서 론
재료 및 방법
재 료
세포 배양 및 처치
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction(RT-PCR) 분석
Real-time PCR 분석
면역분석법(Immunoassay)
Westen blot analysis of p38 and ERK1/2 MAPK phophorylation
siRNA 형질 전환
통 계
결 과
NCI-H292 세포에서 황사가 MUC4와 MUC16 발현에 미치는 영향
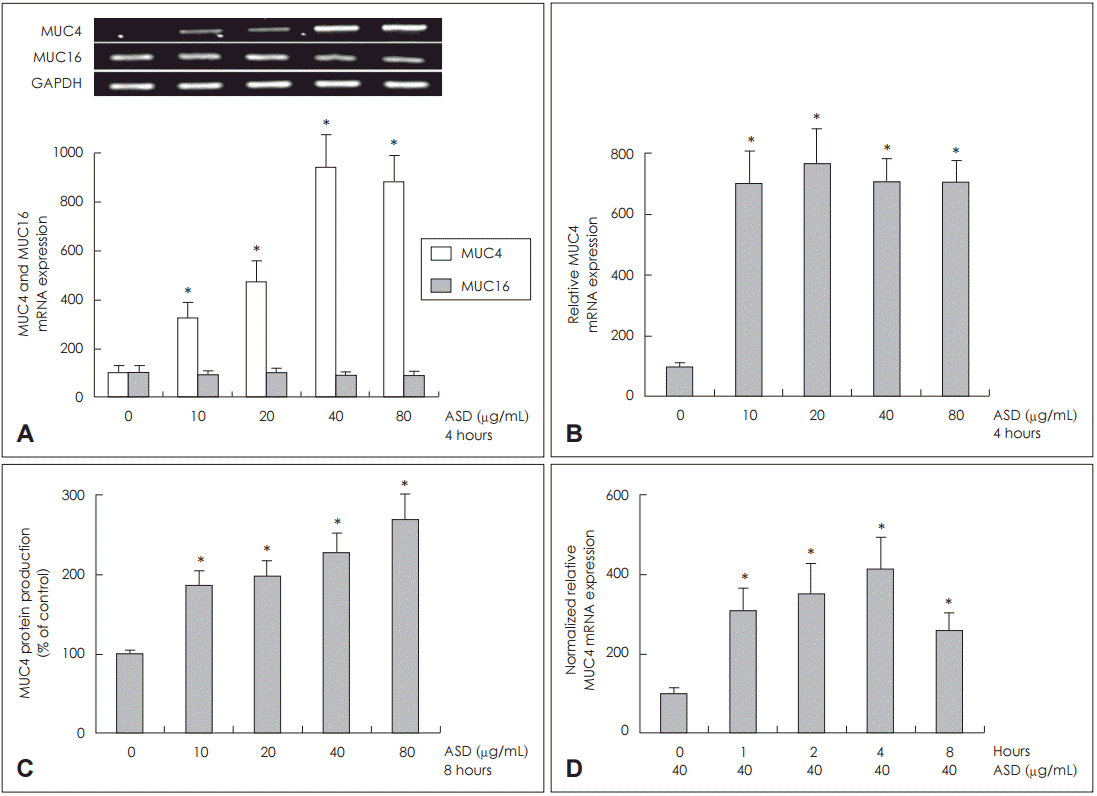 | Fig. 1.Effects of ASD on MUC4 and MUC16 expression in NCI-H292 cells. Results of RT-PCR showed that ASD significantly induced MUC4 mRNA expression. However, ASD did not induce MUC16 mRNA expression (A). Results of real-time PCR and ELISA showed that MUC4 mRNA expression and protein production were significantly increased at all concentration of ASD (B and C). Results of realtime PCR showed that MUC4 mRNA expression was significantly increased at all times, and peaked at 4 hours after exposure to ASD (40 μg/mL) (D). Images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate (n=3). Bars indicate the average±S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *p<0.05 vs. baseline. ASD: Asian sand dust, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, PCR: polymerase chain reaction. |
NCI-H292 세포에서 황사가 ERK1/2 MAPK와 p38 MAPK를 통한 MUC4 발현에 미치는 영향
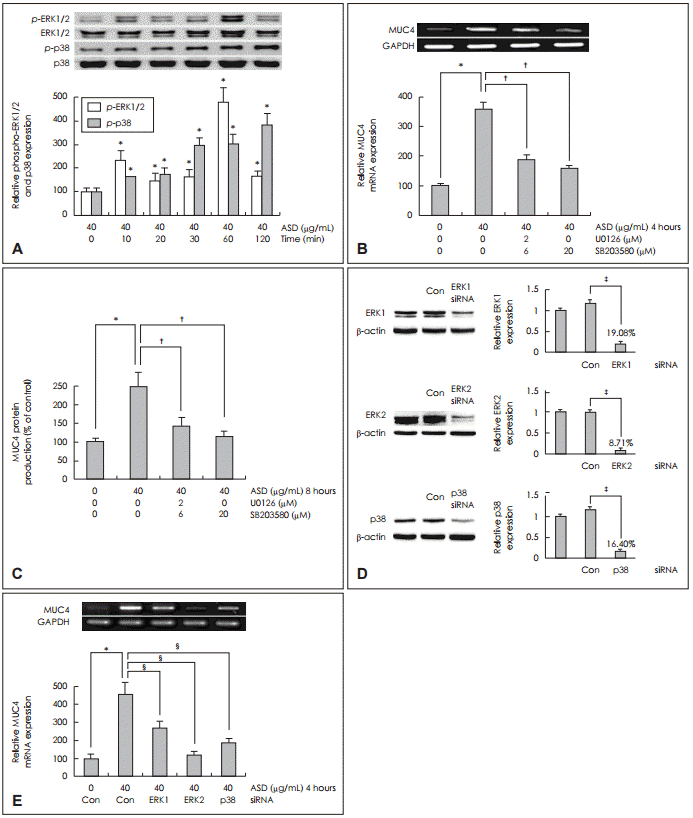 | Fig. 2.Effects of ASD on phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK in NCI-H292 cells. Results of Western blot showed that ASD significantly activated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK (A). Results of real-PCR and ELISA showed that U0126 (ERK1/2 MAPK inhibitor) and SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) significantly inhibited ASD-induced MUC4 mRNA expression and protein production (B and C). Western blot analysis was applied to detect the transfection efficiency (D). Results of RT-PCR showed that knockdown of ERK1, ERK2 and p38 MAPK by siRNA significantly blocked ASD-induced MUC4 mRNA expression (E). Images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate. Bars indicate the average±S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate (n=3). *p<0.05 vs. baseline, †p<0.05 vs. ASD (40 μg/mL) only, ‡p<0.05 vs. control siRNA only, §p<0.05 vs. ASD (40 μg/mL) and control siRNA. ASD: Asian sand dust, Con: control siRNA, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, p38: p38 MAPK, RTPCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, siRNA: small interfering ribonucleic acid, PCR: polymerase chain reaction. |
NCI-H292 세포에서 황사가 TLR4를 통한 MUC4 발현에 미치는 영향
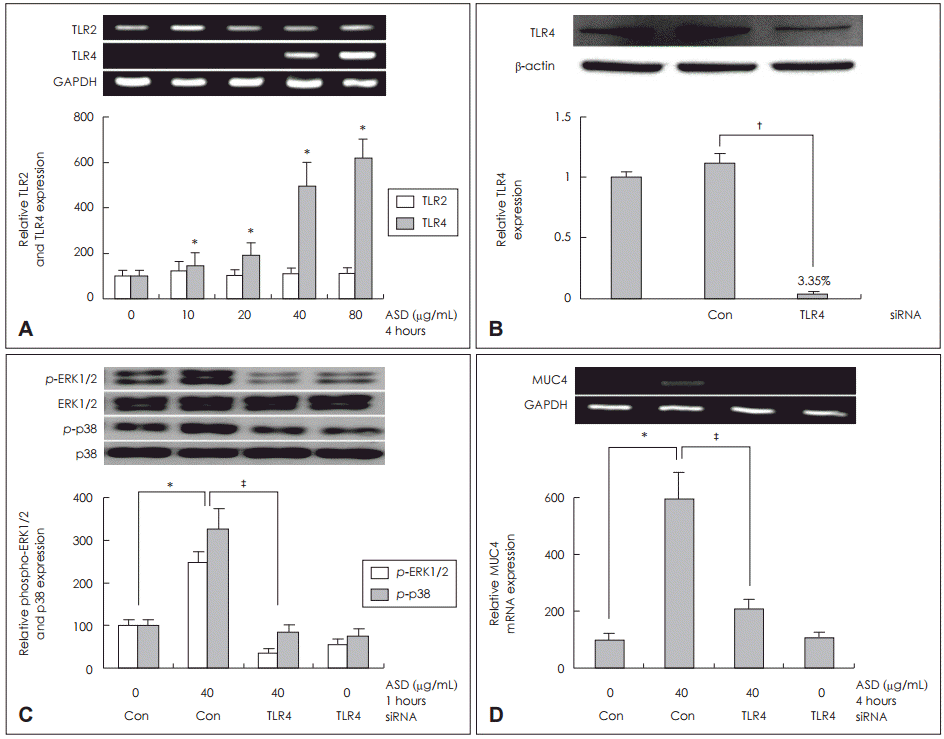 | Fig. 3.Roles of TLR in ASD-induced MUC4 expression in NCI-H292 cells. Results of RT-PCR showed that ASD significantly increased TLR4 mRNA expression in dose dependent-manner. However, TLR2 mRNA expression was not increased (A). Western blot analysis was applied to detect the transfection efficiency (B). Results of RT-PCR showed that knockdown of TLR4 by siRNA significantly blocked ASD-induced MUC4 mRNA expression (C). Results of Western blot showed that knockdown of TLR4 by siRNA significantly blocked ASD-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK (D). Images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate (n=3). Bars indicate the average±S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *p<0.05 vs. baseline, †p<0.05 vs. control siRNA only, ‡p<0.05 vs. ASD (40 μg/mL) and control siRNA. ASD: Asian sand dust, Con: control siRNA, GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, siRNA: small interfering ribonucleic acid, TLR: toll-like receptor, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase. |
하비갑개 점막 상피세포에서 황사가 MUC4 발현에 미치는 영향
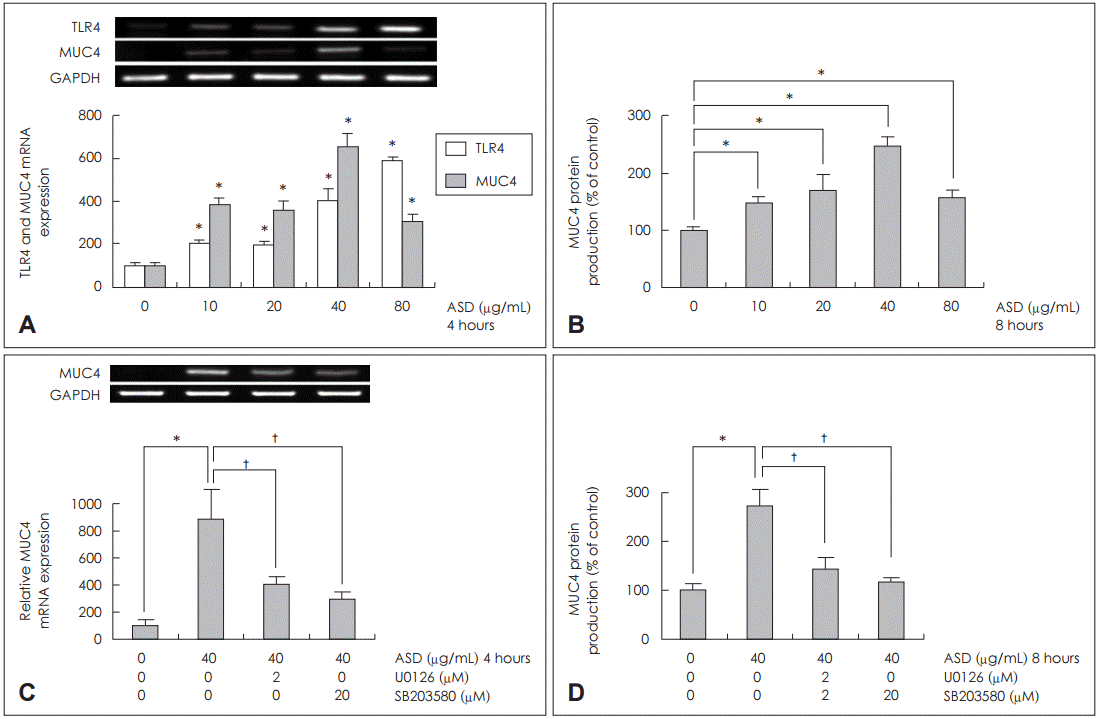 | Fig. 4.Effects of ASD on TLR4 and MUC4 expression in human nasal epithelial cells. Results of RT-PCR showed that ASD significantly induced TLR4 and MUC4 mRNA expression (A). Results of ELISA showed that MUC4 protein production were significantly increased at all concentration of ASD (B). Results of RT-PCR and ELISA showed that U0126 (ERK1/2 MAPK inhibitor) and SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) significantly attenuated ASD-induced MUC4 mRNA expression and protein production (C and D). Images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate (n=3). Bars indicate the average±S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *p<0.05 vs. baseline, †p<0.05 vs. ASD (40 μg/mL) only. ASD: Asian sand dust, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, TLR: toll-like receptor, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase. |
고 찰
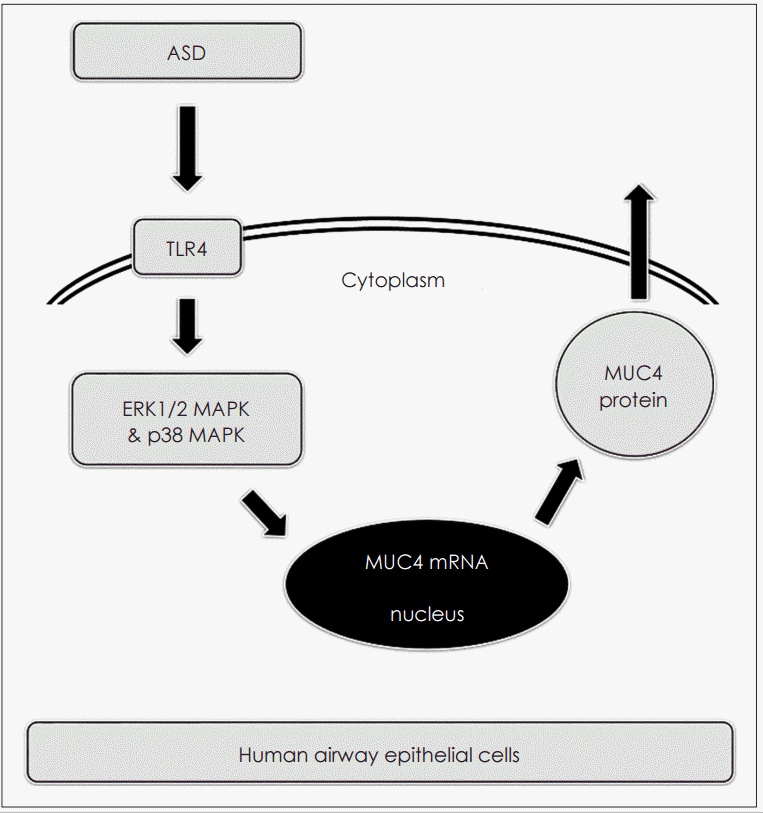 | Fig. 5.The schematic signaling pathway of ASD on MUC4 expression in human airway epithelial cells. ASD induces MUC4 expressions via TLR4-dependent ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. ASD: Asian sand dust, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, TLR: toll-like receptor. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download