서 론
대상 및 방법
대 상
VIN 검사방법
어지럼증 발병양상과 전정신경염의 세부 진단 분류
결과 분석
결 과
Table 1.
안진의 양상
Table 2.
‘0’ means no existing nystagmus. P: patient, VN: vestibular neuritis, SHLV: sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo, SN: spontaneous nystagmus. HSN: post head shake nystagmus, VIN: vibration induced nystagmus, DC: direction changing, RB: right beating nystagmus, LB: left beating nestagnus, ipsi: ipsilateral, cont: contralateral
전정기능검사 결과
Table 3.
| P |
Caloric test |
vHIT |
Rotation chair test |
mCTSIB |
SVV (°) | PN | DC VIN | Overall vestibular status | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak side | CP (%) | Gain (Rt) | Gain (Lt) |
SV |
SHA |
Greatest abnormal test condition | ||||||||||
| Gain DP | TC DP | Gain | Phase | Asymm | ||||||||||||
| P01 | Rt. | 37 | - | - | 12.6* | 7.7* | Normal* | Normal | Normal* | Foam-EC & veering to Rt | Lt 0.5* | - | Ipsi | Caloric VN → compensating* | ||
| P03 | Rt. | 4 | 0.69 | 0.59 | 3.2 | -2.7 | Low | Normal | Normal | Normal | Lt 1.7 | LBt | Ipsi | Non-caloric VN | ||
| P04 | Rt. | 12 | - | - | 13.5 | 10.6 | Normal | Normal | to Lt† | Normal but veering to Rt† | Lt 0.9 | - | Cont | Non-caloric VN | ||
| P05 | Lt. | 8 | 1.17 | 1.13 | 5.1 | -2.7 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Foam-EC & veering to Rt† | Lt 3.6† | - | Cont | Non-caloric VN | ||
| P06 | Rt. | 15 | 1.19 | 1.17 | -3.8 | -17.2† | Low† | Normal | Normal | Foam-EC† | Lt 1.0 | LBt | Cont | Non-caloric VN | ||
| P07 | Rt. | 6 | 1 | 0.95 | 5.5 | -17.2† | Normal | Normal | Normal | Foam-EC† | Rt 0.1 | - | Cont | Non-caloric VN | ||
| P08 | Rt. | 72 |
1.12 Definite saccade |
0.95 Definite saccade |
-18.4 | -2.2 | Low | Lead | to Lt* | Foam-EC | Rt 4.7 | - | Ipsi | Caloric VN → over compensation* | ||
| P09 | Rt. | 24 |
0.78 Definite saccade |
0.87 Definite saccade |
3.3* | -20.0 | Low | Lead | Normal | Foam-EC & veering to Lt* | Lt 2.1* | - | Cont | Caloric VN → over compensation* | ||
| P10 | Lt. | 7 |
1.18 Definite saccadet† |
1.13 | 7.1 | -5.7 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal but veering to Rt† | Lt 1.8 | - | Ipsi | Non-caloric VN | ||
| P11 | Rt. | 3 |
1.08 Definite saccade† |
0.99 Definite saccade† | 10.7 | 9.5 | Low† | Normal | Normal | Foam-EC & veering to Rt† | Lt 0.6 | - | Cont | Non-caloric VN | ||
| P13 | Lt. | 6 | 1.11 | 1.05 | 6.9 | 8.3 | Normal | Normal | to Lt† | Normal | Lt 0.6 | - | Cont | Non-caloric VN | ||
| P15 | Rt. | 7 | 1.08 | 1.06 | 17.6† | -18.3† | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Lt 0.9 | - | Ipsi | Non-caloric VN | ||
positive value represent directional preponderance to right side, negative value represent directional preponderance to left side.
P: patient, CP: canal paresis, vHIT: video head impulse test, SV: step velocity, DP: directional preponderance, TC: time constant, SHA: sinusoidal harmonic acceleration, Asymm: asymmetry, mCTSIB: modified clinical test of sensory interaction in balance, SVV: subjective visual vertical, PN: positional nystagmus, DC VIN: direction changing vibration induced nystagmus, EC: eye closed, ipsi: ipsilateral, cont: contralateral, VN: vestibular neuritis
Ipsi-DC VIN과 cont-DC VIN의 임상양상
고 찰
일측 전정기능 저하 환자에서 진동유발 안진의 방향
정상인에서의 진동유발안진
진동유발안진의 발생원리
자극 측 방향전환 진동유발안진(ipsi DC VIN)의 기전(mechanism)에 대한 추정
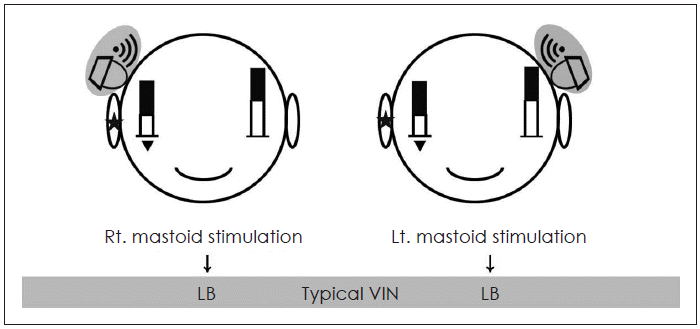 | Fig. 1.Presumed mechanism of typical VIN for mild Rt. VN patient (If interaural attenuation is “0”). White bars mean right and left vestibular function, and black bars mean vibration induced vestibular stimulations. The height of right white bar is lower than left one. Because interaural attenuation is assumed as “0”, all added black bars have same height. So, regardless of the vibration side, Rt VN patient shows left sided nystagmus. Asterisks indicate phathologic side, and Inverted triangle mean weaker vestibular function compared to opposite side. VIN: vibration induced nystagmus, VN: vestibular neuritis. |
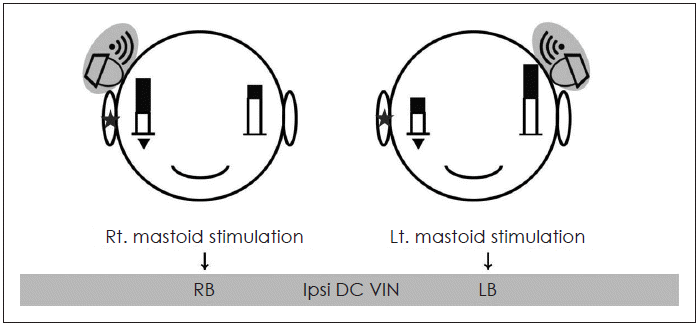 | Fig. 2.Presumed mechanism of ipsi DC VIN for mild Rt VN patient (If interaural attenuation is not “0”). White bars mean right and left vestibular function, and black bars mean vibration induced vestibular stimulations. The height of right white bar is lower than left one. In this figure, because interaural attenuation is assumed as “not 0”, black bar height of vibration side is higher than the opposite side. So, when the vibration is induced on the right side, final vestibular activation of right side overtakes the left side, and patient shows right sided nystagmus. Asterisks indicate phathologic side, and Inverted triangle mean weaker vestibular function compared to opposite side. *interaural attenuation of bone conduction pure tone (250-4000 Hz): 0-10 dB (Ballenger’s Otorhinolaryngoly: Head and Neck Surgery, Chapter 9, p.129). DC: direction changing, VIN: vibration induced nystagmus, VN: vestibular neuritis. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download