서 론
증 례
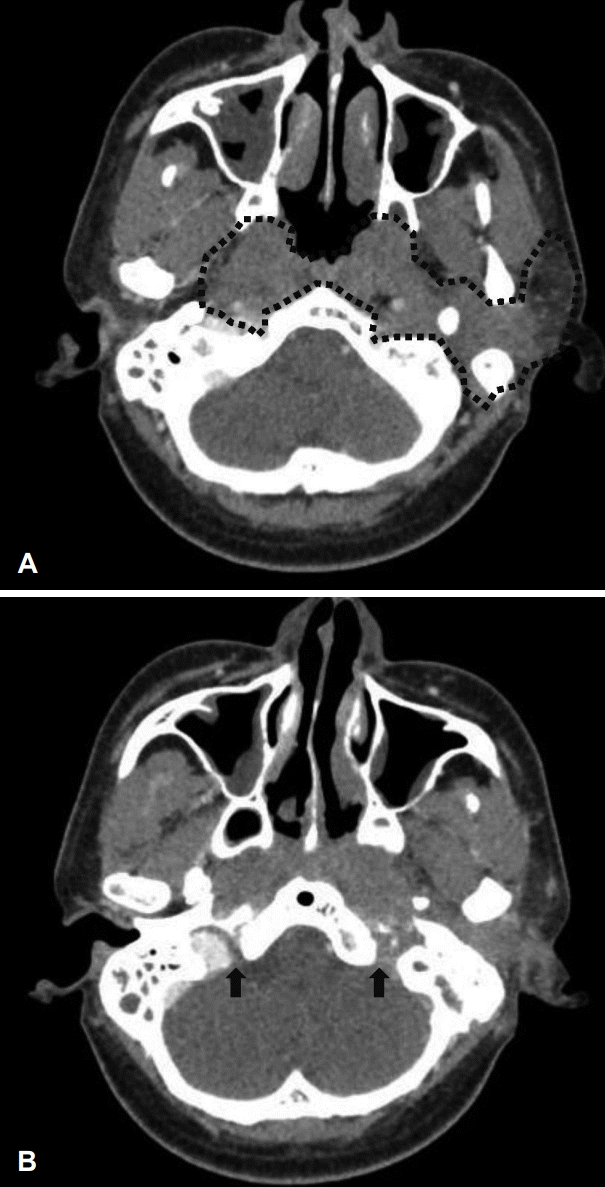 | Fig. 3.Radiologic findings. Axial view of neck computer tomography shows that diffuse infiltrative thickening in both the nasopharynx, parapharyngeal space, left parotid gland, left skull base and both cervical internal carotid artery (black dot-line) (A), and low-attenuation in left jugular foramen is showing comparing to right jugular foramen because of diffuse infiltrative lesion (black arrows) (B). |
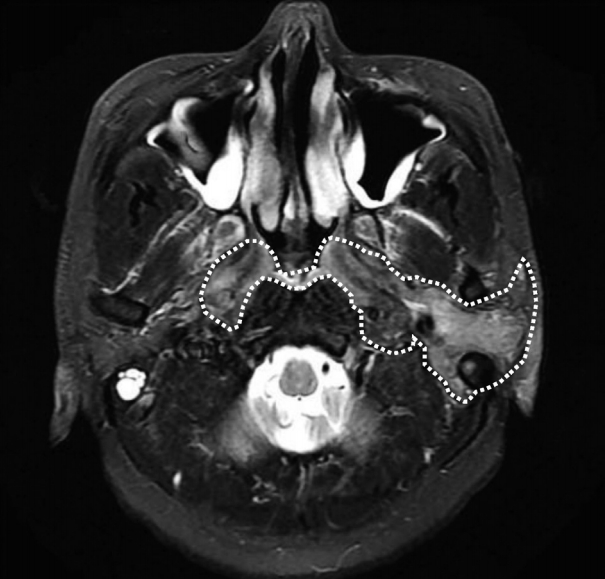 | Fig. 4.Radiologic findings. Axial view of T2-weighted image brain MRI scan shows that diffuse infiltrative homogeneous thickening in both the nasopharynx, parapharyngeal space, left parotid gland, left skull base and both cervical internal carotid artery (white dot-line). |
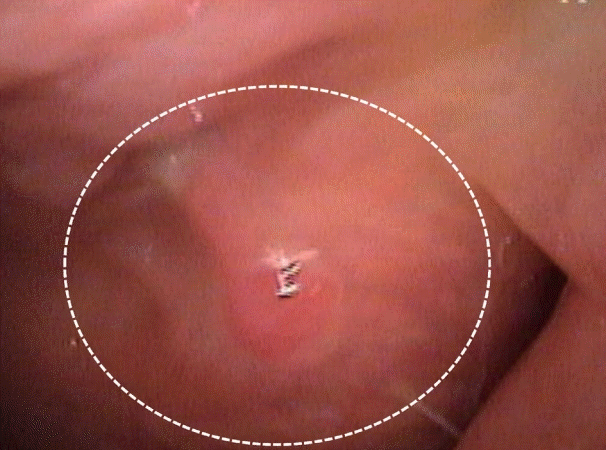
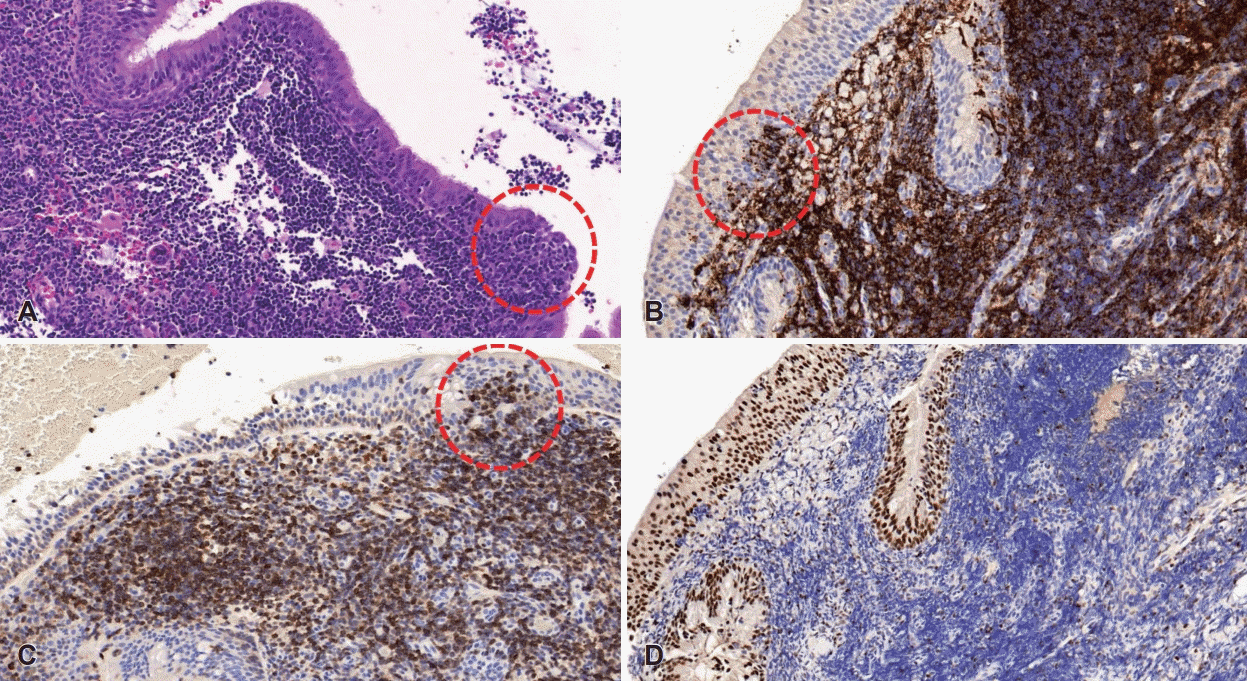 | Fig. 5.Pathological findings. Normal nasopharyngeal architecture is effaced by atypical lymphoid cells. Tumor cells invade epithelial structures to form lymphoepithelial lesions (dot-lined circles) (hematoxylin and eosin staining, ×100) (A). Tumor cells show strong immunoreactivity for B-cell marker; CD20 (×100) (B). Positive staining for BCL2 (×100) (C). No immunoreactivity for BCL6 (×100) (D). |
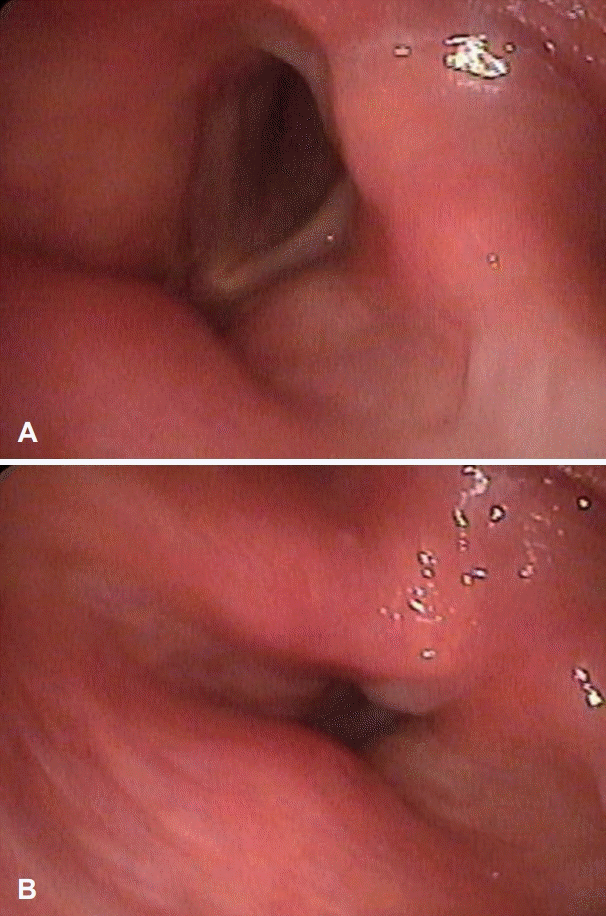
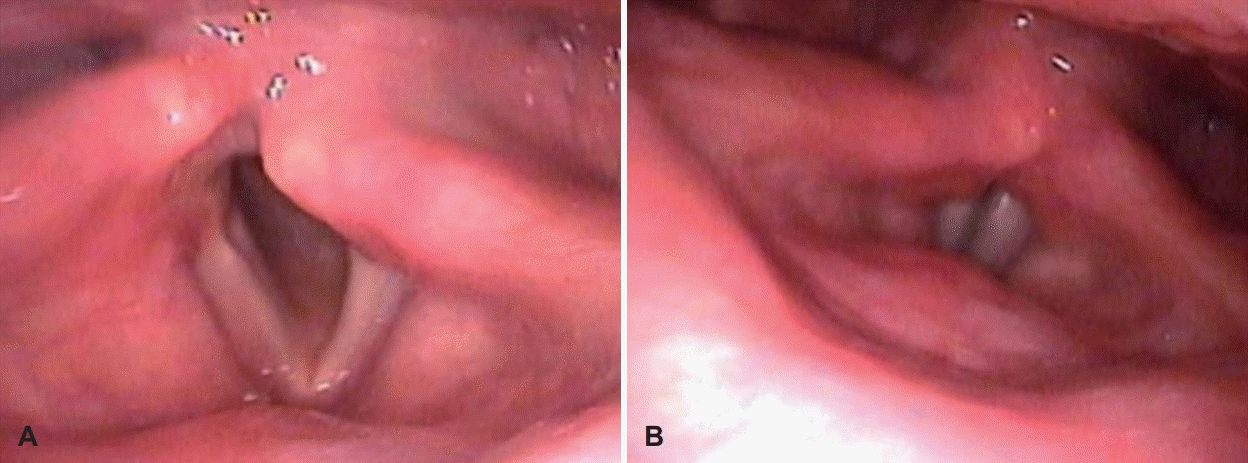 | Fig. 6.Laryngoscopic examination shows that left vocal fold movement was fully recovered after chemotherapy inspiration (A), expiration (B). |
 | Fig. 7.Radiologic findings. After 6 cycles of chemotherapy, axial view of neck computer tomography shows that marked improved state of diffuse infiltrative lymphoma involvement (black dot-line) (A), and high-attenuation in left jugular foramen is showing comparing to initial neck computer tomography (black arrows) (B). |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download