1. Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 2012; 50(1):1–12.

2. Ahn JC, Kim JW, Lee CH, Rhee CS. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic rhinosinusitus, allergic rhinitis, and nasal septal deviation: Results of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2008-2012. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016; 142(2):162–7.
3. Stevens WW, Schleimer RP, Kern RC. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016; 4(4):565–72.

4. Akdis CA, Bachert C, Cingi C, Dykewicz MS, Hellings PW, Naclerio RM, et al. Endotypes and phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: A PRACTALL document of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131(6):1479–90.
5. Agache I, Akdis C, Jutel M, Virchow JC. Untangling asthma phenotypes and endotypes. Allergy. 2012; 67(7):835–46.

6. Taylor DR. Using biomarkers in the assessment of airways disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128(5):927–34.

7. Oyer SL, Mulligan JK, Psaltis AJ, Henriquez OA, Schlosser RJ. Cytokine correlation between sinus tissue and nasal secretions among chronic rhinosinusitis and controls. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123(12):E72–8.

8. Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ, Cui YH, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124(3):478–84.

9. Tokunaga T, Sakashita M, Haruna T, Asaka D, Takeno S, Ikeda H, et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: The JESREC Study. Allergy. 2015; 70(8):995–1003.
10. Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, Bai J, Fan Y, Xia W, et al. Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129(6):1522–8. e5.

11. Ho J, Bailey M, Zaunders J, Mrad N, Sacks R, Sewell W, et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) are increased in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps or eosinophilia. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015; 45(2):394–403.

12. Tojima I, Kouzaki H, Shimizu S, Ogawa T, Arikata M, Kita H, et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells are increased in nasal polyps in patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Clin Immunol. 2016; 170:1–8.

13. Bachert C, Gevaert P, Hellings P. Biotherapeutics in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017; 5(6):1512–6.

14. Gevaert P, Bachert C, Holtappels G, Novo CP, Van der Heyden J, Fransen L, et al. Enhanced soluble interleukin-5 receptor alpha expression in nasal polyposis. Allergy. 2003; 58(5):371–9.

15. Bachert C, Zhang N, Holtappels G, De Lobel L, van Cauwenberge P, Liu S, et al. Presence of IL-5 protein and IgE antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins in nasal polyps is associated with comorbid asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126(5):962–8.

16. Gevaert P, Calus L, Van Bruaene N, Van Zele T, Bachert C, et al. Allergic sensitization, high local IL-5 and IgE predict surgical outcome 12 years after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 135(2):AB238.

17. Van Zele T, Holtappels G, Gevaert P, Bachert C. Differences in initial immunoprofiles between recurrent and nonrecurrent chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2014; 28(3):192–8.

18. Tomassen P, Vandeplas G, Van Zele T, Cardell LO, Arebro J, Olze H, et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137(5):1449–56. e4.

19. Gevaert P, Lang-Loidolt D, Lackner A, Stammberger H, Staudinger H, Van Zele T, et al. Nasal IL-5 levels determine the response to anti-IL-5 treatment in patients with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118(5):1133–41.

20. Gevaert P, Van Bruaene N, Cattaert T, Van Steen K, Van Zele T, Acke F, et al. Mepolizumab, a humanized anti-IL-5 mAb, as a treatment option for severe nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128(5):989–95. e1-8.

21. Bachert C, Mannent L, Naclerio RM, Mullol J, Ferguson BJ, Gevaert P, et al. Effect of subcutaneous dupilumab on nasal polyp burden in patients with chronic sinusitis and nasal polyposis: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016; 315(5):469–79.
22. Kato A. Immunopathology of chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol Int. 2015; 64(2):121–30.

23. Lam EP, Kariyawasam HH, Rana BM, Durham SR, McKenzie AN, Powell N, et al. IL-25/IL-33-responsive TH2 cells characterize nasal polyps with a default TH17 signature in nasal mucosa. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137(5):1514–24.

24. Mjösberg JM, Trifari S, Crellin NK, Peters CP, van Drunen CM, Piet B, et al. Human IL-25- and IL-33-responsive type 2 innate lymphoid cells are defined by expression of CRTH2 and CD161. Nat Immunol. 2011; 12(11):1055–62.

25. Shaw JL, Fakhri S, Citardi MJ, Porter PC, Corry DB, Kheradmand F, et al. IL-33-responsive innate lymphoid cells are an important source of IL-13 in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 188(4):432–9.

26. Kim DK, Jin HR, Eun KM, Mo JH, Cho SH, Oh S, et al. The role of interleukin-33 in chronic rhinosinusitis. Thorax. 2017; 72(7):635–45.

27. Gauvreau GM, O'Byrne PM, Boulet LP, Wang Y, Cockcroft D, Bigler J, et al. Effects of an anti-TSLP antibody on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370(22):2102–10.

28. Lam M, Hull L, McLachlan R, Snidvongs K, Chin D, Pratt E, et al. Clinical severity and epithelial endotypes in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013; 3(2):121–8.

29. Nagarkar DR, Poposki JA, Tan BK, Comeau MR, Peters AT, Hulse KE, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin activity is increased in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 132(3):593–600. e12.

30. Reh DD, Wang Y, Ramanathan M Jr, Lane AP. Treatmentrecalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps is associated with altered epithelial cell expression of interleukin-33. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2010; 24(2):105–9.

31. Li W, Gao P, Zhi Y, Xu W, Wu Y, Yin J, et al. Periostin: Its role in asthma and its potential as a diagnostic or therapeutic target. Respir Res. 2015; 16:57.

32. Kim DW, Kulka M, Jo A, Eun KM, Arizmendi N, Tancowny BP, et al. Cross-talk between human mast cells and epithelial cells by IgE-mediated periostin production in eosinophilic nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 139(5):1692–5. e6.

33. Hanania NA, Wenzel S, Rosén K, Hsieh HJ, Mosesova S, Choy DF, et al. Exploring the effects of omalizumab in allergic asthma: an analysis of biomarkers in the EXTRA study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 187(8):804–11.
34. Hulse KE, Norton JE, Suh L, Zhong Q, Mahdavinia M, Simon P, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is characterized by B-cell inflammation and EBV-induced protein 2 expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131(4):1075–83.

35. Tan BK, Li QZ, Suh L, Kato A, Conley DB, Chandra RK, et al. Evidence for intranasal antinuclear autoantibodies in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128(6):1198–1206. e1.

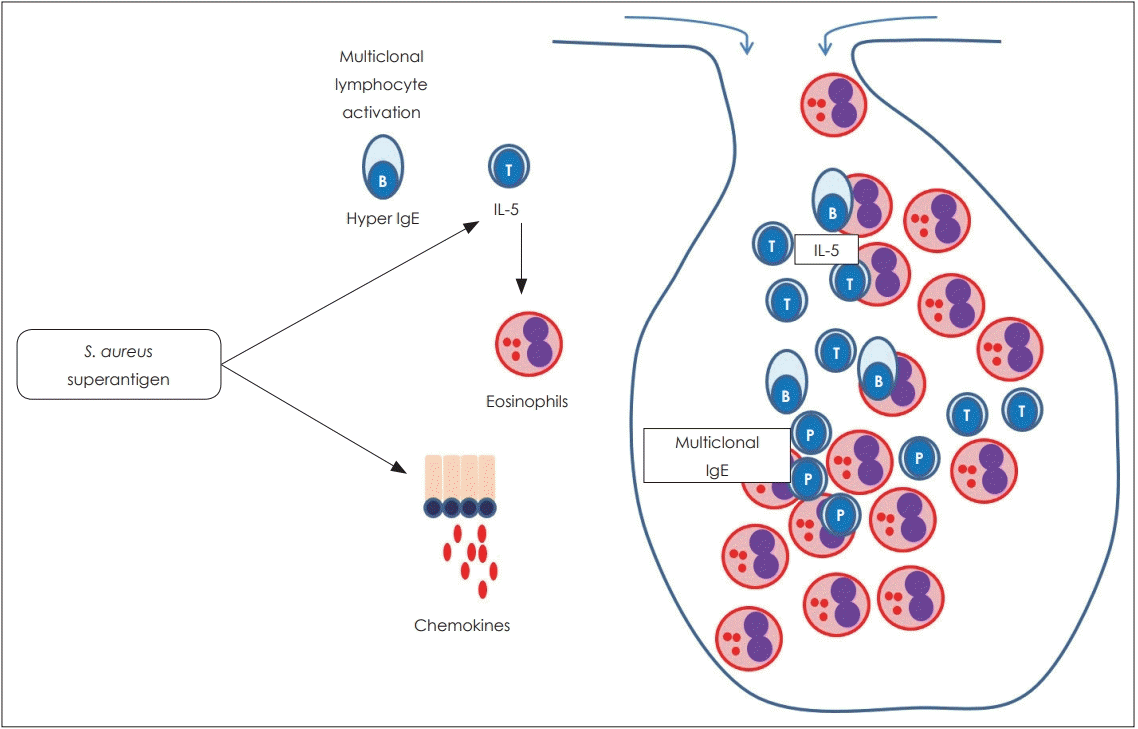
36. Gevaert P, Holtappels G, Johansson SG, Cuvelier C, Cauwenberge P, Bachert C. Organization of secondary lymphoid tissue and local IgE formation to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins in nasal polyp tissue. Allergy. 2005; 60(1):71–9.
37. Van Zele T, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C. Local immunoglobulin production in nasal polyposis is modulated by superantigens. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37(12):1840–7.

38. Suh KS, Park HS, Nahm DH, Kim YK, Lee YM, Park K. Role of IgG, IgA, and IgE antibodies in nasal polyp tissue: Their relationships with eosinophilic infiltration and degranulation. J Korean Med Sci. 2002; 17(3):375–80.

39. Hulse KE, Stevens WW, Tan BK, Schleimer RP. Pathogenesis of nasal polyposis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015; 45(2):328–46.

40. Gevaert P, Calus L, Van Zele T, Blomme K, De Ruyck N, Bauters W, et al. Omalizumab is effective in allergic and nonallergic patients with nasal polyps and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131(1):110–6. e1.

41. Kato A, Peters A, Suh L, Carter R, Harris KE, Chandra R, et al. Evidence of a role for B cell-activating factor of the TNF family in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121(6):1385–92.

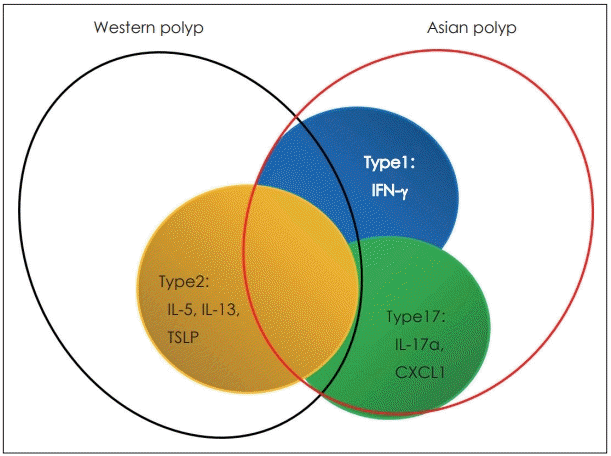
42. Wang X, Zhang N, Bo M, Holtappels G, Zheng M, Lou H, et al. Diversity of TH cytokine profiles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: A multicenter study in Europe, Asia, and Oceania. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 138(5):1344–53.
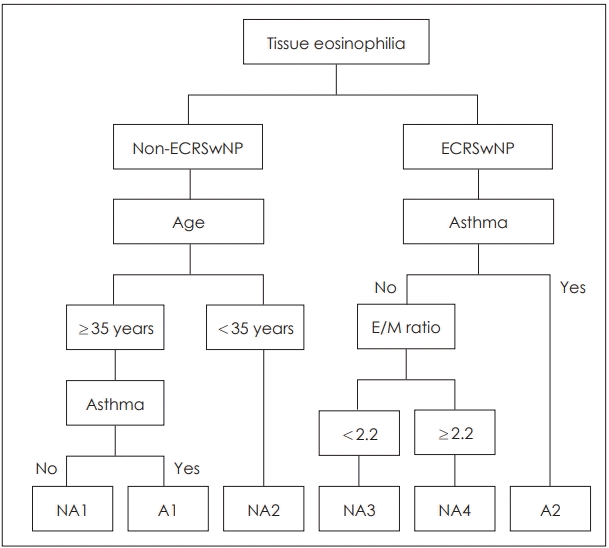
43. Liao B, Liu JX, Li ZY, Zhen Z, Cao PP, Yao Y, et al. Multidimensional endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis and their association with treatment outcomes. Allergy. 2018; 73(7):1459–69.

44. Kim DK, Kang SI, Kong IG, Cho YH, Song SK, Hyun SJ, et al. Two-track medical treatment strategy according to the clinical scoring system for chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10(5):490–502.

45. Kim JW, Huh G, Rhee CS, Lee CH, Lee J, Chung JH, et al. Unsupervised cluster analysis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp using routinely available clinical markers and its implication in treatment outcomes. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019; 9(1):79–86.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download