This article has been
cited by other articles in ScienceCentral.
Abstract
Background
In this study, we assessed the 50% effective concentration (EC50) of sevoflurane for reducing a rocuronium-induced reaction, based on the Dixon's up-and-down method. We also assessed the 50 and 95% effective end-tidal concentration of sevoflurane (ETsev), based on the probit regression curve of the probability of nonwithdrawal reaction.
Methods
We conducted a prospective, double-blind study in 23 males and 24 females. After using 2.5% thiopental sodium (4 mg/kg), anesthesia was induced in the patients. The patients then inhaled sevoflurane with 5 vol% in 6 L/min of oxygen. When the target ETsev was achieved, a nurse injected the intubating dose of rocuronium (0.6 mg/kg) for 5-10 s under the free flow of intravenous fluid. After the nurse evaluated the response, the nurse recorded the maximum heart rate during 30 s and the mean arterial pressure after rocuronium injection.
Results
Based on Dixon's up-and-down method, the EC50 of sevoflurane was 2.5 ± 0.5 vol% in males and 2.5 ± 0.3 vol% in females. The probit regression curve of the probability of nonwithdrawal reaction showed that in males the 50% effective ETsev was 2.4 vol% (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.5-3.1 vol%) and the 95% effective ETsev was 3.5 vol% (95% CI, 2.9-11.0 vol%); in females, the 50% effective ETsev was 2.4 vol% (95% CI, 2.1-2.7 vol%) and the 95% effective ETsev was 3.0 vol% (95% CI, 2.7-4.5 vol%).
Conclusions
The inhalation of sevoflurane during the induction period may provide a simple and reliable means of reducing rocuronium-induced reactions without adverse hemodynamic changes. There was no significant difference between males and females.
Go to :

Keywords: Rocuronium, Sevoflurane, Withdrawal
Introduction
Many rocuronium-induced reactions have been reported. Sudden withdrawal movement and pain during the rocuronium injection may cause injury, an inadequate injection of rocuronium, or sympathetic stimulation. Several pretreatments and techniques have been attempted to blunt or abolish these reactions; however, the treatments do not completely prevent the reactions. Popular methods involve pretreatment with various drugs. We hypothesized that the inhalation of volatile anesthetics during intravenous (IV) induction and the maintenance of an adequate anesthetic depth could reduce rocuronium-induced reactions. In one study, inhalation induction with sevoflurane in children reduced rocuronium-induced withdrawal movement [
1]. However, no previous study has reported the end-tidal concentration of sevoflurane (ETsev) in adults that is needed to reduce arm withdrawal associated with the intubating dose of rocuronium (0.6 mg/kg) during thiopental sodium induction. In addition, the incidence and the degree of withdrawal reactions were significantly higher in female adult patients than in male adult patients [
2,
3].
This purpose of this study was to assess the 50% effective concentration (EC50) of sevoflurane for reducing rocuronium-induced reaction, based on the Dixon's up-and-down method, and to assess the 50 and 95% effective ETsev, based on the probit regression curve of the probability of nonwithdrawal reaction in male and female adult patients.
Go to :

Materials and Methods
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of our hospital. All patients provided written, informed consent. We studied 47 adult patients who were at the American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I or II and who were undergoing general anesthesia for elective surgery. We excluded patients who had a history of neurological deficits; allergies to thiopental or rocuronium; asthma; a body weight greater than 20% of the ideal body weight; an anticipated difficult ventilation; and patients who had received analgesics or sedatives within the previous 24 h.
Patients were allocated to 2 groups, according to their gender (i.e., male group and female group). Premedication was not administered before the induction of anesthesia. Before arriving in the operating room, we required that a 20-gauge IV cannula be placed in the patient's largest vein on the dorsum of the hand in the ward. Ringer's lactate solution was chosen for the IV fluid. All patients were monitored by electrocardiography and pulse oximetry, and for automatic noninvasive blood pressure, end-tidal concentration of CO2 (ETCO2), and ETsev (Dräger; Drägerwerk AG and Co., Lübeck, Germany).
After the free flow of IV fluid was confirmed by gravity, the patient underwent anesthesia induction with 2.5% thiopental sodium (4 mg/kg). After confirming that the patient experienced loss of the eyelash reflex, the patient inhaled sevoflurane with 5 vol% in 6 L/min of oxygen. The heart rate (HR) and the mean arterial pressure (MAP) were recorded. Manual ventilation was adjusted to maintain the ETCO2 between 25 mmHg and 30 mmHg. When the target ETsev was attained, a nurse (who was blinded to ETsev) injected the intubating dose of rocuronium (0.6 mg/kg) for 5-10 s under the free flow of the IV fluid. After the response was evaluated by the nurse, the maximum HR for 30 s and the MAP after the rocuronium injection were recorded. The study was terminated at this point, and the anesthetic was continued at the discretion of the attending anesthesiologist.
Patient data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). We studied 23 male patients and 24 female patients, utilizing Dixon's up-and-down method. Every eight pairs of withdrawal and nonwithdrawal movements were collected for statistical analysis by this method [
4]. The EC
50 based on the Dixon's up-and-down method was defined as the mean of the crossover end-tidal concentration. The withdrawal movement sequences and nonwithdrawal movement sequences were each analyzed by the probit test, which enabled us to derive the ETsev for the nonwithdrawal movement with 95% confidence limits of the mean. The male and female patients' characteristics (i.e., a comparison between the patients in each group with withdrawal movement and nonwithdrawal movement at the rocuronium injection, and a comparison of the EC
50 between the groups) were performed by using chi-square analysis and the Mann-Whitney U test, when appropriate. The MAP and HR before and after the rocuronium injection in the withdrawal patient group and the nonwithdrawal movement patient group were compared by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. The differences in the MAP and HR before and after the rocuronium injection between the withdrawal patient group and the nonwithdrawal movement patient group were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test because of the non-normal distribution and small sample size. The differences were considered statistically significant when P < 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed by SPSS package software, version 19.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Go to :

Results
The data were collected from 23 male and 24 female adult patients.
Fig. 1 show the sequences of withdrawal and nonwithdrawal reactions in the male and female groups, respectively. In the male group, nonwithdrawal reactions were observed in 4 of 5 patients with ETsev 3.0 vol% and in 5 of 9 patients with ETsev 2.5 vol%. Based on the Dixon's up-and-down method, the EC
50 of sevoflurane for a nonwithdrawal reaction with the rocuronium injection was 2.5 ± 0.5 vol% in the male group. The probit regression curve of the probability of the nonwithdrawal reaction showed that the 50% effective ETsev for abolishing the withdrawal reaction during rocuronium injection was 2.4 vol% (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.5-3.1 vol%), and the 95% effective ETsev was 3.5 vol% (95% CI, 2.9-11.0 vol%). In the female group, the nonwithdrawal reaction was observed in 5 of 5 patients with ETsev 3.0 vol% and in 6 of 11 patients with ETsev 2.5 vol%. Based on the Dixon's up-and-down method, the EC
50 of sevoflurane in the female group was 2.5 ± 0.3 vol%. The probit regression curve of the probability of nonwithdrawal reaction showed that the 50% effective ETsev for abolishing the withdrawal reaction with the rocuronium injection was 2.4 vol% (95% CI, 2.1-2.7 vol%) and the 95% effective ETsev was 3.0 vol% (95% CI, 2.7-4.5 vol%).
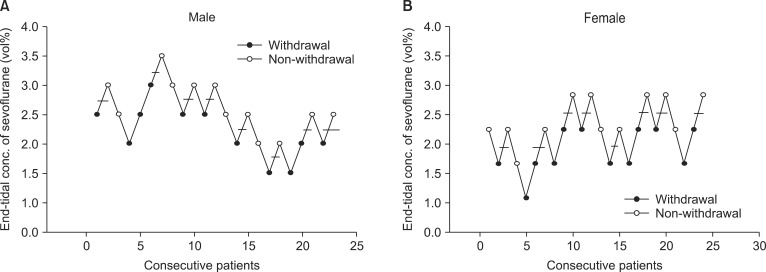 | Fig. 1(A) Data of consecutive withdrawal and nonwithdrawal movement for the predetermined end-tidal concentration of sevoflurane in males (with an initial predetermined concentration of 2.5 vol% for the first patient). We collected eight pairs of withdrawal and nonwithdrawal movement sequences for statistical analysis using the Dixon's up-and-down method. The end-tidal concentration of sevoflurane for abolishing withdrawal movement was 2.5 ± 0.5 vol% in 50% of patients. (B) The data of consecutive withdrawal and nonwithdrawal movement during a predetermined endtidal concentration of sevoflurane in females (with an initial predetermined concentration of 2.5 vol% for the first patient). We collected eight pairs of withdrawal and nonwithdrawal movement sequences for statistical analysis using Dixon's up-and-down method. The end-tidal concentration of sevoflurane for abolishing withdrawal movement was 2.5 ± 0.3 vol% in 50% of patients. 
|
There was no significant difference between the male and female groups in the EC50 of sevoflurane, based on the Dixon's up-and-down method. During the study, hemodynamic stability within 30% of the preoperative values was maintained in all patients.
The patient profiles of the male and the female groups are compared in
Tables 1 and
2 with regard to withdrawal movement and nonwithdrawal movement. The hemodynamic values of patients with withdrawal movement and nonwithdrawal movement are compared in
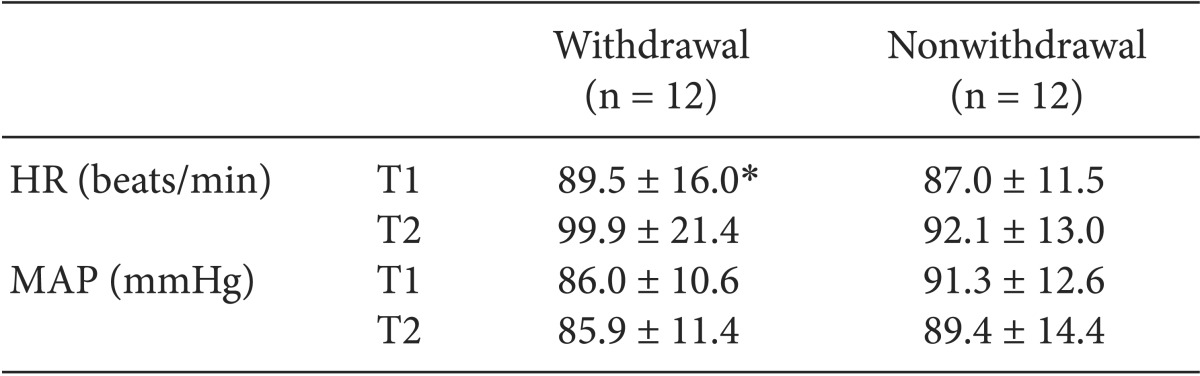
Tables 3 and
4. The HR in the male and female patients with withdrawal movement was significantly higher after the rocuronium injection (P = 0.003) than before the rocuronium injection (P = 0.004), but was not significantly different between the male and female patients with nonwithdrawal movement. The differences in MAP were not statistically significant between patients in the male group and the female group with withdrawal movement and nonwithdrawal movement.
Table 1
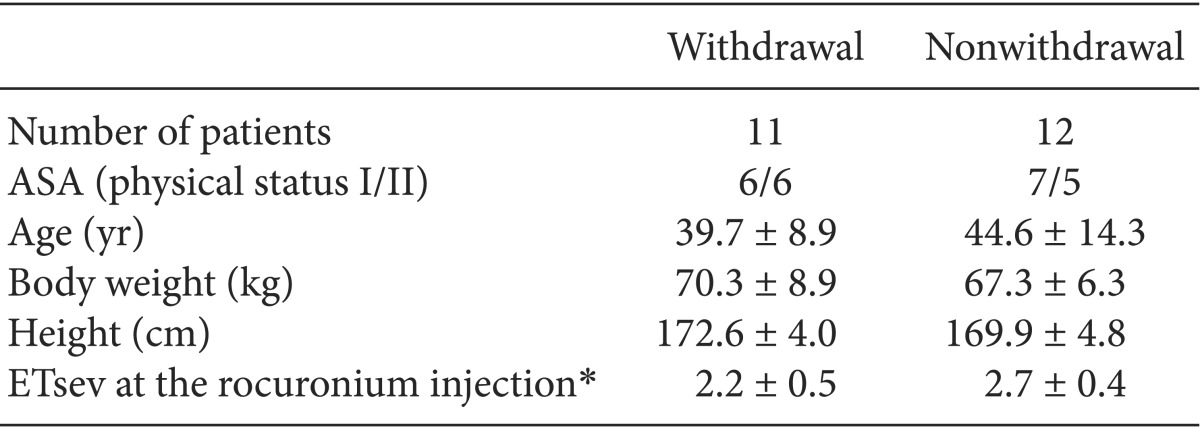

Table 2


Table 3
Male Hemodynamic Profiles
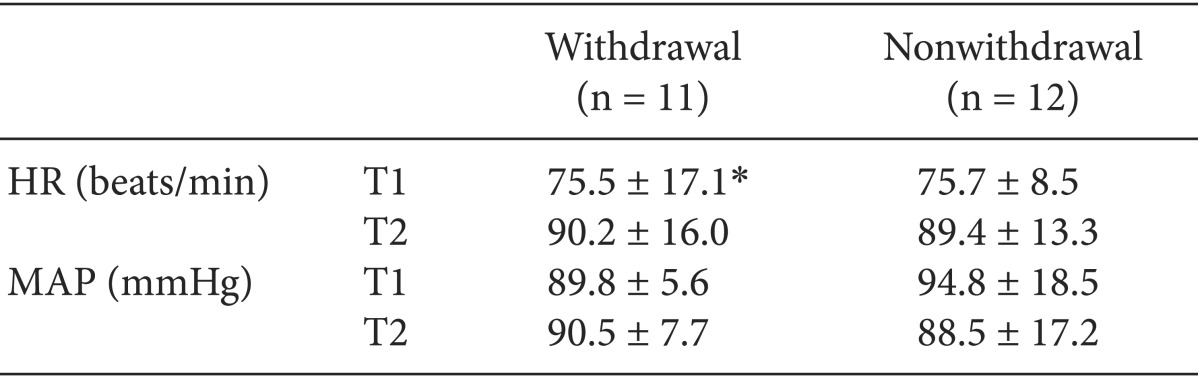

Table 4
Female Hemodynamic Profiles

Go to :

Discussion
Withdrawal reactions in response to the injection of rocuronium were not associated with adverse clinical consequences for the patient's outcome. No patient remembered any pain or withdrawal reaction with the rocuronium injection in the induction period. A withdrawal reaction may result in dislodgement of the venous catheter or an inadequate injection of rocuronium, and rocuronium-induced pain may cause bronchospasm, asthma, or myocardial ischemia attack [
5]. While many theories have been suggested, the exact mechanism of rocuronium-induced reactions is not yet elucidated [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10].
Up to 80% of awake patients or volunteers have reactions with a subparalysing dose of rocuronium [
10]. When rocuronium is used for neuromuscular blockade, withdrawal reactions were lower than in the awake patients [
11]. However, in another study, pediatric patients had an 83% incidence of rocuronium-induced withdrawal reactions during thiopental sodium induction [
7]. The overall incidence of withdrawal reactions and the incidence of severe reactions with the rocuronium injection were significantly higher in female patients than in male patients during the induction of anesthesia [
2,
3]. In addition, women exhibit greater pain sensitivity to a rocuronium injection administered in the luteal phase than in the follicular phase of their menstrual cycle [
12]. However, we did not investigate information about the menstrual cycle.
Various pretreatments with several drugs, nitrous oxide, or a combination of agents, and various techniques to prevent rocuronium-induced withdrawal movement have been suggested with varying success (30-96%); they have not completely eliminated the movement [
3,
7,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. However, these techniques require cumbersome and/or time-consuming procedures, and may have side effects or contraindications.
In this study, we used sevoflurane with the goal of determining the ETsev necessary to eliminate arm withdrawal movement with rocuronium injection in male and female patients during thiopental induction. Based on the Dixon's up-and-down method, the EC50 of sevoflurane for the nonwithdrawal reaction with the rocuronium injection was 2.5 ± 0.5 vol% in the male group and 2.5 ± 0.3 vol% in the female group. There was no significant difference between the male and female groups. On the basis of the probit regression curve of the probability of nonwithdrawal reaction, the 95% effective concentrations were 3.5 vol% in the male group and 3.0 vol% in the female group.
In conclusion, the inhalation of sevoflurane during the induction period may provide a simple and reliable means of reducing rocuronium-induced reactions without adverse hemodynamic changes. The incidence and the degree of withdrawal reactions were significantly higher in the female patients than in the male patients, although the 95% effective concentrations of sevoflurane for the nonwithdrawal reaction with the rocuronium injection were 3.5 vol% in the male group and 3.0 vol% in the female group during thiopental sodium induction.
Go to :










 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download