Abstract
Lateral neck metastasis is an independent risk factor of the loco-regional recurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). Ultrasonography (US) and computed tomography are frequently performed to diagnose the lymph node (LN) metastasis. However, some metastatic LNs can remain after initial treatment and can present as regional recurrences. A 19-year-old woman was diagnosed as having 1.99 cm PTC. No abnormal LNs was detected on preoperative CT and US. She underwent operation and radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy: seven months after RAI therapy, thyroglobulin level was elevated. However, no metastatic LNs were detected on neck CT, US and positron emission tomography-CT. Neck exploration was performed and metastatic PTC was diagnosed in bilateral level III and IV. A radiologist retrospectively reviewed the neck CTs taken before the first surgery and the second surgery. There was no significant difference in the LN appearances of two CTs. On both CT scans, all LNs were very small, homogenously enhanced, without calcification or cystic changes.
Lymph node (LN) metastasis develops in approximately 20% to 90% of patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) [1]. Prophylactic central neck dissection (CND) is frequently performed according to primary tumor stage. However, lateral neck dissection (LND) is not recommended in clinically N0 PTC. However, the incidence of lateral neck metastasis has been reported as 18% to 64% and the incidence of occult lateral neck metastasis, which is not diagnosed by preoperative physical examination and radiologic tests was reported up to 18% [2-4]. Lateral neck metastasis is known as an independent risk factor of the loco-regional recurrence, especially in patients older than 45 years [5-7].
Ultrasonography (US) is a primary imaging modality for preoperative evaluation of LN metastases. Computed tomography (CT) is also frequently performed in many institutions, considering the operator dependency of US. However, the diagnostic sensitivity of radiologic neck evaluation does not exceed 80% [8-11]. Some metastatic LNs can remain after surgery and radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy and can present as regional recurrences.
We present a case of recurrent PTC in lateral neck after initial surgery and postoperative adjuvant RAI treatment. To investigate whether the metastatic LNs were true recurrence or remnant disease undiagnosed before initial surgery, we analyzed and compared the radiologic findings of CT scans before initial surgery and those before revision surgery.
A 19-year-old woman who had been followed up in pediatric department for glycogen storage disease, was referred to the department of otolaryngology with a thyroid mass accidentally detected in neck CT. US with fine needle aspiration biopsy was performed. The size of the thyroid mass was 1.99 cm and the aspiration cytology was consistent with PTC. There was no abnormal LN suspicious for metastasis in CT or US (Figs. 1 and 2). During surgery, gross extrathyroidal extension (ETE) was detected and CND was performed along with total thyroidectomy. Pathologically, multifocal PTCs, with the largest one 1.7 cm extended to perithyroidal soft tissue, and metastasis to 12 of 17 level VI LNs were diagnosed (pT3N1aMx). RAI therapy with 100 mCi 131I was performed 2 months after surgery. Just before RAI therapy, off-Tg level was 8.6 ng/mL with thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) >100.0 µIU/mL. After RAI therapy, whole body scan (WBS) showed no radioiodine uptake in previous thyroid portion nor extrathyroidal uptake. Three months after the RAI therapy, on-Tg level was 5.3 ng/mL. However, no abnormal mass was detected on thyroid bed and neck areas with US.
Seven months after RAI therapy, on-Tg level was 18.1 ng/mL. At that moment, the patient had severe diarrhea, abdominal pain and chest discomfort. Abdominal CT and chest CT showed 1cm-sized nodule in left lower lung and a lobulated mass in anterior mediastinum and central neck. Although the lobulated mass was reported as “recurrent PTC” by a radiologist, it rather seemed like a hypertrophic thymus. There was no additional neck mass reported in neck CT, US suggesting metastatic PTC. However, because there was a high Tg level and multiple central LN metastasis (12/17) was diagnosed in the first operation, we assumed that there the possibility of subclinical lateral LN metastasis was high and performed neck exploration along with left lower lobectomy of lung (by thoracic surgeons). During neck exploration, metastatic PTCs were detected in bilateral level III, IV on frozen biopsy. With the frozen biopsy reports, we performed bilateral LND (bilateral level II, III, IV, and V dissection). Lobulated mass in central neck was cervical thymus. There was no metastatic PTC in central neck. Metastatic PTC was pathologically reported in 6 of 62 LNs (1 in left level III, 1 in left level IV, 2 in right level III, 2 in right level IV). RAI therapy with 150 mCi 131I was performed 2 months after surgery. Just before RAI therapy, off-Tg level was 6.1 ng/mL with TSH 81.0 µIU/mL. After RAI therapy, WBS showed no radioiodine uptake in previous thyroid portion nor extrathyroidal uptake. Two months after the RAI therapy, on-Tg level was 0.2 ng/mL. Five months after the RAI therapy, no recurrent mass was detected by US.
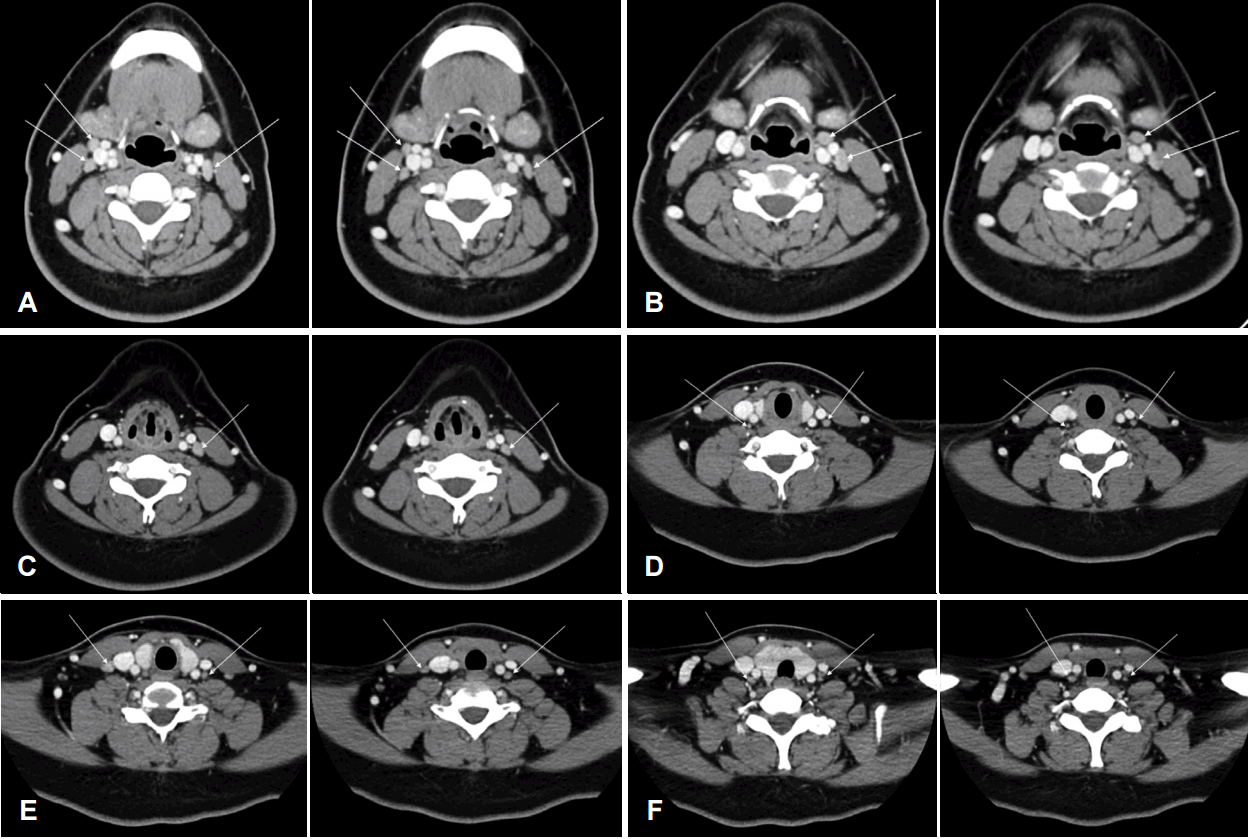
A radiologist retrospectively reviewed the neck CT images taken before the first surgery and before the second surgery(Fig. 2). There was no significant difference in the LN appearances of two CTs. Especially, the LN characteristics of the levels with pathologically proven metastatic PTC were analyzed; right level III, right level IV, left level III, and left level IV. In those neck areas of both CT scans, all LNs were very small (7-11 mm in maximum axial diameter), homogenously enhanced. There were no calcification or cystic change. According to the preexisting criteria, those LNs are considered as benign or reactive lymphadenopathy.
US is the current choice of imaging modality for preoperative evaluation of cervical LN metastases in thyroid cancer. High-resolution sonography improved the characterization of cervical LNs. Several sonographic criteria, such as loss of fatty hilum, hyperechogenecity, round shape, calcification and cystic change, have been used to detect the metastatic LNs [12]. The sensitivity of the neck US for cervical LN metastasis has been reported variable, approximately from 40 up to 60% [8,13,14]. A meta-analysis study showed that the pooled patient based sensitivity for US was 72% and the pooled level-based sensitivity was lower 63% [10].
Despite high resolution and easy accessibility, operator dependency and subjectivity of US make many surgeons order CT scans before surgery. CT has been proven to be an accurate imaging modality for the detection of LN metastasis from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Similarly, some CT criteria can be used to predict the LN metastasis of PTC: for example, strong enhancement without hilar vessel enhancement, heterogeneous enhancement, calcification, or cystic or necrotic change [15]. However, the diagnostic criteria have not been clearly defined yet. Thus, the diagnostic accuracy of CT to predict the LN metastasis of PTC is not conclusive. In the previous studies, patient-based the sensitivity of CT scans was variable, from 57% to 100% [8,13]. The level-based sensitivity was from 34% to 77% for all levels and from 42% to 78% for lateral neck levels [8,13,14].
However, the true sensitivity of CT scan is unknown yet. It is because if there is no suspected LN metastasis by radiologic evaluation, neck dissection is mostly not performed. i.e. Previous studies on diagnostic accuracy of CT included only cases for which LN metastasis was suspected and thus neck dissection was performed. The gold standard to determine the sensitivity of radiologic tests is the pathology. Therefore, missed LN metastasis by radiologic test could have affected the reported sensitivity.
Similarly, the CT criteria for diagnosis of LN metastasis may be incorrect or insufficient. Missed LN metastasis, which was not suspected by radiologic tests, has not been included to previous studies to define the CT criteria of LN metastasis. The study by Som, et al. [15], frequently cited regarding to the CT and MR criteria of LN metastasis, included only the cases in which, LN metastasis was suspected by CT or MRI and neck dissection was performed. Missed cases can give us a lot of information. Like in our case, the metastatic LN of PTC can have variable characters, against our expectations.
We suggest that the diagnostic criteria of the radiologic studies for the LN metastasis of PTC be revised. In addition, considering the risk factors of subclinical lateral neck metastasis, such as age, sex, tumor size, ETE and central LN metastasis, frozen biopsy of the lateral neck LN might be performed during the operation.
REFERENCES
2. Kupferman ME, Patterson M, Mandel SJ, LiVolsi V, Weber RS. Patterns of lateral neck metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004; 130(7):857–60.

3. Wada N, Duh QY, Sugino K, Iwasaki H, Kameyama K, Mimura T, et al. Lymph node metastasis from 259 papillary thyroid microcarcinomas: frequency, pattern of occurrence and recurrence, and optimal strategy for neck dissection. Ann Surg. 2003; 237(3):399–407.
4. Patron V, Bedfert C, Le Clech G, Aubry K, Jegoux F. Pattern of lateral neck metastases in N0 papillary thyroid carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2011; 11:8.

5. Suh YJ, Kwon H, Kim SJ, Choi JY, Lee KE, Park YJ, et al. Factors affecting the locoregional recurrence of conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma after surgery: a retrospective analysis of 3381 patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015; 22(11):3543–9.

6. Ito Y, Miyauchi A, Kihara M, Kobayashi K, Miya A. Prognostic values of clinical lymph node metastasis and macroscopic extrathyroid extension in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr J. 2014; 61(8):745–50.
7. Verburg FA, Mäder U, Tanase K, Thies ED, Diessl S, Buck AK, et al. Life expectancy is reduced in differentiated thyroid cancer patients ≥ 45 years old with extensive local tumor invasion, lateral lymph node, or distant metastases at diagnosis and normal in all other DTC patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98(1):172–80.

8. Kim E, Park JS, Son KR, Kim JH, Jeon SJ, Na DG. Preoperative diagnosis of cervical metastatic lymph nodes in papillary thyroid carcinoma: comparison of ultrasound, computed tomography, and combined ultrasound with computed tomography. Thyroid. 2008; 18(4):411–8.

9. Morita S, Mizoguchi K, Suzuki M, Iizuka K. The accuracy of (18)[F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography, ultrasonography, and enhanced computed tomography alone in the preoperative diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. World J Surg. 2010; 34(11):2564–9.

10. Wu LM, Gu HY, Qu XH, Zheng J, Zhang W, Yin Y, et al. The accuracy of ultrasonography in the preoperative diagnosis of cervical lymph node meta-stasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: a metaanalysis. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81(8):1798–805.

11. Lee DW, Ji YB, Sung ES, Park JS, Lee YJ, Park DW, et al. Roles of ultrasonography and computed tomography in the surgical management of cervical lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2013; 39(2):191–6.

12. Rosário PW, de Faria S, Bicalho L, Alves MF, Borges MA, Purisch S, et al. Ultrasonographic differentiation between metastatic and benign lymph nodes in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Ultrasound Med. 2005; 24(10):1385–9.

13. Ahn JE, Lee JH, Yi JS, Shong YK, Hong SJ, Lee DH, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of CT and ultrasonography for evaluating metastatic cervical lymph nodes in patients with thyroid cancer. World J Surg. 2008; 32(7):1552–8.

14. Jeong HS, Baek CH, Son YI, Choi JY, Kim HJ, Ko YH, et al. Integrated 18F-FDG PET/CT for the initial evaluation of cervical node level of patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: comparison with ultrasound and contrast-enhanced CT. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006; 65(3):402–7.
15. Som PM, Brandwein M, Lidov M, Lawson W, Biller HF. The varied presentations of papillary thyroid carcinoma cervical nodal disease: CT and MR findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994; 15(6):1123–8.
Fig. 1.
US images before initial surgery and before revision surgery. US images of thyroid mass before initial surgery. Papillary carcinoma was found in right lobe of thyroid (arrow) (A). US images of neck LNs before initial surgery. This figure shows very small, homogenously enhanced LN (level III) (black arrow). There was no calcification or cystic change. SCM muscle was seen (white arrow) (B). US images of neck LNs before revision surgery. There were no metastatic LNs at level IV (white arrowhead). Internal jugular vein (black arrow), carotid artery (black arrowhead), and SCM muscle (white arrow) were seen (C). US: ultrasonography, LN: lymph node, SCM: sternocleidomastoid.
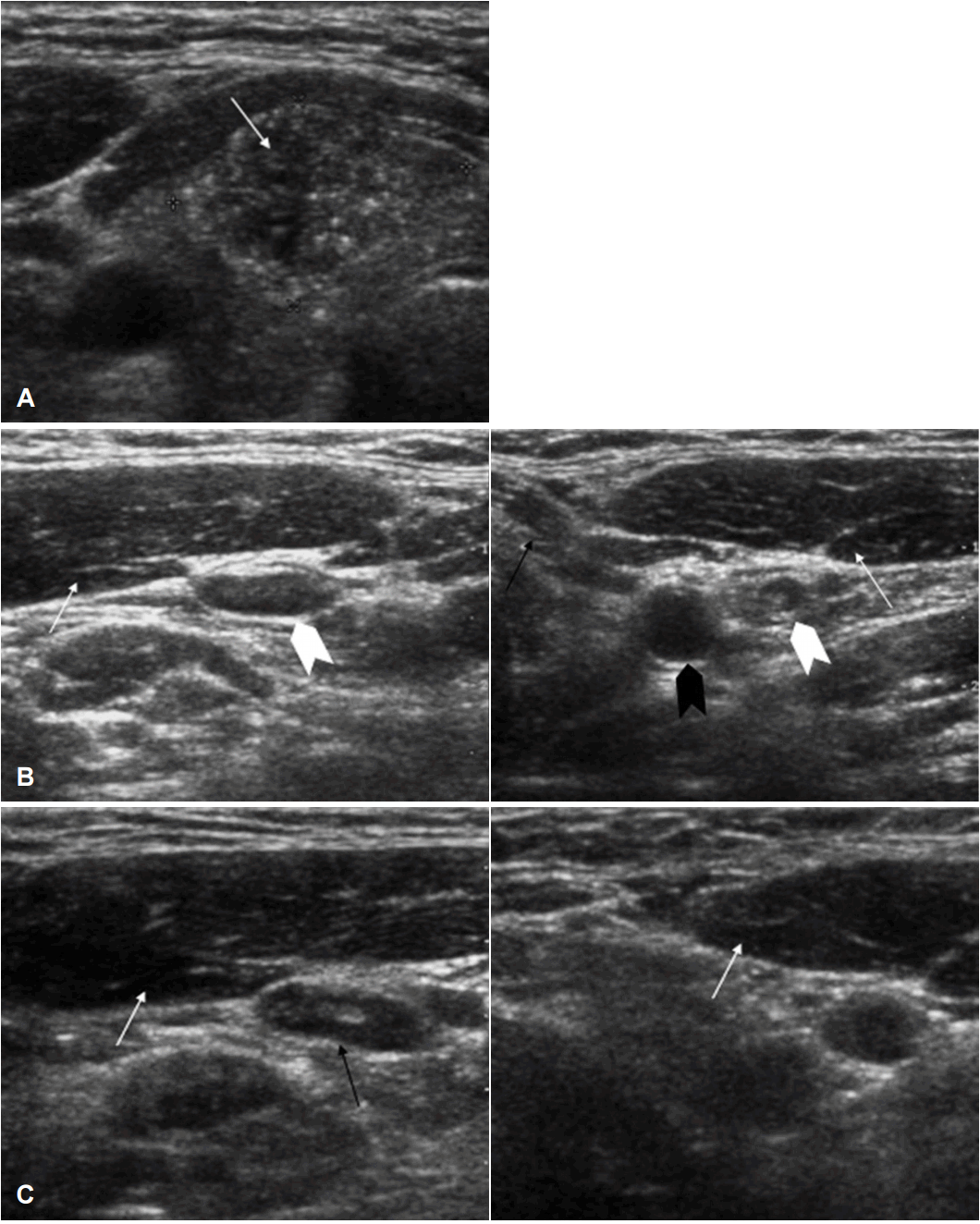
Fig. 2.
Axial contrast-enhanced CT images before initial surgery and before revision surgery. From (A) to (F). CT images before initial surgery, which show LNs in level III and IV, are presented at left side of each image. CT images before revision surgery, which show LNs at the corresponding level with left side images, are presented at right side of each image. White arrows indicate LNs. LN: lymph node.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download