INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture and treatment
RT-PCR analysis of MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC5B mRNA expression
Real-time PCR analysis of MUC5B and EGFR mRNA expression
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis of MUC5B protein
Western blot analysis of EGFR, ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and p38 MAPK phosphorylation
Cell transfection with siRNA for p38 MAPK
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Effect of HG on the expression of major secretary airway mucin genes
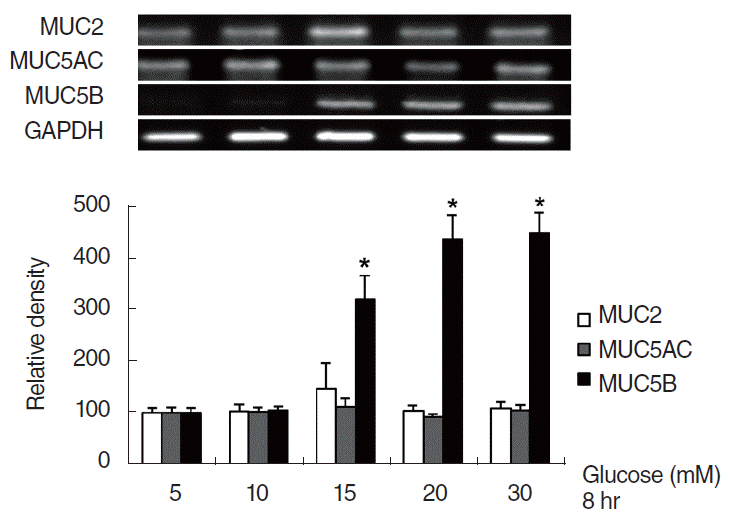 | Fig. 1.Effect of high glucose (HG) on the expression of secretary airway mucins in NCI-H292 cells. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction showed that HG (>15 mM) significantly induced MUC5B mRNA expression. However, glucose did not induce MUC2 or MUC5AC mRNA expression at any concentration examined. Images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate. Bars indicate the mean±standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *P<0.05. |
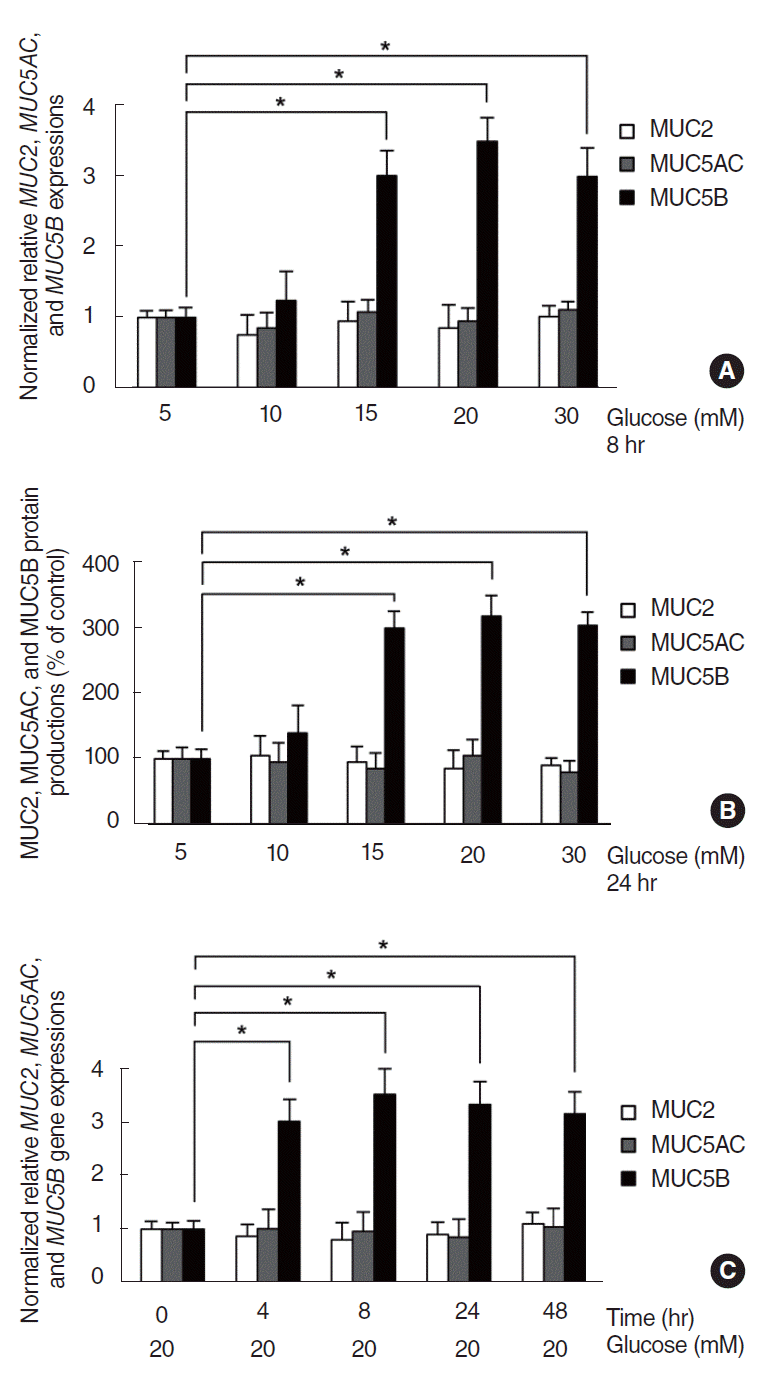 | Fig. 2.Effect of high glucose (HG) on MUC5B expression in NCI-H292 cells. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) showed that MUC5B expression was significantly increased at concentrations higher than 15 mM, compared with the control group (5 mM). However, glucose did not induced MUC2 and MUC5AC expression (A, B). Real-time PCR showed that MUC5B mRNA expression was significantly increased at all times after exposure of glucose (20 mM) (C). Images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate. Bars indicate the mean±standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *P<0.05. |
Effect of HG on the activation of EGFR
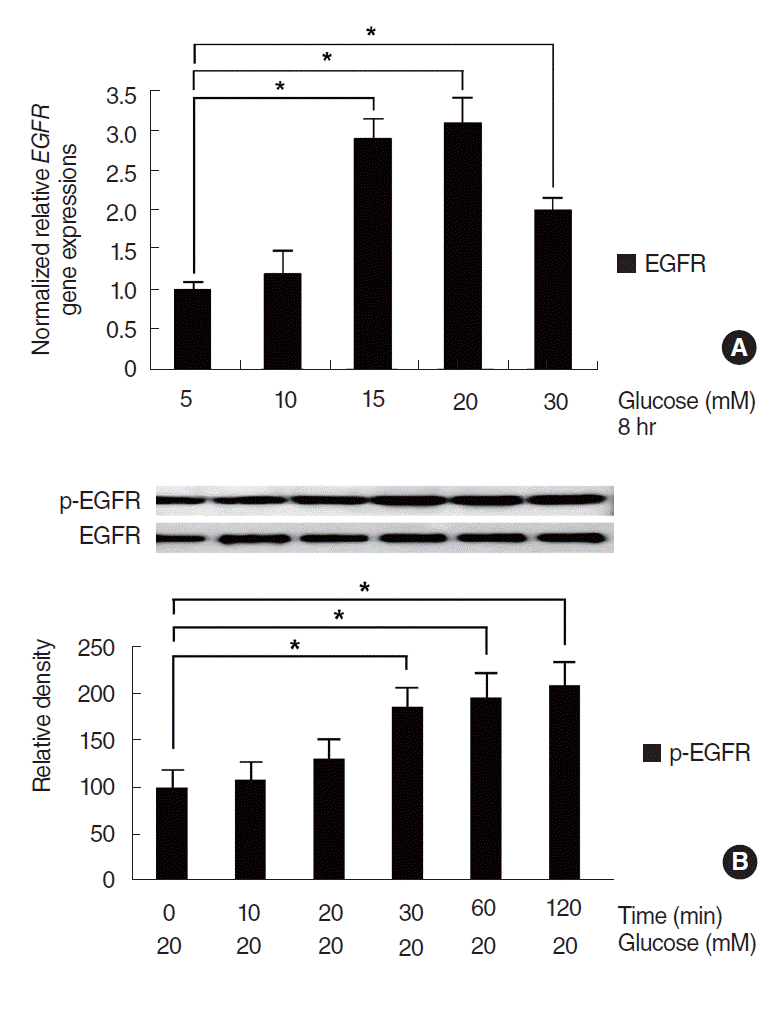 | Fig. 3.Effect of high glucose (HG) on the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in NCI-H292 cells. Real-time polymerase chain reaction showed that EGFR mRNA expression was significantly increased at concentrations higher than 15 mM and peaked at 20 mM of glucose, compared with the control group (5 mM) (A). Western blot showed that HG significantly activated the phosphorylation of EGFR with the lapse of time (B). Images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate. Bars indicate the mean±standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *P<0.05. |
The roles of EGFR, ERK1/2 MAPK, and p38 MAPK on HG-induced MUC5B expression
 | Fig. 4.Roles of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and p38 MAPK on high glucose (HG)-induced MUC5B expression. (A) Western blot showed that HG significantly activated the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK with the lapse of time, but that HG did not activate the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 MAPK. (B, C) Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) showed that SB203580 (a p38 MAPK inhibitor) and AG1478 (an EGFR inhibitor) significantly attenuated HG-induced MUC5B expression, whereas U0126 (an ERK1/2 inhibitor) had no effect. (D) Western blot showed that AG1478 significantly attenuated the HG-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK. (E and F) RT-PCR and ELISA showed that knockdown of p38 MAPK by p38 MAPK siRNA significantly blocked HG-induced MUC5B expression. Images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate. Bars indicate the mean±standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *P<0.05. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download