Ogawa T, Nakamura N, Nakayama Y, Nakakarumai A, Komori C, et al. Changes in auditory brainstem response (ABR) in Kanamycin-induced auditory disturbance model rats. J Toxicol Sci. 2011; 36(6):835–41.

27. Marquez-Gamino S, Sotelo F, Sosa M, Caudillo C, Holguin G, Ramos M, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields induced femoral metaphyseal bone thickness changes in the rat. Bioelectromagnetics. 2008; Jul. 29(5):406–9.

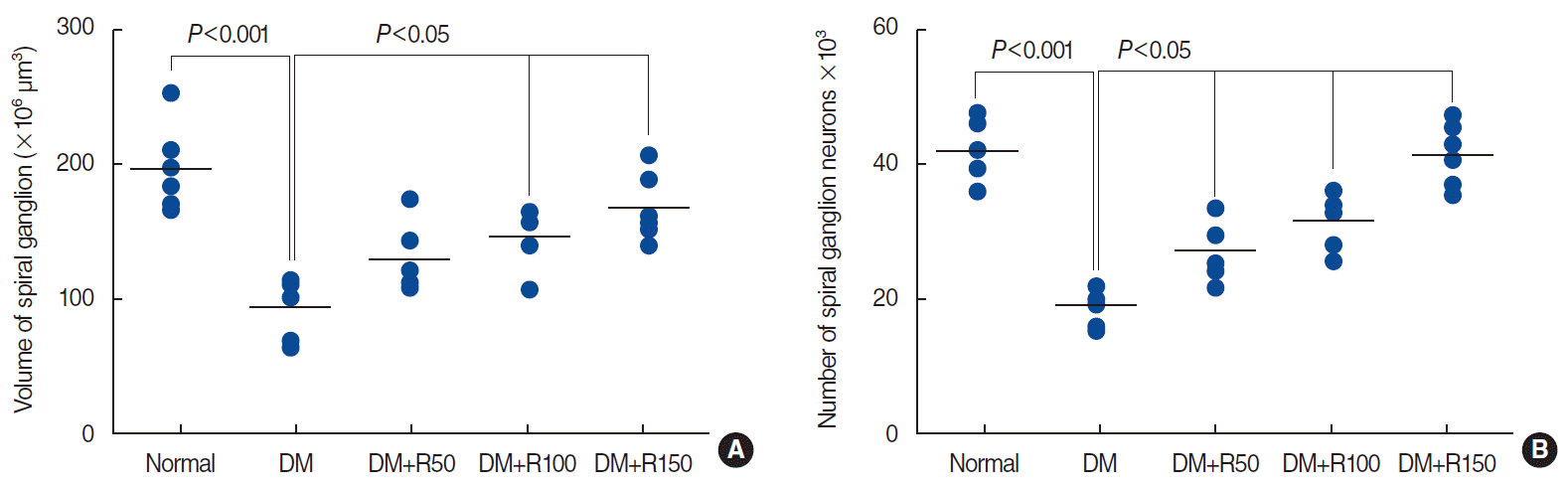
28. Rusznak Z, Szucs G. Spiral ganglion neurones: an overview of morphology, firing behaviour, ionic channels and function. Pflugers Arch. 2009; Apr. 457(6):1303–25.
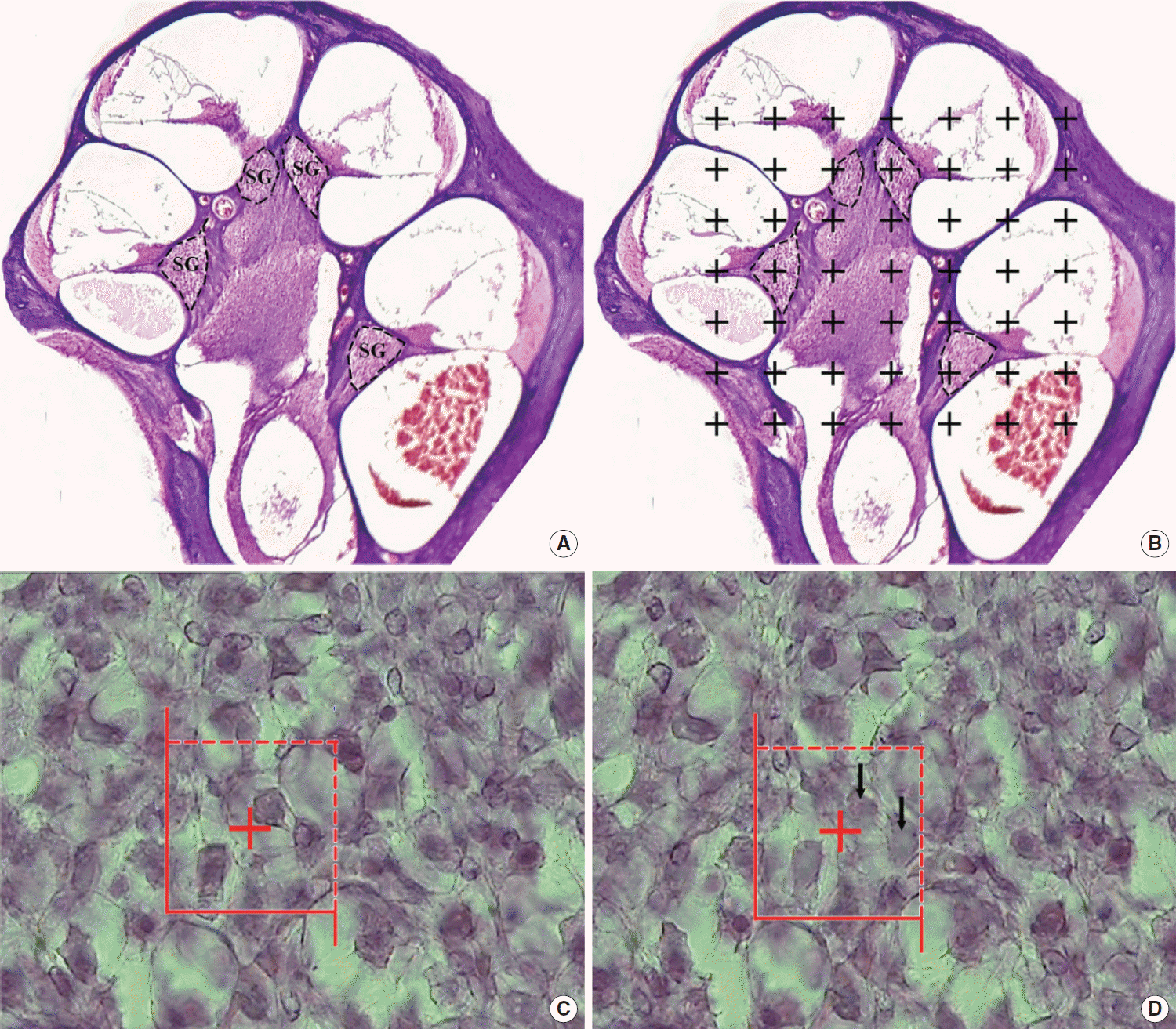
29. Kristiansen SL, Nyengaard JR. Digital stereology in neuropathology. APMIS. 2012; Apr. 120(4):327–40.

30. Schettino AE, Lauer AM. The efficiency of design-based stereology in estimating spiral ganglion populations in mice. Hear Res. 2013; Oct. 304:153–8.

31. Gundersen HJ, Bagger P, Bendtsen TF, Evans SM, Korbo L, Marcussen N, et al. The new stereological tools: disector, fractionator, nucleator and point sampled intercepts and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS. 1988; Oct. 96(10):857–81.

32. Gundersen HJ, Bendtsen TF, Korbo L, Marcussen N, Moller A, Nielsen K, et al. Some new, simple and efficient stereological methods and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS. 1988; May. 96(5):379–94.

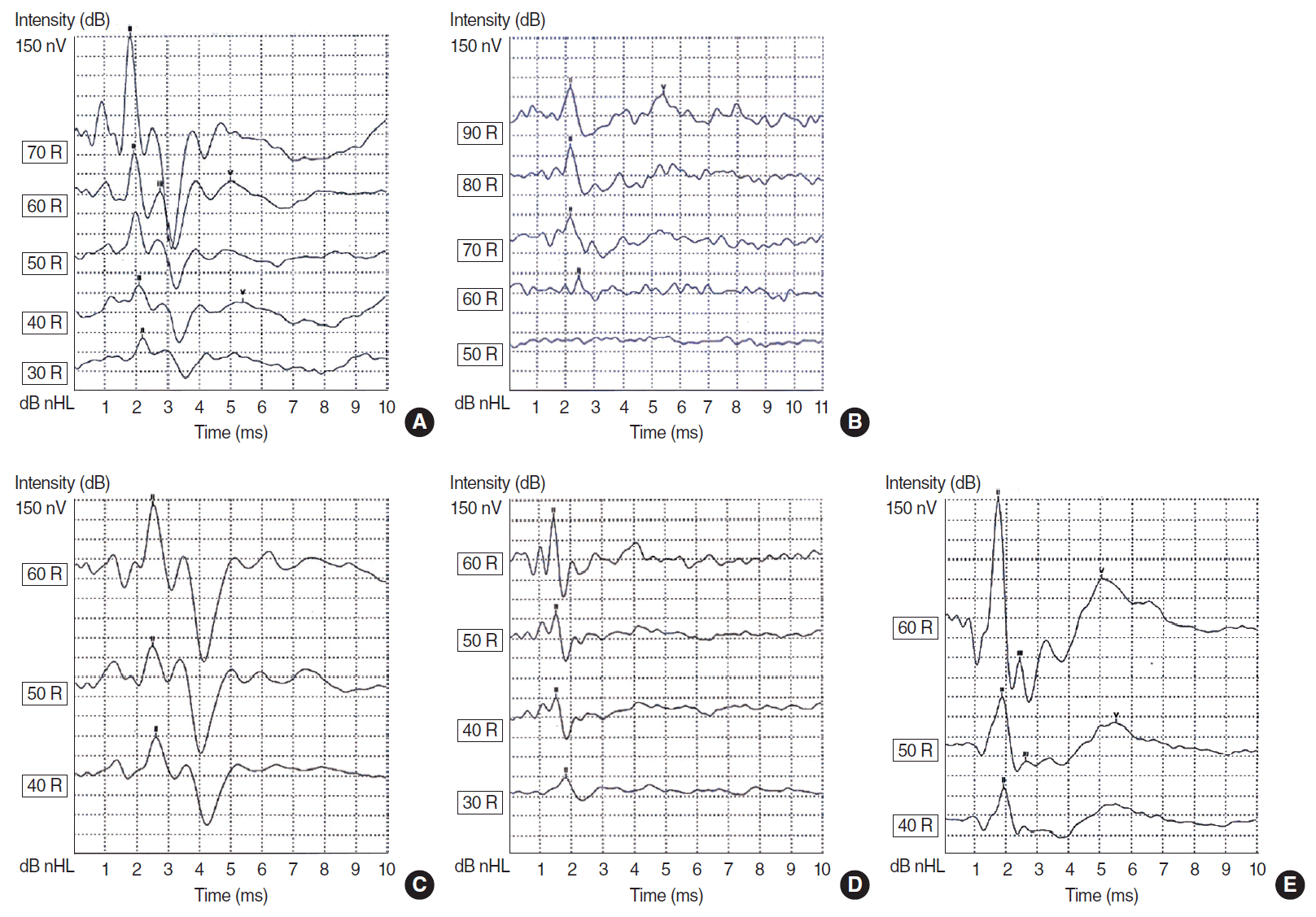
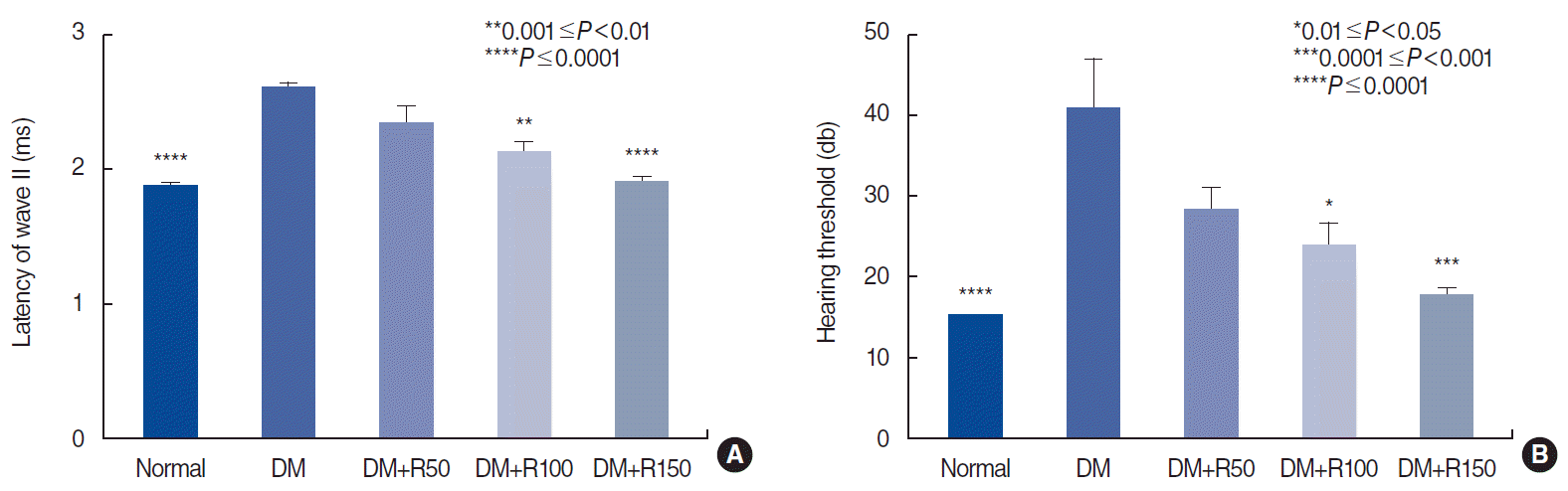
33. Radwan HM, El-Gharib AM, Erfan AA, Emara AA. Auditory brain stem response and cortical evoked potentials in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017; May. 137(5):511–5.

34. Tsuda J, Sugahara K, Hori T, Kanagawa E, Takaki E, Fujimoto M, et al. A study of hearing function and histopathologic changes in the cochlea of the type 2 diabetes model Tsumura Suzuki obese diabetes mouse. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016; Nov. 136(11):1097–106.

35. Hong BN, Kang TH. Distinction between auditory electrophysiological responses in type 1 and type 2 diabetic animal models. Neurosci Lett. 2014; Apr. 566:309–14.

36. Ren J, Ma F, Zhou Y, Xu A, Zhang J, Ma R, et al. Hearing impairment in type 2 diabetics and patients with early diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2018; Jun. 32(6):575–9.

37. Hosseinzadeh H, Nassiri-Asl M. Review of the protective effects of rutin on the metabolic function as an important dietary flavonoid. J Endocrinol Invest. 2014; Sep. 37(9):783–8.

38. Ahmed OM, Moneim AA, Yazid IA, Mahmoud AM. Antihyperglycemic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects and the probable mechanisms of action of Ruta graveolens infusion and rutin in nicotinamide-streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetol Croat. 2010; 39(1):15–35.
39. Tian R, Yang W, Xue Q, Gao L, Huo J, Ren D, et al. Rutin ameliorates diabetic neuropathy by lowering plasma glucose and decreasing oxidative stress via Nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016; Jan. 771:84–92.

40. Lee HS, Kim KR, Chung WH, Cho YS, Hong SH. Early sensorineural hearing loss in ob/ob mouse, an animal model of type 2 diabetes. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2008; Dec. 1(4):211–6.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download