1. Lagerström MC, Schiöth HB. Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008; 7:339–357. PMID:
18382464.

2. Bräuner-Osborne H, Krogsgaard-Larsen P. Sequence and expression pattern of a novel human orphan G-protein-coupled receptor, GPRC5B, a family C receptor with a short amino-terminal domain. Genomics. 2000; 65:121–128. PMID:
10783259.

3. Robbins MJ, Michalovich D, Hill J, Calver AR, Medhurst AD, Gloger I, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of two novel retinoic acid-inducible orphan G-protein-coupled receptors (GPRC5B and GPRC5C). Genomics. 2000; 67:8–18. PMID:
10945465.

4. Strosberg AD. G protein coupled R7G receptors. Cancer Surv. 1996; 27:65–83. PMID:
8909795.
5. Harada Y, Yokota C, Habas R, Slusarski DC, He X. Retinoic acidinducible G protein-coupled receptors bind to frizzled receptors and may activate non-canonical Wnt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007; 358:968–975. PMID:
17521608.

6. Kristiansen K. Molecular mechanisms of ligand binding, signaling, and regulation within the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors: molecular modeling and mutagenesis approaches to receptor structure and function. Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 103:21–80. PMID:
15251227.

7. Robbins MJ, Michalovich D, Hill J, Calver AR, Medhurst AD, Gloger I, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of two novel retinoic acid-inducible orphan G-protein-coupled receptors (GPRC5B and GPRC5C). Genomics. 2000; 67:8–18. PMID:
10945465.

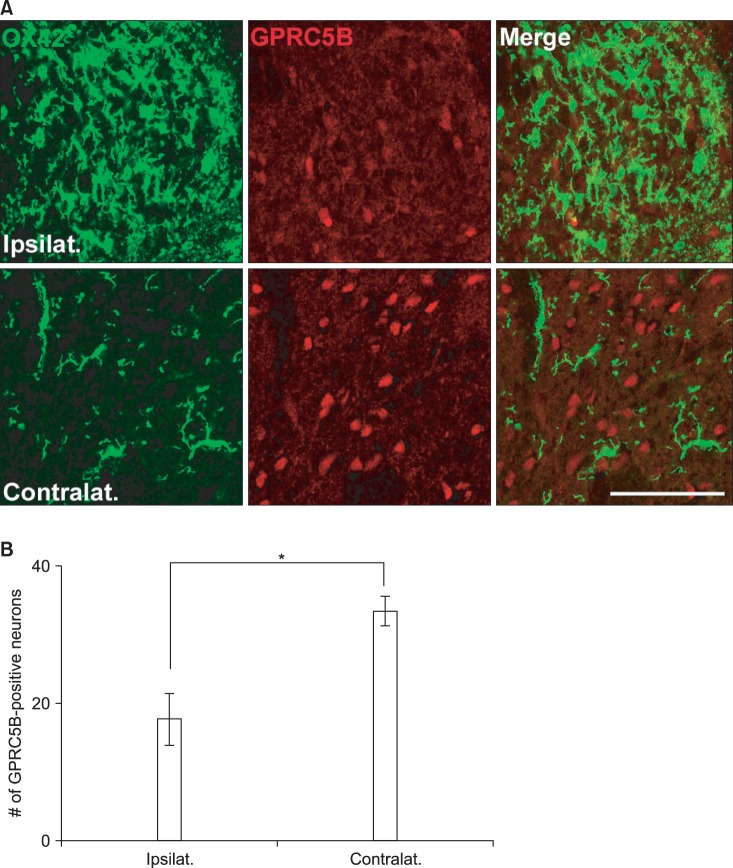
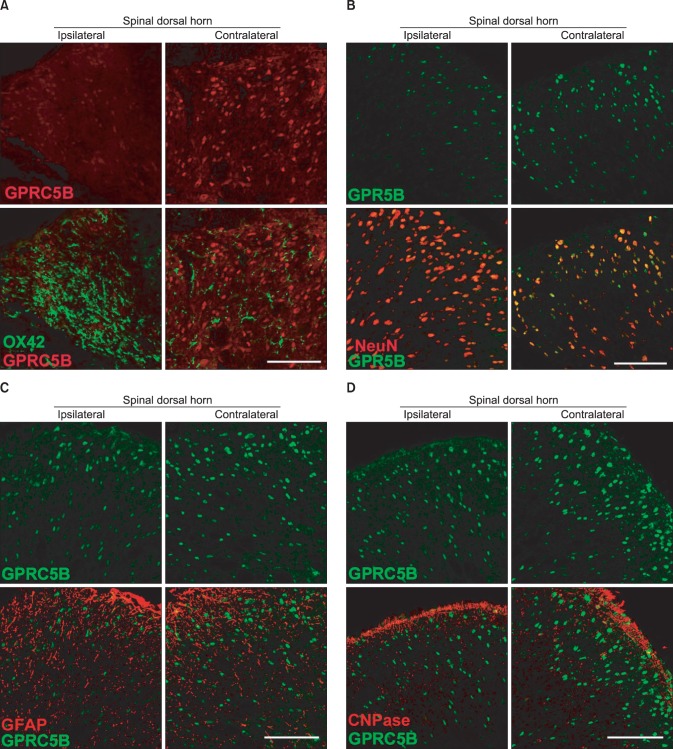
8. Robbins MJ, Charles KJ, Harrison DC, Pangalos MN. Localisation of the GPRC5B receptor in the rat brain and spinal cord. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2002; 106:136–144. PMID:
12393273.

9. Tozaki-Saitoh H, Tsuda M, Miyata H, Ueda K, Kohsaka S, Inoue K. P2Y12 receptors in spinal microglia are required for neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:4949–4956. PMID:
18463248.

10. Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 1994; 53:55–63. PMID:
7990513.
11. Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S, Mizokoshi A, Kohsaka S, Salter MW, et al. P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature. 2003; 424:778–783. PMID:
12917686.

12. Griffin RS, Costigan M, Brenner GJ, Ma CH, Scholz J, Moss A, et al. Complement induction in spinal cord microglia results in anaphylatoxin C5a-mediated pain hypersensitivity. J Neurosci. 2007; 27:8699–8708. PMID:
17687047.

13. Maeda M, Tsuda M, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K, Kiyama H. Nerve injury-activated microglia engulf myelinated axons in a P2Y12 signaling-dependent manner in the dorsal horn. Glia. 2010; 58:1838–1846. PMID:
20665560.

14. Congreve M, Langmead C, Marshall FH. The use of GPCR structures in drug design. Adv Pharmacol. 2011; 62:1–36. PMID:
21907905.

15. Kim SH, Chung JM. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain. 1992; 50:355–363. PMID:
1333581.
16. Tsuda M, Inoue K, Salter MW. Neuropathic pain and spinal microglia: a big problem from molecules in "small" glia. Trends Neurosci. 2005; 28:101–107. PMID:
15667933.

17. Zhuang ZY, Gerner P, Woolf CJ, Ji RR. ERK is sequentially activated in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes by spinal nerve ligation and contributes to mechanical allodynia in this neuropathic pain model. Pain. 2005; 114:149–159. PMID:
15733640.

18. Zhuang ZY, Wen YR, Zhang DR, Borsello T, Bonny C, Strichartz GR, et al. A peptide c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor blocks mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation: respective roles of JNK activation in primary sensory neurons and spinal astrocytes for neuropathic pain development and maintenance. J Neurosci. 2006; 26:3551–3560. PMID:
16571763.






 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download