Abstract
Background
Unlike the right internal jugular vein (RIJV), there is a paucity of data regarding the effect of the Trendelenburg position on the left internal jugular vein (LIJV). The purpose of this study is to investigate the cross-sectional area (CSA) of the LIJV and RIJV and their response to the Trendelenburg position using two-dimensional ultrasound in adult subjects.
Methods
This study enrolled fifty-eight patients with American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status class I-II who were undergoing general anesthesia. CSAs of both the RIJV and LIJV were measured with a two-dimensional ultrasound in the supine position and then in a 10° Trendelenburg position.
Results
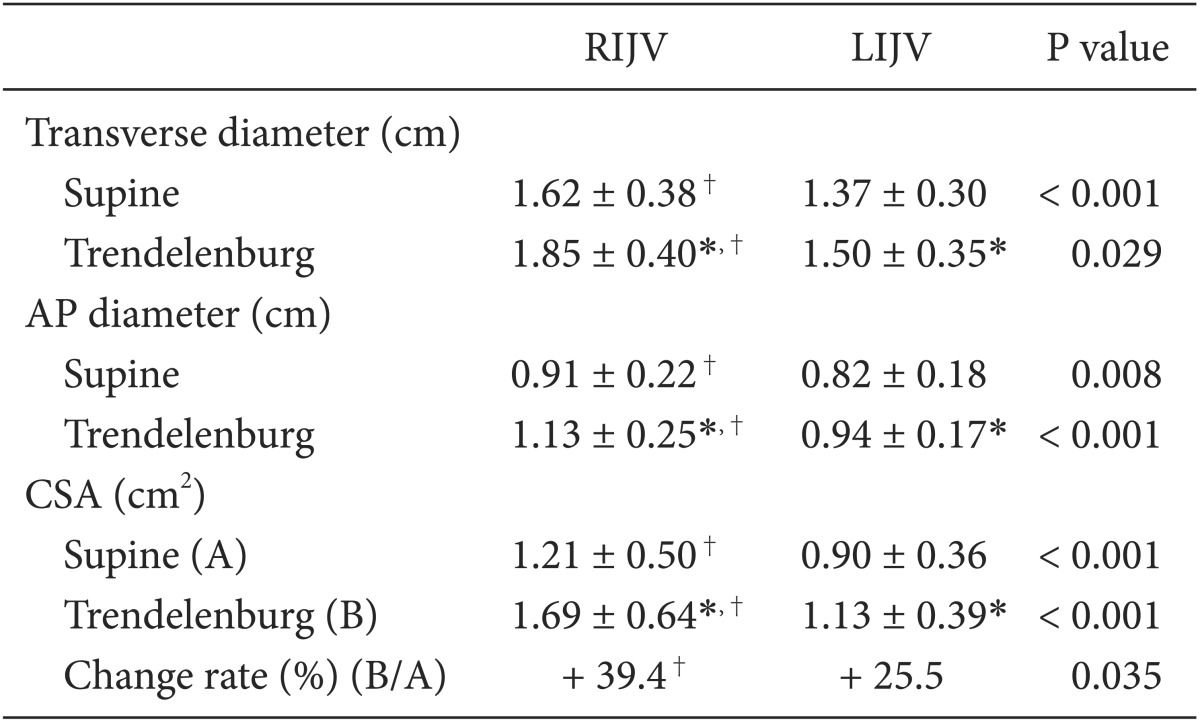
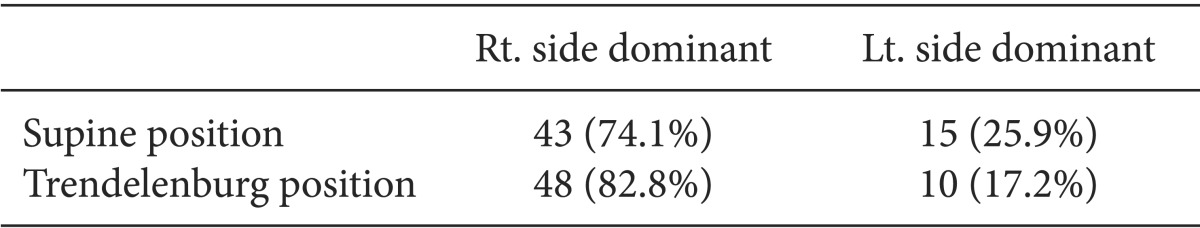
In the supine position, the transverse diameter, anteroposterior diameter, and CSA of the RIJV were significantly larger than those of the LIJV (P < 0.001). Of 58 patients, the RIJV CSA was larger than the LIJV CSA in 43 patients (74.1%), and the LIJV CSA was larger than the RIJV CSA in 15 patients (25.9%). In the Trendelenburg position, CSAs of the RIJV and LIJV increased 39.4 and 25.5%, respectively, compared with the supine position. However, RIJV changed at a rate that was significantly greater than that of the LIJV (P < 0.05). Of 58 patients, the RIJV CSA was larger than the LIJV CSA in 48 patients (82.8%), and the LIJV CSA was larger than the RIJV CSA in 10 patients (17.2%).
Go to : 
Internal jugular venous (IJV) catheterization, one of the routes for central venous cannulation (CVC), allows intravenous access for massive transfusion, fluid resuscitation and monitoring of central venous pressure (CVP) [1]. The traditional blind technique using anatomical landmarks may cause complications such as carotid artery puncture, resulting in uncontrollable bleeding or hematoma, airway compression, and cerebrovascular neurologic problems [2,3,4]. In a previous study, 18% of right IJVs were less than 5 mm in diameter, and the IJV was placed outside the path measured by external landmarks in 5.5% of patients [5,6]. Real-time ultrasound (US)-guided IJV catheterization was introduced to guarantee a higher success rate and lower complication rate for CVC [7,8]. The success rate of IJV cannulation is strongly associated with cross-sectional area (CSA), and various conditions have been studied to maximize right IJV (RIJV) diameter [6,9,10,11]. The CSA of the left IJV (LIJV) has been rarely studied compared to the preferred RIJV. In Korea, there have been no studies that compare the RIJV and LIJV CSAs in a supine position or variations in the CSA of both IJVs in the Trendelenburg position.
This study compared the CSA of the RIJV with the LIJV in a supine position. The diameter changes and CSAs of both IJVs in a 10° Trendelenburg position were investigated with US to explore the possibility of the LIJV as a favorable access point for CVC.
Go to : 
The hospital Institutional Review Board approved this study, and informed consent was obtained from all patients before enrollment. This prospective randomized controlled study included 58 patients between the ages of 18 and 75 years (American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status class I-II) undergoing general anesthesia for abdominal or gynecological surgeries at our hospital from April to July 2013. This study excluded patients with scheduled head and/or neck surgery, previous operations, benign or malignant neck masses, thyroid diseases, or cervical spine diseases. The criteria also excluded patients with history of IJV cannulation, severe cardiopulmonary disease, hemodynamic instability, obesity (BMI of at least 30 kg/m2), and conditions necessitating emergent surgical procedures, as well as patients who were pregnant or on antiplatelet medication. No patients were given preanesthetic medications.
In the operating room, patients were continuously monitored with electrocardiography, pulse oximetry, and noninvasive blood pressure (BP). They breathed 100% O2 prior to induction of general anesthesia and received one half of maintenance fluid over 10 minutes and 4-8 ml/kg/hr fluid of Lactated Ringer's solution through an intravenous line. After confirming stable vital signs, midazolam 0.05 mg/kg and glycopyrrolate 0.2 mg were injected. A remifentanil (1 µg/kg) loading dose was simultaneously administered over 30 seconds, followed by continuous intravenous infusion at 0.1 µg/kg/hr. General anesthesia was induced by propofol 1.0 mg/kg (slowly injected over 30 seconds) and rocuronium 0.6 mg/kg. Patients were intubated and ventilated with 50% oxygen and air. General anesthesia was maintained using sevoflurane (1.0-2.0 vol%) and continuous remifentanil infusion. Patients were mechanically ventilated at a tidal volume (TV) of 6-8 ml/kg and a respiratory rate (RR) of 10 breaths/min with an I : E ratio of 1 : 2. The TV and RR were controlled to maintain the end tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) at 30-40 mmHg following US image collection.
After induction, patients were placed supine with pillows and without head rotation. Transverse US images were obtained on the right and left side of the neck through an 8 MHz two-dimensional linear transducer (Vivid®, GE Healthcare, Haifa, Israel) at the cricoid level parallel to the clavicle. The probe was placed at an angle of approximately 90° on the patient's neck as lightly as possible to avoid significant IJV compression. With consideration for variations of the IJV CSA according to inhalation and exhalation, all measurements of IJV CSA at maximal inhalation and exhalation were recorded based on differences between the two. The mean transverse (T) diameters, anterior-posterior (AP) diameter, and CSA of the RIJV and LIJV were measured using a built-in caliper on the US image of the largest IJV CSA. Patients were then placed in a 10° Trendelenburg position using a protractor (Saehan Tester Co., Busan, Korea) applied to the bed without a pillow. The mean T diameters, AP diameter, and CSA of the RIJV and LIJV were measured using the same methods.
Based on an alpha error of 0.05 and a power of 80%, approximately 42 patients were calculated as a sample size. All statistical analyses were performed using PASW Statistics 18.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Values for all data, except gender, were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Mean T diameters, AP diameter, and CSA of the RIJV and LIJV were compared using an unpaired two-tailed t-test. The paired t-test was used to compare mean T diameters, AP diameter and the CSA of the RIJV and LIJV for the supine and 10° Trendelenburg positions. A P value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Go to : 
Patient demographic characteristics are summarized in Table 1. No patients were excluded from the study due to hemodynamic problems after inducing general anesthesia. Ultrasonography was performed on all patients to visualize the CSA of the LIJV and RIJV. In supine position, the mean T diameters of the RIJV and LIJV were 1.63 ± 0.38 cm and 1.37 ± 0.30 cm (P < 0.001), respectively. The mean AP diameters of the RIJV and LIJV were 0.91 ± 0.22 cm and 0.82 ± 0.18 cm (P < 0.01), respectively. The CSAs of the RIJV and LIJV were 1.21 ± 0.5 cm2 and 0.90 ± 0.36 cm2 (P < 0.001), respectively. As a result, the mean T, AP diameter, and CSA of the RIJV were significantly larger than those of the LIJV (Table 2). Of 58 patients enrolled in this study, 43 (74.1%) patients had a larger RIJV CSA while 15 (25.9%) patients had a larger LIJV CSA (Table 3). In the Trendelenburg position, the T diameter, AP diameter, and CSA of the RIJV were increased by about 13.5, 23.2, and 39.4% compared to the supine position. The T diameter, AP diameter, and CSA of the LIJV were expanded by 9.1, 15.3, and 25.5% respectively. The RIJV was superior to the LIJV in T diameter, AP diameter, and CSA (P < 0.05) (Table 2). While the RIJV CSA was larger than the LIJV CSA in 48 (82.8%) patients, the rest (17.2%) had opposite results (Table 3).
Go to : 
The IJV is frequently used for CVC access due to its anatomic position, which is easy to approach and located out of the surgical field (except with head and neck surgeries). IJV cannulation has a lower rate of complications than subclavian venous cannulation [12]. Many studies have investigated methods of IJV catheterization, and US-guided IJV catheterization is known to increase success rate and reduce complications [7,8]. Furthermore, methods that increase the CSA (e.g. Valsalva maneuver, application of positive end-expiratory pressure and Trendelenburg position) are associated with a higher rate of successful IJV cannulation [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Many past studies have compared IJV CSA with and without ultrasound images [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. However, most studies concern the RIJV and not the LIJV. Few studies, particularly in Korea, have investigated both the right and left IJV CSA in the supine and Trendelenburg positions.
In our study, we measured mean T diameter, AP diameter, and CSA of both the RIJV and LIJV in supine and 10° Trendelenburg positions with a neutral head position. Generally, the 10-20° Trendelenburg position is popular for IJV cannulation. Lobato et al. [12] described that RIJV CSA increased by 25% with the 10° Trendelenburg position. Schreiber et al. [24] reported that IJV CSA increased significantly in the supine position immediately after the 10° Trendelenburg position. Marcus et al. [10] reported that Trendelenburg positions greater than 20° were so steep that they might actually be harmful to the patient and make it more technically difficult to approach. These positions were not recommended even when the patient was hemodynamically unstable and/or seriously obese. Although contralateral rotation of the head did not influence the CSA of the IJV during IJV catheterization [25], Sulek et al. [26] did not recommend head rotation from the midline due to the risk of carotid artery puncture. This was especially true at ≥ 40 degrees, which was associated with increased overlap of the carotid artery and IJV.
The RIJV goes straight into the right atrium with a more consistent relationship between the IJV and common carotid artery [27]. Despite some obvious disadvantages associated with LIJV catheterization, including remote chance of chylothorax following injury or rupture of the thoracic duct [28,29], the LIJV may be used in a few situations as follows: stenosis of the carotid artery, thrombosis of the RIJV, anatomical changes caused by head and neck surgery, and failure of RIJV cannulation [30]. Anatomical knowledge of the LIJV and CSA changes according to patient position are extremely important. With larger LIJV CSA in the Trendelenburg position, there is an increased success rate of LIJV cannulation despite its anatomical demerits. The mean T diameter, AP diameter, and CSA of both the RIJV and LIJV were measured with US images in clinical situations targeting not healthy volunteers but anaesthetized patients. In the supine position, RIJV CSA was significantly larger than LIJV CSA (P < 0.001). In the 10° Trendelenburg position, RIJV CSA increased by 39.4% while that of the LIJV CSA increased by 25.5%. The RIJV CSA increased at a rate that was significantly greater than that of the LIJV CSA (P < 0.001). RIJV cannulation is advantageous because RIJV CSA is larger than LIJV CSA in the supine position and its rate of change was greater than that of the LIJV CSA in the 10° Trendelenburg position, similarly as existing relative research. In a small number of studies on patients in special circumstances such as dialysis and intensive care, the Trendelenburg position was not recommended because it did not increase IJV CSA [18,23].
Pearson correlation coefficients for RIJV CSA and age according to supine and 10° Trendelenburg positions were 0.14 and 0.05, respectively, showing no correlation between the two sets of data. Values for the LIJV CSA were 0.37 and 0.31, respectively, indicating a significant increase in correlation with age. There was no clear explanation for this result. Although a significant increase in LIJV CSA with age was identified, it had little effect on cannulation because RIJV CSA is significantly larger than LIJV CSA. LIJV cannulation under US guidance is recommended over RIJV cannulation in the 10° Trendelenburg position for safety reasons, although the RIJV is the first choice for catheterization. RIJV cannulation has anatomical and technical benefits due to its larger size and rate of CSA increase.
In conclusion, the RIJV should be preferentially selected for IJV cannulation in anesthetized patients in a 10° Trendelenburg position, if not a special situation. For difficult cases of RIJV cannulation, we advise performance of LIJV catheterization under US guidance because 17.2% of LIJVs had a larger CSA than RIJVs with a significant increase in CSA in the 10° Trendelenburg position.
Go to : 
References
1. Chung IS, Kwon MA, Hwang HY, Park JH, Yeo JS, Kim CS, et al. The examination of internal jugular vein and carotid artery in trendelenburg position with head rotation; a prospective, randomized study. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2006; 51:11–16.

2. McGee DC, Gould MK. Preventing complications of central venous catheterization. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:1123–1133. PMID: 12646670.

3. Heath KJ, Woulfe J, Lownie S, Pelz D, Munoz DG, Mezon B. A devastating complication of inadvertent carotid artery puncture. Anesthesiology. 1998; 89:1273–1275. PMID: 9822023.

4. Reuber M, Dunkley LA, Turton EP, Bell MD, Bamford JM. Stroke after internal jugular venous cannulation. Acta Neurol Scand. 2002; 105:235–239. PMID: 11886371.

5. Samy Modeliar S, Sevestre MA, de Cagny B, Slama M. Ultrasound evaluation of central veins in the intensive care unit: effects of dynamic manoeuvres. Intensive Care Med. 2008; 34:333–338. PMID: 17926020.
6. Gordon AC, Saliken JC, Johns D, Owen R, Gray RR. US-guided puncture of the internal jugular vein: complications and anatomic considerations. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1998; 9:333–338. PMID: 9540919.

7. Armstrong PJ, Cullen M, Scott DH. The SiteRite ultrasound machine-an aid to internal jugular vein cannulation. Anaesthesia. 1993; 48:319–323. PMID: 8494135.

8. Tryba M, Kleine P, Zenz M. Sonographic studies for optimizing the cannulation of the internal jugular vein. Anaesthesist. 1982; 31:626–629. PMID: 7158746.
9. Hollenbeck KJ, Vander Schuur BM, Tulis MR, Mecklenburg BW, Gaconnet CP, Wallace SC, et al. Brief report: effects of positive endexpiratory pressure on internal jugular vein cross-sectional area in anesthetized adults. Anesth Analg. 2010; 110:1669–1673. PMID: 20385614.
10. Marcus HE, Bonkat E, Dagtekin O, Schier R, Petzke F, Wippermann J, et al. The impact of Trendelenburg position and positive end-expiratory pressure on the internal jugular cross-sectional area. Anesth Analg. 2010; 111:432–436. PMID: 20484538.

11. Lee SC, Han SS, Shin SY, Lim YJ, Kim JT, Kim YH. Relationship between positive end-expiratory pressure and internal jugular vein cross-sectional area. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2012; 56:840–845. PMID: 22288836.

12. Lobato EB, Florete OG Jr, Paige GB, Morey TE. Cross-sectional area and intravascular pressure of the right internal jugular vein during anesthesia: effects of Trendelenburg position, positive intrathoracic pressure, and hepatic compression. J Clin Anesth. 1998; 10:1–5. PMID: 9526929.

13. Han SS, Han WK, Ko DC, Lee SC. The simultaneous application of positive-end expiratory pressure with the Trendelenburg position minimizes respiratory fluctuations in internal jugular vein size. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014; 66:346–351. PMID: 24910725.

14. Cho YW, Kim DY, Shin SJ, Kim KI. Assessment of the right internal jugular vein cross-sectional area with different levels of positive end-expiratory pressure in patients with controlled ventilation during anesthesia. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013; 64:184–186. PMID: 23460936.

15. Beddy P, Geoghegan T, Ramesh N, Buckley O, O'Brien J, Colville J, et al. Valsalva and gravitational variability of the internal jugular vein and common femoral vein: Ultrasound assessment. Eur J Radiol. 2006; 58:307–309. PMID: 16352411.

16. Lobato EB, Sulek CA, Moody RL, Morey TE. Cross-sectional area of the right and left internal jugular veins. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 1999; 13:136–138. PMID: 10230944.

17. Yoon HK, Lee HK, Jeon YT, Hwang JW, Lim SM, Park HP. Clinical significance of the cross-sectional area of the internal jugular vein. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2013; 27:685–689. PMID: 23642889.

18. Nassar B, Deol GR, Ashby A, Collett N, Schmidt GA. Trendelenburg position does not increase cross-sectional area of the internal jugular vein predictably. Chest. 2013; 144:177–182. PMID: 23392444.

19. Tartière D, Seguin P, Juhel C, Laviolle B, Mallédant Y. Estimation of the diameter and cross-sectional area of the internal jugular veins in adult patients. Crit Care. 2009; 13:R197. PMID: 20003190.

20. Erbabacan E, Köksal GM, Ekici B, Kaya G, Altındaş F. Effects of different modes of ventilation and head position on the size of the vena jugularis interna. Swiss Med Wkly. 2014; 144:w13946. PMID: 24805819.

21. Eksioglu AS, Tasci Yildiz Y, Senel S. Normal sizes of internal jugular veins in children/adolescents aged birth to 18 years at rest and during the Valsalva maneuver. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:673–679. PMID: 24461996.

22. Farina M, Novelli E, Pagani R. Cross-sectional area variations of internal jugular veins during supine head rotation in multiple sclerosis patients with chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency: a prospective diagnostic controlled study with duplex ultrasound investigation. BMC Neurol. 2013; 13:162. PMID: 24188184.

23. Wu HL, Ting CK, Chen CY, Cheng HW, Chan KH, Chang WK, et al. No enlargement of the right internal jugular vein of the dialysis patients in the Trendelenburg position. J Chin Med Assoc. 2013; 76:401–406. PMID: 23664734.
24. Schreiber SJ, Lambert UK, Doepp F, Valdueza JM. Effects of prolonged head-down tilt on internal jugular vein cross-sectional area. Br J Anaesth. 2002; 89:769–771. PMID: 12393779.

25. Armstrong PJ, Sutherland R, Scott DH. The Effect of position and different manoeuvres on internal jugular vein diameter size. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1994; 38:229–231. PMID: 8023661.

26. Sulek CA, Gravenstein N, Blackshear RH, Weiss L. Head rotation during internal jugular vein cannulation and the risk of carotid artery puncture. Anesth Analg. 1996; 82:125–128. PMID: 8712386.

27. Metz S, Horrow JC, Balcar I. A controlled comparison of techniques for locating the internal jugular vein using ultrasonography. Anesth Analg. 1984; 63:673–679. PMID: 6731895.

28. Kwon SS, Falk A, Mitty HA. Thoracic duct injury associated with left internal jugular vein catheterization: anatomic considerations. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002; 13:337–339. PMID: 11875096.

29. Paoletti F, Ripani U, Antonelli M, Nicoletta G. Central venous catheters. Observations on the implantation technique and its complications. Minerva Anestesiol. 2005; 71:555–560. PMID: 16166917.
30. Muralidhar K. Left internal versus right internal jugular vein access to central venous circulation using the Seldinger technique. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 1995; 9:115–116. PMID: 7718748.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download