INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
Table 1.
Audiological analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Comparison of the hearing threshold and WRS between HA-aided and HA-unaided ears
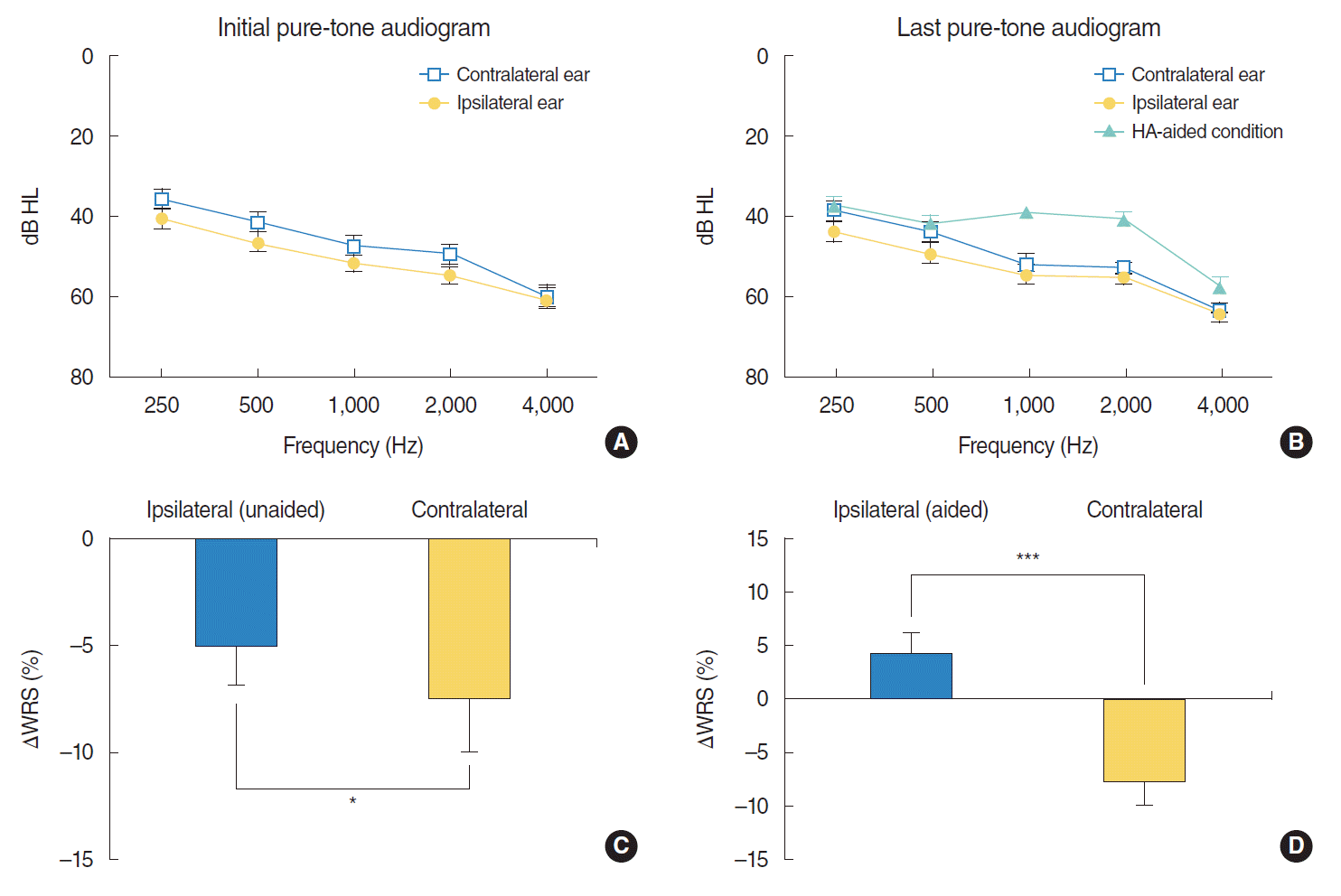 | Fig. 1.Pure-tone audiometry and word recognition test for the ear fitted with a hearing aid (HA) and the contralateral unaided ear in a patient with symmetric sensorineural hearing loss. (A) Initial unaided air-conduction audiometry is performed for the HA-aided (ipsilateral) and the HA-unaided (contralateral) ears. (B) The last unaided air-conduction audiometry session is performed for the ipsilateral and the contralateral ears. Aided air-conduction audiometry for the ipsilateral ear is also performed via a sound field test using a loudspeaker. (C) The ipsilateral ear (unaided condition) shows a significantly smaller decrease in the word recognition score (WRS) than the contralateral ear. ΔWRS indicates difference in the WRS between the first and last tests. (D) ΔWRS in the ipsilateral ear (aided condition) more significantly differs from that in the contralateral ear. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001. |
Effects of the initial hearing threshold on auditory deprivation in the HA-unaided ear
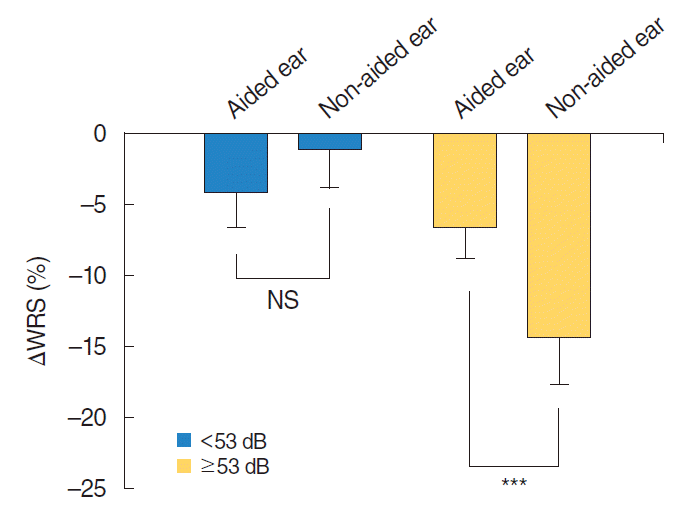 | Fig. 2.Assessment of the decrease in the word recognition score (WRS) depending on the initial hearing threshold in patients with symmetric sensorineural hearing loss who had worn a unilateral hearing aid for more than 1 year. Patients are classified according to a mean pure-tone audiometry thresholds (PTA4) of <53 or ≥53 dB HL. There is no difference in ΔWRS between the aided ear and non-aided ear in patients with an initial hearing threshold of <53 dB HL. However, in patients with an initial hearing threshold of ≥53 dB HL, the decrease in WRS for the non-aided ear is significantly larger than that for the aided ear. PTA4, the average threshold at 500, 1,000, 2,000, and 4,000 Hz; ΔWRS, difference in the WRS between the first and last tests; NS, not significant. ***P<0.001. |
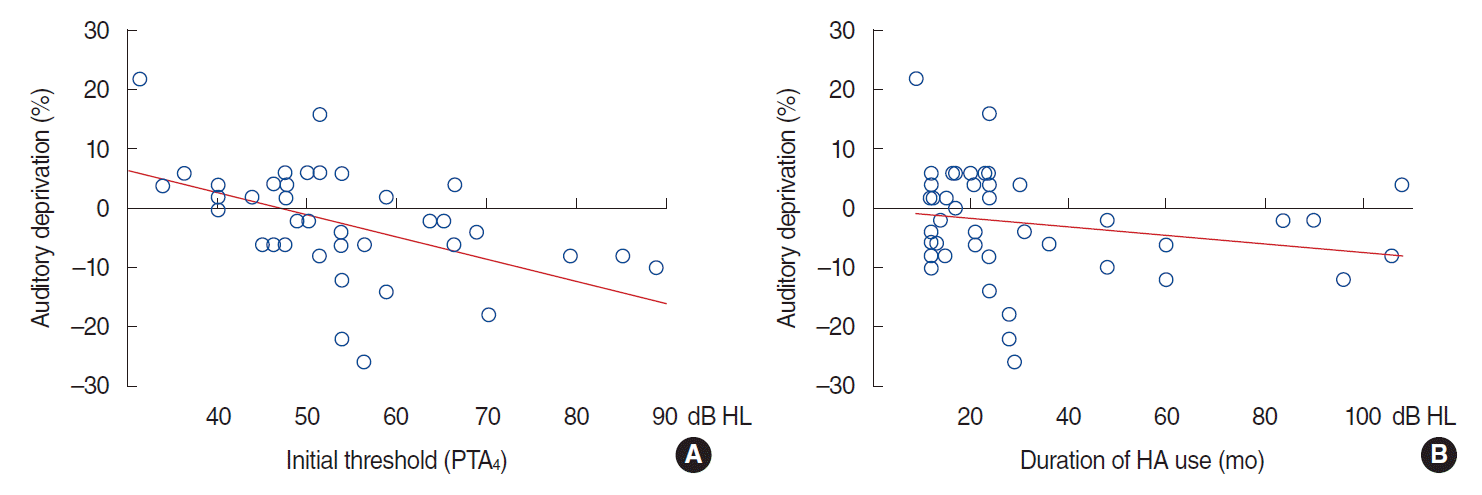 | Fig. 3.Effects of the initial hearing threshold and duration of hearing aid (HA) use on auditory deprivation in the contralateral ears of patients with symmetric sensorineural hearing loss who had worn a unilateral HA for more than 1 year. Auditory deprivation was defined as the difference in changes in the word recognition score between the ipsilateral and contralateral ears. (A) The initial hearing threshold in PTA4 shows a significant negative association with auditory deprivation. Auditory deprivation in the contralateral ear shows a negatively correlation with the initial hearing threshold in PTA4 (y=−0.3759χ+17.770, R2=0.266, P<0.001, χ=initial threshold). (B) The duration of HA use does not have an effect on the severity of auditory deprivation in the unaided ear (y=−0.069χ–4.765, R2=0.0412, P=0.18, χ=duration of HA use). PTA4, the average threshold at 500, 1,000, 2,000, and 4,000 Hz. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download