INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
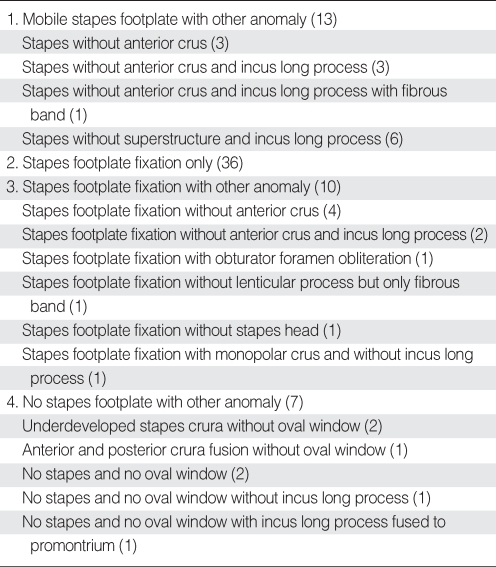
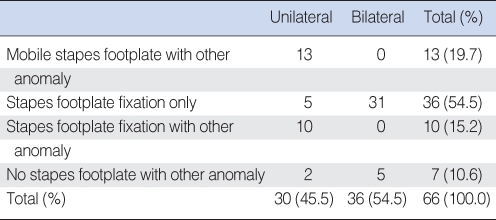
RESULTS
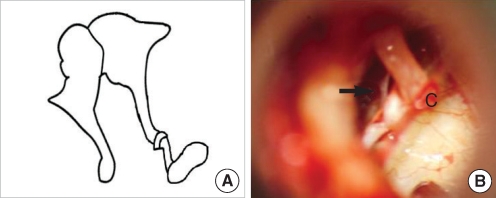 | Fig. 1Stapes without anterior crus. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows no anterior crus of the stapes (arrow).
c: chorda tympani.
|
 | Fig. 2Stapes without anterior crus and incus long process. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Removed incus shows no long process, and removed stapes shows no anterior crus. |
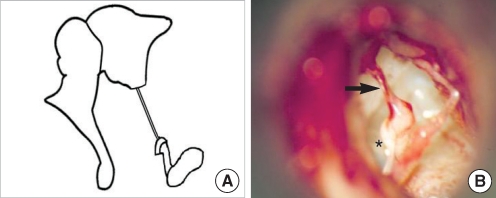 | Fig. 3Stapes without anterior crus and incus long process with fibrous band. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows a fibrous band (arrow) instead of the incus long process and the stapes lacking anterior crus (asterisk). |
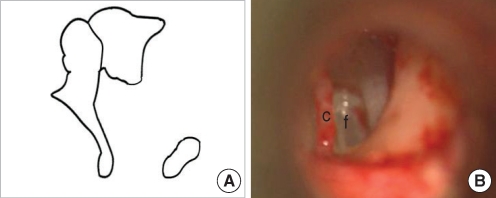 | Fig. 4Stapes without superstructure and incus long process. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows no incus long process and no stapes superstructure.
c: chorda tympani; f: footplate.
|
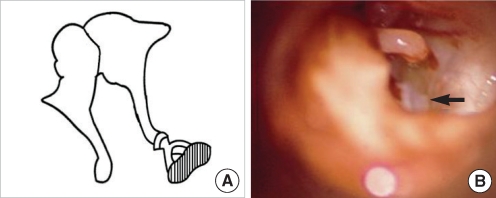 | Fig. 5Stapes footplate fixation. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows half of the stapes footplate remaining (arrow) because of partial fixation of its footplate. |
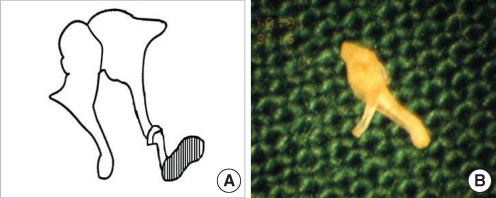 | Fig. 6Stapes footplate fixation without anterior crus. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Removed stapes shows an underdeveloped anterior crus. |
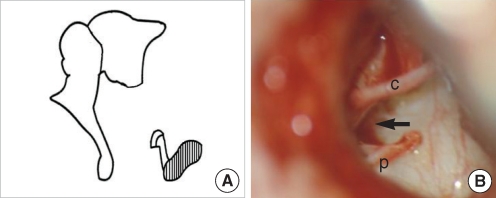 | Fig. 7Stapes footplate fixation without anterior crus and incus long process. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows no incus long process and the stapes lacking anterior crus (arrow) without mobility of its footplate. c: chorda tympani; p: posterior crus. |
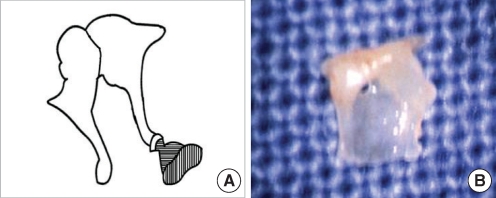 | Fig. 8Stapes footplate fixation with obturator foramen obliteration. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Removed stapes shows a non-perforated obturator foramen. |
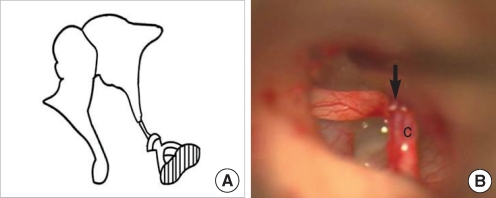 | Fig. 9Stapes footplate fixation without lenticular process: only fibrous band. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows a fibrous band (arrow) instead of the lenticular process of the incus.
c: chorda tympani.
|
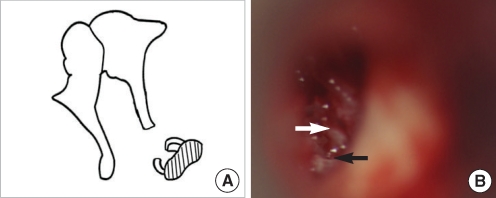 | Fig. 10Stapes footplate fixation without stapes head. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows only anterior (white arrow) and posterior crus (black arrow) without mobility of its footplate. |
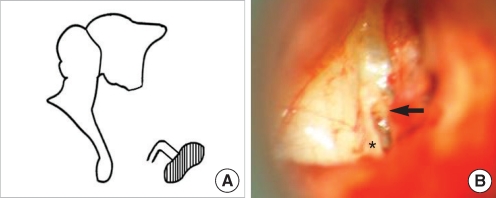 | Fig. 11Stapes footplate fixation with monopolar crus and without incus long process. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows only one crus in the center of the footplate (arrow) and stapes-pyramidal fixation by a bony bar (asterisk). |
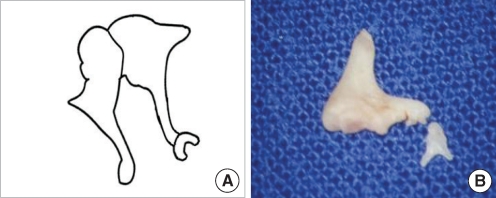 | Fig. 12Underdeveloped stapes crura without oval window. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Removed stapes shows underdeveloped crura. |
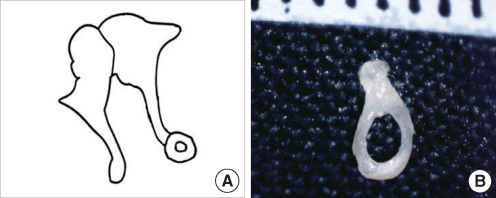 | Fig. 13Anterior and posterior crura fusion without oval window. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Removed stapes shows a crural fusion. |
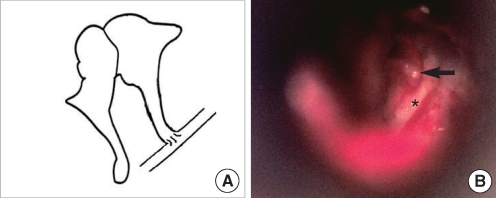 | Fig. 14No stapes and no oval window. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows a long process of the incus (arrow) without the stapes, which is in contact with a downward facial nerve (asterisk) in the mesotympanum. |
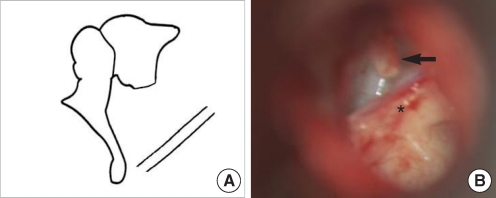 | Fig. 15No stapes and no oval window without incus long process. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows shortening of the incus long process (arrow) without the stapes and downward displacement of the tympanic portion of the facial nerve with a bony bar (asterisk). |
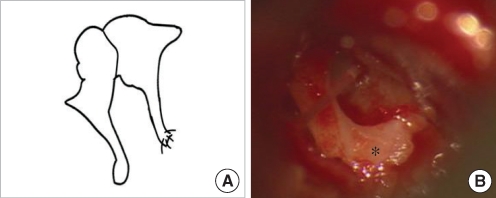 | Fig. 16No stapes and no oval window with incus long process fused to promontorium. (A) Schematic presentation. (B) Operative finding shows the long process of the incus fused to promontorium (asterisk) without the stapes and the oval window. |
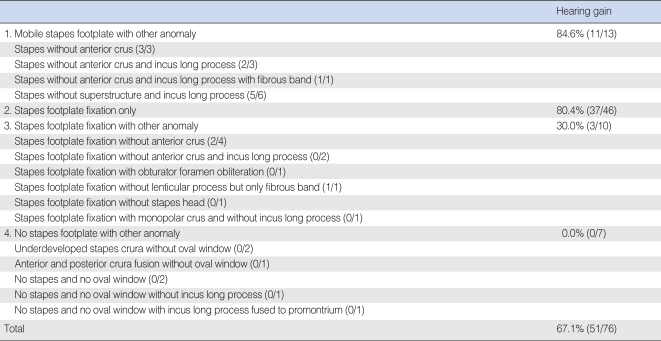
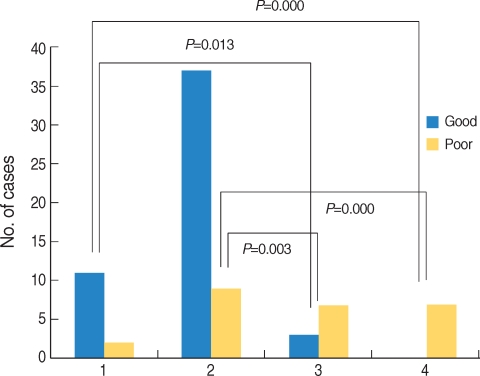 | Fig. 17Comparison of postoperative hearing results of congenital stapes anomaly according to status of stapes footplate (76 ears). Patients with mobile stapes or only stapes footplate fixation had significantly better hearing result than patients with stapes fixation associated with other ossicular anomaly or no stapes footplate.
1: Mobile stapes footplate with other anomaly; 2: Stapes footplate fixation only; 3: Stapes footplate fixation with other anomaly; 4: No stapes footplate with other anomaly; Good: postoperative air-bone gap <20 dB; Poor: postoperative air-bone gap ≥20 dB. Postoperative air-bone gap: postoperative air conduction-preoperative bone conduction.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download