갑상선암으로 진단된 53세 남환의 술 전 CT 검사상 아래와 같은 소견이 보였다. 이 환자에 대한 설명으로 틀린 것은?
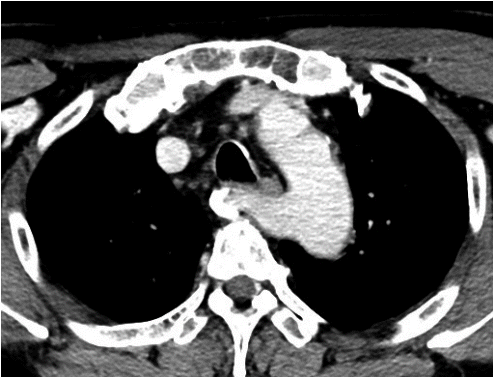
① 주로 좌측의 비되돌이 하후두신경을 동반한다.
② 하후두신경이 경동맥의 전방에서 미주신경의 내측으로부터 기시한다.
③ 다른 선천성 혈관 기형이 동반되지는 않는다.
④ 연하곤란이 동반될 수 있다.
⑤ 후두신경 손상의 가능성은 차이가 없다.
정답 및 해설
답 ④
해 설 A “nonrecurrent” laryngeal nerve may rarely occur on the right side and enters from a more lateral course. Typically, an aberrant retroesophageal subclavian artery (arteria lusoria) or other congenital malformation of the vascular rings is present.
참고 문헌: Flint PW, Haughey BH, Lund VJ, Niparko JK, Robbins KT, Thomas JR, Lesperance MM. Cummings otolaryngology head and neck surgery. 6th ed. Canada: Saunders;2015. p.1904.
The nonrecurrent RLN occurs in 0.5% to 1% of cases and is associated with a right subclavian artery takeoff from the distal aortic arch. The right subclavian in these cases follows a retroesophageal course to the right or, less commonly, between the esophagus and the trachea. 53 Henry found that the symptoms of dysphagia secondary to subclavian interaction with the esophagus (dysphagia lusoria) were not consistently present in cases of nonre-current RLN. When dysphagia is present, dysphagia lusoria is difficult to separate from dysphagia referable to a pathologic condition of the thyroid. Epstein suggests nonrecurrent RLN is associated with compressive symptoms in 10% of patients typically with dysphasia.
The nonrecurrent nerve is at increased risk for paralysis with one study of 31 nonrecurrent nerves at risk demonstrating a 12.9% paralysis rate.
The nonrecurrent RLN derives from the vagus as a direct medial branch in the neck and extends—depending on its level of takeoff from the vagus and generally with a downward looping course—from behind the carotid artery to the laryngeal entry point.
참고 문헌: Randolph GW. Surgery of the thyroid and parathyroid gland. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders;2012. p.311-2.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download