서 론
대상 및 방법
결 과
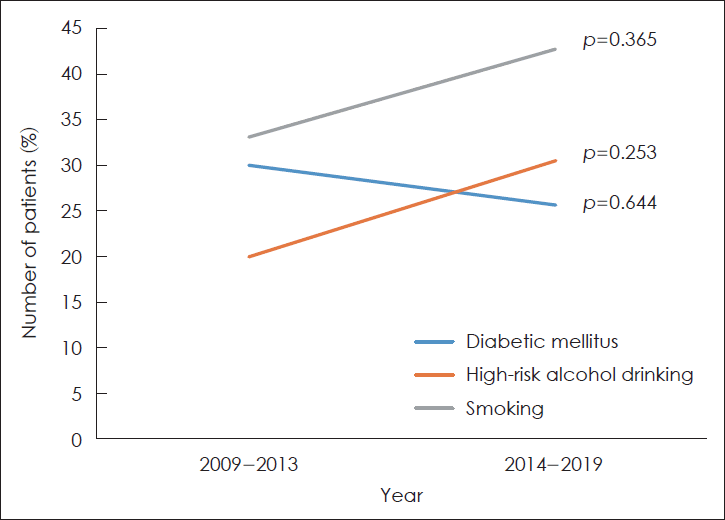 | Fig. 1.Changing trends of number of patients with diabetic mellitus, high-risk alcohol drinking, or smoking history during 10 years. The number of patients with diabetic mellitus (p=0.644) was decreased in the recent 10 years, but it was not statistically significant. The change of number of patients with high-risk alcohol drinking (p=0.253) and smoking history was also statistically insignificant |
Table 1.
Table 2.
Table 3.
Table 4.
Table 5.
Table 6.
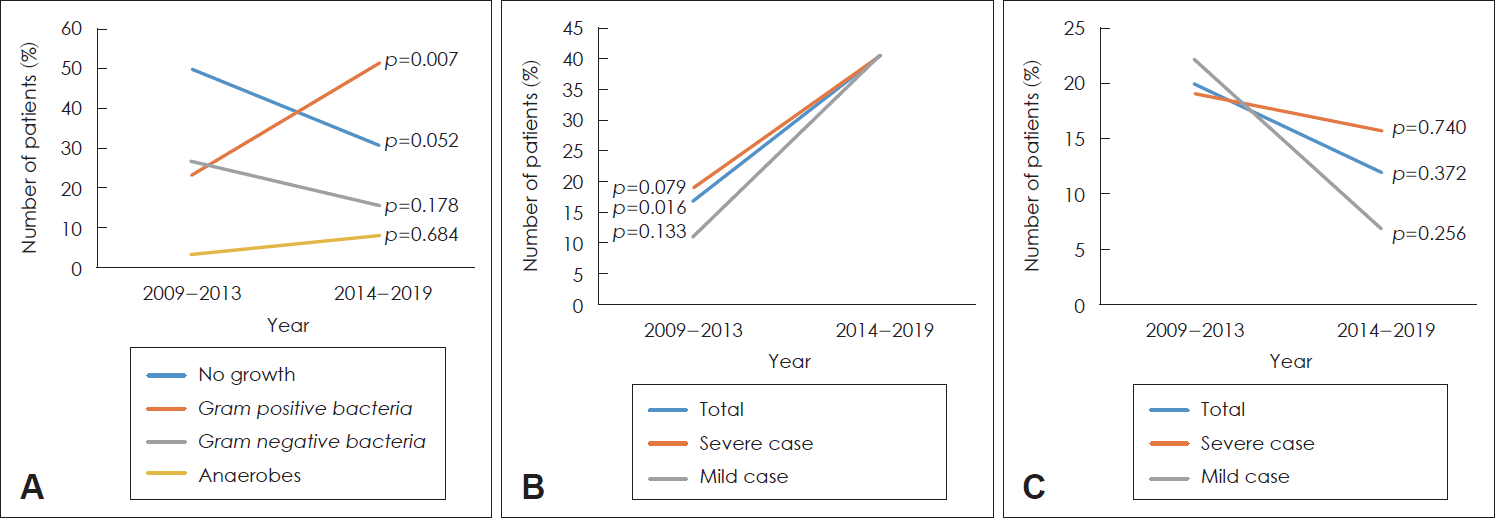 | Fig. 2.Isolation rate of different types of bacteria (A), Streptococcus viridans (B) and Klebsiella pneumonia (C) during each 5 year interval. The isolation rates of gram positive bacteria (p=0.007) was increased significantly between 2009 and 2019. The isolation of anaerobes (p=0.684) was increased and that of gram negative bacteria (p=0.178) was decreased, but they were not statistically significant. The identification of Streptococcus viridans (p=0.016) increased in the recent 10 years with statistical significance. The identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae (p=0.372) was shown to decrease in recent years, but it was not statistically significant. |
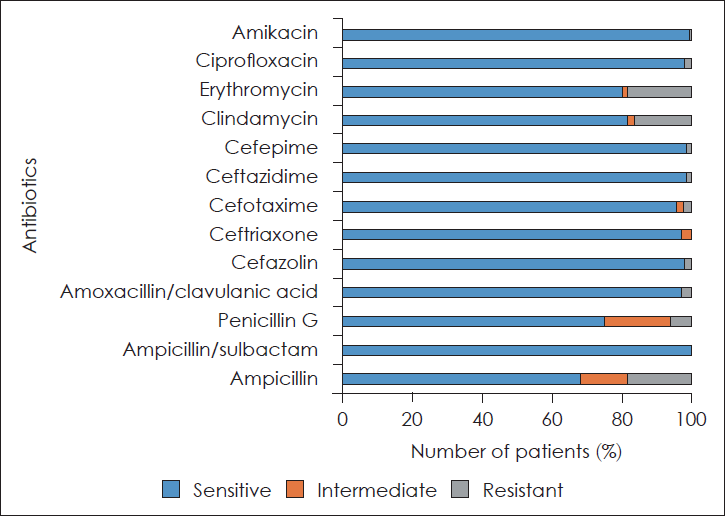
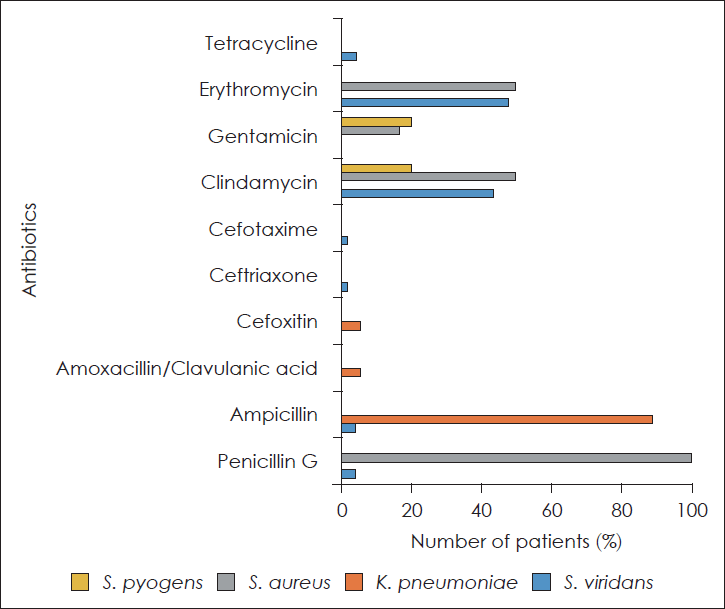 | Fig. 3.Results of antibiotic susceptibility test among mainly isolated bacteria. The isolation rates of clindamycin and erythromycin-resistant S. viridans were respectively 43.4%, 47.8%, but Streptococcus was sensitive to ampicillin and ceftriaxone. All cases except 2 cases with K. pneumonia isolated were resistant to ampicillin and half of them were resistant to clindamycin and erythromycin. S. pyogens: Streptococcus pyogens, S. aureus: Staphylococcus aureus, K. pneumoniae: Klebsiella pneumoniae, S. viridans: Streptococcus viridans. |
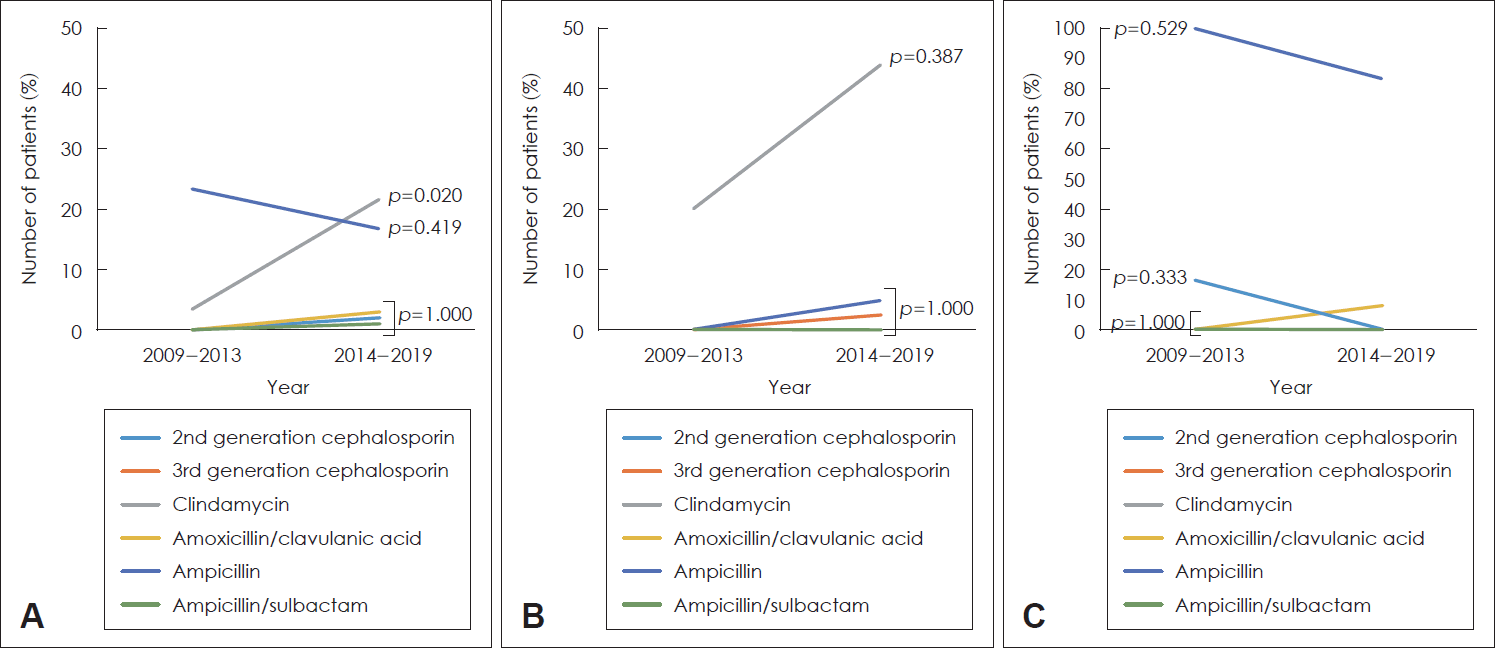 | Fig. 5.Changing trends of antibiotic resistance against all isolated microbes (A), Streptococcus viridans (B) and Klebsiella pneumonia (C) during 10 years. The identification of clindamycin-resistant pathogens was increased with statistically significance (p=0.020), but the change of the isolation of other antibiotics-resistant pathogens were statistically insignificant. The isolation rate of Streptococcus viridans and Klebsiella pneumonia which were resistant to all antibiotics, also changed with statistical insignificance. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download